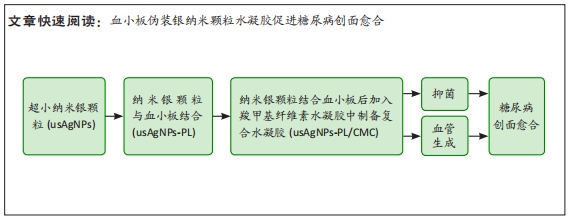
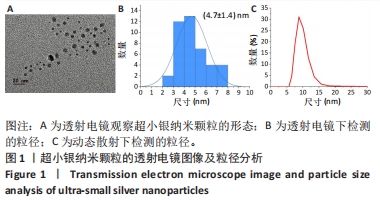
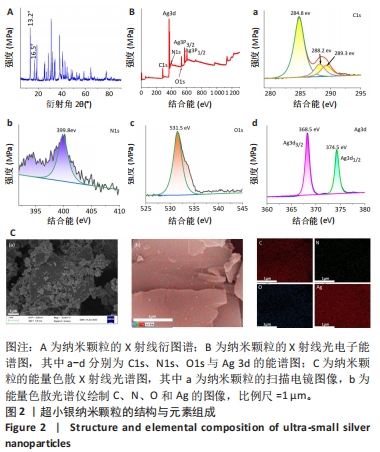
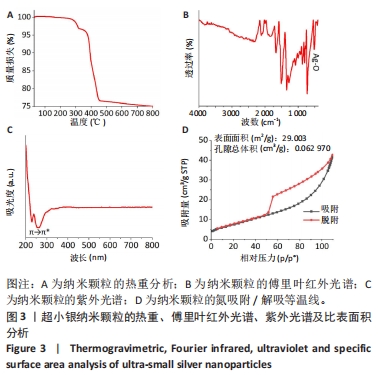
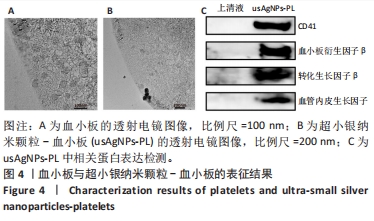
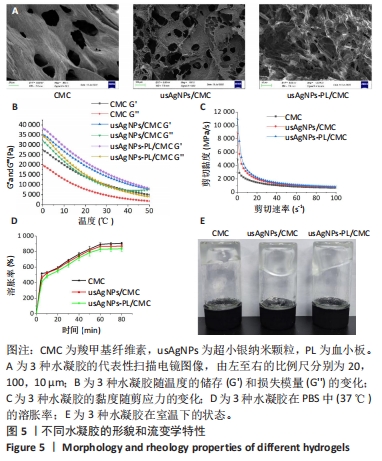
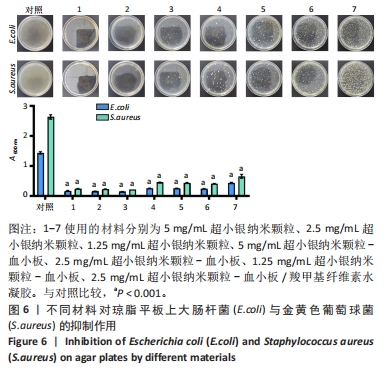
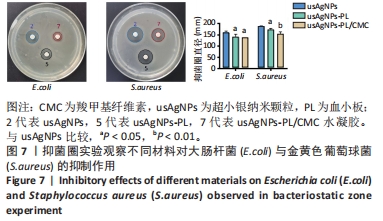
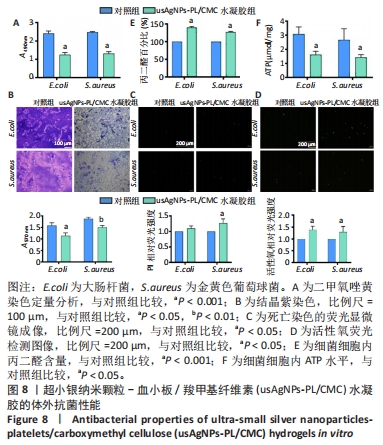
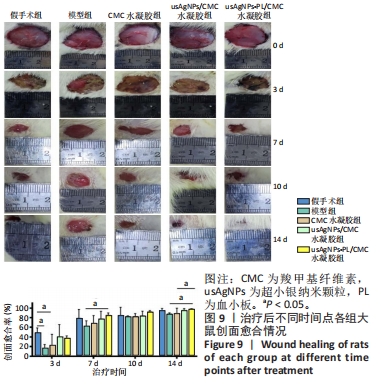
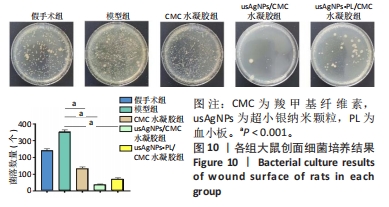
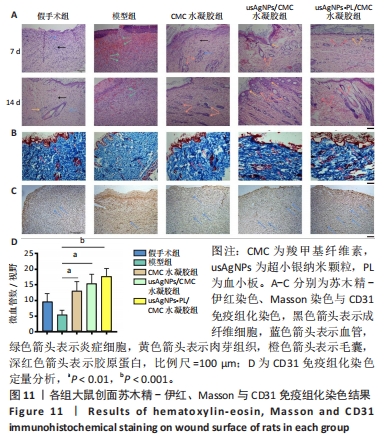
[1] EVERETT E, MATHIOUDAKIS N. Update on management of diabetic foot ulcers. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2018;1411(1):153-165.
[2] FANG PH, LAI YY, CHEN CL, et al. Cobalt protoporphyrin promotes human keratinocyte migration under hyperglycemic conditions. Mol Med. 2022;28(1):71.
[3] BUCH PJ, CHAI Y, GOLUCH ED. Treating Polymicrobial Infections in Chronic Diabetic Wounds. Clin Microbiol Rev. 2019;32(2):e00091-18.
[4] GONZALEZ LS 3RD, SPENCER JP. Aminoglycosides: a practical review. Am Fam Physician. 1998; 58(8):1811-1820.
[5] AMINOV RI. The role of antibiotics and antibiotic resistance in nature. Environ Microbiol. 2009;11(12):2970-2988.
[6] SIRITONGSUK P, HONGSING N, THAMMAWITHAN S, et al. Two-Phase Bactericidal Mechanism of Silver Nanoparticles against Burkholderia pseudomallei. PLoS One. 2016;11(12):e0168098.
[7] YUAN G, TIAN Y, WANG B, et al. Mitigation of membrane biofouling via immobilizing Ag-MOFs on composite membrane surface for extractive membrane bioreactor. Water Res. 2021;209:117940.
[8] DEHNAVI SM, BARJASTEH M, AHMADI SEYEDKHANI S, et al. A Novel Silver-Based Metal-Organic Framework Incorporated into Nanofibrous Chitosan Coatings for Bone Tissue Implants. Int J Pharm. 2023;640:123047.
[9] WANG D, LI S, LI F, et al. Thin film nanocomposite membrane with triple-layer structure for enhanced water flux and antibacterial capacity. Sci Total Environ. 2021;770:145370.
[10] XIONG Y, CHEN L, LIU P, et al. All-in-One: Multifunctional Hydrogel Accelerates Oxidative Diabetic Wound Healing through Timed-Release of Exosome and Fibroblast Growth Factor. Small. 2022;18(1):e2104229.
[11] HUSSAIN Z, THU HE, SHUID AN, et al. Recent Advances in Polymer-based Wound Dressings for the Treatment of Diabetic Foot Ulcer: An Overview of State-of-the-art. Curr Drug Targets. 2018;19(5):527-550.
[12] REHMAN SRU, AUGUSTINE R, ZAHID AA, et al. Reduced Graphene Oxide Incorporated GelMA Hydrogel Promotes Angiogenesis For Wound Healing Applications. Int J Nanomedicine. 2019;14:9603-9617.
[13] WASIAK J, CLELAND H, CAMPBELL F, et al. Dressings for superficial and partial thickness burns. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2013;2013(3):Cd002106.
[14] ETULAIN J. Platelets in wound healing and regenerative medicine. Platelets. 2018; 29(6):556-568.
[15] CECERSKA-HERYĆ E, GOSZKA M, SERWIN N, et al. Applications of the regenerative capacity of platelets in modern medicine. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2022;64: 84-94.
[16] KARTIKA RW, ALWI I, SUYATNA FD, et al. The role of VEGF, PDGF and IL-6 on diabetic foot ulcer after Platelet Rich Fibrin + hyaluronic therapy. Heliyon. 2021; 7(9):e07934.
[17] YU W, YIN N, YANG Y, et al. Rescuing ischemic stroke by biomimetic nanovesicles through accelerated thrombolysis and sequential ischemia-reperfusion protection. Acta Biomater. 2022;140:625-640.
[18] ZHAO X, CHANG L, HU Y, et al. Preparation of Photocatalytic and Antibacterial MOF Nanozyme Used for Infected Diabetic Wound Healing. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2022;14(16):18194-18208.
[19] FU X, GAO Y, YAN W, et al. Preparation of eugenol nanoemulsions for antibacterial activities. RSC Adv. 2022;12(6):3180-3190.
[20] GENG X, QI Y, LIU X, et al. A multifunctional antibacterial and self-healing hydrogel laden with bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes for accelerating diabetic wound healing. Biomater Adv. 2022;133:112613.
[21] MOGHARBEL RT, ALKHAMIS K, FELALY R, et al. Superior adsorption and removal of industrial dye from aqueous solution via magnetic silver metal-organic framework nanocomposite. Environ Technol. 2023:1-17.doi: 10.1080/ 09593330.2023.2178331.
[22] GUO H, ZHANG Y, ZHENG Z, et al. Facile one-pot fabrication of Ag@MOF(Ag) nanocomposites for highly selective detection of 2,4,6-trinitrophenol in aqueous phase. Talanta. 2017;170:146-151.
[23] WANG B, YU J, SUI L, et al. Rational Design of Multi-Color-Emissive Carbon Dots in a Single Reaction System by Hydrothermal. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2020;8(1):2001453.
[24] LIN YH, SIVAKUMAR C, BALRAJ B, et al. Ag-Decorated Vertically Aligned ZnO Nanorods for Non-Enzymatic Glucose Sensor Applications. Nanomaterials (Basel). 2023;13(4):754.
[25] ZHANG M, WANG G, ZHANG X, et al. Polyvinyl Alcohol/Chitosan and Polyvinyl Alcohol/Ag@MOF Bilayer Hydrogel for Tissue Engineering Applications. Polymers (Basel). 2021;13(18):3151.
[26] SEYEDPOUR SF, DADASHI FIROUZJAEI M, RAHIMPOUR A, et al. Toward Sustainable Tackling of Biofouling Implications and Improved Performance of TFC FO Membranes Modified by Ag-MOF Nanorods. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2020; 12(34):38285-38298.
[27] ZHANG M, WANG D, JI N, et al. Bioinspired Design of Sericin/Chitosan/Ag@MOF/GO Hydrogels for Efficiently Combating Resistant Bacteria, Rapid Hemostasis, and Wound Healing. Polymers (Basel). 2021;13(16):2812.
[28] HARANDIZADEH AH, AGHAMIRI S, HOJJAT M, et al. Adsorption of Carbon Dioxide with Ni-MOF-74 and MWCNT Incorporated Poly Acrylonitrile Nanofibers. Nanomaterials (Basel). 2022;12(3):412.
[29] YAN R, GU Y, RAN J, et al. Intratendon Delivery of Leukocyte-Poor Platelet-Rich Plasma Improves Healing Compared With Leukocyte-Rich Platelet-Rich Plasma in a Rabbit Achilles Tendinopathy Model. Am J Sports Med. 2017;45(8):1909-1920.
[30] BANG KH, NA YG, HUH HW, et al. The Delivery Strategy of Paclitaxel Nanostructured Lipid Carrier Coated with Platelet Membrane. Cancers (Basel). 2019;11(6):807.
[31] LIU T, LI M, TANG J, et al. An acoustic strategy for gold nanoparticle loading in platelets as biomimetic multifunctional carriers. J Mater Chem B. 2019;7(13): 2138-2144.
[32] NING CC, LOGSETTY S, GHUGHARE S, et al. Effect of hydrogel grafting, water and surfactant wetting on the adherence of PET wound dressings. Burns. 2014; 40(6):1164-1171.
[33] WANG Z, GAO S, ZHANG W, et al. Polyvinyl alcohol/chitosan composite hydrogels with sustained release of traditional Tibetan medicine for promoting chronic diabetic wound healing. Biomater Sci. 2021;9(10):3821-3829.
[34] ZHOU Y, ZHANG XL, LU ST, et al. Human adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells-derived exosomes encapsulated in pluronic F127 hydrogel promote wound healing and regeneration. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2022;13(1):407.
[35] GUIDONI M, DE SOUSA JÚNIOR AD, ARAGÃO VPM, et al. Liposomal stem cell extract formulation from Coffea canephora shows outstanding anti-inflammatory activity, increased tissue repair, neocollagenesis and neoangiogenesis. Arch Dermatol Res. 2023;315(3):491-503.
[36] KULESH AA, KUKLINA EM, SHESTAKOV VV. The relationship between serum and liquor il-1β, il-6, tnfα, il-10 levels and clinical, cognitive and functional characteristics in acute ischemic stroke. Klin Med (Mosk). 2016;94(9):657-662.
[37] WAN R, WEISSMAN JP, GRUNDMAN K, et al. Diabetic wound healing: The impact of diabetes on myofibroblast activity and its potential therapeutic treatments. Wound Repair Regen. 2021;29(4):573-581.
[38] GOURISHETTI K, KENI R, NAYAK PG, et al. Sesamol-Loaded PLGA Nanosuspension for Accelerating Wound Healing in Diabetic Foot Ulcer in Rats. Int J Nanomedicine. 2020;15:9265-9282.
[39] YANG J, CHEN Z, PAN D, et al. Umbilical Cord-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Exosomes Combined Pluronic F127 Hydrogel Promote Chronic Diabetic Wound Healing and Complete Skin Regeneration. Int J Nanomedicine. 2020;15: 5911-5926.
[40] HUANG L, SHI Y, LI M, et al. Plasma Exosomes Loaded pH-Responsive Carboxymethylcellulose Hydrogel Promotes Wound Repair by Activating the Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor Signaling Pathway in Type 1 Diabetic Mice. J Biomed Nanotechnol. 2021;17(10):2021-2033.
[41] VILLIOU M, PAEZ JI,DEL CAMPO A. Photodegradable Hydrogels for Cell Encapsulation and Tissue Adhesion. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2020;12(34): 37862-37872.
|