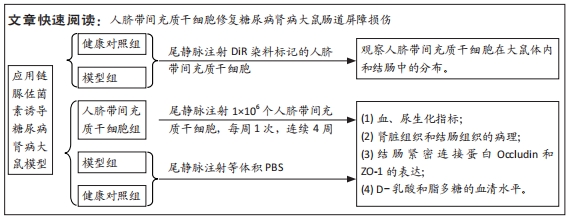
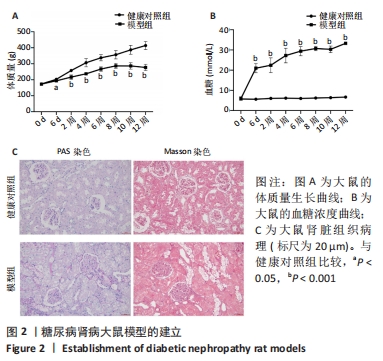
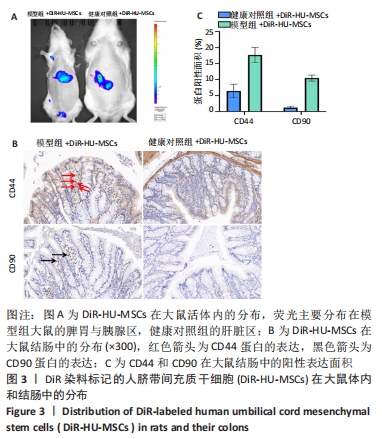
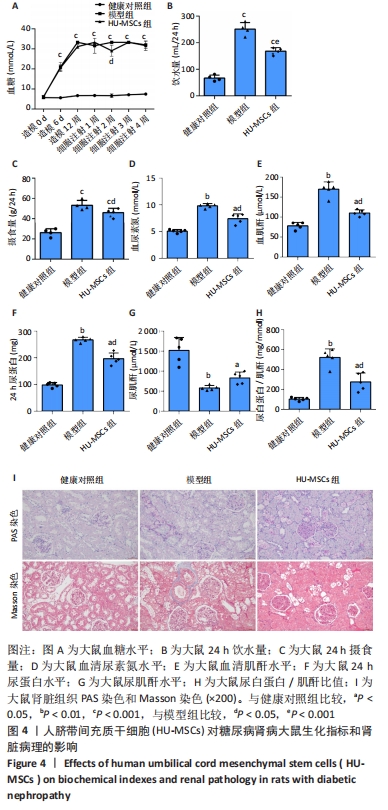
[1] NCD Risk Factor Collaboration (NCD-RisC). Worldwide trends in diabetes since 1980: a pooled analysis of 751 population-based studies with 4.4 million participants. Lancet. 2016;387(10027):1513-1530.
[2] ZIMMET PZ, MAGLIANO DJ, HERMAN WH, et al. Diabetes: a 21st century challenge. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2014;2(1):56-64.
[3] SUN H, SAEEDI P, KARURANGA S, et al. IDF Diabetes Atlas: Global, regional and country-level diabetes prevalence estimates for 2021 and projections for 2045. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2022;183:109119.
[4] KATO M, NATARAJAN R. Diabetic nephropathy--emerging epigenetic mechanisms. Nat Rev Nephrol. 2014;10(9):517-530.
[5] MENG XM, NIKOLIC-PATERSON DJ, LAN HY. TGF-β: the master regulator of fibrosis. Nat Rev Nephrol. 2016;12(6):325-338.
[6] RICO-FONTALVO J, AROCA G, CABRALES J, et al. Molecular Mechanisms of Diabetic Kidney Disease. Int J Mol Sci. 2022;23(15):8668.
[7] CHUNG S, BARNES JL, ASTROTH KS. Gastrointestinal Microbiota in Patients with Chronic Kidney Disease: A Systematic Review. Adv Nutr. 2019;10(5): 888-901.
[8] MEIJERS B, EVENEPOEL P, ANDERS HJ. Intestinal microbiome and fitness in kidney disease. Nat Rev Nephrol. 2019;15(9):531-545.
[9] WANG X, YANG S, LI S, et al. Aberrant gut microbiota alters host metabolome and impacts renal failure in humans and rodents. Gut. 2020; 69(12):2131-2142.
[10] WANG Y, ZHAO J, QIN Y, et al. The Specific Alteration of Gut Microbiota in Diabetic Kidney Diseases-A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Front Immunol. 2022;13:908219.
[11] HAN S, CHEN M, CHENG P, et al. A systematic review and meta-analysis of gut microbiota in diabetic kidney disease: Comparisons with diabetes mellitus, non-diabetic kidney disease, and healthy individuals. Front Endocrinol. 2022;13:1018093.
[12] TANG G, DU Y, GUAN H, et al. Butyrate ameliorates skeletal muscle atrophy in diabetic nephropathy by enhancing gut barrier function and FFA2-mediated PI3K/Akt/mTOR signals. Br J Pharmacol. 2022;179(1):159-178.
[13] LIN W, LI HY, YANG Q, et al. Administration of mesenchymal stem cells in diabetic kidney disease: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2021;12(1):43.
[14] YIN S, LIU W, JI C, et al. hucMSC-sEVs-Derived 14-3-3ζ Serves as a Bridge between YAP and Autophagy in Diabetic Kidney Disease. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2022;2022:3281896.
[15] SALA E, GENUA M, PETTI L, et al. Mesenchymal Stem Cells Reduce Colitis in Mice via Release of TSG6, Independently of Their Localization to the Intestine. Gastroenterology. 2015;149(1):163-176.
[16] YANG S, LIANG X, SONG J, et al. A novel therapeutic approach for inflammatory bowel disease by exosomes derived from human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells to repair intestinal barrier via TSG-6. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2021;12(1):315.
[17] BOSI E, MOLTENI L, RADAELLI MG, et al. Increased intestinal permeability precedes clinical onset of type 1 diabetes. Diabetologia. 2006;49(12): 2824-2827.
[18] ZHONG HJ, YUAN Y, XIE WR, et al. Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Is Associated with More Serious Small Intestinal Mucosal Injuries. PloS one. 2016;11(9): e0162354.
[19] SCHOULTZ I, KEITA ÅV. The Intestinal Barrier and Current Techniques for the Assessment of Gut Permeability. Cells. 2020;9(8):1909.
[20] YAN JT, SUN Q, ZHANG XL, et al. Methods for the evaluation of intestinal mucosal permeability. Sheng Li Xue Bao. 2022;74(4):596-608.
[21] MONACO A, OVRYN B, AXIS J, et al. The Epithelial Cell Leak Pathway. Int J Mol Sci. 2021;22(14):7677.
[22] SHEN L, WEBER CR, RALEIGH DR, et al. Tight junction pore and leak pathways: a dynamic duo. Annu Rev Physiol. 2011;73:283-309.
[23] DENG L, YANG Y, XU G. Empagliflozin ameliorates type 2 diabetes mellitus-related diabetic nephropathy via altering the gut microbiota. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Cell Biol Lipids. 2022;1867(12):159234.
[24] 霍丽霞,朱鸣,王霄一,等. 早期糖尿病肾病患者肠道菌群结构特征及菌群移位的研究[Z]. 湖州市第一人民医院. 2020.
[25] FRIDENSHTEĬN AIA, PETRAKOVA KV, KURALESOVA AI, et al. Precursor cells for osteogenic and hemopoietic tissues. Analysis of heterotopic transplants of bone marrow. Tsitologiia. 1968;10(5):557-567.
[26] LI T, XIA M, GAO Y, et al. Human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells: an overview of their potential in cell-based therapy. Expert Opin Biol Ther. 2015;15(9):1293-1306.
[27] EL OMAR R, BEROUD J, STOLTZ JF, et al. Umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells: the new gold standard for mesenchymal stem cell-based therapies? Tissue Eng Part B Rev. 2014;20(5):523-544.
[28] CHEN L, XIANG E, LI C, et al. Umbilical Cord-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells Ameliorate Nephrocyte Injury and Proteinuria in a Diabetic Nephropathy Rat Model. J Diabetes Res. 2020;2020:8035853.
[29] SZYDLAK R. Biological, chemical and mechanical factors regulating migration and homing of mesenchymal stem cells. World J Stem Cells. 2021;13(6):619-631.
[30] ULLAH M, LIU DD, THAKOR AS. Mesenchymal Stromal Cell Homing: Mechanisms and Strategies for Improvement. iScience. 2019;15:421-438.
[31] WANG S, BAO L, FU W, et al. Protective effect of exosomes derived from bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells on rats with diabetic nephropathy and its possible mechanism. Am J Transl Res. 2021;13(6):6423-6430.
[32] MAO R, SHEN J, HU X. BMSCs-derived exosomal microRNA-let-7a plays a protective role in diabetic nephropathy via inhibition of USP22 expression. Life Sci. 2021;268:118937.
[33] LIN Y, YANG Q, WANG J, et al. An overview of the efficacy and signaling pathways activated by stem cell-derived extracellular vesicles in diabetic kidney disease. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022;13:962635.
[34] YUE Y, YEH JN, CHIANG JY, et al. Intrarenal arterial administration of human umbilical cord-derived mesenchymal stem cells effectively preserved the residual renal function of diabetic kidney disease in rat. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2022;13(1):186.
[35] YU S, CHENG Y, ZHANG L, et al. Treatment with adipose tissue-derived mesenchymal stem cells exerts anti-diabetic effects, improves long-term complications, and attenuates inflammation in type 2 diabetic rats. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2019;10(1):333.
[36] RAFIEE Z, ORAZIZADEH M, NEJAD DEHBASHI F, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells derived from the kidney can ameliorate diabetic nephropathy through the TGF-β/Smad signaling pathway. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2022;29(35): 53212-53224.
[37] LIU Q, LV S, LIU J, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells modified with angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 are superior for amelioration of glomerular fibrosis in diabetic nephropathy. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2020;162:108093.
[38] LEE SE, JANG JE, KIM HS, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells prevent the progression of diabetic nephropathy by improving mitochondrial function in tubular epithelial cells. Exp Mol Med. 2019;51(7):1-14.
[39] ZHANG F, WANG C, WEN X, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells alleviate rat diabetic nephropathy by suppressing CD103+ DCs-mediated CD8+ T cell responses. J Cell Mol Med. 2020;24(10):5817-5831.
[40] LV W, GRAVES DT, HE L, et al. Depletion of the diabetic gut microbiota resistance enhances stem cells therapy in type 1 diabetes mellitus. Theranostics. 2020;10(14):6500-6516.
|