[1] ZHU Y, MEILI S, DONG M, et al. Pathoanatomy and incidence of the posterolateral fractures in bicondylar tibial plateau fractures: a clinical computed tomography-based measurement and the associated biomechanical model simulation. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2014;134:1369-1380.
[2] YAN L, ZHAN Y, XIE X, et al. Ability of modern proximal tibial lateral plates to capture posterolateral tibial plateau fracture fragments. Ann Transl Med. 2022;10(13): 727.
[3] XIE X, ZHAN Y, WANG Y, et al. Comparative Analysis of Mechanism-Associated 3-Dimensional Tibial Plateau Fracture Patterns. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2020;102(5):410-418.
[4] 吕天润,洪顾麒,陈群,等.过伸型胫骨平台骨折的临床治疗[J]. 创伤外科杂志,2019,21(4):252-256.
[5] LOBENHOFFER P, GERICH T, BERTRAM T, et al. Particular posteromedial and posterolateral approaches for the treatment of tibial head fractures. Unfallchirurg. 1997;100(12):957-967.
[6] JOO MS, KANG HJ, YU HK, et al. Outcomes of Primary Volar Locking Plate Fixation of Open Distal Radius Fractures. J Hand Surg Asian Pac Vol. 2022;27(3):517-523..
[7] 张巍, 罗从风, 曾炳芳. 四种不同内固定治疗胫骨平台后外侧剪应力骨折的生物力学研究[J]. 中华创伤骨科杂志,2010,12(11):1069-1073.
[8] 王倞, 李元超, 汪方, 等. 人体松质骨矿质密度与弹性模量关系[J]. 医用生物力学,2014,29(5):465-470.
[9] 杨宗酉, 程晓东, 朱炼, 等. 内侧和外侧锁定钢板固定Schatzker Ⅵ型胫骨平台骨折的有限元分析[J]. 中华创伤骨科杂志,2018,20(2):157-161.
[10] 张强, 巫宗德, 刘亮, 等. 胫骨内侧,外侧解剖锁定钢板固定胫骨中下段外旋型螺旋骨折的有限元分析[J]. 中国组织工程研究,2022,26(36): 5750-5754.
[11] BU G, SUN W, LU Y, et al. Complications associated with hyperextension bicondylar tibial plateau fractures: a retrospective study. BMC Surg. 2021; 21(1):299.
[12] 杨胜松, 王满宜, 荣国威. Schatzker Ⅳ型胫骨平台骨折的分型及治疗[J]. 中华外科杂志,2004,42(19):1161-1164.
[13] 刘付杰. 过伸内翻型胫骨平台骨折的临床特征及手术方案分析[J]. 实用手外科杂志,2022,36(1):122-124.
[14] 刘兆杰, 张金利, 沈啟捷, 等. 过伸内翻型胫骨平台骨折的临床特点及治疗策略[J]. 中华骨科杂志,2019,39(21):1301-1310.
[15] 张世民, 胡孙君, 杜守超, 等. 过伸型胫骨平台骨折研究进展[J]. 中国修复重建外科杂志,2018,32(4):495-500.
[16] CHIBA T, SUGITA T, ONUMA M, et al. Injuries to the posterolateral aspect of the knee accompanied by compression fracture of the anterior part of the medial tibial plateau. Arthroscopy. 2001;17(6):642-647.
[17] 朱燕宾, 陈伟, 张奇, 等. 胫骨平台核心负重区的概念及其临床意义[J]. 中华骨科杂志,2021,41(3):137-140.
[18] 李东阳, 张堃, 李大双, 等. 内侧支撑钢板及排钉固定治疗累及后外侧SchatzkerⅣ型胫骨平台骨折的疗效分析[J]. 中华创伤骨科杂志,2022, 24(10):874-878.
[19] YAN B, SUN J, YIN W. The prevalence of soft tissue injuries in operative Schatzker type IV tibial plateau fractures. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2021; 141(8):1269-1275.
[20] KEOGH P, KELLY C, CASHMAN WF, et al. Percutaneous screw fixation of tibial plateau fractures. Injury. 1992;23(6):387-389.
[21] OHDERA T, TOKUNAGA M, HIROSHIMA S, et al. Arthroscopic management of tibial plateau fractures—comparison with open reduction method. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2003;123:489-493.
[22] DALL OCA C, MALUTA T, LAVINI F, et al. Tibial plateau fractures: compared outcomes between ARIF and ORIF. Strategies Trauma Limb Reconstr. 2012;7:163-175.
[23] WANG J, JIANG B, GUO W, et al. Arthroscopic-assisted balloon tibioplasty versus open reduction internal fixation (ORIF) for treatment of Schatzker II–IV tibial plateau fractures: study protocol of a randomised controlled trial. BMJ Open. 2018;8(8):e21667.
[24] 罗从风, 姜锐, 周曼瑜, 等. 胫骨内侧平台骨折手术治疗失败的原因分析[J]. 中华创伤骨科杂志,2006,8(7):642-646.
[25] HUANG X, ZHI Z, YU B, et al. Stress and stability of plate-screw fixation and screw fixation in the treatment of Schatzker type IV medial tibial plateau fracture: a comparative finite element study. J Orthop Surg Res. 2015;10(1):1-9.
[26] CIFT H, CETIK O, KALAYCIOGLU B, et al. Biomechanical comparison of plate-screw and screw fixation in medial tibial plateau fractures (Schatzker 4). A model study. Orthop Traumatol Surg Res. 2010;96(3):263-267.
[27] 黄玉成, 焦竞, 程文俊, 等. 围关节线钢板治疗伸直内翻型胫骨平台骨折[J]. 中华创伤骨科杂志,2017,19(10):833-839.
[28] 吕天润, 陈群, 李翔, 等. 改良后外侧入路2.4 mm系统桡骨远端锁定钢板治疗胫骨平台后外侧塌陷骨折[J]. 中华创伤骨科杂志,2016,18(10): 851-856. |
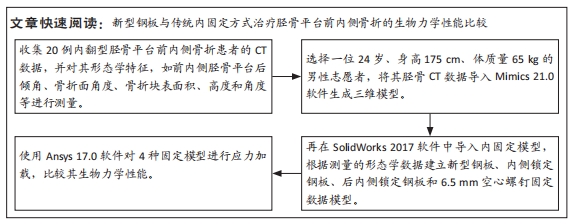
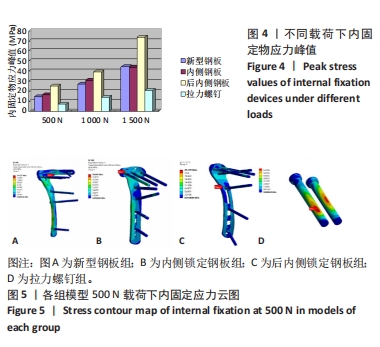
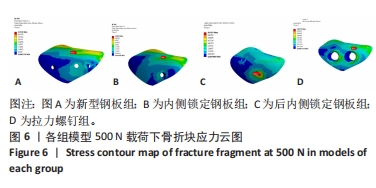
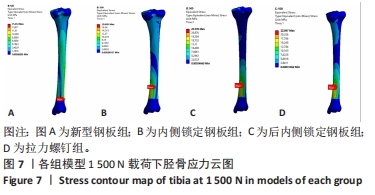
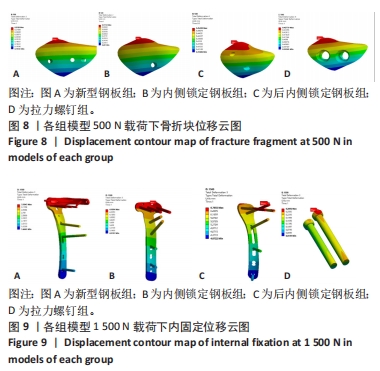
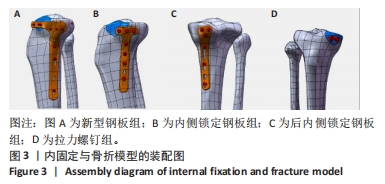
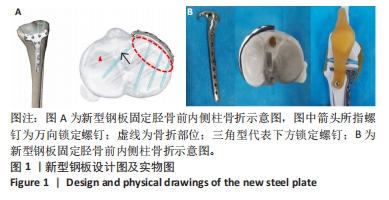 此次研究通过有限元分析方法,对新型钢板与常见3种内固定治疗胫骨平台前内侧柱骨折的力学性能进行比较。
此次研究通过有限元分析方法,对新型钢板与常见3种内固定治疗胫骨平台前内侧柱骨折的力学性能进行比较。