| [1] Avon S L. Forensic odontology: the roles and responsibilities of the dentist.J Can Dent Assoc, 2004;70(7):453-458.[2] Caldas IM, Magalhães T, Afonso A. Establishing identity using cheiloscopy and palatoscopy.Forensic Sci Int.2007;165(1): 1-9.[3] 杨爽,米丛波.放射影像学推断牙龄的方法及应用[J].中华口腔医学研究杂志:电子版, 2012, 6(6):56-59.[4] Abdel Aziz MH, Badr El Dine FM, Saeed NM.Regression equations for sex and population detection using the lip print pattern among Egyptian and Malaysian adult. J Forensic Leg Med. 2016;44:103-110.[5] Hartman D, Drummer O, Eckhoff C, et al. The contribution of DNA to the disaster victim identification (DVI) effort. Forensic Sci Int.2011;205(1-3):52-58.[6] Kim HK, Moon SC,Lee SJ,et al.Three-dimensional biometric study of palatine rugae in children with a mixed-model analysis: A 9-year longitudinal study.AJO-DO. 2012;141(5): 590-597.[7] Thomas CJ,Kotze TJ,Van der Merwe CA.An improved statistical method for the racial classification of man by means of palatal rugae. Arch Oral Biol.1987;32:315-317.[8] Kotrashetti VS,Hollikatti K,Mallapur MD, et al.Determination of palatal rugae patterns among two ethnic populations of India by logistic regression analysis. J Forensic Leg Med. 2011;18(8):360-365. [9] Kapali S,Townsend G,Richards L,et al. Palatal rugae patterns in Australian aborigines and caucasians. Aust Dent J.1997; 42(2): 129-133.[10] Thomas CJ,Kotze TJ.The palatal rugea pattern : a new clasification. Dent Assoc S Afr 1983;38:153-157.[11] English WR,Robison SF,summitt JB,et al.Individuality of human palatal PR.Forensic Sci.1988;33:718-726.[12] Gondivkar SM,Patel S,Gadbail AR,et al. Morphological study of the palatal rugae in western Indian population. J Forensic Leg Med. 2011;18(7):310-312.[13] Santos KC, Fernandes CM, Serra MC. Evaluation of a digital methodology for human identification using palatal rugoscopy. Brazilian Journal of Oral Sciences.2012;10(3):199-203.[14] Jain A,Chowdhary R.Palatal rugae and their role in forensic odontology. J Investig Clin Dent. 2014;5(3):171-178. [15] Santos C,Caldas IM.Palatal rugae pattern in a Portuguese population: a preliminary analysis.J Forensic Sci.2012;57(3): 786-788.[16] Ohtani M, Nishida N, Chiba T, et al. Indication and limitations of using palatal rugae for personal identification in edentulous cases. Forensic Sci Int.2008;176(2-3):178-182.[17] Jacob RF, Shalla CL. Postmortem identification of the edentulous deceased: denture tissue surface anatomy. J Forensic Sci.1987;32(3):698-702.[18] Bernitz H, Stols G. The application of affine transformations in matching distorted forensic samples with a common origin. Forensic Sci Int.2010;201:56-58.[19] Deepak V, Malgaonkar NI,Shah NK, et al.Palatal rugae patterns in orthodontically treated cases, are they a reliable forensic marker.J Int Oral Health.2014;6(5):89-95.[20] Jr P D, Kendrick G S. The effects of tooth movement on the palatine rugae.J Prosthet Dent.1967;18(18):536-542.[21] Mustafa AG, Allouh MZ, Alshehab RM.Morphological changes in palatal rugae patterns following orthodontic treatment.J Forensic Leg Med.2015; 31:19-22.[22] Chen G, Chen S, Zhang X Y, et al. Stable region for maxillary dental cast superimposition in adults, studied with the aid of stable miniscrews. Orthod Craniofac Res.2011;14(2):70-79. [23] Syed S,Alshahrani I,Alshahrani A,et al.Conversion of palatal rugae pattern to scanable Quick Response code in an Arabian population.J Dent Sci.2016;11(3):253-260.[24] Caldas IM,Magalhães T,Afonso A.Establishing identity using cheiloscopy and palatoscopy[J]. Forensic Sci Int.2007; 165(1):1-9.[25] Abdellatif AM,Awad SM,Hammad SM.Comparative study of palatal rugae shape in two samples of Egyptian and Saudi children.Pediatr Dent.2011;21(2):123-128.[26] Nayak P,Acharya AB,Padmini AT,et al. Differences in the palatal rugae shape in two populations of India. Arch Oral Biol.2007;52(10):977-982.[27] Fahmi FM,Al-Shamrani SM,Talic YF.Rugae pattern in a Saudi population sample of males and females. Saudi Dental J. 2001;13(2):92-95. [28] Éverton S. Estracanholli, Kurachi C, Bagnato VS. Tissue Fluorescence Spectroscopy in Death Time Estimation. Forensic Pathology Reviews. Humana Press.2011:6-11.[29] Dohke M, Osato S. Morphological study of the palatal rugae in Japanese.I. Bilateral differences in the regressive evolution of the palatal rugae.Journal of Oral Biosciences.1994; 36(2): 126-140.[30] 李冰,武秀萍,马艳宁,等.利用腭皱特征进行同一认定的指标体系构建[J].中国法医学杂志, 2014,29(6):530-533.[31] 潘菲,李冰,罗晓晋.腭皱唇纹在法医牙科学同一认定中的应用[J].中华老年口腔医学杂志,2015,13(6):355-359.[32] Valeria Hermosilla Venegas, Jaime San Pedro Valenzuela,Mario Cantin Lopez,et al.Palatal rugae: systematic analysis of its shape and dimensions for use in human identification.Int J Morphology.2009;27(3):819-825.[33] Eboh DEO. Palatal rugae patterns of urhobos in abraka, south-southern nigeria.Int J of Morphology.2012;30(2): 709-713.[34] Manjunath S,Bakkannavar SM, Pradeep KG, et al.Palatal rugae patterns among the Indians at Manipal,India.J P BMS. 2012;20(10):1-5. |
.jpg) 文题释义:
腭皱:是指位于硬腭前部,自腭乳头和腭中缝前部向两侧略呈辐射状排列的不规则、不对称软组织嵴。因腭皱的独一无二性,腭皱特点的数字化记录方式可以用于个体身份识别。
牙科法医学:是应用牙科学的信息来鉴别个体身份的科学,其目的是收集、检测以及评价牙科证据而为司法活动提供科学的、具有法律效率的资料。包括咬痕的鉴定,牙齿的鉴定,唾液的鉴定及口腔内软组织创伤的鉴定等。牙科法医学的同一认定则是指运用牙科学方法,利用死者口腔中牙齿、颌骨、口唇和腭部组织等特征的信息来与资料进行比对,进行身份识别的认识活动。
文题释义:
腭皱:是指位于硬腭前部,自腭乳头和腭中缝前部向两侧略呈辐射状排列的不规则、不对称软组织嵴。因腭皱的独一无二性,腭皱特点的数字化记录方式可以用于个体身份识别。
牙科法医学:是应用牙科学的信息来鉴别个体身份的科学,其目的是收集、检测以及评价牙科证据而为司法活动提供科学的、具有法律效率的资料。包括咬痕的鉴定,牙齿的鉴定,唾液的鉴定及口腔内软组织创伤的鉴定等。牙科法医学的同一认定则是指运用牙科学方法,利用死者口腔中牙齿、颌骨、口唇和腭部组织等特征的信息来与资料进行比对,进行身份识别的认识活动。.jpg) 文题释义:
腭皱:是指位于硬腭前部,自腭乳头和腭中缝前部向两侧略呈辐射状排列的不规则、不对称软组织嵴。因腭皱的独一无二性,腭皱特点的数字化记录方式可以用于个体身份识别。
牙科法医学:是应用牙科学的信息来鉴别个体身份的科学,其目的是收集、检测以及评价牙科证据而为司法活动提供科学的、具有法律效率的资料。包括咬痕的鉴定,牙齿的鉴定,唾液的鉴定及口腔内软组织创伤的鉴定等。牙科法医学的同一认定则是指运用牙科学方法,利用死者口腔中牙齿、颌骨、口唇和腭部组织等特征的信息来与资料进行比对,进行身份识别的认识活动。
文题释义:
腭皱:是指位于硬腭前部,自腭乳头和腭中缝前部向两侧略呈辐射状排列的不规则、不对称软组织嵴。因腭皱的独一无二性,腭皱特点的数字化记录方式可以用于个体身份识别。
牙科法医学:是应用牙科学的信息来鉴别个体身份的科学,其目的是收集、检测以及评价牙科证据而为司法活动提供科学的、具有法律效率的资料。包括咬痕的鉴定,牙齿的鉴定,唾液的鉴定及口腔内软组织创伤的鉴定等。牙科法医学的同一认定则是指运用牙科学方法,利用死者口腔中牙齿、颌骨、口唇和腭部组织等特征的信息来与资料进行比对,进行身份识别的认识活动。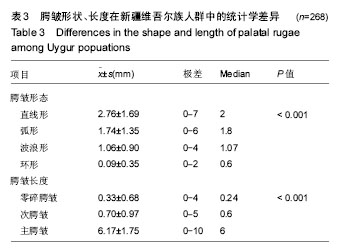
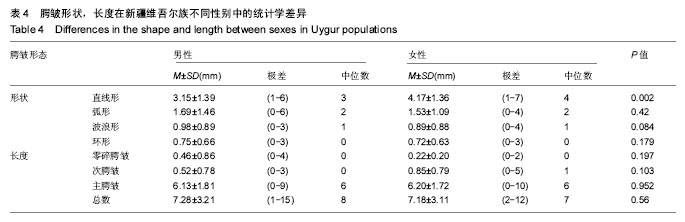
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg) 文题释义:
腭皱:是指位于硬腭前部,自腭乳头和腭中缝前部向两侧略呈辐射状排列的不规则、不对称软组织嵴。因腭皱的独一无二性,腭皱特点的数字化记录方式可以用于个体身份识别。
牙科法医学:是应用牙科学的信息来鉴别个体身份的科学,其目的是收集、检测以及评价牙科证据而为司法活动提供科学的、具有法律效率的资料。包括咬痕的鉴定,牙齿的鉴定,唾液的鉴定及口腔内软组织创伤的鉴定等。牙科法医学的同一认定则是指运用牙科学方法,利用死者口腔中牙齿、颌骨、口唇和腭部组织等特征的信息来与资料进行比对,进行身份识别的认识活动。
文题释义:
腭皱:是指位于硬腭前部,自腭乳头和腭中缝前部向两侧略呈辐射状排列的不规则、不对称软组织嵴。因腭皱的独一无二性,腭皱特点的数字化记录方式可以用于个体身份识别。
牙科法医学:是应用牙科学的信息来鉴别个体身份的科学,其目的是收集、检测以及评价牙科证据而为司法活动提供科学的、具有法律效率的资料。包括咬痕的鉴定,牙齿的鉴定,唾液的鉴定及口腔内软组织创伤的鉴定等。牙科法医学的同一认定则是指运用牙科学方法,利用死者口腔中牙齿、颌骨、口唇和腭部组织等特征的信息来与资料进行比对,进行身份识别的认识活动。