中国组织工程研究 ›› 2024, Vol. 28 ›› Issue (11): 1690-1695.doi: 10.12307/2024.203
• 肌肉肌腱韧带组织构建 tissue construction of the muscle, tendon and ligament • 上一篇 下一篇
芒果苷抑制类风湿关节炎成纤维样滑膜细胞增殖、迁移及炎性因子的表达
胡梦凡1,颜秋慧2,邓梦然2,梁美美2,梁 亮1,3,4,易思思1,3,4,邓家刚5,运晨霞1,3,4
- 1广西中医药大学基础医学院,广西壮族自治区南宁市 530200;2广西中医药大学附属瑞康医院,广西壮族自治区南宁市 530011;3广西高发传染病中西医结合转化医学重点实验室,广西壮族自治区南宁市 530200;4广西特色实验动物病证模型重点实验室,广西壮族自治区南宁市 530200;5广西农作物废弃物功能成分研究协同创新中心,广西壮族自治区南宁市 530200
Mangiferin inhibits proliferation, migration and inflammatory factor expression of fibroblast-like synoviocytes in rheumatoid arthritis
Hu Mengfan1, Yan Qiuhui2, Deng Mengran2, Liang Meimei2, Liang Liang1, 3, 4, Yi Sisi1, 3, 4, Deng Jiagang5, Yun Chenxia1, 3, 4
- 1School of Basic Medicine, Guangxi University of Chinese Medicine, Nanning 530200, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China; 2Ruikang Hospital Affiliated to Guangxi University of Chinese Medicine, Nanning 530011, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China; 3Key Laboratory of Integrative Translational Medicine of Guangxi High Incidence Infectious Diseases, Nanning 530200, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China; 4Key Laboratory of Guangxi Characteristic Experimental Animal Disease Model, Nanning 530200, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China; 5Guangxi Collaborative Innovation Center for Research on Functional Components of Crop Waste, Nanning 530200, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China
摘要:
文题释义:
类风湿关节炎成纤维样滑膜细胞:成纤维样滑膜细胞是引发类风湿关节炎的主要效应细胞,在其中发挥炎症浸润和炎症因子释放的作用。通过控制成纤维样滑膜细胞的炎症反应可有效控制类风湿关节炎进展。TLR7/8信号通路:Toll样受体是机体固有免疫细胞应对外来感染时主要的识别受体,TLR7/8是表达在细胞内膜上的受体,主要识别微生物的单链RNA,通过MyD88或TRIF依赖的信号通路激活NF-κB,诱导细胞因子和趋化因子分泌,在类风湿关节炎的发生发展中发挥重要作用。Resiquimod(R848):是一种小分子免疫调节剂,当R848与TLR7/8结合后,可激活MyD88依赖性信号通路,诱导炎症因子的释放。
背景:芒果苷是一种从芒果叶、树皮、根中提取的双苯吡酮类化合物,前期研究表明芒果苷可以通过NF-κB、JAK/STAT等转录因子的活化发挥抗全身性炎症作用。
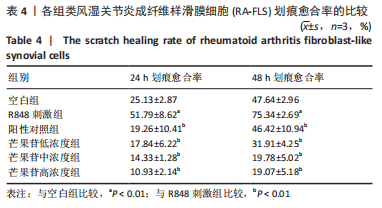
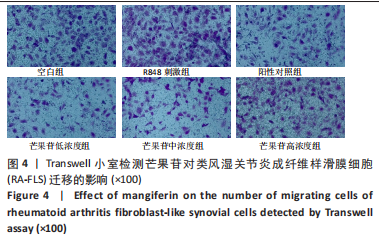
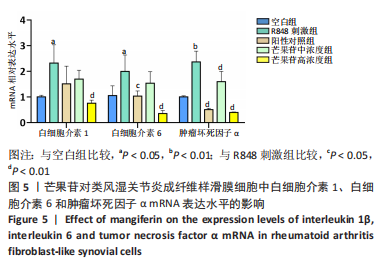
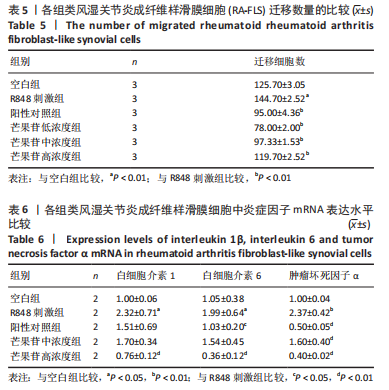
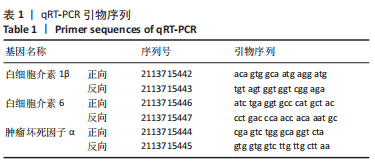
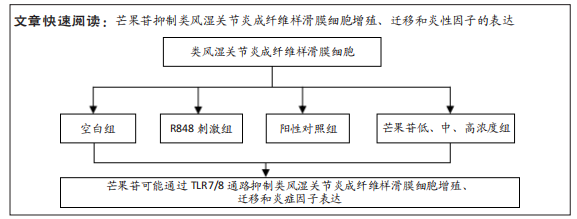
目的:探讨芒果苷对类风湿关节炎成纤维样滑膜细胞(rheumatoid arthritis fibroblast-like synovial cells,RA-FLS)增殖、迁移和炎症因子表达的影响及机制。方法:RA-FLS分为空白组、R848(TLR7/8激动剂)刺激组、芒果苷低、中、高浓度组(2,4,8 μg/mL)、阳性对照组(Cu-CPT8,TLR8通路抑制剂)。CCK-8法检测不同质量浓度芒果苷对RA-FLS毒性的影响并筛选最终细胞用药质量浓度,细胞克隆形成实验检测RA-FLS的增殖能力,划痕实验及Transwell迁移实验检测RA-FLS的迁移能力,qRT-PCR检测RA-FLS中白细胞介素1β、白细胞介素6、肿瘤坏死因子α mRNA的表达。
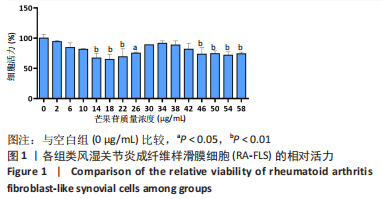
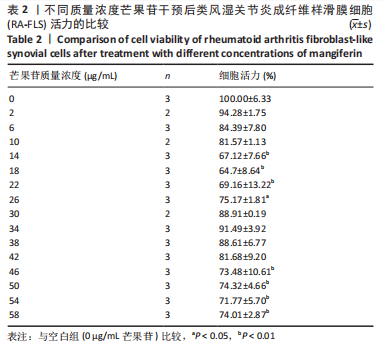
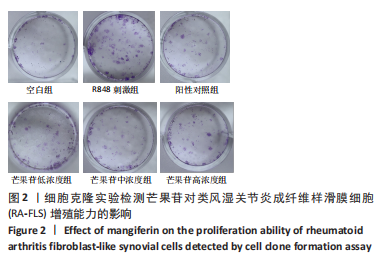
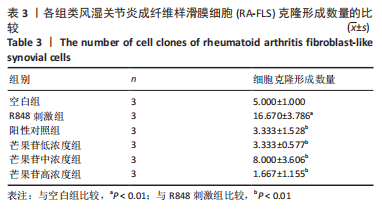
结果与结论:①与空白组比较,2-10 μg/mL的芒果苷干预组对RA-FLS活力有抑制趋势,但差异不显著(P > 0.05),说明对RA-FLS的毒性影响很小;②与R848刺激组比较,芒果苷低、中、高浓度组RA-FLS克隆数、划痕愈合率及迁移细胞数均降低(P < 0.01);芒果苷中浓度和高浓度组白细胞介素1β、白细胞介素6及肿瘤坏死因子α mRNA的表达降低(P < 0.01);③与R848刺激组比较,阳性对照组细胞克隆数、划痕愈合率及迁移细胞数以及白细胞介素6、肿瘤坏死因子α mRNA表达水平显著降低(P < 0.05,P < 0.01);白细胞介素1β mRNA表达水平无明显差异;④结果表明,芒果苷可能通过TLR7/8信号通路抑制RA-FLS增殖、迁移以及炎症因子表达发挥抗类风湿关节炎的作用。
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-8436-0235(运晨霞)
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:组织构建;骨细胞;软骨细胞;细胞培养;成纤维细胞;血管内皮细胞;骨质疏松;组织工程
中图分类号: