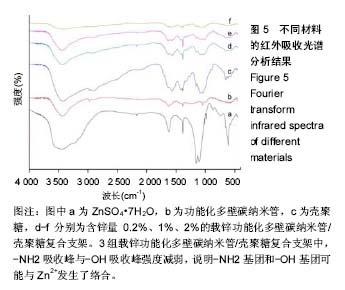
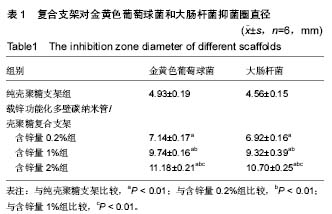
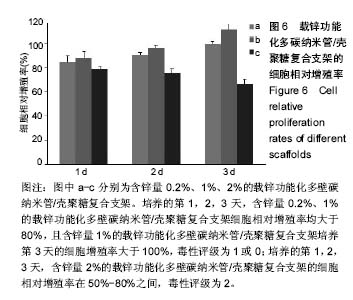
| [1]Delawi D,Kruyt MC,Huipin Y,et al.Comparing autograft, allograft, and tricalcium phosphate ceramic in a goat instrumented posterolateral fusion model. Tissue Eng Part C Methods. 2013; 19(11):821-828. [2]刘守应,王继芳,蔡谞.骨再生的研究进展[J].中国保健医学杂志,2014, 16(1):67-70.[3]杨毅,毕鑫,李多玉,等.人工骨材料修复骨缺损:多种复合后的生物学与力学特征[J].中国组织工程研究,2014,16(18):2582-2587.[4]Rezvani Z,Venugopal JR,Urbanska AM,et al.A bird's eye view on the use of electrospun nanofibrous scaffolds for bone tissue engineering: Current state-of-the-art, emerging directions and future trends.Nanomedicine. 2016;12(7):2181-2200. [5]夏琰,周潘宇,许硕贵.生物材料与支架在骨组织工程领域的研究进展[J].中华损伤与修复杂志(电子版),2012,7(5):516-519.[6]李吉鹏,邓国英,赵庆华.种子细胞-支架复合体在骨组织修复中的研究进展[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2012,20(20):1857-1860.[7]Billström GH,Blom AW,Larsson S,et al.Application of scaffolds for bone regeneration strategies: current trends and future directions. Injury.2013;44 Suppl 1:S28-33.[8]Kosuge D,Khan WS,Haddad B,et al.Biomaterials and scaffolds in bone and musculoskeletal engineering.Curr Stem Cell Res Ther. 2013;8(3):185-191.[9]Pighinelli L,Kucharska M.Chitosan-hydroxyapatite composites. Carbohydr Polym.2013;93(1):256-262.[10]Sowjanya JA,Singh J,Mohita T,et al.Biocomposite scaffolds containing chitosan/alginate/nano-silica for bone tissue engineering.Colloids SurfB Biointerfaces.2013;109:294-300.[11]Calderón L,Harris R,Cordoba-Diaz M,et al.Nano and microparticulate chitosan-based systems for antiviral topical delivery.Eur J Pharm Sci.2013;48(1-2):216-222.[12]Gao C,Cai Y,Kong X,et al.Development and characterization of injectable chitosan-based hydrogels containing dexame thasone/rhBMP-2 loaded hydroxyapatite nanoparticles.Mater Lett.2013;93(1):312-315.[13]Jiang T,Deng M,James R,et al.Micro-and nanofabrication of chitosan structures for regenerative engineering.Acta Biomater. 2014;10(4):1632-1645.[14]Edwards SL,Werkmeister JA,Ramshaw JA,et al.Carbon nanotubes in scaffolds for tissue engineering. Expert Rev Med Devices.2009;6(5):499-505.[15]Sahoo NG,Pan YZ,Li L,et al.Nanocomposites for bone tissue regeneration.Nanomedicine.2013;8(4):639-653.[16]Laurencin CT,Nukavarapu SP,Kumbar SG.Carbon nanotube composite scaffolds for bone tissue engineering :USA, US20090586345[P].2009-09-21.[17]Zdenko S,Dimitrios T,Konstantinos P,et al.Carbon nanotube-polymer composites: Chemistry,processing,mechanical and electrical properties.Prog Polym Sci.2010;35:357-401.[18]Abarrategi A,Gutiérrez MC,Moreno-Vicente C,et al.Multiwall carbon nanotube scaffolds for tissue engineering purposes. Biomaterials.2008;29(1):94-102.[19]Ji Z,Lin G,Lu Q,et al.Targeted therapy of SMMC-7721 liver cancer in vitro and in vivo with carbon nanotubes based drug delivery system.J Colloid Interface Sci.2012;365(1):143-149. [20]Ma Y,Zhou T,Zhao C.Preparation of chitosan-nylon-6 blended membranes containing silver ions as antibacterial materials. Carbohydr Res.2008;343(2):230-237.[21]王昕,张春丽,任广军,等.碳纳米管吸附去除水溶液中锌离子的性能[J].电镀与精饰,2008,30(10):4-6.[22]Hu H,Zhang W,Qiao Y,et al.Antibacterial activity and increased bone marrow stem cell functions of Zn-incorporated TiO2 coatings on titanium.Acta Biomater.2012;8(2):904-915.[23]Niranjan R,Koushik C,Saravanan S,et al.A novel injectable temperature-sensitive zinc doped chitosan/β-glycerophosphate hydrogel for bone tissue engineering.Int J Biol Macromol. 2013; 54:24-29.[24]Applerot G,Lipovsky A,Dror R,et al.Enhanced antibacterial activity of nanocrystalline ZnO due to increased ROS-mediated cell injury. Adv Funct Mater.2009;19:842-852.[25]Nagata M, Lönnerdal B.Role of zinc in cellular zinc trafficking and mineralization in a murine osteoblast-like cell line.J Nutr Biochem. 2011;22(2):172-178. [26]Qiao Y,Zhang W,Tian P,et al.Stimulation of bone growth following zinc incorporation into biomaterials.Biomaterials. 2014;35(25): 6882-6897.[27]袁景,甄平.骨组织工程支架的研究进展[J].医学综述, 2015,21(12): 2126-2130.[28]徐大朋,王绪凯.骨组织工程支架研究进展[J].中国实用口腔科杂志, 2014,7(3):177-181.[29]Jiang T,James R,Kumbar SG,et al.Chitosan as a biomaterial: structure,properties and applications in tissue engineering and drug delivery.Natural and Synthetic Biomedical Polymers.2014; 5:91-113.[30]Niranjan R,Koushik C,Saravanan S,et al.A novel injectable temperature-sensitive zinc doped chitosan/β-glycerophosphate hydrogel for bone tissue engineering.Int J Biol Macromol. 2013; 54:24-29.[31]Rodríguez-Vázquez M,Vega-Ruiz B,Ramos-Zúñiga R,et al.Chitosan and Its Potential Use as a Scaffold for Tissue Engineering in Regenerative Medicine.Biomed Res Int. 2015; 2015:821279.[32]年争好,孙凯,李瑞欣.组织工程骨研究背景与进展[J].中华损伤与修复杂志:电子版,2013,8(5):525-528.[33]Muzzarelli RA,Greco F,Busilacchi A,et al.Chitosan, hyaluronan and chondroitin sulfate in tissue engineering for cartilage regeneration: a review.Carbohydr Polym.2012;89(3):723-739.[34]赵易尔,金丹.壳聚糖复合材料在骨组织工程中的应用[J].基因组学与生物学,2015,34(4):842-848. [35]Zhang BG,Myers DE,Wallace GG,et al.Bioactive coatings for orthopaedic implants-recent trends in development of implant coatings.Int J Mol Sci.2014;15(7):11878-11921.[36]Puvaneswary S,Talebian S,Raghavendran HB,et al.Fabrication and in vitro biological activity of βTCP-Chitosan-Fucoidan composite for bone tissue engineering.Carbohydr Polym. 2015; 134:799-807. [37]Nanda Gopal Sahoo,Yong Zheng Pan,Lin Li,et al.Nanocomposites for bone tissue regeneration. Nanomedicine.2013;8(4):639-653.[38]Edwards SL,Werkmeister JA,Ramshaw JA,et al.Carbon nanotubes in scaffolds for tissue engineering. Expert Rev Med Devices.2009;6(5):499-505.[39]Pan L,Pei X,He R,et al.Multiwall carbon nanotubes/polycaprolactone composites for bone tissue engineering application.Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2012;93:226-234.[40]Venkatesan J,Ryu B,Sudha PN,et al.Preparation and characterization of chitosan-carbon nanotube scaffolds for bone tissue engineering.Int J Biol Macromol.2012;50(2):393-402.[41]Aryaei A,Jayatissa AH,Jayasuriya AC.Mechanical and biological properties of chitosan/carbon nanotube nanocomposite films.J Biomed Mater Res A.2014;102(8):2704-2712. [42]欧阳明,丁纯梅,肖莎,等.壳聚糖及Zn2+模板壳聚糖膜与Zn2+螫合反应的动力学及机理探讨[J].化学世界,2006,47(7):388-394.[43]Ma Y,Zhou T,Zhao C.Preparation of chitosan-nylon-6 blended membranes containing silver ions as antibacterial materials. Carbohydr Res.2008;343(2):230-237.[44]李高青,桑青,崔凯.壳聚糖纳米银复合物基温敏水凝胶的抑菌性及细胞相容性研究[J].中国生化药物杂志,2016,36(6):63-66.[45]Swetha M,Sahithi K,Moorthi A,et al.Synthesis, Characterization, and Antimicrobial Activity of Nano-Hydroxyapatite-Zinc for Bone Tissue Engineering Applications.J Nanosci Nanotechnol. 2012; 12(1):167-172.[46]Tripathi A,Saravanan S,Pattnaik S,et al.Bio-composite scaffolds containing chitosan/nano-hydroxyapatite/ nano-copper-zinc for bone tissue engineering.Int J Biol Macromol.2012;50(1):294-299.[47]Jin G,Cao H,Qiao Y,et al.Osteogenic activity and antibacterial effect of zinc ion implanted titanium.Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2014;117:158-165. [48]Qiao Y,Zhang W,Tian P,et al.Stimulation of bone growth following zinc incorporation into biomaterials.Biomaterials. 2014;35(25): 6882-6897.[49]余增丽,李云,郑艾.锌对体外培养小鼠胎鼠前肢骨发育的影响[J].中华预防医学杂志,2002,36(2):97-99.[50]马丽英,李灵芝,李云,等.锌缺乏和过量对小鼠胚胎体外骨形成的影响[J].营养学报,2000,22(1):18-21. |
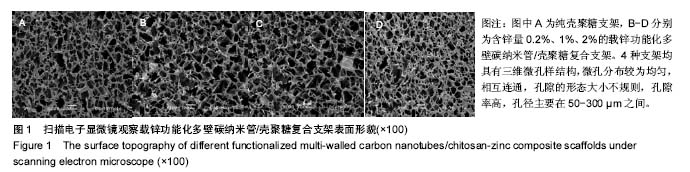
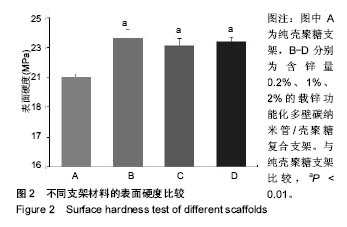
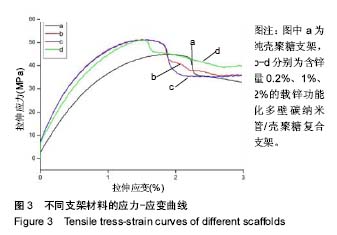
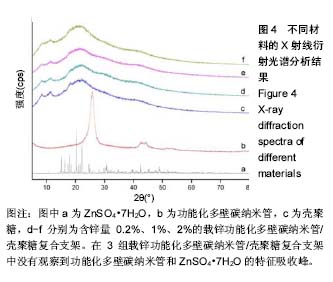
.jpg)
.jpg)