[1] 汪海平,刘芸,胡思前. ZrO2气凝胶材料的制备、改性及应用研究进展[J].江汉大学学报(自然科学版),2023,51(2):15-26.
[2] 徐臻,王斐,印霞,等. ZrO2纳米纤维的最新进展:从结构设计到新兴应用[J].中国科学:材料科学(英文版),2023,66(2):421-440.
[3] LINH NB, JANG DW, LEE BT. Collagen immobilization of multi-layered BCP-ZrO2 bone substitutes to enhance bone formation. Appl Surf Sci. 2015;345:238-248.
[4] HU C, SUN J, LONG C, et al. Synthesis of nano zirconium oxide and its application in dentistry. Nanotechnol Rev. 2019;8(1):396-404.
[5] WANG W, HOU FY, WANG H, et al. Fabrication and characterization of Ni-ZrO2 composite nano-coatings by pulse electrodeposition. Scr Mater. 2005;53(5):613-618.
[6] KONG YM, BAE CJ, LEE SH, et al. Improvement in biocompatibility of ZrO2-Al2O3 nano-composite by addition of HA. Biomaterials. 2005;26(5):509-517.
[7] YU W, WANG X, ZHAO J, et al. Preparation and mechanical properties of reinforced hydroxyapatite bone cement with nano-ZrO2. Ceram Int. 2015;41(9):10600-10606.
[8] WANG G, LIU X, ZREIQAT H, et al. Enhanced effects of nano-scale topography on the bioactivity and osteoblast behaviors of micron rough ZrO2 coatings. Colloid Surface B. 2011;86(2):267-274.
[9] PANG XF, HUANG Y, CAO XY. Preparation and Features of Nano-ZrO2/HA Coating on Surface of Titanium Materials in Dental-Implant. Adv Mater Res. 2011;295:491-495.
[10] LV M, LV W, CHEN H, et al. Biotribological properties of nano zirconium dioxide and hydroxyapatite-reinforced polyetheretherketone (HA/ZrO2/PEEK) biocomposites. Iran Polym J. 2021;30(11):1127-1136.
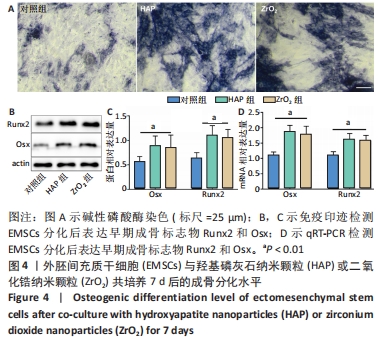
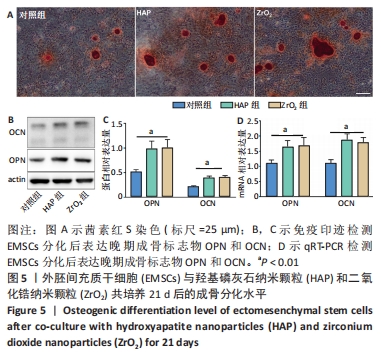
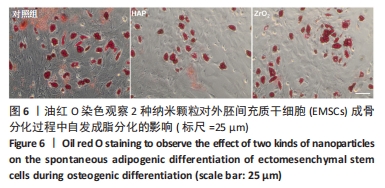
[11] SHI W, WANG Z, BIAN L, et al. Periodic Heat Stress Licenses EMSC Differentiation into Osteoblasts via YAP Signaling Pathway Activation. Stem Cells Int. 2022;2022:3715471.
[12] DENG W, SHAO F, HE Q, et al. EMSCs Build an All-in-One Niche via Cell-Cell Lipid Raft Assembly for Promoted Neuronal but Suppressed Astroglial Differentiation of Neural Stem Cells. Adv Mater. 2019;31(10):e1806861.
[13] CHEN Q, ZHANG Z, LIU J, et al. A fibrin matrix promotes the differentiation of EMSCs isolated from nasal respiratory mucosa to myelinating phenotypical Schwann-like cells. Mol Cells. 2015;38(3):221-228.
[14] SHI W, QUE Y, ZHANG X, et al. Functional tissue-engineered bone-like graft made of a fibrin scaffold and TG2 gene-modified EMSCs for bone defect repair. NPG Asia Mater. 2021;13(1):28.
[15] DHIVYA S, AJITA J, SELVAMURUGAN N. Metallic nanomaterials for bone tissue engineering. J Biomed Nanotechnol. 2015;11(10):1675-1700.
[16] LIU X, MIAO Y, LIANG H, et al. 3D-printed bioactive ceramic scaffolds with biomimetic micro/nano-HAp surfaces mediated cell fate and promoted bone augmentation of the bone-implant interface in vivo. Bioact Mater. 2021;12:120-132.
[17] DU M, CHEN J, LIU K, et al. Recent advances in biomedical engineering of nano-hydroxyapatite including dentistry, cancer treatment and bone repair. Compos Part B-Eng. 2021;215:108790.
[18] SHI W, WU Y, WU J, et al. NPS-Crosslinked Fibrin Gels Load with EMSCs to Repair Peripheral Nerve Injury in Rats. Macromol Biosci. 2023;23(3):e2200381.
[19] HAARHAUS M, CIANCIOLO G, BARBUTO S, et al. Alkaline Phosphatase: An Old Friend as Treatment Target for Cardiovascular and Mineral Bone Disorders in Chronic Kidney Disease. Nutrients. 2022;14(10):2124.
[20] JUNG JH, HONG CM, JO I, et al. Reliability of Alkaline Phosphatase for Differentiating Flare Phenomenon from Disease Progression with Bone Scintigraphy. Cancers (Basel). 2022;14(1):254.
[21] SHU J, TAN A, LI Y, et al. The correlation between serum total alkaline phosphatase and bone mineral density in young adults. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2022;23(1):467.
[22] YIN X, TENG X, MA T, et al. RUNX2 recruits the NuRD(MTA1)/CRL4B complex to promote breast cancer progression and bone metastasis. Cell Death Differ. 2022;29(11):2203-2217.
[23] NING K, YANG B, CHEN M, et al. Functional Heterogeneity of Bone Marrow Mesenchymal Stem Cell Subpopulations in Physiology and Pathology. Int J Mol Sci. 2022;23(19):11928.
[24] ABOU NEEL EA, KG AR, SAMSUDIN AR. Mineralized nodule formation in primary osteoblasts culture in titanium doped phosphate glass and in-house prepared freeze dried demineralized bone extracts. Mater Chem Phys. 2022;276:125425.
[25] LIN C, CHEN Z, GUO D, et al. Increased expression of osteopontin in subchondral bone promotes bone turnover and remodeling, and accelerates the progression of OA in a mouse model. Aging (Albany NY). 2022;14(1):253-271.
[26] SALAMA RHM, ALI SS, SALAMA THM, et al. Dietary Effects of Nanopowder Eggshells on Mineral Contents, Bone Turnover Biomarkers, and Regulators of Bone Resorption in Healthy Rats and Ovariectomy-Induced Osteoporosis Rat Model. Appl Biochem Biotechnol. 2023;195(8):5034-5052.
[27] SAFIAGHDAM H, NOKHBATOLFOGHAHAEI H, FARZAD-MOHAJERI S, et al. 3D-printed MgO nanoparticle loaded polycaprolactone β-tricalcium phosphate composite scaffold for bone tissue engineering applications: In-vitro and in-vivo evaluation. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2023;111(3):322-339.
[28] LIU S, LI K, SHEN Q, et al. Electroactive MnO2-poly (3, 4-ethylenedioxythiophene) composite nanocoatings enhance osteoblastic electrical stimulation. Appl Surf Sci. 2021;545:148827.
[29] WU Z, MENG Z, WU Q, et al. Biomimetic and osteogenic 3D silk fibroin composite scaffolds with nano MgO and mineralized hydroxyapatite for bone regeneration. J Tissue Eng. 2020; 11:2041731420967791.
[30] TARAFDER S, DAVIES NM, BANDYOPADHYAY A, et al. 3D printed tricalcium phosphate scaffolds: Effect of SrO and MgO doping on in vivo osteogenesis in a rat distal femoral defect model. Biomater Sci. 2013;1(12):1250-1259.
[31] SHAO RX, QUAN RF, WANG T, et al. Effects of a bone graft substitute consisting of porous gradient HA/ZrO2 and gelatin/chitosan slow-release hydrogel containing BMP-2 and BMSCs on lumbar vertebral defect repair in rhesus monkey. J Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2018;12(3): e1813-e1825. |