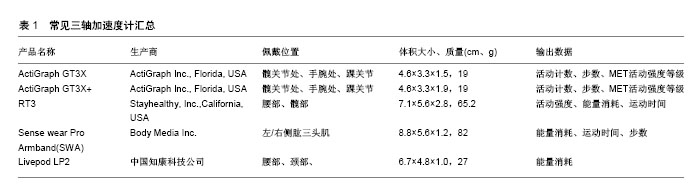
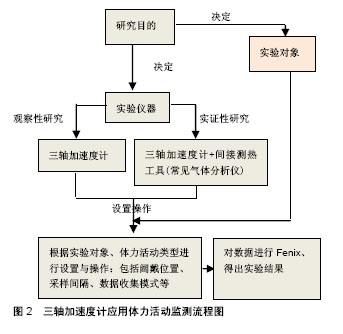
| [1] Dyrstad SM,Hansen BH,Holme IM,et al.Comparison of self-reported versus accelerometer-measured physical activity. Med Sci Sports Exerc.2014;46(1):99-106.[2] Johnson M,Yun J,McCubbin JA.Validity evidence for self-report with assistance to measure physical activity behavior in adults with intellectual disabilities.Intellect Dev Disabil. 2014;52(4):273-281.[3] John D,Tyo B,Bassett DR. Comparison of four ActiGraph accelerometers during walking and running . Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2010;42(2):368-374.[4] Mayagoitia RE,Nene AV,Veltink PH.Accelerometer and rate gyroscope measurement of kinematics an inexpensive alternative to optical motion analysis systems.J Biomech.2002;35(4):537-542.[5] Henriksen M,Lund H,Moe-Nilssen R,et al.Test–retest reliability of trunk accelerometric gait analysis.Gait Posture. 2004;19(3):288-297.[6] Davey NP.Acquisition and analysis of aquatic stroke data from an accelerometer based system. Masters of Philosophy Dissertation. Griffith University.Queensland. 2004:93-100.[7] 黄贯伦,林国全.以惯性测量装置应用于不同鞋子对跳远运动表现之比较[J].中原体育学报,2014,(4):140-146.[8] Shirota K,Watanabe K,Kurihara Y. Measurement and analysis of golf swing using 3-D acceleration and gyro sensor. IEEE.SICE Annual Conference.2012:356-360. [9] Williamson R,Andrews BJ. Detecting absolute human knee angle and angular velocity using acceleromaters and rate gyroscopes. Med Biol Eng Comput.2001;39(3):294-302.[10] 黄钰萍.三轴加速计应用于患者功能性活动坐到站评估之探究[J].医学与健康期刊,2015,4(1):6-10.[11] Favre J,Aissaoui R,Jolles BM,et al.Functional calibration procedure for 3D knee joint angle description using inertial sensors. J Biomech.2009; 42(14):2330-2335.[12] 焦纯,董秀珍,杨国胜.人体运动量及能耗的测量方法[J].国外医学:生物医学工程分册,2002,25(5):196-202.[13] Hinckson EA,Curtis A. Measuring physical activity in children and youth living with intellectual disabilities: A systematic review. Res Dev Disabil. 2013;34(1):72-86.[14] Vathsangam H,Emken B,Schroeder E,et al.Energy estimation of treadmill walking using on-body accelerometers and gyroscopes. Conf Proc IEEE Eng Med Biol Soc. 2010;2010:6497-6501. [15] Vathsangam H,Emken BA,Schroeder ET,et al. Hierarchical linear models for energy prediction using inertial sensors : a comparative study for treadmill walking. J Ambient Intell Humaniz Comput. 2013; 4(6):747-758.[16] Guinhouya CB,Huhert H,Dupont G,et al.Relationship between the MTI accelerometer (Actigraph) counts and running speed during continuous and intermittent exercise. J Sports Sci Med. 2005;4(4): 534-542.[17] Rowlands AV,Thomas PW,Eston RG,et al.Validation of the RT3 triaxial accelerometer for the assessment of physical activity.Med Sci Sport Exe.2004;36(3):518- 524.[18] Rowlands AV,Stone MR,Eston RG.Influence of speed and step frequency during walking and running on motion sensor output. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2007;39(4):716-727.[19] 林玉琼,张予亲,余杰霖.三轴加速度计运动表的信效度研究[J].文化体育学刊,2014,17:55-58.[20] Hussey J,Bennett K,Dwyer JO,et al.Validation of the RT3 in the measurement of physical activity in children.J Sci Med Sport.2009; 12(1):130-133.[21] 陆乐,戴剑松,徐波. 加速度传感器测量不同速度运动时能量消耗的研究[J].西安体育学院学报,2013,30(1):104-107.[22] DeVoe D,Gotshall R,McArthur T.Comparison of the RT3 research tracker and TriTrac R3D acceleromerers.Percept Mot Skills.2003;97: 510-518.[23] 戴剑松,顾忠科,徐凯,等. RT3三轴加速度传感器测量多种类型身体活动效度研究[J].成都体育学院学报,2015,41(6):100-16,121.[24] 朱琳,陈佩杰.应用三轴加速度计(GT3X+)监测广州高中生日常体力活动的研究[J].广州体育学院学报,2013,33(1):85-88,96.[25] Peters TM,Moore SC,Xiang YB,et al.Accelerometer-measured physical activity in Chinese adults. Am J Prev Med. 2010 ;38(6): 583-591.[26] 傅丽兰,陈毓君.三度空间加速计于跑步机行走之向量大小及能量消耗与耗氧量相关性研究[J].物理治疗,2005,30(2):75-77.[27] Terrier P,Aminian K,Schutz Y.Can accelerometery accurately predict the energy cost of uphill/downhillwalking? Ergonomics.2001;44(1):48-62. [28] 郭珍汝.三轴加速规在森林步道行走能量消耗之研究[D].台湾大学,2008: 78-93.[29] 朱卫红.上肢活动加速度与能量消耗特征初探[J].苏州大学,2009.[30] Kim Y,Lee J,Bai Y,et al. Comparison between Sensewear Mini Armband and Actigraph accelerometers in classifying physical activity intensities in youth. Medicine &Science in Sports &Exercise.2012;44 (5):S478.[31] Berntsen S,Hageberg R,Aandstad A,et al. Objective assessment of sedentary behaviour and light physical activity in free living activities.Medicine&Science in Sports &Exercise.2012;44 (5):S490.[32] 王军利,张冰,贾丽雅,等.4种运动传感器测量身体活动能耗的有效性研究[J].天津体育学院学报,2012,27(5):427-431.[33] 赵壮壮,陈培友.不同加速度传感器测量人体走跑运动能量消耗对比研究[J].北京体育大学学报,2013,36(4):77-81.[34] McClain JJ,Craig CL,Sisson SB,et al.Comparison of Lifecorder EX and ActiGraph accelerometers under free-living conditions. Appl Physio Nutrit Metabol.2007;32(4):753-761. [35] Trost SG,McIver KL,Pate RR. Conducting accelerometet-based activity assessments in field-based research. Med Sci Sports Exe.2005;37(11): S531-S543.[36] 孙泊,刘宇,庄涛,等.基于腰部加速度计的行走能耗建模实验研究[J].体育科学,2013,33(4):36-40.[37] Howe CA,Staudenmayer JW,Freedson PS.Accelerometer prediction of energy expenditure: Vector magnitude versus vertical axis.Med Sci Sports Exe. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2009;41(12):2199-2206.[38] Audrey S,Bell S,Hughes R,et al.Adolescent perspectives on wearing accelerometers to measure physical activity in population-based trials. Eur J Public Health. 2013;23(3):475-480.[39] Robertson W,Stewart-Brown S,Wilcock E,et al. Utility of accelerometers to measure physical activity in children attending an obesity treatment intervention. J Obes.2011;2011. pii: 398918.[40] 刘又慈,傅丽兰,陈亮伃. 不同佩戴位置之三轴加速计于登阶运动时的能量消耗预估[J].体育学院论丛,2006,17(2):89-92.[41] 王佩凡,崔秀里. 不同配戴位置之三轴加速计于桌球正手运动时的能量消预估[J].交大体育学刊,2016,12(12).[42] Hesketh KR. Physical activity and sedentary behavior during pregnancy and postpartum,measured using hip and wrist-worn accelerometers. Preventive Medicine Reports.2017;10:337-345. [43] Sirichana W,Dolezal BA,Neufeld EV,et al.Wrist-worn triaxial accelerometry predicts the energy expenditure of non-vigorous daily physical activities. J Sci Med Sport. 2017; 20(8):761-765.[44] 廖立同,相子元.身体不同位置加速度分析跑步机跑步身体活动量之研究[J].华人运动生物力学期刊,2009,6(1)32-36.[45] Scott JJ,Rowlands AV,Cliff DP,et al.Comparability and feasibility of wrist- and hip-worn accelerometers in free-living adolescents. J Sci Med Sport. 2017;20(12):1101-1106. [46] Mannini A,Intille SS,Rosenberger M,et al. Activity recognition using a single accelerometer placed at the wrist or ankle. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2013,45 (11) :2193-2203.[47] Kumahara H,Tanaka H,Schutz Y. Daily physical activity assessment: what is the importance of upper limb movements vs whole body movements? Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord. 2004;28(9): 1107-1110.[48] Cleland I,Kikhia B,Nugent C,et al.Optimal placement of accelerometers for the detection of everyday activities. Sensors (Basel). 2013;13(7):9183-9200. [49] Zhang JH,Macfarlane DJ,Sobko T. Feasibility of a Chest-worn accelerometer for physical activity measurement. J Sci Med Sport. 2016;19(12):1015-1019.[50] Plasqui G,Westerterp KR.Physical activity assessment with accelerometers: An evaluation against doubly labeled water. Obesity (Silver Spring). 2007;15(10):2371-2389.[51] Chen KY,Bassett DR Jr. The technology of accelerometry-based activity monitors: current and future. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2005;37(11 Suppl):S490-500.[52] 王超,陈佩杰,庄洁,等. 加速度计以不同采样间隔测量儿童青少年日常体力活动时间的一致性研究[J].中国运动医学杂志,2012,31(9):759-765, 771.[53] 贺刚,黄雅君,王香生.加速度计在儿童体力活动测量中的应用[J].体育科学,2011,31(8):72-76.[54] Bassett DR,Troiano RP,McClain JJ,et al. Wolff Accelerometer- based physical activity: total volume per day and standardized measures. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2015;47(4):833-838.[55] 王欢,王馨塘,佟海青,等. 三种加速度计测量多种身体活动的效度比较[J].体育科学,2014,34(5):45-49.[56] Eston RG,Rowlands AV,Ngledew DK. Validity of heart rate,pedometry,and accelerometry for predicting the energy cost of children's activities. J Appl Physiol (1985). 1998;84(1):362-371.[57] Matthew CE. Calibration of accelerometer output for adults. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2005;37(11 Suppl):S512-5522.[58] Leung W,Siebert EA,Yun J. Measuring physical activity with accelerometers for individuals with intellectual disability: A systematic review. Res Dev Disabil. 2017;67:60-70.[59] Trost SG,Loprinzi PD,Moore R,et al.Comparison of aceelerometer cut points for predicting activity intensity in youth. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2011;43(7):1360-1365.[60] Crouter SE,Churilla JR,Bassett DR Jr. Estimating energy expenditure using accelerometers. Eur J Appl Physiol. 2006;98(6):601-612. [61] 汤强,盛蕾,朱卫红. 体力活动研究中加速度计的应用[J].体育科学,2009, 29(1):79-81.[62] 王金昊,邱俊,李之俊. 跑台运动中运动员能量消耗的3种测试方法的比较研究[J]. 西安体育学院学报,2014,31(5): 582-588.[63] Mannini A,Sabatini AM. Machine learning methods for classifying human physical activity from on-body accelerometers. Sensors. Sensors (Basel). 2010;10(2):1154-1175.[64] Staudenmayer J,Pober D,Crouter S,et al. An artificial neural network to estimate physical activity energy expenditure and identify physical activity type from an accelerometer. J Appl Physiol.2009;107(4): 1300-1307.[65] Trost SG,Wong WK,Pfeiffer KA,et al. Aritificial neural networks to predict activity type and energy expenditure in youth. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2012;44(9):1801-1809. [66] 陈庆果,彭彪,杨世军,等.基于神经网络模型的加速度计活动强度算法研究[J].天津体育学院学报,2017,32(1): 45-50.[67] 林昱安.穿戴式装置于陆上与水中运动之信效度检验[J].运动表现期刊, 2017,4(1):63-65. |
.jpg)

.jpg)
.jpg)