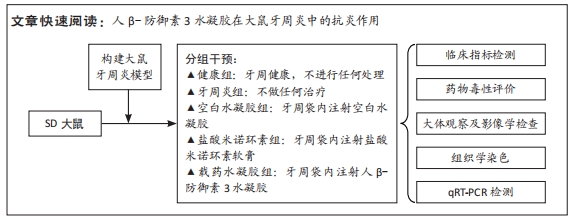
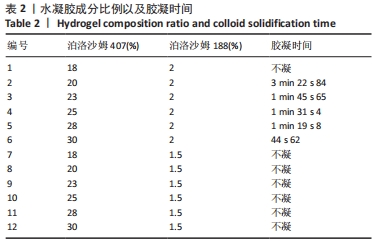
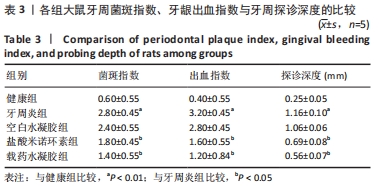
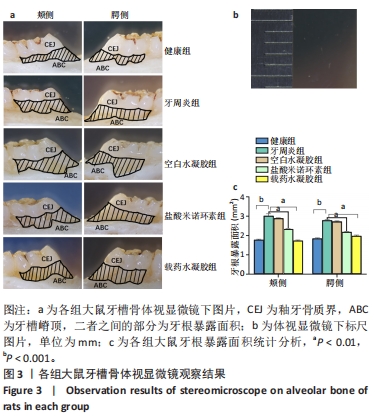
[1] HEISS E, HERHAUS C, KLIMO K, et al. Nuclear factor kappa B is a molecular target for sulforaphane-mediated anti-inflammatory mechanisms. J Biol Chem. 2001;276(34):32008-32015.
[2] HAJISHENGALLIS G. Periodontitis: from microbial immune subversion to systemic inflammation. Nat Rev Immunol. 2015;15(1):30-44.
[3] SLOTS J. Periodontitis: facts, fallacies and the future. Periodontol 2000. 2017; 75(1):7-23.
[4] LOOS BG, VAN DYKE TE. The role of inflammation and genetics in periodontal disease. Periodontology 2000. 2020;83(1):26-39.
[5] 朱燕燕.派力奥口腔用药引起黑舌1例[J].甘肃医药,2014,33(9):719-720.
[6] NOGUCHI T, SHIBA H, KOMATSUZAWA H, et al. Syntheses of prostaglandin E2 and E-cadherin and gene expression of beta-defensin-2 by human gingival epithelial cells in response to Actinobacillus actinomycetemcomitans. Inflammation. 2003; 27(6):341-349.
[7] OUHARA K, KOMATSUZAWA H, YAMADA S, et al. Susceptibilities of periodontopathogenic and cariogenic bacteria to antibacterial peptides, beta-defensins, and LL37, produced by human epithelial cells. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2005;55(6):888-896.
[8] MAISETTA G, BATONI G, ESIN S, et al. In vitro bactericidal activity of human beta-defensin 3 against multidrug-resistant nosocomial strains. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2006;50(2):806-809.
[9] LAMONT RJ, KOO H, HAJISHENGALLIS G. The oral microbiota: dynamic communities and host interactions. Nat Rev Microbiol. 2018;16(12):745-759.
[10] NIYONSABA F, KIATSURAYANON C, CHIEOSILAPATHAM P, et al. Friends or Foes? Host defense (antimicrobial) peptides and proteins in human skin diseases. Exp Dermatol. 2017;26(11):989-998.
[11] NIYONSABA F, KIATSURAYANON C, OGAWA H. The role of human beta-defensins in allergic diseases. Clin Exp Allergy. 2016;46(12):1522-1530.
[12] TAKAHASHI M, UMEHARA Y, YUE H, et al. The Antimicrobial Peptide Human beta-Defensin-3 Accelerates Wound Healing by Promoting Angiogenesis, Cell Migration, and Proliferation Through the FGFR/JAK2/STAT3 Signaling Pathway. Front Immunol. 2021;12:712781.
[13] SEMPLE F, MACPHERSON H, WEBB S, et al. Human beta-defensin 3 affects the activity of pro-inflammatory pathways associated with MyD88 and TRIF. Eur J Immunol. 2011;41(11):3291-3300.
[14] WANG H, WATANABE H, OGITA M, et al. Effect of human beta-defensin-3 on the proliferation of fibroblasts on periodontally involved root surfaces. Peptides. 2011;32(5):888-894.
[15] LI L, JIANG H, CHEN R, et al. Human beta-defensin 3 gene modification promotes the osteogenic differentiation of human periodontal ligament cells and bone repair in periodontitis. Int J Oral Sci. 2020;12(1):13.
[16] SHESHALA R, QUAH SY, TAN GC, et al. Investigation on solution-to-gel characteristic of thermosensitive and mucoadhesive biopolymers for the development of moxifloxacin-loaded sustained release periodontal in situ gels. Drug Deliv Transl Res. 2019;9(2):434-443.
[17] 陈小燕,单倩倩,陆晓燕.恶性肿瘤患者口腔pH值与口腔黏膜炎发生率相关性[J].交通医学,2022,36(4):439-440.
[18] 崔桓,冯松福,陆晓和.将水凝胶作为药物缓释载体的研究进展[J].当代医药论丛,2020,18(4):18-20.
[19] 夏侗樑,董家辰,束蓉.水凝胶缓释系统在牙周组织再生中的应用[J].上海交通大学学报(医学版),2021,41(7):959-962.
[20] LE TP, YU Y, CHO IS, et al. Injectable Poloxamer Hydrogel Formulations for Intratympanic Delivery of Dexamethasone. J Korean Med Sci. 2023;38(17):e135.
[21] 黄永杰,马守栋,苗青,等.牙周炎治疗用原位凝胶的研究进展[J].中国药房, 2018,29(10):1430-1435.
[22] 徐雨生,廖川江,段美娟.泊洛沙姆作为温度敏感型凝胶基质的安全性评价[J].食品与药品,2021,23(4):337-341.
[23] PLEMMENOS G, EVANGELIOU E, POLIZOGOPOULOS N, et al. Central Regulatory Role of Cytokines in Periodontitis and Targeting Options. Curr Med Chem. 2021; 28(15):3032.
[24] LIAO CH, FEI W, SHEN ZH, et al. Expression and distribution of TNF-alpha and PGE2 of periodontal tissues in rat periodontitis model. Asian Pac J Trop Med. 2014;7(5):412-416.
[25] BARRETT JP, COSTELLO DA, O’SULLIVAN J, et al. Bone marrow-derived macrophages from aged rats are more responsive to inflammatory stimuli. J Neuroinflammation. 2015;12:67.
[26] CUI D, LYU J, LI H, et al. Human β-defensin 3 inhibits periodontitis development by suppressing inflammatory responses in macrophages. Mol immunol. 2017;91:65-74.
[27] 杨再波,华炜,邹毅,等.人β防御素应用于慢性牙周炎治疗的作用机制研究[J].临床口腔医学杂志,2018,34(12):711-714.
[28] Nehls C, Bohling A, Podschun R, et al. Influence of disulfide bonds in human beta defensin-3 on its strain specific activity against Gram-negative bacteria. Biochim Biophys Acta Biomembr. 2020;1862(8):183273.
[29] Belibasakis GN, Bostanci N. The RANKL-OPG system in clinical periodontology. J Clin Periodontol. 2012;39(3):239-248.
[30] PARK OJ, KIM J, AHN KB, et al. A 15-amino acid C-terminal peptide of beta-defensin-3 inhibits bone resorption by inhibiting the osteoclast differentiation and disrupting podosome belt formation. J Mol Med (Berl). 2017;95(12):1315-1325.
|