中国组织工程研究 ›› 2026, Vol. 30 ›› Issue (20): 5349-5360.doi: 10.12307/2026.146
• 生物材料综述 biomaterial review • 上一篇
水凝胶在眼科疾病中的应用与发展趋势
刘淑婷,邱沐恩,李 卫
- 北京体育大学体能训练学院,北京市 100084
-
接受日期:2025-05-26出版日期:2026-07-18发布日期:2025-12-03 -
通讯作者:李卫,教授,北京体育大学体能训练学院,北京市 100084 -
作者简介:刘淑婷,女,2001年生,天津市人,汉族,硕士,主要从事运动训练理论与实践方面的研究。 -
基金资助:国家蹦床队体能保障服务,国家体育总局服务项目(BUS20240236),项目负责人:李卫
Application and development trend of hydrogels in ophthalmic diseases
Liu Shuting, Qiu Muen, Li Wei
- School of Physical Training, Beijing Sport University, Beijing 100084, China
-
Accepted:2025-05-26Online:2026-07-18Published:2025-12-03 -
Contact:Li Wei, Professor, School of Physical Training, Beijing Sport University, Beijing 100084, China -
About author:Liu Shuting, MS, School of Physical Training, Beijing Sport University, Beijing 100084, China -
Supported by:National Trampoline Team Physical Fitness Support Service, State Sports General Administration Service Project, No. BUS20240236 (to LW)
摘要:
文题释义:
眼表:包括角膜、结膜和泪腺、副泪腺、睑板腺和相关的结构。
眼底:指眼球后段的底部,包括视网膜、脉络膜、视神经头、黄斑、视网膜中央动脉和静脉等。
背景:水凝胶凭借良好的组织相容性以及可调控的理化特性和光响应行为,在角膜再生、玻璃体替代、晶状体修复及视网膜再生等组织工程领域显示出广泛应用前景。
目的:梳理水凝胶在眼科疾病治疗中的主要研究进展,涵盖材料类型及其在组织修复、药物递送与3D打印应用方面的情况,同时探讨当前存在的问题与未来发展趋势。
方法:以“Hydrogel,Ophthalmology,Tissue engineering,Drug transport,3D printing”为英文检索词,以“水凝胶,眼科,组织工程,药物运输,3D打印”为中文检索词,检索PubMed数据库、中国知网建库至2025年2月发表的相关文献,根据纳入与排除标准,最终纳入145篇文献进行综述。
结果与结论:水凝胶在角膜损伤修复、玻璃体替代材料及眼底药物缓释等方面取得了初步成果。已有研究指出,通过调节光照条件可实现材料交联度与力学性能的动态调控,从而满足眼部不同部位的治疗要求。在3D打印等技术辅助下,水凝胶的个性化应用能力也进一步增强。部分动物实验结果显示水凝胶在组织修复与药效释放方面具有良好前景,然而目前大多数数据仍来源于鼠类或兔类模型,尚缺乏与人类生理更接近的高阶动物研究;此外,现有成果在临床转化路径中还未与实际需求实现有效对接。总体来看,水凝胶作为眼科组织工程和递药平台具备应用潜力,但临床转化过程仍需解决材料改良、实验模型可靠性和成果落地等关键问题。未来若能通过配方优化、建立更合适的研究模型,并加强学科间的协同,将有望加速水凝胶在眼科精准治疗中的实际应用。
https://orcid.org/0009-0005-7191-9465 (刘淑婷)
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:生物材料;骨生物材料;口腔生物材料;纳米材料;缓释材料;材料相容性;组织工程
中图分类号:
引用本文
刘淑婷, 邱沐恩, 李 卫. 水凝胶在眼科疾病中的应用与发展趋势[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2026, 30(20): 5349-5360.
Liu Shuting, Qiu Muen, Li Wei. Application and development trend of hydrogels in ophthalmic diseases[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2026, 30(20): 5349-5360.
1970年,水凝胶初次被应用到隐形眼镜制造中,此种隐形眼镜所用的柔软、透氧材料,显著增强了佩戴者的舒适度,并且开启了水凝胶在眼科应用的开端[21]。后续水凝胶不仅提高眼部药物的利用度和治疗效果[22],还通过引入光交联技术[23],实现了对水凝胶物理化学性质的精准把握,加大了它在组织工程与再生医学当中的应用潜力。中山眼科中心制造出多种水凝胶,实现了药物不间断释放,提高了治疗效率[24-26]。
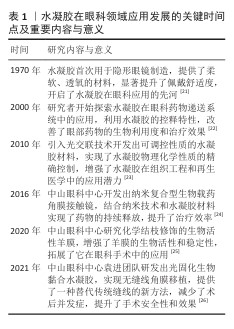
2.2 水凝胶的种类 水凝胶根据来源可分为天然水凝胶和合成水凝胶(图3),水凝胶的主要成分是水溶性聚合物,主要交联方式包括物理交联和化学交联。化学交联方法常见的有自由基引发的链式聚合反应和生物正交点击反应[27-28]。自由基引发的链式聚合反应是合成水凝胶中最常用的方法,通常以甲基丙烯酸酯功能化预聚物为基础,通过链式生长机制形成交联网络[29];生物正交点击反应具有反应活性高、选择性好、反应条件温和等特点,有利于形成结构稳定、内容物包封良好的水凝胶[28,30]。
2.2.1 天然材料 诸如胶原蛋白、明胶、透明质酸、壳聚糖、丝素蛋白等天然水凝胶材料来源丰富,具备较好的生物相容性与生物降解性。天然材料水凝胶的力学性能较弱,但该分子链上的活性基团为功能修饰提供了切入点[31],可利用接枝改性、多重交联或与其他聚合物复合等方法对水凝胶的物理性质进行调控,以改进其力学性能和功能属性,进而适应不同生物医学应用的要求[32]。
明胶:源自胶原蛋白,属于Ⅰ型胶原蛋白的衍生产物,呈现出良好的水溶性、温度敏感性、高生物相容性、可降解的特点和低抗原性[33]。作为细胞外基质里的主要组成成分,明胶所含有的序列为精氨酸 -甘氨酸-天冬氨酸,可提升细胞黏附性,同时改善细胞微环境[34]。天然明胶水凝胶存在力学性能差、稳定性欠佳、降解速度快等问题,为克服这些问题,增强材料的机械强度、稳定性及细胞相容性,研究者把甲基丙烯酸酯基团连接到明胶侧链上合成了甲基丙烯酸酯化明胶,甲基丙烯酸酯明胶在紫外光、可见光照射时可发生链式光聚合,水凝胶的弹性模量(3.3-110 kPa)可借助甲基丙烯酸酯取代度与浓度进行调节,进而形成具备可调节力学性能、高生物相容性和低免疫原性的水凝胶[35]。YANG等[35]开发出一种依托甲基丙烯酸酯明胶的水凝胶,与传统水凝胶相比对,甲基丙烯酸酯明胶既具备天然水凝胶的优势又有合成水凝胶的长处,在生物医学领域应用十分广泛,被视作当下最具代表性的水凝胶材料之一。
透明质酸:是一种亲水性较好、呈现电负性的线性非磺化糖胺聚糖,由D-乙酰氨基葡萄糖和D-葡萄糖醛酸连接形成[36],为细胞外基质里的主要成分,在皮肤、软骨、玻璃体等组织中广泛存在,也在炎症反应和血管生成的进程当中起到关键作用[37]。透明质酸因优秀的黏弹性、生物相容性、可降解性及亲水性在再生医学方面呈现出巨大的应用潜力[38]。传统透明质酸水凝胶鉴于侧链彼此结合较为松散,导致力学强度偏低,并且容易受到水解和降解方面的影响[39]。为优化透明质酸的理化性质,可借助化学修饰方式去改变透明质酸分子上的羟基和羧基等活性基团,例如,在透明质酸链上添加甲基丙烯酸酯基团后,借助紫外线照射可完成光交联,形成机械强度更高、能装填生物活性因子的透明质酸水凝胶[40],强化细胞之间的黏附能力。SHEN等[41]利用甲基丙烯酸酯基团和猪源脱细胞角膜基质水凝胶构建了双交联双网络复合水凝胶,不仅弥补了透明质酸细胞黏附性不足的缺陷,还表现出良好的促进再生生物活性、附着能力及力学性能,该水凝胶能毫无缝隙地闭合不同形状及大小的角膜缺损,为角膜细胞打造理想的生长空间,助力角膜再上皮化与间质实现再生,同时切实抑制瘢痕的生成,推动透明角膜的重建工作。
胶原蛋白:作为稳定的三螺旋结构蛋白,具有高度可把握的生物力学特性,整体基本结构由重复三肽组成,分子长度大致为300 nm[42]。胶原蛋白具有良好的生物相容性、物理力学性能及较低的免疫原性,同时也是极为关键的细胞外基质蛋白之一,可作为细胞的支架以支持细胞增殖,是结缔组织的核心构成要素[43]。Ⅰ型、Ⅱ型和Ⅲ型胶原蛋白的含量占总胶原蛋白的90%以上,在生物医学领域有着大范围的应用[44],三螺旋结构赋予了胶原蛋白一定的抗蛋白酶能力[45-46]。为强化胶原蛋白的机械强度与耐用能力,可借助交联剂或对其侧链上的光敏基团进行化学修饰,诸如甲基丙烯酸酯和环氧丙基甲基丙烯酸酯,使材料在紫外光、可见光照射的条件下交联,形成稳定性和机械强度更好的水凝胶[47],在组织工程、再生医学、药物递送与生物传感等领域均体现出显著的应用价值[48-49]。
丝素蛋白:作为常见的天然纤维蛋白,组成结构和细胞外基质较为相似[25]。丝素蛋白由一条疏水重链和一条由甘氨酸-丙氨酸-甘氨酸-丙氨酸-甘氨酸-甘氨酸-丝氨酸-丙氨酸/丝氨酸/酪氨酸?重复序列组成的相对柔软灵活的亲水轻链构成,而且借助二硫键加以连接,赋予它出色的稳定性和柔韧性[20,50-51]。丝素蛋白因突出的生物相容性、生物降解性、透气性及抗菌特点,在推动伤口愈合和组织修复方面成效显著[52-54]。丝素蛋白水凝胶具有独特的半结晶结构,展现出优异的力学性能、多孔性及可控的药物释放能力,成为一种智能高分子生物材料,在伤口敷料、药物递送及组织工程等领域得到广泛应用[50-51,55]。通过化学修饰可进一步优化丝素蛋白的力学性能及生物功能,以满足不同应用需求[51,56-57]。QIAN等[58]开发了一种基于无机Zn2+诱导自组装的甘草酸和丝素蛋白光交联甲基丙烯酸丝素聚合物杂化水凝胶,该水凝胶具备快速原位光交联能力、良好的组织黏附性及机械强度,能够调节炎症微环境并促进伤口愈合。MEI等[59]构建了一种新型水凝胶体系M@M-Ag-Sil-MA,该体系由甲基丙烯氧化丝蛋白水凝胶、二甲双胍负载的介孔二氧化硅微球及银纳米颗粒组成,甲基丙烯氧化丝蛋白赋予水凝胶体系良好的光交联能力,并能精准控制银纳米颗粒的释放,以抑制细菌增殖并创造无菌微环境;M@M-Ag-Sil-MA通过调节免疫微环境抑制中性粒细胞胞外陷阱形成,减少促炎因子的释放,促进成纤维细胞迁移及血管生成,从而加快伤口愈合。
壳聚糖:是一种由氨基葡萄糖(2-氨基-2-脱氧葡萄糖)和乙酰氨基葡萄糖(2-乙酰氨基-2-脱氧葡萄糖)通过β-1,4-糖苷键连接而成的线性多糖共聚物,主要来源于海洋甲壳类动物,由几丁质去乙酰化得到。壳聚具有优异的生物相容性、抗菌性及黏附性,在伤口敷料、组织工程及药物输送等领域得到广泛应用[60-62]。壳聚糖分子上的氨基和羟基等活性基团可与不同的交联剂或聚合物结合,优化材料的理化性质及功能[63]。通过在壳聚糖结构中引入甲基丙烯酸酯等光敏基团,在紫外线或蓝光照射下,光引发剂产生自由基诱导壳聚糖分子间的共价交联,从而形成水凝胶,该水凝胶的机械性能和结构可通过浓度调控,以适应不同应用需求[63-66]。由于出色的亲水性、生物相容性、无毒性及广谱抗菌、抗肿瘤和抗氧化等特性,壳聚糖水凝胶在药物输送及组织工程领域备受关注[64,67]。
2.2.2 合成材料 合成水凝胶的材料如聚乙二醇、聚丙烯酸、聚乙烯醇与聚丙烯酰胺,一般借助化学交联来形成水凝胶。与天然水凝胶相比较,合成水凝胶具有可调控的结构、较高的机械强度以及可掌控的生物降解性,但生物相容性欠佳,可能存在生物毒性与免疫排斥风险[25,36,68]。
聚乙二醇:聚乙二醇分子上有丰富的侧链活性基团,可利用化学修饰或使其与蛋白质、药物结合,以此优化药代动力学和药效学特性。聚乙二醇可提升生物相容性、弱化免疫原性、减少网状内皮系统对物质的清除率,进而延长药物在体内的循环半衰
期[69-70]。聚乙二醇及其衍生物被大量应用于医疗器械的涂层,或者作为药物、生物活性分子的输送载体,也可以辅助细胞培养和干细胞分化[51,71]。
采用丙烯酸酯基团修饰聚乙二醇可以制备能光聚合的聚乙二醇二丙烯酸酯[72],该水凝胶的快速光交联能力可实现对细胞或药物的包裹,同时拥有可调节的力学性能、良好的细胞附着性、高效的控释本领,并且具备抗菌和抗氧化属性,在组织工程和药物递送领域呈现出广阔的应用前景[73]。
聚乙烯醇:由醋酸乙烯进行聚合及醇解反应生成,含有众多的羟基,能溶于水进而形成氢键,为一种可实现生物降解的半结晶合成聚合物,具有良好的生物相容性、黏附性和较好的机械性能[74],在伤口敷料与药物递送系统应用广泛[75]。单独使用聚乙烯醇存在一定局限,如耐水方面表现差、生物活性有限、不能有效吸收渗出液、无法实现持续的药物释放,将聚乙烯醇与其他材料复合起来或进行化学修饰,可用来制备生物相容性好、能降解且具备抗菌能力的伤口敷料[76-77],将聚乙烯醇与紫外光固化甲基丙烯酸酯或RGD多肽聚合物相结合,可增加细胞黏附性,同时扩大聚乙烯醇在软组织工程中的潜在应用可能[78]。
聚丙烯酸:是丙烯酸单体借由共价键聚合所形成的水溶性聚合物,分子的结构中含有顺式双键及羧基,赋予它较强的亲水能力和良好的黏附能力[79]。依靠甲基丙烯酸开展修饰,可制备水下键合的聚丙烯酸水凝胶涂层,赋予惰性材料水下黏附的能力,这在伤口敷料领域有着不可忽视的应用价值[80]。通过调控聚丙烯酸的侧链结构与交联手段可形成多功能水凝胶[81],例如将聚丙烯酸与聚丙烯酰胺相结合,在光照情形下可推动聚合物从液态转为固态,应用于靶向药物传送及持续控释[82]。
聚丙烯酰胺:由丙烯酰胺均聚、共聚而形成,是一种热稳定性佳的线性聚合物[83],拥有大量的酰胺基团,可协助形成氢键,故而具备良好的水溶性及化学活性,在医疗和其他工业领域均有大量应用[81]。聚丙烯酰胺的机械性能良好,但细胞黏附性欠佳,常将它与天然水凝胶结合以改良生物相关性能,例如,LI等[84]研发了一种以聚丙烯酰胺为基础的抗菌水凝胶,该水凝胶将丙烯酰胺和多巴胺-透明质酸-ε-聚(L-赖氨酸)作为基础,经过蓝光照射能迅速交联成凝胶,与伤口形态相契合,同时供应有效的抗菌阻挡屏障,加快感染伤口的愈合。
2.3 水凝胶在眼科领域的应用
2.3.1 水凝胶在眼科组织工程中的应用 在眼科组织工程中,生物材料必须能够与机体相互作用以诱导组织再生、重塑并最终完全降解。水凝胶具有良好的机械适应性和生物相容性,能够在其网络结构中封装活细胞,并允许按需调整物理和化学性质,因此在眼科组织工程领域展现出广阔的应用前景[85]。用于眼科组织工程中的水凝胶见表2。
水凝胶在角膜组织工程中的应用:近年来,水凝胶在角膜组织工程中的应用成为研究热点,尤其在角膜基质修复和玻璃体替代物的研发方面。研究人员致力于利用水凝胶构建组织工程角膜基质,以促进角膜修复和再生。LI等[86]设计了一种水凝胶,通过硫代烯化学反应实现快速交联,展现出良好的生物相容性和高透明度,兔角膜损伤模型研究表明该水凝胶可加速角膜上皮化、减少角膜瘢痕和雾霾形成、促进角膜组织再生。ZHAO等[87]开发了一种由甲基丙烯酸酯明胶和氧葡聚糖组成的双网络水凝胶,与传统纤维蛋白胶等商用黏合剂相比,该水凝胶具有更高的透光性、抗酶降解能力及优异的黏附强度,在角膜修复应用中该水凝胶能够长期稳定附着在角膜表面,促进角膜快速再上皮化。YAZDANPANAH等[88]合成一种水凝胶角膜基质,交联后的该水凝胶呈现出出色的生物力学性能、稳定性和生物黏附性,可有效对全层角膜穿孔及组织缺损进行闭合,为角膜修复给出了一种新型材料。LI等[89]进一步开发出一种复合水凝胶用于促进圆锥角膜修复,该水凝胶可直接在兔角膜深层基质缺损处实现固化,无空隙填充并支撑角膜上皮及基质再生长,为角膜疾病的治疗供应了新的解决办法。
水凝胶在玻璃体替代物中的应用:视网膜脱离与视网膜损伤的治疗借助玻璃体替代物,一般传统玻璃体替代品以气体和硅油为主,但这些材料均存在某些缺陷,硅油植入后要进行二次手术移除,同时气体替代物的稳定性处于较差水平[96]。水凝胶因良好的透明程度、合适的力学性能及良好的生物相容性,可作为一种理想的玻璃体替代物。RAIA等[90]开发出一种以过氧化物酶交联的透明质酸水凝胶,采用调控交联密度此水凝胶展现出优良的机械强度及膨胀性能,在维持眼内压和实现视网膜定位方面效果较好,基于猪眼玻璃体去除模型的实验结果表明,该水凝胶植入后眼部形态和眼压恢复正常,为玻璃体替代创造了新的机会。WANG等[91]研制出一种以N-丙烯酰氨基酰胺和羧甜菜碱丙烯酰胺为基础的双聚合物水凝胶,该水凝胶不仅拥有良好的透明性和稳定性,还能在体温条件下迅速凝胶化,表现出极微弱的纤维化反应,而且术后没有不良影响,对其他眼内组织结构无损害。
2.3.2 水凝胶在眼科药物输送中的应用 目前眼科药物主要采用局部给药方式,其中滴眼液是最常见的给药形式[97-98],然而,由于泪液的分泌和眼睑的机械运动,滴眼液在眼表的停留时间极短,药物利用率较低;此外,眼部的多重屏障(如结膜、巩膜及血眼屏障)进一步限制了药物向眼底的有效递送[99-100]。为提高眼科药物递送效率,近年来开发了多种新型给药系统,其中水凝胶因可降解的三维聚合物网络结构可高效负载药物并实现持续释放,成为研究的热点[101](表3)。
(1)水凝胶在干眼症治疗中的应用:干眼症是一种多因素疾病,病理机制涉及泪膜不稳定、泪液高渗透压等。炎症在干眼症的发生和发展中起着关键作用,因此,抑制眼表炎症被认为是有效的治疗策略之一[109]。环孢素属于常用的免疫抑制剂范畴,可显著抑制炎症的进展,但环孢素不溶于水,导致其疗效受限[110]。LIN等[102]构建出一种由邻硝基苯醇修饰聚乙二醇和甲基丙烯酸酯修饰透明质酸构成的载药水凝胶,此载药水凝胶可植入泪道逐步实现环孢素的稳定释放,在家兔干眼症模型中增加泪液分泌、舒缓眼表炎症,进而推动眼表上皮损伤的修复,为攻克难治性干眼症提供了一种新的治疗手段。DAI等[103]借助甲基丙烯酸酯修饰的丝素蛋白,并与吲哚菁绿纳米颗粒组合,打造了一种水凝胶泪道栓,该泪道栓拥有良好的生物相容性、生物降解性及力学性能,能起到有效阻断泪道的效果,提升泪膜稳定性,并且推动角膜杯状细胞的生长,在干眼症治疗里展现出显著的应用价值。
(2)水凝胶在角膜化学烧伤治疗中的应用:角膜化学烧伤是严重的眼科急症,其中强碱性物质造成的烧伤可引发角膜严重炎症,导致角膜新生血管的形成,从而导致角膜混浊甚至失明,因此,及时治疗角膜化学烧伤至关重要[111]。SOIBERMAN等[104]设计了一种基于透明质酸和地塞米松的结膜下注射水凝胶,该水凝胶经交联后可提高地塞米松的生物利用度,并实现持续释放,在大鼠角膜碱烧伤模型中该水凝胶可靶向巨噬细胞,减少角膜炎症反应。相关研究人员还通过蓝光诱导巯基反应合成了一种透明质酸水凝胶,发现与透明质酸滴眼液相比,该水凝胶不仅能有效促进角膜上皮再生,还可减少新生血管的形成,为角膜碱烧伤提供了一种新的治疗策略[105]。
此外,HUANG等[106]利用光引发自由基聚合设计了一种基于丙烯酸明胶和甲基丙烯酸酯基团的水凝胶复合材料,并将它作为曲霉素-奥龙-西诺酮载体,用于抑制角膜新生血管。XEROUDAKI等[107]进一步优化了水凝胶系统,利用纤维素纳米纤维控制猪皮肤胶原蛋白,进行化学交联和光交联形成双交联水凝胶,该水凝胶不仅具有良好的光学透明度和机械强度,还能在体外持续释放药物达60 d,抑制角膜炎症反应和血管增生,为角膜移植术后的角膜基质病变治疗提供了新思路。
(3)水凝胶在视网膜新生血管疾病中的应用:视网膜新生血管和脉络膜新生血管是导致视网膜失明的主要原因之一。玻璃体内注射抗血管内皮生长因子药物可有效阻断血管内皮生长因子活性,从而抑制新生血管的形成,是目前治疗眼部新生血管疾病的主要策略[112-113],然而,频繁玻璃体注射可能增加眼内炎的发生率。研究者提出利用水凝胶负载药物以实现长期缓释,从而减少玻璃体注射频率,提高患者依从性,并降低眼部感染风险[114]。SHEN等[108]开发了一种眼内注射水凝胶系统,该水凝胶具有良好的生物相容性和稳定性,并可在兔眼中实现缓慢释放,减少玻璃体注射频率。目前,视网膜新生血管治疗方法包括抗玻璃体注射、激光光凝和光动力治疗。
随着水凝胶的发展,研究者不断探索它在更高精度和复杂功能实现中的应用潜力。水凝胶的可调结构与化学修饰能力,为新兴的生物制造技术,特别是3D打印技术提供了理想的材料基础。3D打印作为近年来快速发展的制造手段,能够实现组织或器官结构的精细构建,而水凝胶因良好的流变特性、生物相容性和可光交联性已成为3D生物打印中最常用的“生物墨水”之一。
在现有的背景环境中,水凝胶不仅承担细胞支架或药物载体的角色,还影响到3D打印构建组织结构的稳定性与功能性,审视水凝胶在3D打印技术中的具体应用及其面临的长处与挑战,在进一步推动它于眼科等再生医学领域开展临床转化方面意义重大。
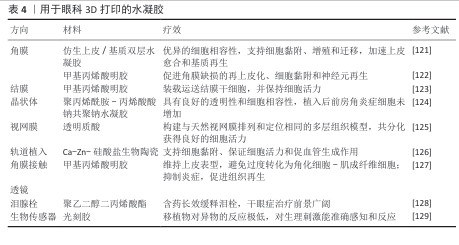
2.3.3 3D打印在眼科应用中的研究进展 3D打印属于先进的生物制造技术范畴,凭借计算机软件对数字模型实施分层识别且以指令样式传输到打印机,达成三维物体的逐层叠建[115-116],最常采用的生物3D打印技术为基于挤压的打印和基于光的打印[117]。光基打印主要涉及数字光处理打印、立体光刻打印以及激光辅助打印,由于光基打印精度高、分辨率高、打印速度迅速、反应条件温和,适合打印具有高活性、高分辨率的细胞结构,因此在组织工程跟再生医学领域起到重要应用[118-120](表4)。
(1) 3D打印水凝胶在角膜组织工程中的应用:由于角膜结构复杂,角膜再生一直是眼科研究的一大挑战。3D打印技术的出现为角膜修复提供了新的解决方案。HE等[121]设计并合成了聚乙二醇二丙烯酸酯水凝胶,并利用3D生物打印机构建了负载兔角膜上皮细胞和脂肪源间充质干细胞的角膜支架,该支架具有足够的力学强度、高透光率和形状保真度,具备合适的溶胀度和降解率,能够支持细胞黏附、增殖和迁移,并且在打印过程中保持较高的细胞存活率;动物实验结果表明,该水凝胶支架可促进角膜上皮细胞的修复、加速基质再生,为角膜组织工程提供了一种高效的再生环境。角膜的曲率在角膜上皮恢复和再生过程中起着重要作用。天然角膜上皮在不同区域的黏附性有所不同,研究表明泪膜和上皮在曲面上的稳定性优于平面[130]。XU等[122]利用胶原蛋白和甲基丙烯酸明胶水凝胶,通过温控3D打印技术制备了具有光滑曲率结构的角膜修复材料,发现3D打印曲面支架能够有效促进角膜基质再生,凸出结构不仅有助于抑制成纤维细胞的增殖,还能促进角膜缺损区域的上皮化、细胞黏附和神经元再生,为角膜移植术和角膜修复提供了一种创新方案。
(2) 3D打印水凝胶在结膜组织工程中的应用:结膜是眼表的重要组成部分,包括眼睑结膜、穹窿结膜和球结膜,其完整性对维持泪膜稳定性和保护眼表至关重要[131-132]。严重的结膜损伤(如免疫疾病、创伤、化学或热烧伤)会影响眼表功能,甚至导致视力丧失,因此结膜重建对于恢复眼健康至关重要[133]。基于结膜干细胞的干细胞治疗已成为结膜重建的重要策略之一。ZHONG等[123]开发了一种基于数字光处理生物打印技术的结膜干细胞体外扩增方法,并利用水凝胶负载递送结膜干细胞,3D打印水凝胶具有可调节的力学性能和优异的细胞相容性,能够维持结膜干细胞的高活力并支持其自我更新能力,通过构建兔结膜下注射模型,该水凝胶展示了良好的可注射性和提高植入后细胞存活率,为3D打印在眼表再生中的应用提供了一种新的微创治疗策略。
(3) 3D打印在人工晶状体中的应用:人工晶状体植入为白内障的主要治疗手段,传统人工晶体材料的标准化设计难以契合个性化需求[134],3D打印技术在个性化晶状体制造事宜上展现出巨大潜力,可依照患者的眼球参数精准定制镜片的构造,借此改善矫正效果和视觉的品质[135]。LI等[86]采用3D打印技术制备了聚丙烯酰胺-丙烯酸钠水凝胶人工晶状体,该材料体现出较好的透明性与细胞兼容性,与人晶状体上皮细胞培养期间未观察到较为明显的细胞毒性,与传统的人工晶状体比,3D打印水凝胶晶状体植入后未引起明显的前房炎症反应,表明它具有潜在的临床应用意义。3D打印技术可精准操纵人工晶状体的形态和光学参数以实现患者的个性化需求,但结构定制化过渡到功能精确匹配仍有挑战,如何对人工晶状体的光学性能和长期稳定性进行优化仍需进一步探索。
(4) 3D打印水凝胶在视网膜组织工程中的应用:视网膜为多层的复杂组织结构,其结构的完整性和视觉功能关系十分密切[136]。3D打印技术在视网膜再生领域的研究数量渐增,经由构建仿生视网膜组织,为视网膜疾病的治疗给出了新的思路。WANG等[125]提出了一种把物理和化学信号整合的策略,采用3D打印方式构建层状视网膜组织模型,研究团队借助甲基丙烯酸酯修饰的透明质酸作为生物墨水,打出甲基丙烯酸酯修饰透明质酸-视网膜色素上皮细胞层以及甲基丙烯酸酯修饰透明质酸-视网膜祖细胞层,还通过调控营养因子与生长因子的梯度引导细胞分化成感光细胞,可有效模拟视网膜的自然排列情形,加快感光细胞的存活分化。在视网膜工程领域中,3D打印技术仍处在早期探索阶段,未来应优化细胞支架材料、提高视网膜细胞存活水平,探究如何实现视网膜的功能性再生。
(5) 3D打印在眼科设备中的应用:近年来,3D打印技术在眼科设备的研发中取得了显著进展,包括个性化角膜隐形眼镜、泪管栓塞以及生物传感器等领域,这些创新设备不仅提升了患者的治疗体验,还推动了精准医疗的发展。
3D打印角膜隐形眼镜:屈光不正属于常见眼部疾病范畴,平行光线经过眼睛的光学系统后无法准确把焦点落在视网膜上,未予矫正的屈光不正是全球造成眼睛失明的第二大原因,矫正屈光不正可明显提升生活质量,还可产生社会经济效益[137]。3D打印技术可按照患者的个体需求定制与患者角膜曲率和屈光度相匹配的隐形眼镜,进而提升佩戴的舒适度与矫正成效。例如,JIA等[127]基于生物墨水,利用数字光处理生物打印技术制作了水凝胶透镜,这种水凝胶镜片具有优异的透光性、机械稳定性、亲水性和生物相容性,能够稳固地附着于角膜上皮细胞并维持其上皮表型,防止过度角质化及肌成纤维细胞转化;此外,该镜片还可激活Ⅱ型免疫反应促进组织再生,抑制炎症反应,表明数字光处理生物打印的水凝胶镜片可作为矫正屈光不正的潜在治疗方案。
3D打印泪管栓塞:眼药水是治疗干眼症的常见方法,但由于药液易被泪液冲刷生物利用度较低,治疗效果有限[138]。近年来,3D打印技术被用于制造泪管栓塞,以提高眼药的滞留时间并增强治疗效果。XU等[128]采用3D打印技术制备了地塞米松负载的泪塞,该泪塞由聚乙二醇二丙烯酸酯和聚乙二醇400组成,形成了半互穿网络,实现不同浓度药物的可控负载。这一研究表明,3D打印可用于制造具有长期缓释效果的载药泪塞,为干眼症治疗提供了新的策略。
3D打印生物传感器:生物传感器是一类结合生物细胞与传感器的智能设备,其中活细胞作为传感元件的一部分,能够精准感知并检测体内的微小生理变化[139]。前房角因其特殊的免疫特性和透明性,是生物传感器植入的重要靶点[140]。
KAVAND等[129]利用双光子聚合技术,基于胰岛微组织进行3D打印,成功开发出一种生物混合传感器,该传感器采用光树脂材料固定于前房角,因优异的透明度和生物相容性而受到关注。结果表明,该传感器可灵敏感知生理刺激,并与宿主组织良好整合。体内移植实验结果显示,移植20周后,角膜的异物反应最低,透明度及组织形态保持稳定;此外,传感器维持了胰岛细胞的功能完整性,使用基因编码的Ca2+指示剂监测发现,移植2-4 d后胰岛内出现毛细血管新生,表明该技术对组织工程和再生医学具有重要意义。
该文为未来生物传感器在组织工程和医疗诊断中的应用奠定了基础,同时也为眼科疾病的检测和治疗提供了新思路。结合先进的功能材料,通过4D打印(即在3D打印的基础上增加对外界刺激的响应能力)可实现具有动态调节能力的智能生物传感器。例如,模拟自然眼组织功能的4D打印技术,可再现副交感神经兴奋时释放乙酰胆碱所引发的瞳孔收缩现象[141-145],这一技术进步不仅能提升眼科疾病的检测精度,还能通过复制眼组织的结构和功能,推进个性化医疗的发展。
| [1] ZHANG X, M VJ, QU Y, et al. Dry Eye Management: Targeting the Ocular Surface Microenvironment. Int J Mol Sci. 2017; 18(7):1398. [2] JANAGAM DR, WU L, LOWE TL. Nanoparticles for drug delivery to the anterior segment of the eye. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2017;122:31-64. [3] ALVES M, ASBELL P, DOGRU M, et al. TFOS Lifestyle Report: Impact of environmental conditions on the ocular surface. Ocul Surf. 2023;29:1-52. [4] VAN SETTEN GB. Ocular surface allostasis-when homeostasis is lost: challenging coping potential, stress tolerance, and resilience. Biomolecules. 2023;13(8):1246. [5] XUAN M, WANG S, LIU X, et al. Proteins of the corneal stroma: importance in visual function. Cell Tissue Res. 2016;364(1):9-16. [6] MCTIERNAN CD, SIMPSON FC, HAAGDORENS M, et al. LiQD Cornea: Pro-regeneration collagen mimetics as patches and alternatives to corneal transplantation. Sci Adv. 2020;6(25):eaba2187. [7] YUE L, WEILAND JD, ROSKA B, et al. Retinal stimulation strategies to restore vision: Fundamentals and systems. Prog Retin Eye Res. 2016;53:21-47. [8] ROSKA B, SAHEL JA. Restoring vision. Nature. 2018;557(7705):359-367. [9] DEL AMO EM, RIMPELÄ AK, HEIKKINEN E, et al. Pharmacokinetic aspects of retinal drug delivery. Prog Retin Eye Res. 2017;57:134-185. [10] CUNHA-VAZ J, BERNARDES R, LOBO C. Blood-retinal barrier. Eur J Ophthalmol. 2011;21 Suppl 6:S3-9. [11] GOTE V, SIKDER S, SICOTTE J, et al. Ocular Drug Delivery: Present Innovations and Future Challenges. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2019;370(3):602-624. [12] JUMELLE C, GHOLIZADEH S, ANNABI N, et al. Advances and limitations of drug delivery systems formulated as eye drops. J Control Release. 2020;321: 1-22. [13] CABRERA FJ, WANG DC, REDDY K, et al. Challenges and opportunities for drug delivery to the posterior of the eye. Drug Discov Today. 2019;24(8): 1679-1684. [14] SRIPETCH S, LOFTSSON T. Topical drug delivery to the posterior segment of the eye: Thermodynamic considerations. Int J Pharm. 2021;597:120332. [15] NAGAI N, OTAKE H. Novel drug delivery systems for the management of dry eye. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2022;191:114582. [16] XIE G, LIN S, WU F, et al. Nanomaterial-based ophthalmic drug delivery. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2023;200:115004. [17] HE J, SUN Y, GAO Q, et al. Gelatin methacryloyl hydrogel, from standardization, performance, to biomedical application. Adv Healthc Mater. 2023;12(23):e2300395. [18] HE J, SUN Y, GAO Q, et al. Gelatin Methacryloyl Hydrogel, from Standardization, Performance, to Biomedical Application. Adv Healthc Mater. 2023;12(23):e2300395. [19] WU M, LIU H, ZHU Y, et al. Mild Photothermal-Stimulation Based on Injectable and Photocurable Hydrogels Orchestrates Immunomodulation and Osteogenesis for High-Performance Bone Regeneration. Small. 2023;19(28):e2300111. [20] KIM SH, HONG H, AJITERU O, et al. 3D bioprinted silk fibroin hydrogels for tissue engineering. Nat Protoc. 2021;16(12): 5484-5532. [21] HIRANO J. [Hydrogel contact lenses]. Nippon Ganka Gakkai Zasshi. 1971;75(11): 2193-2197. [22] AMMAR HO, SALAMA HA, GHORAB M, et al. Development of dorzolamide hydrochloride in situ gel nanoemulsion for ocular delivery. Drug Dev Ind Pharm. 2000;36(11):1330-1339. [23] HOU Y, SCHOENER CA, REGAN KR, et al. Photo-cross-linked PDMSstar-PEG hydrogels: synthesis, characterization, and potential application for tissue engineering scaffolds. Biomacromolecules. 2010;11(3):648-656. [24] DELPLACE V, OBERMEYER J, SHOICHET MS. Local Affinity Release. ACS Nano. 2016; 10(7):6433-6436. [25] BAKHSHANDEH H, ATYABI F, SOLEIMANI M, et al. Biocompatibility improvement of artificial cornea using chitosan-dextran nanoparticles containing bioactive macromolecules obtained from human amniotic membrane. Int J Biol Macromol. 2021;169:492-499. [26] ZHAO X, LI S, DU X, et al. Natural polymer-derived photocurable bioadhesive hydrogels for sutureless keratoplasty. Bioact Mater. 2021;8:196-209. [27] CHOI JR, YONG KW, CHOI JY, et al. Recent advances in photo-crosslinkable hydrogels for biomedical applications. Biotechniques. 2019;66(1):40-53. [28] PEREIRA RF, BARRIAS CC, BÁRTOLO PJ, et al. Cell-instructive pectin hydrogels crosslinked via thiol-norbornene photo-click chemistry for skin tissue engineering. Acta Biomater. 2018;66:282-293. [29] LIN CC, KI CS, SHIH H. Thiol-norbornene photo-click hydrogels for tissue engineering applications. J Appl Polym Sci. 2015;132(8):41563. [30] JIANG Y, CHEN J, DENG C, et al. Click hydrogels, microgels and nanogels: emerging platforms for drug delivery and tissue engineering. Biomaterials. 2014; 35(18):4969-4985. [31] DIMATTEO R, DARLING NJ, SEGURA T. In situ forming injectable hydrogels for drug delivery and wound repair. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2018;127:167-184. [32] QI L, ZHANG C, WANG B, et al. Progress in Hydrogels for Skin Wound Repair. Macromol Biosci. 2022;22(7):e2100475. [33] CHOI YH, KIM SH, KIM IS, et al. Gelatin-based micro-hydrogel carrying genetically engineered human endothelial cells for neovascularization. Acta Biomater. 2019; 95:285-296. [34] HASSANZADEH P, KAZEMZADEH-NARBAT M, ROSENZWEIG R, et al. Ultrastrong and Flexible Hybrid Hydrogels based on Solution Self-Assembly of Chitin Nanofibers in Gelatin Methacryloyl (GelMA). J Mater Chem B. 2016;4(15):2539-2543. [35] YANG LJ, OU YC. The micro patterning of glutaraldehyde (GA)-crosslinked gelatin and its application to cell-culture. Lab Chip. 2005;5(9):979-984. [36] QIU Y, MA Y, HUANG Y, et al. Current advances in the biosynthesis of hyaluronic acid with variable molecular weights. Carbohydr Polym. 2021;269:118320. [37] FENN SL, OLDINSKI RA. Visible light crosslinking of methacrylated hyaluronan hydrogels for injectable tissue repair. J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater. 2016;104(6):1229-1236. [38] ZHENG J, WANG Y, WANG Y, et al. Gelatin/Hyaluronic Acid Photocrosslinked Double Network Hydrogel with Nano-Hydroxyapatite Composite for Potential Application in Bone Repair. Gels. 2023; 9(9):742. [39] SKARDAL A, ATALA A. Biomaterials for integration with 3-D bioprinting. Ann Biomed Eng. 2015;43(3):730-746. [40] LIN H, LIU J, ZHANG K, et al. Dynamic mechanical and swelling properties of maleated hyaluronic acid hydrogels. Carbohydr Polym. 2015;123:381-389. [41] SHEN X, LI S, ZHAO X, et al. Dual-crosslinked regenerative hydrogel for sutureless long-term repair of corneal defect. Bioact Mater. 2022;20:434-448. [42] ZHOU N, LIU YD, ZHANG Y, et al. Pharmacological Functions, Synthesis, and Delivery Progress for Collagen as Biodrug and Biomaterial. Pharmaceutics. 2023;15(5):1443. [43] VARMA S, ORGEL JP, SCHIEBER JD. Nanomechanics of Type I Collagen. Biophys J. 2016;111(1):50-56. [44] GELSE K, PÖSCHL E, AIGNER T. Collagens-structure, function, and biosynthesis. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2003;55(12):1531-1546. [45] TAKAHASHI S, GEENEN D, NIEVES E, et al. Collagenase degrades collagen in vivo in the ischemic heart. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1999;1428(2-3):251-259. [46] NAOMI R, RATANAVARAPORN J, FAUZI MB. Comprehensive Review of Hybrid Collagen and Silk Fibroin for Cutaneous Wound Healing. Materials (Basel). 2020; 13(14):3097. [47] BROWN BN, BADYLAK SF. Extracellular matrix as an inductive scaffold for functional tissue reconstruction. Transl Res. 2014;163(4):268-285. [48] SORUSHANOVA A, DELGADO LM, WU Z, et al. The Collagen Suprafamily: From Biosynthesis to Advanced Biomaterial Development. Adv Mater. 2019;31(1):e1801651. [49] HAO S, TIAN C, BAI Y, et al. Corrigendum to “Photo-crosslinkable hyaluronic acid microgels with reactive oxygen species scavenging capacity for mesenchymal stem cell encapsulation” [Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 243 (2023) 124971]. Int J Biol Macromol. 2025;307(Pt 1):141300. [50] WANI SUD, GAUTAM SP, QADRIE ZL, et al. Silk fibroin as a natural polymeric based bio-material for tissue engineering and drug delivery systems-A review. Int J Biol Macromol. 2020;163:2145-2161. [51] LI G, SUN S. Silk Fibroin-Based Biomaterials for Tissue Engineering Applications. Molecules. 2022;27(9):2757. [52] MAZUREK Ł, SZUDZIK M, RYBKA M, et al. Silk Fibroin Biomaterials and Their Beneficial Role in Skin Wound Healing. Biomolecules. 2022;12(12):1852. [53] GHOLIPOURMALEKABADI M, SAPRU S, SAMADIKUCHAKSARAEI A, et al. Silk fibroin for skin injury repair: Where do things stand? Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2020;153:28-53. [54] PATIL PP, REAGAN MR, BOHARA RA. Silk fibroin and silk-based biomaterial derivatives for ideal wound dressings. Int J Biol Macromol. 2020;164:4613-4627. [55] ASAKURA T, WILLIAMSON MP. A review on the structure of Bombyx mori silk fibroin fiber studied using solid-state NMR: An antipolar lamella with an 8-residue repeat. Int J Biol Macromol. 2023;245:125537. [56] WU X, ZHOU M, JIANG F, et al. Marginal sealing around integral bilayer scaffolds for repairing osteochondral defects based on photocurable silk hydrogels. Bioact Mater. 2021;6(11):3976-3986. [57] KIM SH, YEON YK, LEE JM, et al. Precisely printable and biocompatible silk fibroin bioink for digital light processing 3D printing. Nat Commun. 2018;9(1):1620. [58] QIAN Y, ZHENG Y, JIN J, et al. Immunoregulation in Diabetic Wound Repair with a Photoenhanced Glycyrrhizic Acid Hydrogel Scaffold. Adv Mater. 2022;34(29):e2200521. [59] MEI J, ZHOU J, KONG L, et al. An injectable photo-cross-linking silk hydrogel system augments diabetic wound healing in orthopaedic surgery through spatiotemporal immunomodulation. J Nanobiotechnology. 2022;20(1):232. [60] ELVIRI L, BIANCHERA A, BERGONZI C, et al. Controlled local drug delivery strategies from chitosan hydrogels for wound healing. Expert Opin Drug Deliv. 2017;14(7):897-908. [61] SHARIATINIA Z, JALALI AM. Chitosan-based hydrogels: Preparation, properties and applications. Int J Biol Macromol. 2018;115:194-220. [62] AGHBASHLO M, AMIRI H, MOOSAVI BASRI SM, et al. Tuning chitosan’s chemical structure for enhanced biological functions. Trends Biotechnol. 2023;41(6):785-797. [63] PEERS S, MONTEMBAULT A, LADAVIÈRE C. Chitosan hydrogels for sustained drug delivery. J Control Release. 2020;326: 150-163. [64] ABOUREHAB MAS, PRAMANIK S, ABDELGAWAD MA,et al. Recent Advances of Chitosan Formulations in Biomedical Applications. Int J Mol Sci. 2022;23(18): 10975. [65] SHEN Y, TANG H, HUANG X, et al. DLP printing photocurable chitosan to build bio-constructs for tissue engineering. Carbohydr Polym. 2020;235:115970. [66] KO HS, YANG DH, KIM A, et al. Visible light-curable methacrylated glycol chitosan hydrogel patches for prenatal closure of fetal myelomeningocele. Carbohydr Polym. 2023;311:120620. [67] ABD EL-HACK ME, EL-SAADONY MT, SHAFI ME, et al. Antimicrobial and antioxidant properties of chitosan and its derivatives and their applications: A review. Int J Biol Macromol. 2020;164:2726-2744. [68] D’SOUZA AA, SHEGOKAR R. Polyethylene glycol (PEG): a versatile polymer for pharmaceutical applications. Expert Opin Drug Deliv. 2016;13(9):1257-1275. [69] KOLATE A, BARADIA D, PATIL S, et al. PEG - a versatile conjugating ligand for drugs and drug delivery systems. J Control Release. 2014;192:67-81. [70] KONG XB, TANG QY, CHEN XY, et al. Polyethylene glycol as a promising synthetic material for repair of spinal cord injury. Neural Regen Res. 2017; 12(6):1003-1008. [71] KRUTKRAMELIS K, XIA B, OAKEY J. Monodisperse polyethylene glycol diacrylate hydrogel microsphere formation by oxygen-controlled photopolymerization in a microfluidic device. Lab Chip. 2016; 16(8):1457-1465. [72] YAO S, CHI J, WANG Y, et al. Zn-MOF Encapsulated Antibacterial and Degradable Microneedles Array for Promoting Wound Healing. Adv Healthc Mater. 2021;10(12): e2100056. [73] REKOWSKA N, TESKE M, ARBEITER D, et al. Biocompatibility and thermodynamic properties of PEGDA and two of its copolymer. Annu Int Conf IEEE Eng Med Biol Soc. 2019;2019:1093-1096. [74] KAMOUN EA, LOUTFY SA, HUSSEIN Y, et al. Recent advances in PVA-polysaccharide based hydrogels and electrospun nanofibers in biomedical applications: A review. Int J Biol Macromol. 2021;187: 755-768. [75] BARROS ARAÚJO CB, DA SILVA SOARES IL, DA SILVA LIMA DP, et al. Polyvinyl Alcohol Nanofibers Blends as Drug Delivery System in Tissue Regeneration. Curr Pharm Des. 2023;29(15):1149-1162. [76] JIN SG. Production and Application of Biomaterials Based on Polyvinyl alcohol (PVA) as Wound Dressing. Chem Asian J. 2022;17(21):e202200595. [77] GOLDVASER M, EPSTEIN E, ROSEN O, et al. Poly(vinyl alcohol)-methacrylate with CRGD peptide: A photocurable biocompatible hydrogel. J Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2022; 16(2):140-150. [78] WANG L, DUAN L, LIU G, et al. Bioinspired Polyacrylic Acid-Based Dressing: Wet Adhesive, Self-Healing, and Multi-Biofunctional Coacervate Hydrogel Accelerates Wound Healing. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2023;10(16):e2207352. [79] LIU J, HU N, XIE Y, et al. Polyacrylic Acid Hydrogel Coating for Underwater Adhesion: Preparation and Characterization. Gels. 2023;9(8):616. [80] SIMEONOV M, KOSTOVA B, VASSILEVA E. Interpenetrating Polymer Networks of Polyacrylamide with Polyacrylic and Polymethacrylic Acids and Their Application for Modified Drug Delivery - a Flash Review. Pharm Nanotechnol. 2023;11(1):25-33. [81] ONUKI Y, NISHIKAWA M, MORISHITA M, et al. Development of photocrosslinked polyacrylic acid hydrogel as an adhesive for dermatological patches: involvement of formulation factors in physical properties and pharmacological effects. Int J Pharm. 2008;349(1-2):47-52. [82] SHIMAMOTO T, NAKAKUBO T, NOJI T, et al. Design of PG-Surfactants Bearing Polyacrylamide Polymer Chain to Solubilize Membrane Proteins in a Surfactant-Free Buffer. Int J Mol Sci. 2021;22(4):1524. [83] WOLFEL A, JIN M, PAEZ JI. Current strategies for ligand bioconjugation to poly(acrylamide) gels for 2D cell culture: Balancing chemo-selectivity, biofunctionality, and user-friendliness. Front Chem. 2022;10:1012443. [84] LI J, SHEN J, ZHUANG B, et al. Light-triggered on-site rapid formation of antibacterial hydrogel dressings for accelerated healing of infected wounds. Biomater Adv. 2022;136:212784. [85] FERRACCI G, ZHU M, IBRAHIM MS, et al. Photocurable Albumin Methacryloyl Hydrogels as a Versatile Platform for Tissue Engineering. ACS Appl Bio Mater. 2020;3(2): 920-934. [86] LI L, LU C, WANG L, et al. Gelatin-Based Photocurable Hydrogels for Corneal Wound Repair. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2018;10(16):13283-13292. [87] ZHAO X, LI S, DU X, et al. Natural polymer-derived photocurable bioadhesive hydrogels for sutureless keratoplasty. Bioact Mater. 2021;8:196-209. [88] YAZDANPANAH G, SHEN X, NGUYEN T, et al. A Light-Curable and Tunable Extracellular Matrix Hydrogel for In Situ Suture-Free Corneal Repair. Adv Funct Mater. 2022; 32(24):2113383. [89] LI M, WEI R, LIU C, et al. A “T.E.S.T.” hydrogel bioadhesive assisted by corneal cross-linking for in situ sutureless corneal repair. Bioact Mater. 2023;25:333-346. [90] RAIA NR, JIA D, GHEZZI CE, et al. Characterization of silk-hyaluronic acid composite hydrogels towards vitreous humor substitutes. Biomaterials. 2020;233:119729. [91] WANG H, WU Y, CUI C, et al. Antifouling Super Water Absorbent Supramolecular Polymer Hydrogel as an Artificial Vitreous Body. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2018;5(11):1800711. [92] XIANG Y, ZOU M, ZHANG Y, et al. Drug-loaded and Blue-ray Filtered Hydrogel as a Potential Intraocular Lens for Cataract Treatment. Pharm Nanotechnol. 2020;8(4):302-312. [93] DE GROOT JH, VAN BEIJMA FJ, HAITJEMA HJ, et al. Injectable intraocular lens materials based upon hydrogels. Biomacromolecules. 2001;2(3):628-634. [94] WORTHINGTON KS, GREEN BJ, RETHWISCH M, et al. Neuronal Differentiation of Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells on Surfactant Templated Chitosan Hydrogels. Biomacromolecules. 2016;17(5):1684-1695. [95] TAM RY, SMITH LJ, SHOICHET MS. Engineering Cellular Microenvironments with Photo- and Enzymatically Responsive Hydrogels: Toward Biomimetic 3D Cell Culture Models. Acc Chem Res. 2017;50(4): 703-713. [96] HE B, YANG J, LIU Y, et al. An in situ-forming polyzwitterion hydrogel: Towards vitreous substitute application. Bioact Mater. 2021; 6(10):3085-3096. [97] VANEEV A, TIKHOMIROVA V, CHESNOKOVA N, et al. Nanotechnology for Topical Drug Delivery to the Anterior Segment of the Eye. Int J Mol Sci. 2021;22(22):12368. [98] AWWAD S, MOHAMED AHMED AHA, SHARMA G, et al. Principles of pharmacology in the eye. Br J Pharmacol. 2017;174(23):4205-4223. [99] WANG C, PANG Y. Nano-based eye drop: Topical and noninvasive therapy for ocular diseases. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2023;194:114721. [100] WANG X, LUAN F, YUE H, et al. Recent advances of smart materials for ocular drug delivery. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2023; 200:115006. [101] PAN J, LIAO H, GONG G, et al. Supramolecular nanoarchitectonics of phenolic-based nanofiller for controlled diffusion of versatile drugs in hydrogels. J Control Release. 2023;360:433-446. [102] LIN T, WANG W, CHEN T, et al. A lacrimal duct drug delivery system based on photo-induced hydrogel for dry eye and allergic conjunctivitis therapy. Compos Part B. 2023;266: 111014. [103] DAI M, XU K, XIAO D, et al. In Situ Forming Hydrogel as a Tracer and Degradable Lacrimal Plug for Dry Eye Treatment. Adv Healthc Mater. 2022;11(19):e2200678. [104] SOIBERMAN U, KAMBHAMPATI SP, WU T, et al. Subconjunctival injectable dendrimer-dexamethasone gel for the treatment of corneal inflammation. Biomaterials. 2017;125:38-53. [105] PARK SK, HA M, KIM EJ, et al. Hyaluronic acid hydrogels crosslinked via blue light-induced thiol-ene reaction for the treatment of rat corneal alkali burn. Regen Ther. 2022;20:51-60. [106] HUANG C, QI X, CHEN H, et al. Monolith/Hydrogel composites as triamcinolone acetonide carriers for curing corneal neovascularization in mice by inhibiting the fibrinolytic system. Drug Deliv. 2022; 29(1):18-30. [107] XEROUDAKI M, RAFAT M, MOUSTARDAS P, et al. A double-crosslinked nanocellulose-reinforced dexamethasone-loaded collagen hydrogel for corneal application and sustained anti-inflammatory activity. Acta Biomater. 2023;172:234-248. [108] SHEN C, ZHAO X, REN Z, et al. In Situ Formation of Injectable Gelatin Methacryloyl (GelMA) Hydrogels for Effective Intraocular Delivery of Triamcinolone Acetonide. Int J Mol Sci. 2023;24(5):4957. [109] HAN Y, JIANG L, SHI H, et al. Effectiveness of an ocular adhesive polyhedral oligomeric silsesquioxane hybrid thermo-responsive FK506 hydrogel in a murine model of dry eye. Bioact Mater. 2021;9:77-91. [110] LUSCHMANN C, HERRMANN W, STRAUSS O, et al. Ocular delivery systems for poorly soluble drugs: an in-vivo evaluation. Int J Pharm. 2013;455(1-2):331-337. [111] YU J, SHEN Y, LUO J, et al. Upadacitinib inhibits corneal inflammation and neovascularization by suppressing M1 macrophage infiltration in the corneal alkali burn model. Int Immunopharmacol. 2023;116:109680. [112] REZZOLA S, BELLERI M, GARIANO G, et al. In vitro and ex vivo retina angiogenesis assays. Angiogenesis. 2014;17(3):429-442. [113] GROSSNIKLAUS HE, KANG SJ, BERGLIN L. Animal models of choroidal and retinal neovascularization. Prog Retin Eye Res. 2010;29(6):500-519. [114] PATEL D, PATEL SN, CHAUDHARY V, et al. Complications of intravitreal injections: 2022. Curr Opin Ophthalmol. 2022;33(3):137-146. [115] NORMAN J, MADURAWE RD, MOORE CM, et al. A new chapter in pharmaceutical manufacturing: 3D-printed drug products. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2017;108:39-50. [116] HUANG W, ZHANG X. 3D Printing: Print the future of ophthalmology. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2014;55(8):5380-5381. [117] AL-KINANI AA, ZIDAN G, ELSAID N, et al. Ophthalmic gels: Past, present and future. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2018;126:113-126. [118] LI W, WANG M, MA H, et al. Stereolithography apparatus and digital light processing-based 3D bioprinting for tissue fabrication. iScience. 2023;26(2):106039. [119] MATAI I, KAUR G, SEYEDSALEHI A, et al. Progress in 3D bioprinting technology for tissue/organ regenerative engineering. Biomaterials. 2020;226:119536. [120] GUNGOR-OZKERIM PS, INCI I, ZHANG YS, et al. Bioinks for 3D bioprinting: an overview. Biomater Sci. 2018;6(5):915-946. [121] HE B, WANG J, XIE M,et al. 3D printed biomimetic epithelium/stroma bilayer hydrogel implant for corneal regeneration. Bioact Mater. 2022;17:234-247. [122] XU Y, LIU J, SONG W, et al. Biomimetic Convex Implant for Corneal Regeneration Through 3D Printing. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2023;10(11):e2205878. [123] ZHONG Z, DENG X, WANG P,et al. Rapid bioprinting of conjunctival stem cell micro-constructs for subconjunctival ocular injection. Biomaterials. 2021;267:120462. [124] LI JW, LI YJ, HU XS, et al. Biosafety of a 3D-printed intraocular lens made of a poly(acrylamide-co-sodium acrylate) hydrogel in vitro and in vivo. Int J Ophthalmol. 2020;13(10):1521-1530. [125] WANG P, LI X, ZHU W, et al. 3D bioprinting of hydrogels for retina cell culturing. Bioprinting. 2018;11:e00029. [126] WANG J, PENG Y, CHEN M, et al. Next-generation finely controlled graded porous antibacterial bioceramics for high-efficiency vascularization in orbital reconstruction. Bioact Mater. 2022;16:334-345. [127] JIA S, YANG J, LAU AD, et al. Digital light processing-bioprinted poly-NAGA-GelMA-based hydrogel lenticule for precise refractive errors correction. Biofabrication. 2023;15(3).doi: 10.1088/1758-5090/accaab. [128] XU X, AWWAD S, DIAZ-GOMEZ L, et al. 3D Printed Punctal Plugs for Controlled Ocular Drug Delivery. Pharmaceutics. 2021;13(9):1421. [129] KAVAND H, VISA M, KÖHLER M, et al. 3D-Printed Biohybrid Microstructures Enable Transplantation and Vascularization of Microtissues in the Anterior Chamber of the Eye. Adv Mater. 2024;36(1):e2306686. [130] PARK S, JUNG WH, PITTMAN M, et al. The Effects of Stiffness, Fluid Viscosity, and Geometry of Microenvironment in Homeostasis, Aging, and Diseases: A Brief Review. J Biomech Eng. 2020;142(10): 100804. [131] SVITOVA TF, LIN MC. Dynamic interfacial properties of human tear-lipid films and their interactions with model-tear proteins in vitro. Adv Colloid Interface Sci. 2016;233:4-24. [132] ZHAO L, JIA Y, ZHAO C,et al. Ocular surface repair using decellularized porcine conjunctiva. Acta Biomater. 2020;101: 344-356. [133] WITT J, MERTSCH S, BORRELLI M,et al. Decellularised conjunctiva for ocular surface reconstruction. Acta Biomater. 2018;67:259-269. [134] LIN H, OUYANG H, ZHU J, et al. Lens regeneration using endogenous stem cells with gain of visual function. Nature. 2016;531(7594):323-328. [135] DEBELLEMANIÈRE G, FLORES M, MONTARD M,et al. Three-dimensional Printing of Optical Lenses and Ophthalmic Surgery: Challenges and Perspectives. J Refract Surg. 2016;32(3):201-204. [136] RATTNER A, NATHANS J. Macular degeneration: recent advances and therapeutic opportunities. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2006;7(11):860-872. [137] HARB EN, WILDSOET CF. Origins of Refractive Errors: Environmental and Genetic Factors. Annu Rev Vis Sci. 2019;5:47-72. [138] LIU LC, CHEN YH, LU DW. Overview of Recent Advances in Nano-Based Ocular Drug Delivery. Int J Mol Sci. 2023;24(20): 15352. [139] WANG C, ZHANG Z, WANG J, et al. Biohybrid materials: Structure design and biomedical applications. Mater Today Bio. 2022;16:100352. [140] STREILEIN JW. Unraveling immune privilege. Science. 1995;270(5239):1158-1159. [141] HEINRICH MA, LIU W, JIMENEZ A, et al. 3D Bioprinting: from Benches to Translational Applications. Small. 2019;15(23):e1805510. [142] 闫锐,王一宇,刘雪,等.负载外泌体的水凝胶在神经损伤再生与创面修复中的应用[J].中国组织工程研究,2025,29(34): 7439-7446. [143] 陈森林,朱舟,万乾炳.Janus微/纳米颗粒在生物医学中的应用[J].中国组织工程研究,2025,29(28):6101-6109. [144] 奚海翔,段洁,徐平,等.紫丁香苷-壳聚糖水凝胶抑制椎间盘的退变[J].中国组织工程研究,2025,29(28):5968-5976. [145] EKBLAD T, BERGSTRÖM G, EDERTH T, et al. Poly(ethylene glycol)-containing hydrogel surfaces for antifouling applications in marine and freshwater environments. Biomacromolecules. 2008;9(10): 2775-2783. |
| [1] | 刘 洋, 刘东辉, 徐 磊, 展 旭, 孙昊博, 康 凯. 刺激响应型可注射水凝胶在心肌梗死精准化治疗中的作用与趋势[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2026, 30(8): 2072-2080. |
| [2] | 王 峥, 程 吉, 于金龙, 刘文红, 王召红, 周鲁星. 水凝胶材料在脑卒中治疗中的应用进展与未来展望[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2026, 30(8): 2081-2090. |
| [3] | 郭宇超, 倪前伟, 尹 晨, 吉格尔·赛义力汗, 高 瞻. 季铵化壳聚糖紧急止血材料:合成、机制与应用[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2026, 30(8): 2091-2100. |
| [4] | 王奇飒, 卢雨征, 韩秀峰, 赵文玲, 石海涛, 徐 哲. 3D打印甲基丙烯酰化透明质酸/脱细胞皮肤水凝胶支架的细胞相容性[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2026, 30(8): 1912-1920. |
| [5] | 刘宏杰, 牟秋菊, 申玉雪, 梁 飞, 祝丽丽. 金属有机框架/羧甲基壳聚糖-氧化海藻酸钠/富血小板血浆水凝胶促糖尿病感染创面愈合[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2026, 30(8): 1929-1939. |
| [6] | 周红丽, 王晓龙, 郭 蕊, 姚轩轩, 郭 茹, 周熊涛, 何祥一. 纳米羟基磷灰石/海藻酸钠/聚己内酯/阿仑膦酸钠支架的制备及表征[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2026, 30(8): 1962-1970. |
| [7] | 姚茵璇, 温素如, 陈超盛, 温 鑫, 冯可滢, 邝枣园, 张 文. 载葛根素双网络可注射水凝胶促进皮肤创面修复[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2026, 30(20): 5201-5213. |
| [8] | 许艺璇, 姚 俊, 刘旭璐, 李新莲, 刘志雄, 张志红. 含万古霉素的猪皮脱细胞外基质水凝胶促进皮肤感染创面愈合[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2026, 30(20): 5214-5228. |
| [9] | 曹雨晴, 郭美玲, 刘 峰, 魏俊超. 多糖基水凝胶的制备、分类及在皮肤损伤修复中的应用[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2026, 30(20): 5257-5269. |
| [10] | 徐亚伟, 孟世龙, 张 徐, 汪成杰, 袁一峰, 史晓林, 王 娇, 刘 康. 中药有效成分结合水凝胶修复骨缺损:成功与挑战[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2026, 30(20): 5295-5303. |
| [11] | 何贞贞, 黄汉记, 王嘉伟, 谢庆条, 江献芳. 生物支架在炎症驱动颞下颌关节骨及软骨破坏及结构性损伤修复中的作用[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2026, 30(20): 5312-5320. |
| [12] | 王梓桐, 吴子健, 杨傲飞, 毛 田, 方 楠, 王志刚. 生物材料调控微环境失衡治疗脊髓损伤[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2026, 30(20): 5321-5330. |
| [13] | 王洁燕, 姚佳沂, 辛颖童, 张馨文, 李日旺, 刘大海. 壳聚糖水凝胶载药系统治疗口腔溃疡更安全有效的解决方案[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2026, 30(20): 5331-5340. |
| [14] | 周孝辉, 王思怡, 周启云, 何 钊, 贾玉娟, 王元斌, 马建武, 陈 刚, 郑 峰, 褚耿磊. 纳米羟基磷灰石-聚醚碳酸酯脲静电纺丝膜促进骨缺损修复[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2026, 30(20): 5134-5142. |
| [15] | 詹 蕾, 吴丽娜, 李 欢, 刘 敏, 陈 涛, 蒲小兵, 周长春. 负载淫羊藿苷的丝素蛋白水凝胶促进腱骨愈合[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2026, 30(20): 5178-5787. |
眼球暴露于外界环境,为减少外界因素影响,存在多重屏障,如角膜、结膜和血眼屏障(由血水屏障和血视网膜屏障组成)[1,9-10],这些屏障在保护眼睛的同时也降低了治疗药物的浓度和递送效率,因此,开发能够持续给药并穿透眼屏障的创新剂型至关重要[11]。目前眼部治疗药物主要以滴眼液为主,但药物生物利用度低,眨眼和泪液冲洗会导致药物迅速脱落,并且难以到达眼后段。玻璃体注射是眼底治疗的重要手段,但因注射频繁患者依从性差,并存在感染和眼内炎风险[12-16]。
为解决此类问题,智能材料的开发在生物医学领域有着重要意义,尤其是在弥补眼科药物递送不足、达成高效递送方面,水凝胶技术展示出巨大潜力[17]。水凝胶表现出较好的生物相容性以及较低的细胞毒性,可以促进细胞增殖、维持细胞表型,并为细胞的附着、迁徙以及药物的存储与释放提供理想的支撑结构和空间,被认为是组织工程、药物传递过程和生物3D打印领域的重要材料[18]。
水凝胶可借助溶液交联形成凝胶体,实现液体到固体相态的转变,交联状态可通过环境因素(如温度、pH值、光照条件)来实现调控,进而对最终的力学性能和生物学特性产生影响[19]。水凝胶反应平稳、条件易控,在角膜再生、玻璃体替代、晶状体修复及视网膜再生等组织工程领域显示出广泛应用,在眼科给药递送方面,水凝胶可对干眼症、角膜炎和视网膜新生血管病变等疾病进行治疗,强化药物的靶向性和释放功效[20]。在3D打印中水凝胶的应用同样备受瞩目,已普遍用于角膜、结膜、晶状体、视网膜、眼窝植入物和其余眼科设备的制造。该综述着重探讨水凝胶在眼科领域的最新研究动态,涉及其组织工程、药物递送及3D打印领域的应用情况及未来发展走向。
1.1.1 检索人及检索时间 由第一作者在 2025年2月进行检索。
1.1.2 文献检索时限 各数据库建库至2025年2月。
1.1.3 检索数据库 PubMed数据库、中国知网。
1.1.4 检索词 英文检索词为“Hydrogel,Ophthalmology,Tissue engineering,Drug transport,3D printing”,中文检索词为“水凝胶,眼科,组织工程,药物运输,3D打印”。
1.1.5 检索文献类型 研究原著及综述。
1.1.6 手工检索情况 手工查阅相关书籍。
1.1.7 检索策略 中国知网与PubMed数据库检索策略见图1。
1.1.8 检索文献量 初步检索得到文献689篇,包括英文文献 639篇、中文文献50篇,其中PubMed 数据库639篇、中国知网50篇。
1.2 入组标准
纳入标准:①研究内容为水凝胶在眼科诊治中的相关应用;②文献质量、相关性、可靠性高,或创新性较为突出的文献;③优先选择最近15年内发表的文献。
排除标准:①与研究主题无关的文献;②重复性文献;③观点陈旧或存在争议的文献。
1.3 文献质量评价和筛选 共检索到689篇文献,初筛剔除重复文献后,通过泛读对剩余文献的标题、摘要进行筛选,无法判别时精读全文,选取与主题更为相符的文献,最终纳入符合要求的文献145篇,包括英文文献142篇、中文文献3篇。文献筛选流程详见图2。
在眼科再生医学领域,生物材料的应用正不断推动组织工程角膜、组织工程视网膜等技术的发展,3D打印技术的引入,加速了生物材料在眼科的创新应用。近年来,水凝胶因优异的生物相容性、高含水量和可调控的网络结构,在组织工程、药物递送和生物3D打印等领域备受关注。虽然部分水凝胶尚未应用于临床,但它在医疗领域的潜力巨大,例如,EKBLAD等[145]利用2-羟基甲基丙烯酸乙酯和聚乙二醇甲基丙烯酸乙酯,通过紫外辐照自由基聚合制备了聚乙二醇基水凝胶涂层,该涂层在人工海水中经6个月测试表现出优异的稳定性和防污性能,同时对复杂流体(如蛋白质和血浆)具有低吸附性,具备简易量产的优势。
随着植入式医疗器械的普及,如何降低材料在体内的微生物、蛋白质和血小板黏附风险,成为医疗研究的重要课题。防污水凝胶涂层可有效减少炎症、血栓形成等不良反应,并延长植入物的使用寿命。虽然此类防污水凝胶最初用于海洋抗污领域,但它们在生物医学方面同样具备广阔前景。未来,通过提升生物相容性、调控降解速率及优化机械性能,该类水凝胶有望在医疗器械表面涂层领域发挥重要作用。
3.2 水凝胶在眼科应用的前景与挑战 该综述全面探讨了水凝胶的类型、作用机制及其在眼科领域的应用,重点关注组织工程、药物递送和3D打印等方面。水凝胶具有光响应特性,可通过调节光照强度和时间精确控制理化性质。由于眼睛作为外部器官对光高度敏感,这一特性为水凝胶在眼科学研究中的应用提供了独特优势。水凝胶的亲水性多孔结构使其具有良好的生物相容性,不仅可作为组织工程材料用于角膜或玻璃体替代,还可包封药物,实现精准的眼底给药;此外,3D打印技术进一步增强了水凝胶在个性化治疗中的适应性。目前,研究人员已利用水凝胶递送药物、基因、生物活性分子和干细胞,并构建角膜隐形眼镜、人工玻璃体等生物替代结构,推动眼科治疗的精准化和安全性。
尽管实验研究已取得积极进展,水凝胶在眼科临床应用方面仍面临诸多挑战:科技成果的转化率较低,主要受限于产品开发与临床应用的脱节,转化路径复杂,需要明确的技术评价标准、专业机构的理论指导及资金支持;动物研究仍以小鼠和家兔为主,较少采用与人类生理更接近的猴子模型,导致实验结果的外推性受限。因此,提高实验设计的科学性、优化动物模型,并加强对材料作用机制、药物分布及代谢的深入研究,是推动水凝胶临床应用的关键。未来,解决技术瓶颈、加强跨学科合作并优化资源配置,将有助于加速水凝胶在眼科疾病诊疗中的临床转化。一旦这些挑战得到克服,该材料有望在眼科精准治疗领域发挥重要作用。
为加快水凝胶技术的临床落地,建议从以下几个方面着手:鼓励材料科学家、生物工程师、临床眼科专家和药剂师之间开展紧密合作,从临床需求出发开展材料设计和性能优化,确保水凝胶产品在结构、生物相容性、力学性能等方面满足临床使用的实际需求;支持建设集研发、中试和临床前验证为一体的转化医学平台,为科研成果提供从实验室走向临床的中间桥梁,解决技术转化过程中的标准化、规范化和规模化问题;鼓励科技成果向企业转移转化,推动医工企联合开发,依托市场需求开展目标明确的产品迭代,为水凝胶材料的临床使用提供现实基础和商业路径。
眼科疾病影响全球数百万人,当前的治疗方法如滴眼液和玻璃体注射存在生物利用度低、药效持续时间短等局限性。水凝胶因良好的生物相容性、可控的物理化学性质以及光响应特性,在组织工程、药物递送和3D打印等领域展现出广阔的应用前景,然而该材料的临床转化仍面临诸多挑战。该文综述了水凝胶在眼科疾病中的应用,重点介绍了水凝胶的种类及其在眼科中的应用,包括组织工程、药物运输和3D打印。此外,还指出了水凝胶的局限性和未来发展前景。
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||