中国组织工程研究 ›› 2018, Vol. 22 ›› Issue (28): 4544-4549.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.0321
• 组织构建基础实验 basic experiments in tissue construction • 上一篇 下一篇
烟酰胺N-甲基转移酶基因多态性与手球运动能力的关联性
陈 伟1,李江华2,顾建仁1,陈 丰1,夏 华1,张 彬1,焦启斌1,郑 凤3
- 1苏州市体育科学研究所,江苏省苏州市 215131;2国家体育总局水上项目训练监控及干预重点实验室,江西师范大学体育学院,江西省南昌市 330022;3苏州市体育运动学校,江苏省苏州市 215131
Nicotinamide N-methyl transferase gene polymorphism and its correlation with the athletic ability of handball players
Chen Wei1, Li Jiang-hua2, Gu Jian-ren1, Chen Feng1, Xia Hua1, Zhang Bin1, Jiao Qi-bin1, Zheng Feng3
- 1Suzhou Institute for Sports Science, Suzhou 215131, Jiangsu Province, China; 2Key Laboratory of Water Sports Training Monitoring and Intervention of General Administration of Sport of China, Sports College of Jiangxi Normal University, Nanchang 330022, Jiangxi Province, China; 3Suzhou Sports School, Suzhou 215131, Jiangsu Province, China
摘要:
文章快速阅读:
.jpg) 文题释义:
基因多态性:是指在一个生物群体中,同时和经常存在两种或多种不连续的变异型或基因型(genotype)或等位基因(allele),从本质上来讲,多态性的产生在于基因水平上的变异,一般发生在基因序列中不编码蛋白的区域和没有重要调节功能的区域,通常分为3大类:DNA片段长度多态性、DNA重复序列多态性、单核苷酸多态性。
烟酰胺N-甲基转移酶基因多态性与运动能力的关联:烟酰胺N-甲基转移酶基因表达水平与机体能量代谢高度相关,其DNA序列上单核苷酸变异引起的多态性位点多达几百个,某些多态性变异对机体烟酰胺N-甲基转移酶基因的活性或表达水平具有明显的调控作用。多态性可以通过调控烟酰胺N-甲基转移酶基因的表达水平影响机体能量代谢,与人体运动能力具有密切联系。
文题释义:
基因多态性:是指在一个生物群体中,同时和经常存在两种或多种不连续的变异型或基因型(genotype)或等位基因(allele),从本质上来讲,多态性的产生在于基因水平上的变异,一般发生在基因序列中不编码蛋白的区域和没有重要调节功能的区域,通常分为3大类:DNA片段长度多态性、DNA重复序列多态性、单核苷酸多态性。
烟酰胺N-甲基转移酶基因多态性与运动能力的关联:烟酰胺N-甲基转移酶基因表达水平与机体能量代谢高度相关,其DNA序列上单核苷酸变异引起的多态性位点多达几百个,某些多态性变异对机体烟酰胺N-甲基转移酶基因的活性或表达水平具有明显的调控作用。多态性可以通过调控烟酰胺N-甲基转移酶基因的表达水平影响机体能量代谢,与人体运动能力具有密切联系。
.jpg) 文题释义:
基因多态性:是指在一个生物群体中,同时和经常存在两种或多种不连续的变异型或基因型(genotype)或等位基因(allele),从本质上来讲,多态性的产生在于基因水平上的变异,一般发生在基因序列中不编码蛋白的区域和没有重要调节功能的区域,通常分为3大类:DNA片段长度多态性、DNA重复序列多态性、单核苷酸多态性。
烟酰胺N-甲基转移酶基因多态性与运动能力的关联:烟酰胺N-甲基转移酶基因表达水平与机体能量代谢高度相关,其DNA序列上单核苷酸变异引起的多态性位点多达几百个,某些多态性变异对机体烟酰胺N-甲基转移酶基因的活性或表达水平具有明显的调控作用。多态性可以通过调控烟酰胺N-甲基转移酶基因的表达水平影响机体能量代谢,与人体运动能力具有密切联系。
文题释义:
基因多态性:是指在一个生物群体中,同时和经常存在两种或多种不连续的变异型或基因型(genotype)或等位基因(allele),从本质上来讲,多态性的产生在于基因水平上的变异,一般发生在基因序列中不编码蛋白的区域和没有重要调节功能的区域,通常分为3大类:DNA片段长度多态性、DNA重复序列多态性、单核苷酸多态性。
烟酰胺N-甲基转移酶基因多态性与运动能力的关联:烟酰胺N-甲基转移酶基因表达水平与机体能量代谢高度相关,其DNA序列上单核苷酸变异引起的多态性位点多达几百个,某些多态性变异对机体烟酰胺N-甲基转移酶基因的活性或表达水平具有明显的调控作用。多态性可以通过调控烟酰胺N-甲基转移酶基因的表达水平影响机体能量代谢,与人体运动能力具有密切联系。摘要
背景:研究证实,烟酰胺N-甲基转移酶基因(nieotinamideN-methyl-transferase,NNMT)多态性与人体有氧运动能力相关。手球是一种混氧运动,比赛或平时训练中无氧运动占一定比例,主要进行有氧运动。
目的:探讨NNMT基因单核苷酸多态性位点rs2256292与手球运动能力的关联。
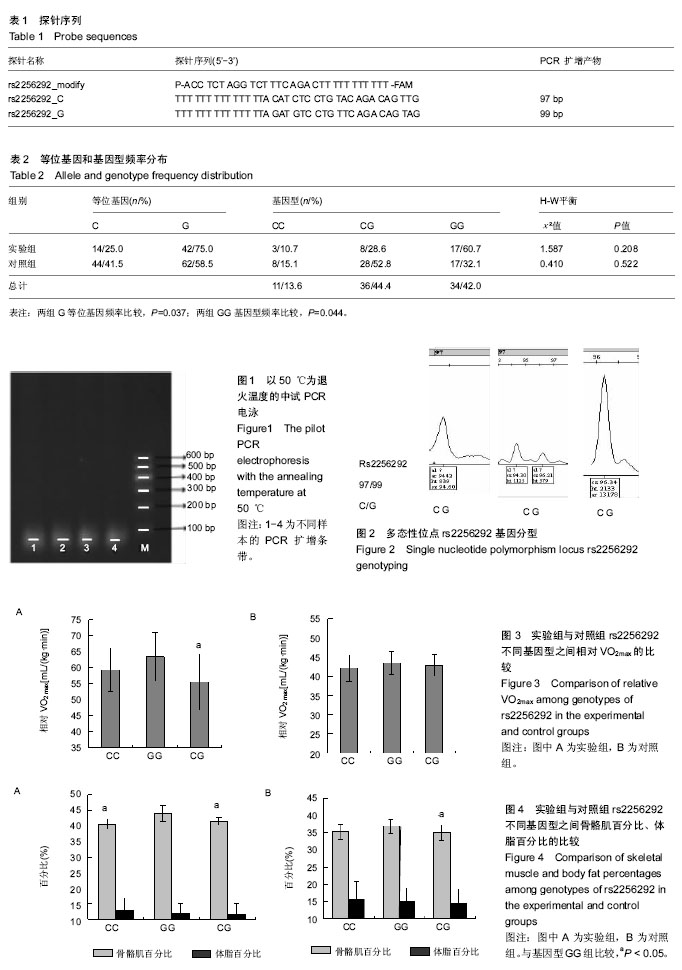
方法:采用PCR-LDR方法检测28名中国国家青年男子手球队运动员(实验组)和53名普通男学生(对照组)NNMT基因单核苷酸多态性位点rs2256292,测试相对最大摄氧量VO2 max和骨骼肌百分比、体脂百分比身体成分指标。
结果与结论:①实验组G等位基因和GG基因型频率显著高于对照组(P < 0.05);②在28名运动员中,基因型GG组相对VO2 max明显高于基因型CG组(P < 0.05);在53名普通学生中,基因型GG组、基因型CG组及基因型CC组间相对VO2 max无差异;③在28名运动员中,基因型GG组骨骼肌百分比高于基因型CC组、基因型CG组(P < 0.05);在53名普通学生中,基因型GG组骨骼肌百分比高于基因型CG组(P < 0.05);④在28名运动员中,基因型GG组、基因型CG组及基因型CC组间体脂百分比无差异;在53名普通学生中,基因型GG组、基因型CG组及基因型CC组间体脂百分比无差异;⑤结果表明,NNMT基因单核苷酸多态性位点rs2256292与手球运动能力明显相关,运动员更倾向于G等位基因,基因型GG携带者运动能力较强。
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:组织构建;骨细胞;软骨细胞;细胞培养;成纤维细胞;血管内皮细胞;骨质疏松;组织工程
ORCID: 0000-0001-9403-4778(陈伟)
中图分类号:
.jpg) 文题释义:
基因多态性:是指在一个生物群体中,同时和经常存在两种或多种不连续的变异型或基因型(genotype)或等位基因(allele),从本质上来讲,多态性的产生在于基因水平上的变异,一般发生在基因序列中不编码蛋白的区域和没有重要调节功能的区域,通常分为3大类:DNA片段长度多态性、DNA重复序列多态性、单核苷酸多态性。
烟酰胺N-甲基转移酶基因多态性与运动能力的关联:烟酰胺N-甲基转移酶基因表达水平与机体能量代谢高度相关,其DNA序列上单核苷酸变异引起的多态性位点多达几百个,某些多态性变异对机体烟酰胺N-甲基转移酶基因的活性或表达水平具有明显的调控作用。多态性可以通过调控烟酰胺N-甲基转移酶基因的表达水平影响机体能量代谢,与人体运动能力具有密切联系。
文题释义:
基因多态性:是指在一个生物群体中,同时和经常存在两种或多种不连续的变异型或基因型(genotype)或等位基因(allele),从本质上来讲,多态性的产生在于基因水平上的变异,一般发生在基因序列中不编码蛋白的区域和没有重要调节功能的区域,通常分为3大类:DNA片段长度多态性、DNA重复序列多态性、单核苷酸多态性。
烟酰胺N-甲基转移酶基因多态性与运动能力的关联:烟酰胺N-甲基转移酶基因表达水平与机体能量代谢高度相关,其DNA序列上单核苷酸变异引起的多态性位点多达几百个,某些多态性变异对机体烟酰胺N-甲基转移酶基因的活性或表达水平具有明显的调控作用。多态性可以通过调控烟酰胺N-甲基转移酶基因的表达水平影响机体能量代谢,与人体运动能力具有密切联系。