中国组织工程研究 ›› 2018, Vol. 22 ›› Issue (20): 3172-3177.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.0257
• 组织构建与生物力学 tissue construction and biomechanics • 上一篇 下一篇
颞下颌关节有限元模型的生物力学特征
詹 翔
- 西南医科大学附属医院放射科,四川省泸州市 646000
Biomechanical properties of the finite element model of temporomandibular joint
Zhan Xiang
- Department of Radiology, the Affiliated Hospital of Southwest Medical University, Luzhou 646000, Sichuan Province, China
摘要:
文章快速阅读:
.jpg) 文题释义:
颞下颌关节(temporomandibular joint,TMJ):简称下颌关节,是颌面部唯一的左右双侧联动关节,包括颞骨关节、窝关节盘、关节周围的关节囊、关节韧带及下颌骨髁突等组织结构,维持较为复杂的生理形态功能。颞下颌关节的神经来自咬肌神经及耳颞神经的耳前支。其血液供给来自上颌动脉、咽升动脉及耳后动脉等的分支,关节盘除其中央部分外,均有动脉供养。颞下颌关节具有双侧协同运动能力,从而构成统一的功能性能单元,具备言语、表情等性能。颞下颌关节疾病一般包括常见的损伤、紊乱病,进而造成颞下颌关节不正常的生理状态及一些心理障碍等病症。
下颌骨髁状突:略呈椭圆形,由一横嵴把髁状突顶分为前后2个斜面,前斜面覆盖着较厚的纤维软骨,是关节的功能区,很多关节病最早破坏此区。两侧髁状突的长轴略偏向后方,其延长线成145°-160°角,这个角度可使下颌做侧方运动时不致左右脱位。颞骨关节面的凹部为关节窝,容纳髁状突。凸部为关节结节,是主要承受咀嚼压力区。关节窝比髁状突大得多,这使髁状突运动时非常灵活,能在较大的窝内做回旋运动,这对咀嚼运动有重要意义。
文题释义:
颞下颌关节(temporomandibular joint,TMJ):简称下颌关节,是颌面部唯一的左右双侧联动关节,包括颞骨关节、窝关节盘、关节周围的关节囊、关节韧带及下颌骨髁突等组织结构,维持较为复杂的生理形态功能。颞下颌关节的神经来自咬肌神经及耳颞神经的耳前支。其血液供给来自上颌动脉、咽升动脉及耳后动脉等的分支,关节盘除其中央部分外,均有动脉供养。颞下颌关节具有双侧协同运动能力,从而构成统一的功能性能单元,具备言语、表情等性能。颞下颌关节疾病一般包括常见的损伤、紊乱病,进而造成颞下颌关节不正常的生理状态及一些心理障碍等病症。
下颌骨髁状突:略呈椭圆形,由一横嵴把髁状突顶分为前后2个斜面,前斜面覆盖着较厚的纤维软骨,是关节的功能区,很多关节病最早破坏此区。两侧髁状突的长轴略偏向后方,其延长线成145°-160°角,这个角度可使下颌做侧方运动时不致左右脱位。颞骨关节面的凹部为关节窝,容纳髁状突。凸部为关节结节,是主要承受咀嚼压力区。关节窝比髁状突大得多,这使髁状突运动时非常灵活,能在较大的窝内做回旋运动,这对咀嚼运动有重要意义。
.jpg) 文题释义:
颞下颌关节(temporomandibular joint,TMJ):简称下颌关节,是颌面部唯一的左右双侧联动关节,包括颞骨关节、窝关节盘、关节周围的关节囊、关节韧带及下颌骨髁突等组织结构,维持较为复杂的生理形态功能。颞下颌关节的神经来自咬肌神经及耳颞神经的耳前支。其血液供给来自上颌动脉、咽升动脉及耳后动脉等的分支,关节盘除其中央部分外,均有动脉供养。颞下颌关节具有双侧协同运动能力,从而构成统一的功能性能单元,具备言语、表情等性能。颞下颌关节疾病一般包括常见的损伤、紊乱病,进而造成颞下颌关节不正常的生理状态及一些心理障碍等病症。
下颌骨髁状突:略呈椭圆形,由一横嵴把髁状突顶分为前后2个斜面,前斜面覆盖着较厚的纤维软骨,是关节的功能区,很多关节病最早破坏此区。两侧髁状突的长轴略偏向后方,其延长线成145°-160°角,这个角度可使下颌做侧方运动时不致左右脱位。颞骨关节面的凹部为关节窝,容纳髁状突。凸部为关节结节,是主要承受咀嚼压力区。关节窝比髁状突大得多,这使髁状突运动时非常灵活,能在较大的窝内做回旋运动,这对咀嚼运动有重要意义。
文题释义:
颞下颌关节(temporomandibular joint,TMJ):简称下颌关节,是颌面部唯一的左右双侧联动关节,包括颞骨关节、窝关节盘、关节周围的关节囊、关节韧带及下颌骨髁突等组织结构,维持较为复杂的生理形态功能。颞下颌关节的神经来自咬肌神经及耳颞神经的耳前支。其血液供给来自上颌动脉、咽升动脉及耳后动脉等的分支,关节盘除其中央部分外,均有动脉供养。颞下颌关节具有双侧协同运动能力,从而构成统一的功能性能单元,具备言语、表情等性能。颞下颌关节疾病一般包括常见的损伤、紊乱病,进而造成颞下颌关节不正常的生理状态及一些心理障碍等病症。
下颌骨髁状突:略呈椭圆形,由一横嵴把髁状突顶分为前后2个斜面,前斜面覆盖着较厚的纤维软骨,是关节的功能区,很多关节病最早破坏此区。两侧髁状突的长轴略偏向后方,其延长线成145°-160°角,这个角度可使下颌做侧方运动时不致左右脱位。颞骨关节面的凹部为关节窝,容纳髁状突。凸部为关节结节,是主要承受咀嚼压力区。关节窝比髁状突大得多,这使髁状突运动时非常灵活,能在较大的窝内做回旋运动,这对咀嚼运动有重要意义。摘要
背景:颞下颌关节的结构存在形态不规整及复杂性,因此获取CT数据及三维建模存在困难问题,探求可靠的三维建模方法模拟仿真颞下颌关节,对颞下颌关节紊乱病症的研究有重要的临床意义。
目的:基于螺旋CT扫描数据,建立颞下颌关节的软、硬整体组织三维模型。
方法:选取面部骨性结构无异常、正常发育,且无错牙合畸形的成年男性个体1例。①获取颞下颌关节的CT扫描数据,通过影像提取法构建颞下颌关节三维有限元模型;②根据实际人体颞下颌关节的运动状况,设定模型的功能参数,从而进行有限元模拟分析。
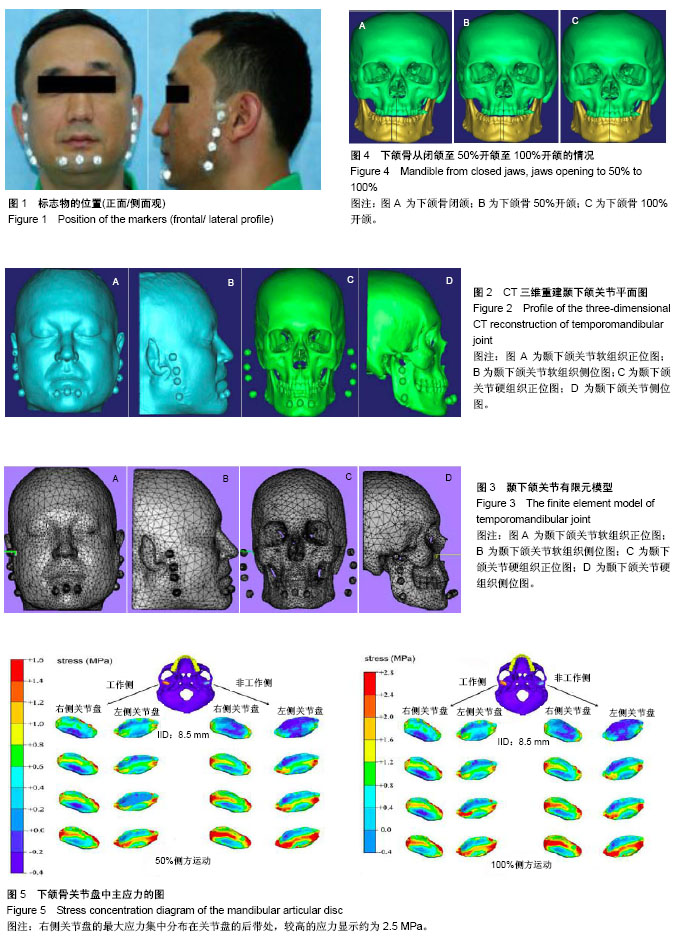
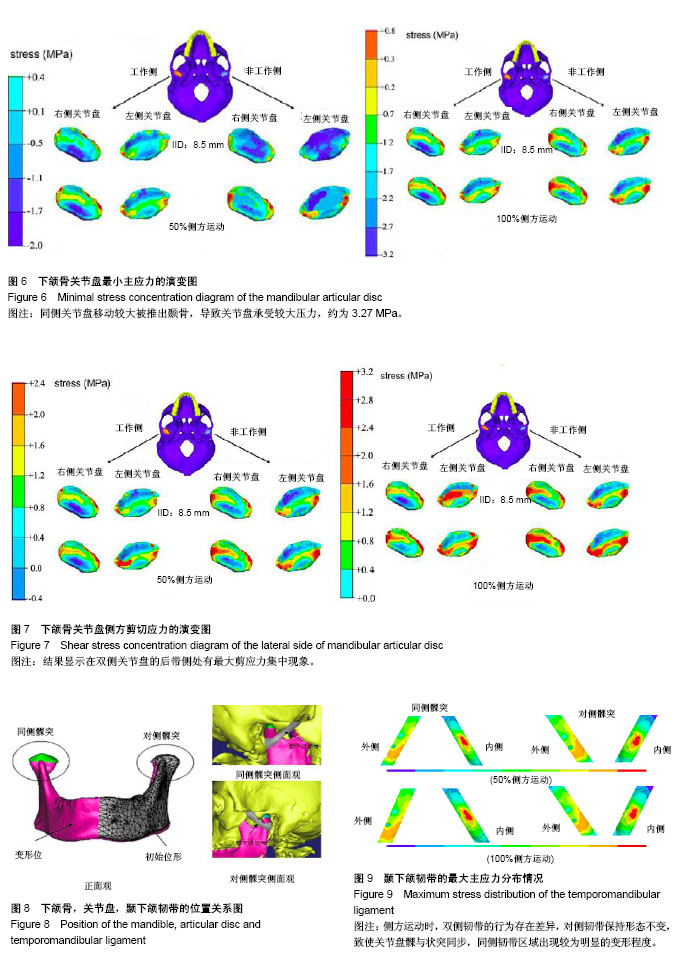
结果与结论:①通过数值模拟表明,当下颌侧方处于运动状态时,对侧关节盘与同侧关节盘的应力情况分布均不相同;同侧关节盘呈现较高的应力分布情况,主要集中在关节盘的侧方/后带部位;颞骨下壁遭受颞下颌关节盘的巨大压迫,因此使得同侧关节盘的髁状突侧方产生扭曲变形,所以其最容易穿孔或受损;②在建立的模型上模拟分析颞下颌关节侧方功能运动情况,并进行有限元分析,获得应力分布图,进而为髁状突骨折及颞下颌关节置换等手术提供相应的理论依据。
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:组织构建;骨细胞;软骨细胞;细胞培养;成纤维细胞;血管内皮细胞;骨质疏松;组织工程
ORCID: 0000-0002-2989-8497(詹翔)
中图分类号:
.jpg) 文题释义:
颞下颌关节(temporomandibular joint,TMJ):简称下颌关节,是颌面部唯一的左右双侧联动关节,包括颞骨关节、窝关节盘、关节周围的关节囊、关节韧带及下颌骨髁突等组织结构,维持较为复杂的生理形态功能。颞下颌关节的神经来自咬肌神经及耳颞神经的耳前支。其血液供给来自上颌动脉、咽升动脉及耳后动脉等的分支,关节盘除其中央部分外,均有动脉供养。颞下颌关节具有双侧协同运动能力,从而构成统一的功能性能单元,具备言语、表情等性能。颞下颌关节疾病一般包括常见的损伤、紊乱病,进而造成颞下颌关节不正常的生理状态及一些心理障碍等病症。
下颌骨髁状突:略呈椭圆形,由一横嵴把髁状突顶分为前后2个斜面,前斜面覆盖着较厚的纤维软骨,是关节的功能区,很多关节病最早破坏此区。两侧髁状突的长轴略偏向后方,其延长线成145°-160°角,这个角度可使下颌做侧方运动时不致左右脱位。颞骨关节面的凹部为关节窝,容纳髁状突。凸部为关节结节,是主要承受咀嚼压力区。关节窝比髁状突大得多,这使髁状突运动时非常灵活,能在较大的窝内做回旋运动,这对咀嚼运动有重要意义。
文题释义:
颞下颌关节(temporomandibular joint,TMJ):简称下颌关节,是颌面部唯一的左右双侧联动关节,包括颞骨关节、窝关节盘、关节周围的关节囊、关节韧带及下颌骨髁突等组织结构,维持较为复杂的生理形态功能。颞下颌关节的神经来自咬肌神经及耳颞神经的耳前支。其血液供给来自上颌动脉、咽升动脉及耳后动脉等的分支,关节盘除其中央部分外,均有动脉供养。颞下颌关节具有双侧协同运动能力,从而构成统一的功能性能单元,具备言语、表情等性能。颞下颌关节疾病一般包括常见的损伤、紊乱病,进而造成颞下颌关节不正常的生理状态及一些心理障碍等病症。
下颌骨髁状突:略呈椭圆形,由一横嵴把髁状突顶分为前后2个斜面,前斜面覆盖着较厚的纤维软骨,是关节的功能区,很多关节病最早破坏此区。两侧髁状突的长轴略偏向后方,其延长线成145°-160°角,这个角度可使下颌做侧方运动时不致左右脱位。颞骨关节面的凹部为关节窝,容纳髁状突。凸部为关节结节,是主要承受咀嚼压力区。关节窝比髁状突大得多,这使髁状突运动时非常灵活,能在较大的窝内做回旋运动,这对咀嚼运动有重要意义。