| [1]中蓝晨光化工研究设计院有限公司. 2014~2015年世界塑料工业进展[J]. 塑料工业,2016,44(3):1-46.[2]张丽. 我国聚氨酯产业现状分析及展望(待续)[J]. 化学工业, 2015,33(1):15-18.[3]张丽. 我国聚氨酯产业现状分析及展望(续完)[J]. 化学工业, 2015,33(Z1):12-22.[4]4,4'-Methylenediphenyl diisocyanate and polymeric 4,4'-methylenediphenyl diisocyanate. IARC Monogr Eval Carcinog Risks Hum. 1999;71 Pt 3:1049-1058.[5]Concise International Chemical Assessment Document 27, DIPHENYLMETHANE DIISOCYANATE (MDI), WHO, 2000.[6]Schwab SJ. Hemodialysis vascular access: the Achilles' heel remains. Kidney Int. 2007;72(6):665-666.[7]Cornelis T, Usvyat LA, Tordoir JH, et al. Vascular access vulnerability in intensive hemodialysis: a significant Achilles' heel. Blood Purif. 2014;37(3):222-228.[8]US Renal Data System: USRDS 2002 Annual Data Report. Bethesda, National Institutes of Health, National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases, 2002, chapt 4.[9]2003 annual report: ESRD clinical performance measures project. Am J Kidney Dis. 2004;44(2 Suppl 1):A5-6, S1-92.[10]李绍雄,刘益军.聚氨酯树脂及其应用[M].北京:化学工业出版社,2004:305.[11]李汾.医用聚氨酯弹性体[J].科技情报开发与经济, 2001,11(4): 95-96.[12]潘才元.功能高分子[M].北京:科学出版社,2006.[13]钟金汤.偶氮染料及其代谢产物的化学结构与毒性关系的回顾与前瞻[J].环境与职业医学,2004,21(1):58-62.[14]徐德珍,贺一训. 偶氮染料中微量芳香胺类的分析方法现状[J].印染,1996(3):26-30.[15]杨晓芬,李军湘.N-氯代丁二酰亚胺8-羟基喹哪啶分光光度法测定水中苯胺类化合物的方法研究[J].内蒙古石油化工, 2002, 27(1):25-26.[16]马立斌,宋春娟.甲萘酚代替萘乙二胺测定水中苯胺类化合物[J].河北工业科技,2000,17(4):21-22.[17]杨晓芬,赵美萍,李元宗,等.水中苯胺类化合物的分光光度法测定[J].分析化学,2002,30(5):540-543.[18]Longo M, Cavallaro A. Determination of aromatic amines at trace level by derivatization with heptafluorobutyric an hydride and gas Chromatography-electron-capture negative-ion chemical ionization analysis spectrometry. J Chromatogr A. 1996;753:91-100.[19]Kataoka H. Derivatization reactions for the determination of amines by gas chromatography and their applications in environmental analysis. J Chromatogr A.1996;733(1-2): 19-34.[20]Schmidt TC, Less M, Haas R, et al. Gas chromatographic determination of aromatic amines in water samples after solid-phase extraction and derivatization with iodine. I. Derivatization. J Chromatogr A. 1998;810(1-2):161-172.[21]海勇,田树盛.致癌芳香胺的检测[J].印染助剂,2005,22(9):42-45.[22]Huang M, Tai C, Zhou Q, et al. Preparation of polyaniline coating on a stainless-steel wire using electroplating and its application to me determination of six aromatic amines using headspace splid-phase micrextraction. J Chromatogr A. 2004; 1048(2):257-262.[23]Kataoka H. Derivatization reactions for the determination of amines by gas chromatography and their applications in environmental analysis. J Chromatogr A. 1996;733(1-2): 19-34.[24]Brede C, Skjevrak I, Herikstad H. Determination of primary aromatic amines in water food simulant using solid-phase analytical derivatization followed by gas chromatography coupled with mass spectrometry. J Chromatogr A. 2003; 983(1-2):35-42.[25]Singh V, Gupta M, Jain A, et al. Determination of aromatic primary amines at microg l(-1) level in environmental waters by gas chromatography-mass spectrometry involving N-allyl-n'-arylthiourea formation and their on-line pyrolysis to aryl isothiocyanates. J Chromatogr A. 2003;1010(2):243-253.[26]Chang WY, Sung YH, Huang SD. Analysis of carcinogenic aromatic amines in water samples by solid-phase microextraction coupled with high-performance liquid chromatography. Analytica Chimica Acta. 2003; 495(1): 109-122.[27]陈为都,王小妹,黄仲立. IPDI 及MDI 型聚氨酯预聚体中游离二异氰酸酯含量测定[J] .聚氨酯工业,2009,24(2):43-46.[28]姚洁,胡晓佳,王庆印,等.4,4'-二苯甲烷二异氰酸酯的高效液相色谱分析[J].化学通报, 2008(6):457-460.[29]栾杨,李翎,王晓云,等.高效液相色谱测定车间空气中4,4'-二苯甲烷二异氰酸酯[J] .中国公共卫生, 1999,15(10):937-938.[30]姚洁,王公应.4,4'-二苯甲烷二异氰酸酯的HPLC分析[J].天然气化工, 2005,30(5): 68-70.[31]张敏,雷兴红. 涂料中游离甲苯二异氰酸酯的气相色谱测定法[J]. 环境与健康杂志,2003,20(6):364-365.[32]郭巧珍,杜振霞. UPLC-MS/MS测定二苯甲烷二异氰酸酯[J]. 质谱学报,2011, 32(2):112-116.[33]Zhu Y, Wang M, Du H, et al. Organic analysis by ion chromatography. 1. Determination of aromatic amines and aromatic diisocyanates by cation-exchange chromatography with amperometric detection. J Chromatogr A. 2002;956(1-2): 215-220.[34]黄甫.苯胺及其衍生物的毛细管电泳行为研究[J].理化检验化学分册,2003,39(12): 696-699. |
.jpg)
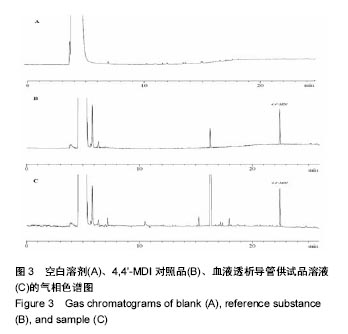
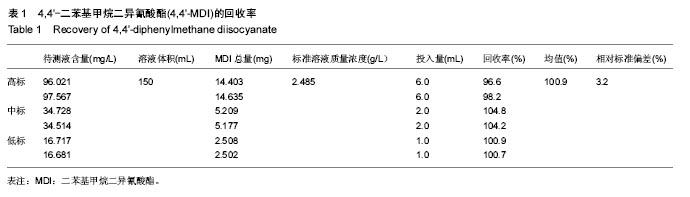
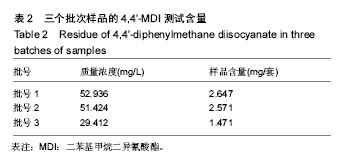
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)