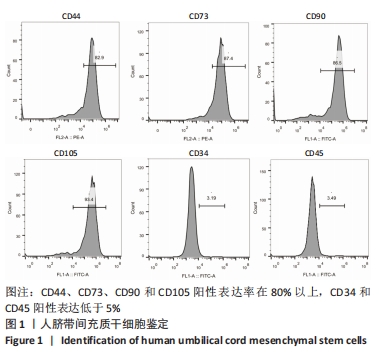
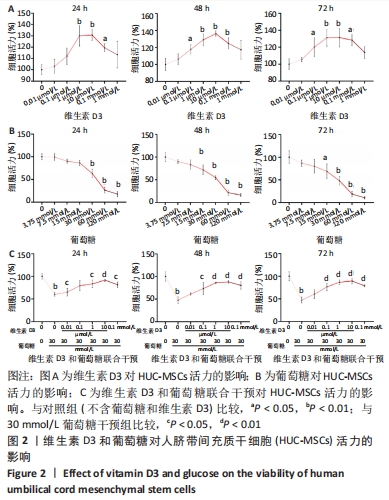
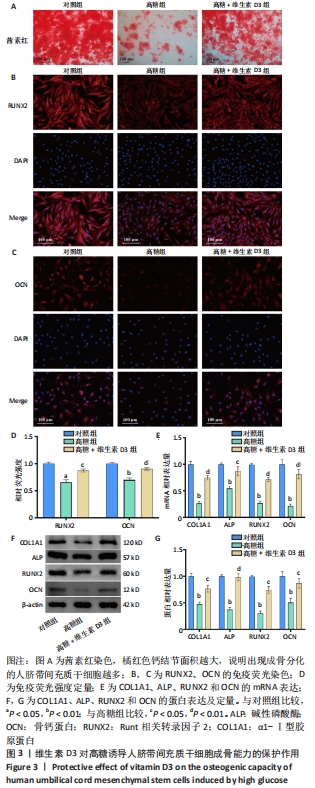
[1] 中国老年2型糖尿病防治临床指南编写组,中国老年医学学会老年内分泌代谢分会,中国老年保健医学研究会老年内分泌与代谢分会,等.中国老年2型糖尿病防治临床指南(2022年版)[J].中华内科杂志,2022,61(1):12-50.
[2] LORENTZON M, ABRAHAMSEN B. Osteoporosis epidemiology using international cohorts. Curr Opin Rheumatol. 2022;34(5):280-288.
[3] 嵇星辰,王明欣,陈少华,等.中国绝经后2型糖尿病患者骨质疏松影响因素的Meta分析[J].中国全科医学,2023,26(4):504-511.
[4] 柳飞扬,吴坚.糖尿病合并骨质疏松的中医研究进展[J].中国骨质疏松杂志,2023,29(1):124-128.
[5] 邴学震,金智生.糖尿病性骨质疏松的中医认识及临床治疗现状[J].中国中医基础医学杂志,2019,25(11):1623-1626.
[6] CAVATI G, PIRROTTA F, MERLOTTI D, et al. Role of Advanced Glycation End-Products and Oxidative Stress in Type-2-Diabetes-Induced Bone Fragility and Implications on Fracture Risk Stratification. Antioxidants (Basel). 2023;12(4):928.
[7] MOHSIN S, BANIYAS MM, ALDARMAKI RS, et al. An update on therapies for the treatment of diabetes-induced osteoporosis. Expert Opin Biol Ther. 2019;19(9):937-948.
[8] NAPOLI N, CHANDRAN M, PIERROZ DD, et al. Mechanisms of diabetes mellitus-induced bone fragility. Nat Rev Endocrinol. 2017;13(4):208-219.
[9] MARINO S, AKEL N, LI S, et al. Reversal of the diabetic bone signature with anabolic therapies in mice. Bone Res. 2023;11(1):19.
[10] CHIODINI I, GAUDIO A, PALERMO A, et al. Management of bone fragility in type 2 diabetes: Perspective from an interdisciplinary expert panel. Nutr Metab Cardiovasc Dis. 2021;31(8):2210-2233.
[11] YAHAO G, XINJIA W. The Role and Mechanism of Exosomes from Umbilical Cord Mesenchymal Stem Cells in Inducing Osteogenesis and Preventing Osteoporosis. Cell Transplant. 2021;30: 9636897211057465.
[12] WANG Q, XIA Q, MENG M, et al. miR-153-3p inhibits osteogenic differentiation of BMSCs by down-regulating the expression of RUNX2 in a high glucose environment. Am J Transl Res. 2022;14(10):7027-7039.
[13] KLABKLAI P, PHETFONG J, TANGPORNCHAROEN R, et al. Annexin A2 Improves the Osteogenic Differentiation of Mesenchymal Stem Cells Exposed to High-Glucose Conditions through Lessening the Senescence. Int J Mol Sci. 2022;23(20):12521.
[14] CHEN B, HE Q, YANG J, et al. Metformin suppresses Oxidative Stress induced by High Glucose via Activation of the Nrf2/HO-1 Signaling Pathway in Type 2 Diabetic Osteoporosis. Life Sci. 2023;312:121092.
[15] KODA S, WADA K, YAMAKAWA M, et al. Associations of Plasma 25-Hydroxy Vitamin D and Dietary Vitamin D Intake with Insulin Resistance in Healthy Japanese Women. J Nutr Sci Vitaminol (Tokyo). 2023;69(1):46-52.
[16] AVILA CASTILLO A, HAGEMANN T, HOFFMANN A, et al. Associations between vitamin D, immunoglobulin E concentrations, and obesity. Front Nutr. 2023;10:1147407.
[17] SHARAFI SM, YAZDI M, GOODARZI-KHOIGANI M, et al. Effect of Vitamin D Supplementation on Serum 25-Hydroxyvitamin D and Homeostatic Model of Insulin Resistance Levels in Healthy Pregnancy: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Iran J Med Sci. 2023;48(1):4-12.
[18] ZHAN D, ZHAO J, SHI Q, et al. 25-hydroxyvitamin D3 inhibits oxidative stress and ferroptosis in retinal microvascular endothelial cells induced by high glucose through down-regulation of miR-93. BMC Ophthalmol. 2023;23(1):22.
[19] SLOBOGEAN GP, BZOVSKY S, O’HARA NN, et al. Effect of Vitamin D3 Supplementation on Acute Fracture Healing: A Phase II Screening Randomized Double-Blind Controlled Trial. JBMR Plus. 2022;7(1): e10705.
[20] 中华医学会骨质疏松和骨矿盐疾病分会.维生素D及其类似物的临床应用共识[J].中华内分泌代谢杂志,2018,34(3):187-200.
[21] KIM SY, LEE JY, PARK YD, et al. Hesperetin alleviates the inhibitory effects of high glucose on the osteoblastic differentiation of periodontal ligament stem cells. PLoS One. 2013;8(6):e67504.
[22] ELUMALAI S, KARUNAKARAN U, MOON JS, et al. High glucose-induced PRDX3 acetylation contributes to glucotoxicity in pancreatic β-cells: Prevention by Teneligliptin. Free Radic Biol Med. 2020;160:618-629.
[23] ZHAO D, LIU D, SHI W, et al. Association between Maternal Blood Glucose Levels during Pregnancy and Birth Outcomes: A Birth Cohort Study. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2023;20(3):2102.
[24] WANG Y, ZHANG L, WU Y, et al. Peptidome analysis of umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cell (hUC-MSC) conditioned medium from preterm and term infants. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2020;11(1):414.
[25] TOZOUR JN, DELAHAYE F, SUZUKI M, et al. Intrauterine Hyperglycemia Is Associated with an Impaired Postnatal Response to Oxidative Damage. Stem Cells Dev. 2018;27(10):683-691.
[26] HUANG Z, CHEN G, WU H, et al. Ebselen restores peri-implantitis-induced osteogenic inhibition via suppressing BMSCs ferroptosis. Exp Cell Res. 2023;427(2):113612.
[27] KOU Y, RONG X, TANG R, et al. Eldecalcitol prevented OVX-induced osteoporosis through inhibiting BMSCs senescence by regulating the SIRT1-Nrf2 signal. Front Pharmacol. 2023;14:1067085.
[28] XIAOLING G, SHUAIBIN L, KAILU L. MicroRNA-19b-3p promotes cell proliferation and osteogenic differentiation of BMSCs by interacting with lncRNA H19. BMC Med Genet. 2020;21(1):11.
[29] ZHAO G, LUO WD, YUAN Y, et al. LINC02381, a sponge of miR-21, weakens osteogenic differentiation of hUC-MSCs through KLF12-mediated Wnt4 transcriptional repression. J Bone Miner Metab. 2022;40(1):66-80.
[30] MI B, YAN C, XUE H, et al. Inhibition of Circulating miR-194-5p Reverses Osteoporosis through Wnt5a/β-Catenin-Dependent Induction of Osteogenic Differentiation. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2020;21:814-823.
[31] KAWABATA T, TOKUDA H, KUROYANAGI G, et al. Incretin accelerates platelet-derived growth factor-BB-induced osteoblast migration via protein kinase A: The upregulation of p38 MAP kinase. Sci Rep. 2020; 10(1):2341.
[32] SUN X, KOMATSU T, LIM J, et al. Nutrient-dependent requirement for SOD1 in lifespan extension by protein restriction in Drosophila melanogaster. Aging Cell. 2012;11(5):783-793.
[33] LIU Y, WANG N, ZHANG S, et al. Autophagy protects bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells from palmitate‑induced apoptosis through the ROS‑JNK/p38 MAPK signaling pathways. Mol Med Rep. 2018; 18(2):1485-1494.
[34] LIU B, GAN X, ZHAO Y, et al. Inhibition of HMGB1 reduced high glucose-induced BMSCs apoptosis via activation of AMPK and regulation of mitochondrial functions. J Physiol Biochem. 2021;77(2):227-235.
[35] GAO C, QIAO J, LI SS, et al. The levels of bone turnover markers 25(OH)D and PTH and their relationship with bone mineral density in postmenopausal women in a suburban district in China. Osteoporos Int. 2017;28(1):211-218.
[36] WATERHOUSE M, EBELING PR, MCLEOD DSA, et al. The effect of monthly vitamin D supplementation on fractures: a tertiary outcome from the population-based, double-blind, randomised, placebo-controlled D-Health trial. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2023;11(5): 324-332.
[37] UENISHI K, TOKIWA M, KATO S, et al. Stimulation of intestinal calcium absorption by orally administrated vitamin D3 compounds: a prospective open-label randomized trial in osteoporosis. Osteoporos Int. 2018;29(3):723-732.
[38] MANOJ P, DERWIN R, GEORGE S. What is the impact of daily oral supplementation of vitamin D3 (cholecalciferol) plus calcium on the incidence of hip fracture in older people? A systematic review and meta-analysis. Int J Older People Nurs. 2023;18(1):e12492.
[39] ELSAYYAD NME, GOMAA I, SALEM MA, et al. Efficient lung-targeted delivery of risedronate sodium/vitamin D3 conjugated PAMAM-G5 dendrimers for managing osteoporosis: Pharmacodynamics, molecular pathways and metabolomics considerations. Life Sci. 2022;309:121001.
[40] XIONG Y, ZHANG Y, XIN N, et al. 1α,25-Dihydroxyvitamin D3 promotes bone formation by promoting nuclear exclusion of the FoxO1 transcription factor in diabetic mice. J Biol Chem. 2017;292(49): 20270-20280.
|