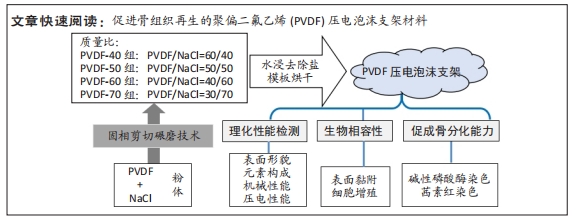
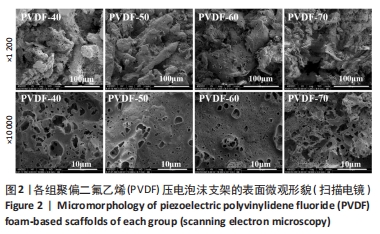
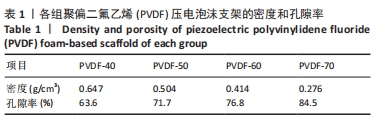
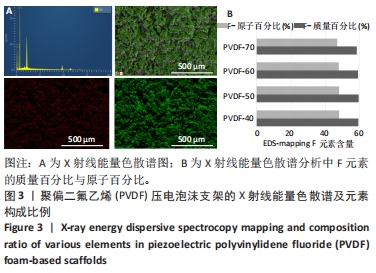
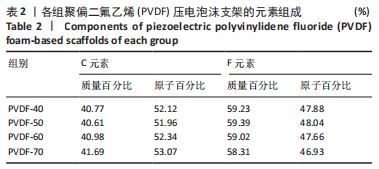
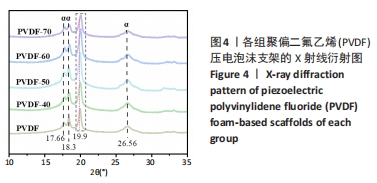
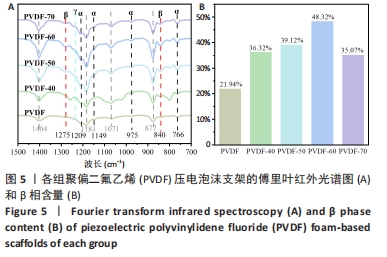
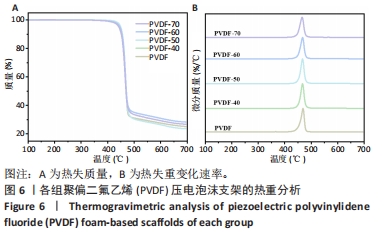
[1] DONG Y, SURYANI L, ZHOU X, et al. Synergistic Effect of PVDF-Coated PCL-TCP Scaffolds and Pulsed Electromagnetic Field on Osteogenesis. Int J Mol Sci. 2021;22(12):6438.
[2] KHARE D, BASU B, DUBEY AK. Electrical stimulation and piezoelectric biomaterials for bone tissue engineering applications. Biomaterials. 2020;258:120280.
[3] KITSARA M, BLANQUER A, MURILLO G, et al. Permanently hydrophilic, piezoelectric PVDF nanofibrous scaffolds promoting unaided electromechanical stimulation on osteoblasts. Nanoscale. 2019;11(18): 8906-8917.
[4] RIBEIRO C, SENCADAS V, CORREIA DM, et al. Piezoelectric polymers as biomaterials for tissue engineering applications. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2015;136:46-55.
[5] 张学慧.电活性骨修复材料的研究现状与挑战[J].口腔材料器械杂志,2022,31(1):1-5.
[6] 熊莹,许燕,周建平,等.组织工程研究中的电活性生物材料[J].中国组织工程研究,2019,23(34):5523-5530.
[7] VIJAYAKANTH T, LIPTROT DJ, GAZIT E, et al. Recent Advances in Organic and Organic–Inorganic Hybrid Materials for Piezoelectric Mechanical Energy Harvesting. Adv Funct Mater. 2022;32(17):2109492.
[8] KIM D, HAN SA, KIM JH, et al. Biomolecular Piezoelectric Materials: From Amino Acids to Living Tissues. Adv Mater. 2020;32(14): e1906989.
[9] LIU Z, WAN X, WANG ZL, et al. Electroactive Biomaterials and Systems for Cell Fate Determination and Tissue Regeneration: Design and Applications. Adv Mater. 2021;33(32):e2007429.
[10] 代香林,姚喜军,张文凤,等.可降解生物压电复合材料在骨组织工程中的研究进展[J].生物医学工程研究,2021,40(4):455-460.
[11] MAHAPATRA SD, MOHAPATRA PC, ARIA AI, et al. Piezoelectric Materials for Energy Harvesting and Sensing Applications: Roadmap for Future Smart Materials. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2021;8(17):e2100864.
[12] WANG AD, CHEN CF, QIAN JL, et al. Enhanced Electrical Properties of PVDF Thin Film by Addition of NaCl by Near-Electric-Field 3D Printing. J Electron Mater. 2021;50(8):4781-4786.
[13] 许言,李平,赖春花,等.血管化骨再生中压电生物材料的应用[J].中国组织工程研究,2023,27(7):1126-1132.
[14] RIBEIRO C, CORREIA DM, RIBEIRO S, et al. Piezoelectric poly(vinylidene fluoride) microstructure and poling state in active tissue engineering. Eng Life Sci. 2015;15(4):351-356.
[15] MOKHTARI F, AZIMI B, SALEHI M, et al. Recent advances of polymer-based piezoelectric composites for biomedical applications. J Mech Behav Biomed. 2021;122:104669.
[16] 马超,赵林,卢灿辉,等.固相力化学改性高聚物的方法研究[J].高分子通报,2011(8):48-52.
[17] FISS BG, RICHARD AJ, DOUGLAS G, et al. Mechanochemical methods for the transfer of electrons and exchange of ions: inorganic reactivity from nanoparticles to organometallics. Chem Soc Rev. 2021;50(14): 8279-8318.
[18] PU ZL, JIANG J, LI Y J, et al. Upcycling of waste artificial turf for high-performance wood-plastic composites. J Appl Polym Sci. 2022;139(45): e53115.
[19] HUA ZK, SHI XR, CHEN YH. Preparation, structure, and property of highly filled polyamide 11/BaTiO3 piezoelectric composites prepared through solid-state mechanochemical method. Polym Composite. 2019;40:E177-E185.
[20] ZHAO B, ZHAO C, WANG C, et al. Poly (vinylidene fluoride) foams: a promising low-k dielectric and heat-insulating material. J Mater Chem C. 2018;6(12):3065-3073.
[21] MARTINS P, LOPES AC, LANCEROS-MENDEZ S. Electroactive phases of poly(vinylidene fluoride): Determination, processing and applications. Prog Polym Sci. 2014;39(4):683-706.
[22] CAI X, LEI T, SUN D, et al. A critical analysis of the α, β and γ phases in poly(vinylidene fluoride) using FTIR. RSC Adv. 2017;7(25):15382-15389.
[23] GREGORIO JR, CESTARI M. Effect of crystallization temperature on the crystalline phase content and morphology of poly(vinylidene fluoride). J Polym SCI Pol Phys. 1994;32(5):859-870.
[24] PANDA AK, SITARAMGUPTA VSN, PANDYA HJ, et al. Electrical stimulation waveform-dependent osteogenesis on PVDF/BaTiO(3) composite using a customized and programmable cell stimulator. Biotechnol Bioeng. 2022;119(6):1578-1597.
[25] NIU H, ZHANG H, YUE W, et al. Micro-Nano Processing of Active Layers in Flexible Tactile Sensors via Template Methods: A Review. Small. 2021;17(41):e2100804.
[26] CHEN C, BAI ZK, CAO YZ, et al. Enhanced piezoelectric performance of BiCl3/PVDF nanofibers-based nanogenerators. Compos Sci Technol. 2020;192:108100.
[27] ZHANG Y, YE L, ZHANG BP, et al. Characteristics and performance of PVDF membrane prepared by using NaCl coagulation bath: Relationship between membrane polymorphous structure and organic fouling. J Membrane Sci. 2019;579:22-32.
[28] PAN H, NA B, LV R, et al. Polar phase formation in poly(vinylidene fluoride) induced by melt annealing. J Polym Sci Part B. 2012;50(20): 1433-1437.
[29] RUAN L, YAO X, CHANG Y, et al. Properties and Applications of the β Phase Poly(vinylidene fluoride). Polymers (Basel). 2018;10(3):228.
[30] UNNITHAN AR, SASIKALA ARK, SHRESTHA BK, et al. Remotely Actuated Magnetic Nanocarpets for Bone Tissue Engineering: Non-Invasive Modulation of Mechanosensitive Ion Channels for Enhanced Osteogenesis. Adv Funct Mater. 2022;32(50):2201311.
[31] MADURANGA KARUNARATHNE WAH, CHOI YH, PARK SR, et al. Bisphenol A inhibits osteogenic activity and causes bone resorption via the activation of retinoic acid-related orphan receptor α. J Hazard Mater. 2022;438:129458.
[32] STAEHLKE S, REBL H, NEBE B. Phenotypic stability of the human MG-63 osteoblastic cell line at different passages. Cell Biol Int. 2019;43(1): 22-32.
[33] FOIS MG, TAHMASEBI BIRGANI ZN, GUTTENPLAN APM, et al. Assessment of Cell-Material Interactions in Three Dimensions through Dispersed Coaggregation of Microsized Biomaterials into Tissue Spheroids. Small. 2022;18(29):e2202112.
[34] WANG A, LIU Z, HU M, et al. Piezoelectric nanofibrous scaffolds as in vivo energy harvesters for modifying fibroblast alignment and proliferation in wound healing. Nano Energy. 2018;43:63-71.
[35] MCCARTHY C, CAMCI-UNAL G. Low Intensity Pulsed Ultrasound for Bone Tissue Engineering. Micromachines (Basel). 2021;12(12):1488.
[36] CHEN J, LI S, JIAO Y, et al. In Vitro Study on the Piezodynamic Therapy with a BaTiO(3)-Coating Titanium Scaffold under Low-Intensity Pulsed Ultrasound Stimulation. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2021;13(41): 49542-49555.
[37] CAI K, JIAO Y, QUAN Q, et al. Improved activity of MC3T3-E1 cells by the exciting piezoelectric BaTiO(3)/TC4 using low-intensity pulsed ultrasound. Bioact Mater. 2021;6(11):4073-4082. |