中国组织工程研究 ›› 2024, Vol. 28 ›› Issue (11): 1696-1703.doi: 10.12307/2023.967
• 组织构建临床实践 clinical practice in tissue construction • 上一篇 下一篇
构建女方因素异常受精的预测模型及验证
周 超1,李 欢2,庾广聿1,于春梅3,陈 迪1,唐程民1,莫秋菊2,覃仁利4,黄新梅5
- 1广西壮族自治区南溪山医院,广西壮族自治区桂林市 541000;2中国人民解放军联勤保障部队第九二四医院,广西壮族自治区桂林市 541000;3常州市妇幼保健院,江苏省常州市 213000;4柳州市人民医院,广西壮族自治区柳州市 545000;5富川瑶族自治县人民医院,广西壮族自治区贺州市 542700
Construction and validation of a nomogram model to predict abnormal female factors in in vitro fertilization
Zhou Chao1, Li Huan2, Yu Guangyu1, Yu Chunmei3, Chen Di1, Tang Chengmin1, Mo Qiuju2, Qin Renli4, Huang Xinmei5
- 1Nanxishan Hospital of Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, Guilin 541000, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China; 2The 924th Hospital of PLA Joint Logistic Support Force, Guilin 541000, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China; 3Changzhou Maternal and Child Health Care Hospital, Changzhou 213000, Jiangsu Province, China; 4Liuzhou People’s Hospital, Liuzhou 545000, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China; 5Fuchuan Yao Autonomous County People’s Hospital, Hezhou 542700, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China
摘要:
文题释义:
异常受精:是基于固定时间段为体外授精后(17±1) h时,通过对胚胎形态学观察未出现原核(0PN)、出现1个原核(1PN)、出现3个及以上原核(多PN)以及任何原核情况下只有1个或3个及以上极体的统称,异常受精会使可利用胚胎数显著下降,进而影响体外受精与胚胎移植的临床结局。体外受精:是指哺乳动物的精子和卵子在体外人工控制的环境中完成受精过程的技术。人类体外受精主要分为常规体外受精与卵胞浆内单精子显微注射,在常规体外受精过程中,一般在人绒毛膜促性腺激素注射后36-38 h取卵,取卵后2-4 h进行加精,即使卵细胞与精子处于培养皿中共培养。加精后的16-18 h进行原核细胞的观察,即对胚胎受精情况评估,只有当胚胎出现2个极体与2个原核的情况下,才被定义为正常受精卵,因此,常规体外受精取卵后,面临的首要问题为是否受精以及是否为正常受精问题。
背景:降低异常受精率是提高体外受精应用效能与降低患者经济压力的有效手段。然而,现阶段对异常受精的研究主要集中于探讨原核类型及其产生机制,以及对异常受精所形成胚胎、染色体倍性与利用价值的分析,缺乏基于回顾性研究而建立的异常受精临床预测模型。
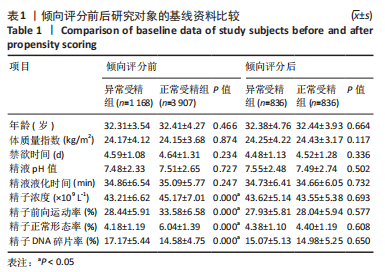
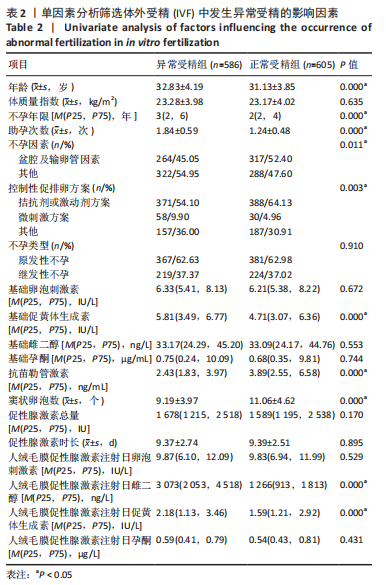
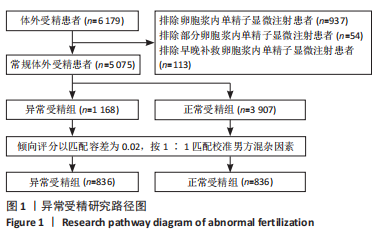
目的:构建常规体外受精中基于女方因素发生异常受精的临床预测模型列线图。方法:回顾性分析2017年3月至2022年3月于广西壮族自治区南溪山医院接受常规体外受精助孕治疗患者共5 075例,以匹配容差为0.02按1∶1倾向评分校准男方混杂因素,匹配成功1 672例,根据维也纳共识,以正常受精能力值≥60%的患者纳入正常受精组(836例),< 60%的患者纳入异常受精组(836例),通过模型组∶验证组=7∶3随机抽样获得模型组与验证组;采用单因素分析筛选模型组发生异常受精的影响因素,并采用套索算法(LASSO)挑选出最佳匹配因素,将其纳入多因素向前逐步Logistic回归,找出其独立影响因素并绘制列线图;最后采用受试者工作曲线、校准曲线、临床决策曲线、临床影响曲线对该预测模型进行区分度与准确度及临床应用效能验证。
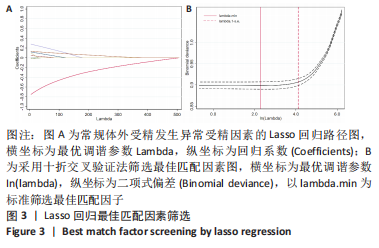
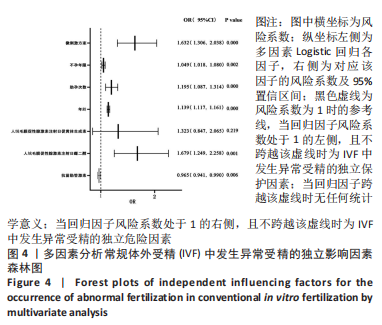
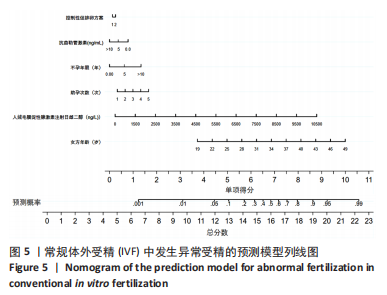
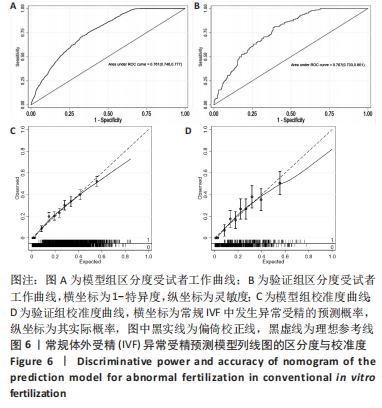
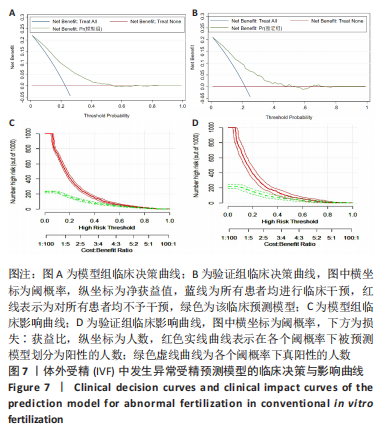
结果与结论:①单因素分析发生异常受精的影响因素为年龄、控制性促排卵方案、助孕次数、不孕年限、不孕因素、抗苗勒管激素、窦状卵泡数、基础促黄体生成素、人绒毛膜促性腺激素注射日促黄体生成素、人绒毛膜促性腺激素注射日雌二醇(P < 0.05);②LASSO回归进一步筛选出的最佳匹配因素为年龄、微刺激方案、助孕次数、不孕年限、抗苗勒管激素、人绒毛膜促性腺激素注射日促黄体生成素、人绒毛膜促性腺激素注射日雌二醇(P < 0.05);③多因素向前逐步Logistic回归结果显示发生异常受精的独立影响因素为年龄、微刺激方案、助孕次数、不孕年限、抗苗勒管激素、人绒毛膜促性腺激素注射日雌二醇;④受试者工作曲线显示模型组曲线下面积为0.761(0.746,0.777),验证组曲线下面积为0.767(0.733,0.801),说明该模型具有较好的区分度;校准曲线平均绝对误差0.044,Hosmer-Lemeshow检验表明该模型预测异常受精的概率与实际异常受精的概率无统计学差异(P > 0.05),具有较好的一致性与准确性;临床决策曲线与临床影响曲线显示,模型组和验证组分别在阈概率值为0.00-0.52与0.00-0.48时具有临床最大净获益,且在该阈概率范围内具有较好的临床应用效能;⑤结果表明,基于年龄、微刺激方案、助孕次数、不孕年限、抗苗勒管激素、人绒毛膜促性腺激素注射日雌二醇构建女方常规体外受精发生异常受精的预测模型列线图,具有较好的区分度与准确度以及临床应用效能。
https://orcid.org/0000-0001-9843-6731(周超)
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:组织构建;骨细胞;软骨细胞;细胞培养;成纤维细胞;血管内皮细胞;骨质疏松;组织工程
中图分类号: