| [1] Rodricks DJ, Patil S, Pulido P, et al. Press-fit condylar design total knee arthroplasty: fourteen to seventeen-year follow-up. Bone Joint Surg Am. 2007;(3): 88-89.[2] Vessely MB, Whaley AL, Harmsen WS, et al. Long-term survivorship and failuremodes of 1000 cemented condylar total knee arthroplasties. Clin Orthop. 2006; (452): 28-29.[3] Jeffery RS, Morris RW, Denham RA. Coronal alignment after total kneereplacement. Bone Joint Surg Br. 1991;(73): 709-711.[4] Rand JA, Coventry MB. Ten-year evaluation of geometric total knee arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1988; (232): 168-170.[5] Berend ME, Ritter MA, Meding JB et al. Tibial component failure mechanisms intotal knee arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2004; (428): 26-29.[6] Bargren JH, Blaha JD, Freeman MA. Alignment in total knee arthroplasty.Correlated biomechanicaland clinical observations. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1983; (173): 178-179.[7] Hvid I, Nielsen S. Total condylar knee arthroplasty: prosthetic componentpositioning and radiolucent lines. Acta Orthop Scand. 1984; (55): 160-162.[8] Lotke PA, Ecker ML. Influence of positioning of prosthesis in total kneereplacement. Bone Joint Surg Am. 1977;(59):77-80.[9] Ritter MA, Faris PM, Keating KM et al. Postoperative alignment of total kneereplacement. Its effect on survival. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1994; (299): 153-155.[10] Mahaluxmivala J, Bankes MJ, Nicolai P, et al. The effect surgeon experience oncomponent positioning in 673 press fit condylar posterior cruciate-sacrificingtotal knee arthroplasties. Arthroplasty.2001;(16): 635-636.[11] Petersen TL, Engh GA. Radiographic assessment of knee alignment after total knee arthroplasty. Arthroplasty. 1988;(3): 67-70.[12] Engh GA, Petersen TL. Comparative experience with intramedullary and extramedullary alignment in total knee arthroplasty. Arthroplasty. 1990; (5):1-3.[13] Teter KE, Bregman D, Colwell Jr CW. The efficacy of intramedullary femoral alignment in total knee replacement. Clin Orthop. 1995; (321): 117-120.[14] Parratte S, Pagnano MW, Trousdale RT, et al. Effect of postoperative mechanical axis alignment on the fifteen-year survival of modern, cemented total knee replacements. Bone Joint Surg Am. 2010;(92): 2143-2145.[15] Bellemans J, Colyn W, Vandenneucker H, et al. Is neutral mechanical alignmentnormal for all patients? The concept of constitutional varus. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2012;(470):45-57.[16] Innocenti B, Bellemans J, Catani F. Deviations from optimal alignment in TKA: is there a biomechanical difference between femoral or tibial component alignment. 2015;133(21):391-400.[17] 田书畅,姚庆强,黎明,等.iASSIST智能辅助定位系统在人工全膝关节置换术中的应用[J].中国数字医学,2016,12(3): 26-29.[18] Lin SJ, Lee CY, Huang KC, et al. Improved femoral component rotation in advanced genu valgum deformity using computerassisted measured resection total knee arthroplasty. J Orthop Surg Res.2015;10: 135.[19] Heyse TJ,Tibesku CO.Improved tibial component rotation in TKA using patient-specifi c instrumentation. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2015; 135(5):697-701.[20] Heyse TJ, Tibesku CO. Improved femoral component rotation in TKA using patient-specific instrumentation.Knee.2014;21(1):268-271.[21] Innocenti B, Bellemans J, Catani F. Deviations from optimal alignment in TKA: Is there a biomechanical difference between femoral or tibial component alignment? J Arthroplasty. 2016;31(1):295-301.[22] Daniilidis K,Tibesku CO.Frontal plane alignment after total knee arthroplasty using patient-specific instruments.Int Orthop. 2013;37(1): 45-50.[23] 李伟,方学伟,周游,等.基于MRI技术全膝关节置换术中个体化导航模板的基础研究[J].中华关节外科杂志: 电子版, 2015,9(1) :71-77.[24] Shen C,Tang ZH,Hu JZ,et al.Patient-specific instrumentation does not improve accuracy in total knee arthroplasty. Orthopedics. 2015;38(3): e178-188.[25] Bae DK, Song SJ, Heo DB, et al. Does the severity of preoperativevarus deformity influence postoperative alignment in bothconventional and computer-assisted total knee arthroplasty? Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc.2013;21(10): 2248-2254.[26] Brinkman JM, Bubra PS, Walker P, et al. Midterm results using a medial pivot total knee replacement compared with the Australian National Joint Replacement Registry data. ANZ J Surg. 2014;84(3): 172-176.[27] Brandon SC, Miller RH, Thelen DG, et al. Selective lateral muscle activation in moderate medial knee osteoarthritis subjects does not unload medial knee condyle. J Biomech. 2014;47(6):1409-1415.[28] Hussain SM, Wang Y, Muller DC, et al. Association between index-to-ring finger length ratio and risk of severe knee and hip osteoarthritis requiring total joint replacement. Rheumatology. 2014; 53(7):1200-1207.[29] Singh JA, Lewallen DG. Cerebrovascular disease is associated with outcomes after total knee arthroplasty: A us total joint registry study. J Arthroplasty. 2014;29(1):40-43.[30] Liu YH,Wang TM, Wei IP, et al.Effects of bilateral medial knee osteoarthritis on intra- and inter-limb contributions to body support during gait. J Biomech. 2014;47(2):445-450.[31] Alghadir A, Omar MT, Al-Askar AB, et al.Effect of low-level laser therapy in patients with chronic knee osteoarthritis: A single-blinded randomized clinical study. Lasers Med Sci. 2014;29(2):749-755. [32] Cram P, Lu X, Kate SL, et al, Total knee arthroplasty volume, utilization, and outcomes among Medicare beneficiaries, 1991-2010. JAMA. 2012; 308(12):1227-1236.[33] Mason J, Fehring T, Estok R, et al. Meta-analysis of alignment outcome in computer-assisted total knee arthroplasty surgery. Arthroplasty. 2007;(22):1097-1099.[34] Yau WP, Chiu KY, Tang WM. Computer navigation did not improve alignment in a lower-volume total knee practice. Clin Orthop Relat Res.2008;(466):935-938.[35] 王伟,徐永胜,吕龙,等. 红外线计算机导航与传统人工全膝关节置换的相关性研究[J].内蒙古医学杂志, 2013,45(2):129-132.[36] 刘峰,张勇,朱庭标,等. 3D打印截骨导板辅助TKA治疗膝外翻畸形[J]. 中国骨与关节损伤杂志, 2017,32(3):329-330.[37] 严志强,张乐,王新亮,等.计算机辅助设计兔解剖型人工膝关节假体[J].广东医学,2014,35(13):1997-2001.[38] Xiao J, Wang C, Zhu L, et al. Improved method for planning intramedullary guiding rod entry point in total knee arthroplasty. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2014;134(5): 693-698.[39] Hasegawa M, Miyazaki S, Yamaguchi T, et al. Comparison of midterm outcomes of minimally invasive computer-assisted vs minimally invasive Jig-based total knee arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 2017;32(1): 43-46.[40] Bae DK, Song SJ, Park CH, et al. A Comparison of the medium-term results of total knee arthroplasty using computer-assisted and conventional techniques to treat patients with extraarticular femoral deformities. J Arthroplasty. 2017;32(1): 71-78.[41] Miyasaka T, Kurosaka D, Saito M, et al. Accuracy of computed tomography-based navigation-assisted total knee arthroplasty: Outlier Analysis. J Arthroplasty. 2017;32(1):47-52.[42] Fujimoto E, Sasashige Y, Nakata K, et al. Technical considerations and accuracy improvement of accelerometer-based portable computer navigation for performing distal femoral resection in total knee arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 2017;32(1):53-60.[43] Liodakis E, Antoniou J, Zukor DJ, et al. Navigated vs conventional total knee arthroplasty: is there a difference in the rate of respiratory complications and transfusions. J Arthroplasty. 2016;31(10): 2273-2277.[44] Zhu M, Ang CL, Yeo SJ, et al. Minimally invasive computer-assisted total knee arthroplasty compared with conventional total knee arthroplasty: a prospective 9-year follow-up. J Arthroplasty. 2016;31(5): 1000-1004. |
.jpg)

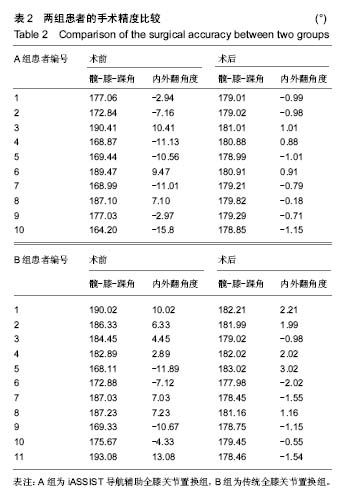
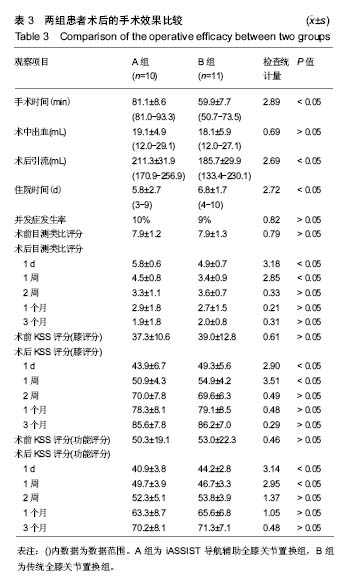
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)