中国组织工程研究 ›› 2024, Vol. 28 ›› Issue (18): 2925-2931.doi: 10.12307/2024.047
• 骨与关节综述 bone and joint review • 上一篇 下一篇
脊髓损伤后重建膀胱排尿反射在神经源性膀胱中的运用与展望
展立芬,艾 坤,曾学究,梁柔筠,丁强盛,张 泓
- 湖南中医药大学针灸与推拿康复学院,湖南省长沙市 410208
-
收稿日期:2023-03-16接受日期:2023-04-22出版日期:2024-06-28发布日期:2023-08-26 -
通讯作者:张泓,教授,博士生导师,湖南中医药大学针灸与推拿康复学院,湖南省长沙市 410208 -
作者简介:展立芬,女,1995年生,云南省宣威市人,汉族,博士,主要从事神经系统疾病的中西医结合康复机制与临床研究。 -
基金资助:国家自然科学基金面上项目(82274666),项目负责人:张泓;国家自然科学基金面上项目(81874510),项目负责人:艾坤;湖南中医药大学学科建设揭榜挂帅项目(22JBZ013),项目负责人:张泓
Application and prospect of reconstructing bladder micturition reflex in neurogenic bladder after spinal cord injury
Zhan Lifen, Ai Kun, Zeng Xuejiu, Liang Rouyun, Ding Qiangsheng, Zhang Hong
- School of Acupuncture and Moxibustion and Massage Rehabilitation, Hunan University of Chinese Medicine, Changsha 410208, Hunan Province, China
-
Received:2023-03-16Accepted:2023-04-22Online:2024-06-28Published:2023-08-26 -
Contact:Zhang Hong, Professor, Doctoral supervisor, School of Acupuncture and Moxibustion and Massage Rehabilitation, Hunan University of Chinese Medicine, Changsha 410208, Hunan Province, China -
About author:Zhan Lifen, MD, School of Acupuncture and Moxibustion and Massage Rehabilitation, Hunan University of Chinese Medicine, Changsha 410208, Hunan Province, China -
Supported by:National Natural Science Foundation of China (General Program), No. 82274666 (to ZH); National Natural Science Foundation of China (General Program), No. 81874510 (to AK); Discipline Construction Unveiling and Leading Project of Hunan University of Chinese Medicine, No. 22JBZ013 (to ZH)
摘要:
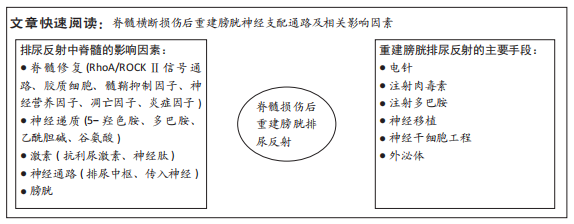
文题释义:
神经源性膀胱:是一类由于神经系统病变导致的膀胱和尿道功能障碍,进而产生一系列下尿路症状的疾病总称,是脊髓损伤后严重的合并症。
脊髓修复:脊髓遭受内外源性损伤后会产生一系列损伤后表现,通过各种手段促进损伤脊髓修复可以有效改善脊髓损伤后并发症。
背景:脊髓损伤后导致的膀胱功能障碍是临床治疗的难点与研究的热点,修复损伤脊髓、重塑膀胱排尿反射通路是根本的治疗手段。
目的:总结脊髓横断损伤后重建膀胱的神经支配通路及相关影响因素。方法:通过计算机检索中国知网、万方数据库、PubMed数据库、Web of Science数据库中与重建排尿反射机制、神经源性膀胱与排尿反射和脊髓修复有关的文献,中文检索词为“神经源性膀胱;脊髓损伤;排尿反射;脊髓修复”,英文检索词为“Neurogenic Bladder;Spinal cord injury;micturition reflex;Spinal cord repair”。
结果与结论:在重建膀胱排尿反射过程中涉及较多的因素,包括脊髓受损区域的修复与重建、排尿中枢的重塑、膀胱组织及体内外物质激素的变化,在此过程中主要存在以下问题:①排尿作为一个复杂的过程,重建排尿反射中涉及位点较多,可选取主要作用位点进行深入研究,以突破重建排尿反射通路上存在的疑点;②正常的排尿反射机制复杂,脊髓横断损伤后,中枢神经系统中控制或参与排尿反射的中枢核团是否发生了代偿及相应的代偿机制有待进一步探究;③脊髓横断损伤后中枢与膀胱的信息交流中断,中枢与膀胱是否存在直接的信息连接尚待进一步探究;④脊髓横断损伤后,重建排尿反射与体液之间的关系尚待进一步研究。在重建膀胱排尿反射中,通过干预治疗促进脊髓修复、神经反射重构、物质代谢和膀胱组织结构调整是治疗的关键,中医与西医各有其法。
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-4037-677X (展立芬)
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:人工关节;骨植入物;脊柱;骨折;内固定;数字化骨科;组织工程
中图分类号:
引用本文
展立芬, 艾 坤, 曾学究, 梁柔筠, 丁强盛, 张 泓. 脊髓损伤后重建膀胱排尿反射在神经源性膀胱中的运用与展望[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2024, 28(18): 2925-2931.
Zhan Lifen, Ai Kun, Zeng Xuejiu, Liang Rouyun, Ding Qiangsheng, Zhang Hong. Application and prospect of reconstructing bladder micturition reflex in neurogenic bladder after spinal cord injury[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(18): 2925-2931.
胸腰段椎体处于人体力学中“动静结合点”,为遭受暴力损伤的常见位点[8]。其中,脊髓中T10脊髓节段横断损伤后,高位排尿中枢与低位排尿中枢之间的联系中断,低位排尿中枢的兴奋与抑制失去控制,膀胱传入冲动信号到达交感-副交感神经核后出现过度兴奋的表现,支配膀胱功能的外周自主神经之间出现支配异常,进而使得逼尿肌出现无抑制性收缩,自主排尿功能丧失、排尿反射消失,出现膀胱障碍,即神经源性膀胱,表现为膀胱储尿和排尿功能障碍[9-10]。当脊髓损伤休克期过后,由于高位中枢丧失对脊髓区域交感-副交感排尿中枢的抑制,出现膀胱逼尿肌和尿道括约肌之间的神经支配异常,进而表现为逼尿肌和尿道括约肌之间的收缩、舒张异常,即逼尿肌和尿道括约肌协同失调,失去正常的储尿和排尿功能。随着疾病的发展,脊髓区域和泌尿道之间的关系可能会发生变化,使得储尿和排尿功能得以恢复,但是仍然无法完全恢复至健康的水平。另外,膀胱也可能出现逼尿肌功能亢进、逼尿肌与尿道括约肌失去平衡、逼尿肌无力及尿道括约肌功能亢进的症状。
为达到恢复膀胱功能的目的,需要尽可能恢复脊髓与膀胱之间的正常支配互动,然而在脊髓遭遇不可逆的损伤后,恢复其正常功能尤为困难,因此,寻找新的途径恢复或重建其功能尤为关键,亦为研究的难点与热点。
2.2 重建的概念及意义 神经功能的重建即神经功能的修复与补充。人体在受到损伤后机体会出现一系列的反应来抵御外界伤害,面临不可逆性损伤,机体会出现替代性功能,用来弥补失去的功能和结构,这一过程称为重建。在神经系统中功能的重建具有十分重要的意义,在一定程度上可以尽可能地挽回丧失的功能,补充所需要的功能,提高患者的生存能力和生活质量。
在T10节段完全性脊髓横断所引起的神经源性膀胱病理改变中,重建膀胱排尿反射对缓解症状、提高患者生活质量具有重要意义,这也是治疗神经源性膀胱的重要立足点之一。在神经源性膀胱的膀胱排尿反射重建中,相关神经递质、分子物质及神经通路发挥着重要角色。
2.3 排尿反射中脊髓的影响因素 脊髓是控制储尿与排尿的初级神经中枢,可通过神经支配调节尿道括约肌和逼尿肌功能活动,参与构成排尿反射的神经传导通路。当脊髓受到机体内外源损伤后正常的排尿反射遭受破坏,在重建排尿反射过程中修复受损的脊髓尤为重要,通过调节细胞、物质代谢等促进脊髓功能的修复是重要的途径之一。
脊髓遭受横断性损伤后,中枢神经系统与损伤脊髓横断面以下的联系被切断。研究表明,当中枢神经系统与膀胱之间的神经支配联系被切断以后,损伤脊髓区域以下会发生可塑性变化,即出现“脊髓-下泌尿道”神经反射通路,但仍不能取代正常的排尿反射,目前研究中针对“脊髓-下泌尿道”神经反射通路的来源存在争议,部分学者认为这可能是一个新产生的脊髓内神经通路,也有学者认为这一神经通路存在于人体发育阶段,在病理情况下被激活并承担相应的“职责”[11]。脊髓遭受损伤刺激后,修复和再生受损的脊髓组织是重建脊髓功能的关键点。现阶段的研究表明,脊髓遭受横断性损伤后损伤局部物质代谢十分复杂,受损脊髓组织的再生和功能恢复是一个极其复杂的过程,大量动物实验表明,脊髓遭受物理损伤后受损神经轴突的再生功能仍存在,但需要一个漫长和复杂的过程才能通过轴突再生和侧支长芽的方式恢复部分功能[12]。脊髓损伤后,因出血、炎症、细胞凋亡和星形胶质细胞活化等因素[13],受损区域出现轴突损伤、血-脊髓屏障破坏[14-15],进而影响受损脊髓的修复,因此,改善受损脊髓的微环境可促进脊髓功能的修复。
重建膀胱反射功能,与重组脊髓中膀胱排尿反射通路和改变膀胱传入神经元特性密切相关[16],因此,对于脊髓完全横断性损伤,促进轴突功能的修复和重建下尿路神经支配的关键点在于改善脊髓损伤后损伤区域的环境变化,阻断脊髓继发性损伤,同时也是干预治疗脊髓损伤后包括膀胱功能异常在内的一系列并发症的关键靶点之一。
2.3.1 脊髓修复
(1) RhoA/ROCKⅡ信号通路:Rho是一种小分子鸟苷三磷酸酶,它来自RAS家族,主要参与细胞的有丝分裂、黏附、收缩、运动和分裂,以及调节细胞骨架等生命过程,其功能是促进细胞的生长和发育,并且可以帮助细胞维持正常的功能。RhO可调控神经细胞形态发生、轴突与树突的导航与生长、塑形和神经细胞间突触形成[17-20]。Rho激酶和p160 ROCK是Rho的两种重要下游效应分子,它们在中枢神经系统中的表达量显著高于ROCKⅡ,可以促进神经元的发育,从而改善神经系统的功能和性能。
最近的研究表明,脊髓损伤后轴突的再生受到阻碍,而这一阻碍可以被Rho/ROCKⅡ通路有效地检测和控制。Rho/ROCK信号通路中的关键分子包括Rho、ROCK和肌球蛋白轻链(MLC)。RhoA是Rho家族的一个主要异构体,而ROCKⅡ是Rho下游最重要的效应分子之一,存在于大脑、脊髓和肌肉中[21-22],因此RhoA/ROCKⅡ信号通路是脊髓损伤后轴突再生抑制性信号传递的关键通路。在重建排尿反射的过程中,脊髓横断损伤区域轴突之间的信号交流是关键点之一,通过构建脊髓之间的轴突联系可以搭建脊髓与膀胱之间的信息交流,从而调整膀胱异常的神经支配状态,RhoA/ROCKⅡ信号通路可承担起这一“职责”。研究表明,脊髓损伤后RhoA、ROCKⅡ蛋白在损伤区域大量表达,阻断了轴突之间的信号传递[23],因此,阻断RhoA/ROCKⅡ信号通路的激活和表达是促进脊髓修复的作用点之一。
(2)胶质细胞:脊髓损伤后,参与形成瘢痕的星形胶质细胞经由幼稚星形胶质细胞转变为反应性星形胶质细胞,继而形成瘢痕[24]。在脊髓损伤的早期阶段,反应性星形胶质细胞发挥着重要的神经保护和修复作用,但随着损伤的加剧,它们的数量急剧增加,最终形成了胶质瘢痕,这些瘢痕会阻碍轴突的再生[25-27]。
脊髓损伤后,急性细胞死亡或损伤会导致细胞源性与血液源性损伤相关的分子模式、ATP的释放、氧化应激以及兴奋性毒性的失衡,从而改变星形胶质细胞的功能,并对它们的外观、基因表达以及增殖产生重要的影响[28]。研究表明,转录激活因子3在调节脊髓损伤后星形胶质细胞增生和瘢痕形成方面发挥着重要作用[29],它不仅可以促进信号传导,还可以激活星形胶质细胞,从而促进中枢神经损伤反应性星形胶质细胞增生和胶质瘢痕的形成,为脊髓损伤的治疗提供了有效支持。在脊髓损伤模型中,选择性敲除星形胶质细胞中的转录激活因子3基因,可减少神经胶质纤维酸性蛋白的表达与胶质瘢痕的形成,这将有助于减轻受损部位的炎症反应,从而促进功能的恢复[30]。由此可见,星形胶质细胞的活化状态是脊髓损伤修复过程中微环境的关键点之一。
(3)髓鞘抑制因子:髓鞘是神经组织中一种特殊的结构,由胶质细胞包裹而成,可以增强轴突信号的传导,并且可以沿着有髓神经纤维呈跳跃式传导,在神经信号传递过程中发挥着重要作用。脊髓损伤后,神经传导功能恢复的生物学基础之一就是损伤部位形成新的髓鞘,这一过程依赖于胶质细胞,这也是轴突再生的关键点之一[31]。
研究表明脊髓损伤可能会造成严重损伤,包括局部组织缺血、缺氧、炎症细胞浸润以及其他一系列的病理改变,这些改变可能会导致轴突的变形、髓鞘的损伤以及神经元的凋亡。当脊髓受到损伤时,星形胶质细胞、小胶质细胞以及其他细胞会被激活,导致大量胶质细胞的产生,这些胶质细胞会在受损部位的外围形成一个明显的瘢痕,在瘢痕的中心则会形成一个纤维化的瘢痕。脊髓损伤会导致少突胶质细胞的增殖和分化,但是它们无法形成髓鞘;会导致髓鞘内的多种抑制性蛋白质(包括髓磷脂相关糖蛋白、Nogo蛋白及少突胶质细胞髓磷脂糖蛋白)的大量生成[32],这些细胞外的信号因子会与受体NgR1结合形成复合受体[33],并最终激活下游的Rho/ROCK信号通路[34-35];当ROCK被激活时,经过磷酸化肌球蛋白轻链的多个下游靶点,能够有效促进肌肉细胞的分裂,从而阻断轴突的发育[36]。由上可看出,脊髓损伤后受损轴突髓鞘的补充来源被切断,抑制因子大量产生,使轴突生长受到抑制,因此,要促进髓鞘修复,降低或阻止髓鞘生长抑制因子的表达尤为关键。
(4)神经营养因子:在中枢神经系统中的分布十分广泛,其中神经生长因子尤其突出,它们在脊髓组织中的生物功能由酪氨酸激酶A受体和p75神经营养素受体共同调节[37],从而促进神经细胞的生长和发育,提高神经系统的功能和效率。神经生长因子和其受体酪氨酸激酶A在促进交感神经元和感觉神经元的存活方面发挥着重要作用,同时也能够传递出神经支配的反向信号[38-39]。众多研究结果表明,神经生长因子及其受体Trka可以促进神经功能的恢复[40-42],在修复受损的脊髓方面具有广阔的前景。
(5)凋亡因子:细胞凋亡也被称为程序性细胞死亡,是脊髓损伤后发生的一种严重功能障碍[43],可导致神经元组织无法正常再生[44],从而影响患者的恢复过程。近年来的研究发现,Caspases在细胞内的胞质溶胶中具有独特的功能,它能够有效切断天冬氨酸残基,从而引起细胞凋亡[45]。研究表明至少有11种Caspase参与凋亡信号的调控,包括Caspase-3、Caspase-6、Caspase-8和Caspase-9等,其中Caspase-3是最重要的,它可以启动和执行细胞早期凋亡[46-49]。
线粒体膜由含有电压依赖性阴离子通道的外膜和调节电子传递链的内膜组成,其在维持线粒体氧化和ATP产生的关键基质金属蛋白酶等方面具有重要作用[50-51]。线粒体介导的凋亡会导致神经细胞的持续损失[52],因此,保护线粒体功能可以有效阻止或减轻这一过程[53]。
Bcl-2基因家族是重要的抗凋亡基因,它可以抑制细胞凋亡,在脊髓损伤后其可以抑制神经元细胞凋亡,从而起到重要的保护作用。研究表明Bcl-2具有多重保护作用,可以有效抑制钙超载、兴奋性氨基酸和缺血缺氧等因素对神经元凋亡的影响,保护神经系统免受损害。Bcl-2具有可诱导性,主要表现在通过诱导其在神经组织中的表达来达到保护神经功能的目的,进而增加神经抗损伤的能力[54-56]。最近的研究发现,脊髓损伤可以显著提高Bcl-2基因的表达,这有助于加速其活性,同时也可以有效阻止细胞凋亡[57]。
(6)炎症因子:当脊髓受损时损伤区域会出现炎症反应,包括缺血缺氧和脱髓鞘等,在这种情况下,大量的炎症因子会分泌,导致小胶质细胞和巨噬细胞活化,形成局部炎症微环境[58];当处于炎症状态时,胞浆内会形成多种蛋白复合物受体,这些受体被称为nod小体样受体家族(NOD-like receptors,NLRP),其中NLRP3对于炎症的诊断和治疗具有至关重要的作用[59]。当白细胞介素1β和白细胞介素18被过度释放时,NLRP3的活性就会显著提高,从而加剧脊髓损伤[60],甚至可能引发更加严重的后果。
2.3.2 神经递质
(1) 5-羟色胺:5-羟色胺能受体属于G蛋白偶联受体,是中枢神经系统重要递质之一,可激活细胞内第二信使级联反应传递兴奋或者抑制信号。5-羟色胺能神经纤维广泛存在于正常大鼠脊髓中,5-羟色胺2A受体分布在腰骶部脊髓运动神经元和膀胱组织中,5-羟色胺可能通过脊上、脊髓及腰骶核水平参与调控下尿路排尿的神经控制[61]。研究发现,在膀胱组织中运用5-羟色胺能受体亚型的激动剂、抑制剂会对尿道外括约肌的舒缩活动产生影响,从而影响排尿量、残余尿量及排尿效率等相关排尿功能[62-63];研究发现脊髓损伤后,损伤节段5-羟色胺能神经纤维以下的纤维数量明显减少[64],因此,调节5-羟色胺能神经纤维和5-羟色胺能受体可对膀胱的神经支配和膀胱肌肉运动变化产生影响。
(2)多巴胺:中枢神经系统中的多巴胺信号可调节排尿功能,在膀胱功能正常的情况下,膀胱功能障碍时脑区内多巴胺能神经元兴奋,脑桥排尿中枢的多巴胺受体在接收兴奋性刺激后产生大量多巴胺信号[65];研究表明,多巴胺可以在脊髓水平协助和调节排尿功能,脊髓损伤后多巴胺能神经元参与了脊髓内神经的可塑性变化,对储尿和排尿功能产生调节,其中激活多巴胺D2样受体促进排尿反射[66]。因此,多巴胺能神经元和多巴胺受体的变化可能会对受损脊髓区域以下膀胱储尿和排尿功能的神经调节产生影响,有待进一步深入研究。
(3)乙酰胆碱:胆碱能神经是膀胱逼尿肌功能的关键支柱,它通过副交感神经节后纤维释放乙酰胆碱,激活膀胱逼尿肌内的M受体,从而使膀胱收缩和放松,实现尿液的排出和排尿。M受体的种类繁多,但以M2和M3受体最为普遍,它们是最常见的两种受体。乙酰胆碱与M2受体有着紧密的关联,乙酰胆碱可以促进膀胱逼尿肌的收缩,而M2受体可以抑制乙酰环化酶的活性,进而抑制β受体的活性[67],最终实现膀胱逼尿肌的放松。研究表明,膀胱逼尿肌上乙酰胆碱酯酶阳性神经纤维减少与损伤节段有关[68],其可以通过改善膀胱组织中M2型受体的表达来改善神经源性膀胱模型大鼠的膀胱功能[69]。乙酰胆碱作为中枢递质参与并影响神经信号的传递,从而对排尿中枢和膀胱的神经支配产生影响,同时,乙酰胆碱可以通过神经纤维投射对膀胱功能产生调节,探究脊髓损伤后乙酰胆碱的变化有利于研究重建膀胱功能。
(4)谷氨酸:是一种重要的酸性氨基酸,它不仅可以促进突触兴奋传递,而且还可以促进蛋白质、多肽和脂肪酸的合成,在哺乳动物脑内的含量更是极其丰富。在膀胱排尿反射中,谷氨酸可传导兴奋性信号,与腰骶脊髓节段副交感神经区神经突触后膜上的谷氨酸受体结合后激活膀胱逼尿肌,刺激排尿反射通路,进而影响膀胱排尿功能[70-71]。研究表明谷氨酸能突触存在于胸段脊髓的交感神经区,当脊髓受损时这些氨基酸会堆积且大量释放,从而使得膀胱平滑肌的收缩加剧,故抑制脊髓损伤后谷氨酸能突触的释放,可以调节膀胱功能。现已有谷氨酸受体拮抗剂运用于膀胱过度活动综合征的治疗[72],因此,谷氨酸受体拮抗剂是重建膀胱排尿反射的潜在作用点之一。
2.3.3 激素
(1)抗利尿激素:是肾脏水排泄最重要的决定因素,在维持水平衡中起着核心作用。抗利尿激素被释放到脑脊液中,并被运输到神经垂体和垂体中隆起[73]。神经垂体生物合成和分泌抗利尿激素主要受血浆渗透性变化和血压及血容量变化的调节[74]。有学者发现,神经源性膀胱患者的尿量、尿渗透压和抗利尿激素分泌24 h节律变化紊乱[75],且体位也会对抗利尿激素的分泌产生影响,在坐位状态下,由于回心血量减少,体液流向下肢组织间隙,血压偏低,而低血压会刺激抗利尿激素的释放,从而影响尿液的生成[76]。现阶段对神经源性膀胱与抗利尿激素的关系之间暂无详尽的研究,有待进一步探究。
(2)神经肽:是生物体内的一类生物活性多肽,可整合神经系统和身体其他系统功能,在膀胱组织中有分布,可通过产生兴奋和抑制的刺激调节膀胱功能,参与了脊髓损伤后排尿反射异常[77]。脊髓损伤导致逼尿肌反射亢进,从而使血管活性肠肽、降钙素基因相关肽、神经肽Y和P物质的含量大幅度降低[78],而内皮素1的含量大幅度增加。实验证实,当大鼠接受内皮素1受体A拮抗剂治疗时,肌电图检查结果表明,膀胱的非排空性收缩的振幅和频率都有了显著下降[79]。
2.3.4 神经通路
(1)排尿中枢:脑桥排尿中枢在排尿过程中扮演着至关重要的角色,它的M区和L区可以从中脑导水管灰质中获取神经信息,这些信息可以激活或者阻断膀胱的功能,见图3。脊髓损伤可能导致大脑的反向损伤,这种损伤可能会导致感知和运动皮质的灰质体积显著下降,损伤的脊髓会导致髓质、脑桥、中脑和内囊的退化[80-83],这些退化会影响膀胱的正常运作,这种改变主要是由于膀胱刺激的传递和脊髓内突触的重建所导致的[84]。
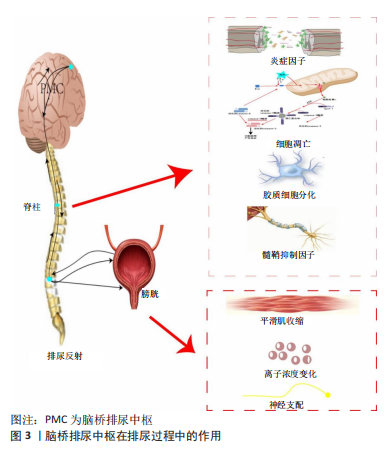
脑桥排尿中枢发出下行的神经纤维到脊髓中,以谷氨酸为神经递质激活腰骶部脊髓中的自主神经节前神经元,同时也有以γ-氨基丁酸和甘氨酸为神经递质的纤维,抑制腰骶部脊髓中控制尿道外括约肌的运动神经元[85]。脑桥排尿中枢可能通过这些信息传输给腰骶膀胱运动神经元,从而产生兴奋信号。当脑桥排尿中枢被激活时会导致膀胱内压的升高[86-87],影响腰骶背根神经节的抑制性神经元[88],这些神经元通过γ-氨基丁酸和甘氨酸神经递质来抑制Onuf核的运动神经元,从而达到减轻膀胱内压的目的。当尿道外括约肌松弛时,大脑的下丘脑、额皮质以及其他更高层次的神经系统会开始调控膀胱,释放尿液。
脑桥排尿中枢神经元可直接投射到骶副交感核的节前神经元,也可直接投射到骶灰质后联合的中间神经元。骶副交感节前神经元轴突沿盆神经走行,激活位于盆丛的副交感节后神经元,使之释放乙酰胆碱,通过刺激M2和M3受体引起膀胱收缩[89]。对于大鼠骶上脊髓横断及干预治疗后上述神经递质的变化尚无明确研究,因此这是一个可以观察重建排尿反射中枢机制的切入点。
(2)传入神经:在下尿路中,储存和排出尿液的过程受到来自胸部和腰部脊髓的双侧神经控制。神经纤维在人体的3个主要部分中分布得非常广泛:盆神经、腹下神经和交感链及骶部躯体神经[90],其中阴部神经是最重要的。
C神经纤维与 A-Delta神经纤维构成了一个复杂的神经网络,它们可以将外界的机械刺激转化为神经冲动,从而让人们可以感知到膀胱的疼痛[91]。这种神经网络的功能是将外界的刺激转化为神经冲动,从而让人们可以及时发现并采取相应的措施,以缓解膀胱的不适症状。研究表明,C传入神经纤维对于排尿过程起着至关重要的作用,它不仅能够激活或唤醒排尿反应,还能够有效帮助膀胱内的刺激物和细菌被有效清除,从而有效防止膀胱受到损伤[92]。全球公认,C纤维介导的感觉神经通路在膀胱受到外界化学刺激如疼痛、张力等就会接收到这些信号,并开始释放出自发性的放电活性,而这种活性随着膀胱压力的升高而不断提升,从而促进预防机制性排尿反射,降低膀胱的容积、促进刺激物和细菌的排出[93-94]。然而,如果C神经纤维的传入性活动超出了正常范围就可能出现尿意和排尿异常的症状[95],特别是在骶上脊髓横断的情况下,这种传入性C神经纤维的传入性更是不可忽视。排尿困难可能与多种因素有关,其中膀胱排尿反射机制可能起着重要作用[96]。
膀胱排尿反射建立在神经反射上。对于脊髓横断损伤的患者,其反射通路发生了重大改变,这主要是因为激活无髓鞘的C类神经纤维,它们穿越后根进入S2-4后角,随后激活骶副交感节前神经,并进一步穿越骶前神经、盆神经,最终传导至膀胱,以完成对尿液的储存与排出。这一反射通路属于脊髓横断损伤后脊髓排尿反射的重建通路之一[97]。
2.3.5 膀胱 在膀胱排尿反射中,膀胱作为感受器和效应器在脊髓损伤后处于异常的神经支配中,膀胱平滑肌组织长时间处于紧张状态中肌肉组织产生纤维化,对膀胱的收缩功能产生恶性循环,阻碍正常的膀胱功能。重建排尿反射中延缓膀胱组织纤维化具有重要意义。
结缔组织生长因子可以抑制纤维化的发生,并且可以通过增加细胞外胶原蛋白的含量来改善膀胱的结构,从而减缓纤维化的发展。在正常生理状态下,结缔组织生长因子的表达水平较低,但在病理状态下,它的表达量会显著增加。转化生长因子β是一类极其复杂的生物学细胞因子,其功能不仅可以影响人类的生理功能[98],还可以影响人类的免疫系统,从而影响人类的健康状态。其中,转化生长因子β1已被证实是体内多种器官炎症和纤维化的重要参与因子之一,目前大量的研究证实,结缔组织生长因子在转化生长因子β1的诱导下可启动和维持纤维化[99]。转化生长因子β1/Smad信号通路是纤维化的经典信号通路[100],有研究表明,脊神经横断神经源性膀胱大鼠的膀胱纤维化病变与转化生长因子β1/Smad信号通路的激活相关[101]。
2.4 重建膀胱排尿反射的主要手段 在重建膀胱排尿反射中,通过干预治疗促进脊髓修复、神经反射重构、物质代谢和膀胱组织结构调整是治疗的关键,中医与西医各有其法。
(1)电针:2017年《JAMA》一项多中心大样本随机对照研究,从临床角度证明了电针具有改善膀胱功能的重要作用[102]。对于逼尿肌-膀胱颈协同失调的治疗而言,一线西药如α受体阻滞药等存在一定耐受性及不良反应,膀胱出口扩容或造瘘等手术有创且成本较高,间歇导尿或留置导尿等保守措施疗效不稳定,电针被认为是一种安全高效、低廉便捷的极富潜力的治疗方式。研究发现,肌肉神经电刺激可以通过躯体感受器传递到中枢神经系统,激活脊髓运动神经元,有效地改善神经肌肉连接,缓解肌肉萎缩和纤维化的症状[103-109];另一方面,针灸可以诱导机体中再生干细胞的生长,抑制星形胶质细胞的形成,有效刺激神经再生,同时还可以提高细胞因子和营养因子的表达,有助于神经细胞的再生。通过电针刺激不仅能够激活轴突的重建[109],还能够累积多种内源性神经营养因子,有效阻断早期的细胞凋亡,从而有助于神经系统的正常功能以及神经元的再生与修复[110-112]。
(2)注射肉毒素:A型肉毒素被认为能够抑制神经肌肉接头的突触,从而减少-肌肉信号的传导,有助于减轻尿路内压的升高[112],因此被广泛应用于治疗逼尿肌过度活动所导致的尿失禁。然而有研究表明,长期服用A型肉毒素会导致尿潴留和尿失禁[113]。
(3)注射多巴胺:脊髓作为一个富含酪氨酸羟化酶及其相关神经元的重要组织,一旦受损,酪氨酸羟化酶的合成量将明显增加,从而影响脊髓损伤后膀胱的排尿反射,而采用特异性激活多巴胺D2样受体的方法有助于改善脊髓损伤模型大鼠的自发排尿功能。多巴胺D2受体激动剂可作为药物治疗脊髓损伤后排尿功能障碍[114]。
(4)神经移植:当前,采取脊髓正常反射通路重建神经源性膀胱人工反射弧来改善膀胱功能已成为一种可行且有效的治疗手段,其中“腱-脊髓-膀胱”和“腹壁-脊髓中枢-膀胱”两种技术均已被广泛应用[115-116],但其优缺点仍然存在争议,因此还需要进一步的临床试验来验证其疗效。
(5)神经干细胞工程:神经干细胞是神经系统中最重要的组成部分,它们具有强大的分化能力,可以诱导神经元、星形胶质细胞和少突胶质细胞的形成,为神经系统的修复提供了重要的支持,具有巨大的应用潜力。通过神经干细胞移植和内源性神经干细胞培养,能够将星形胶质细胞转移到受损神经系统,从而实现特定的治疗效果。研究结果显示在受损的细胞群落中,有一些细胞会被诱导转变成星形胶质细胞,而另一些则会被转变成神经元[117-118],这种转变的原因是:受损细胞群落中的髓鞘蛋白可以阻止细胞转变成星形胶质细胞[119],从而有效促进神经干细胞的定向功能神经元形成。
(6)外泌体:随着外泌体介导细胞间通讯功能的发现,外泌体逐渐成为疾病发生发展生物标志物检测的热点。miRNA是平滑肌功能表型的重要调节因子,在多种平滑肌相关疾病的发病机制中发挥重要作用,如 miRNA对血管平滑肌的发育和功能调节具有重要作用[120]、miRNA对胃肠道平滑肌的分化和重塑也有显著影响等,故将组织外泌体与 miR-Seq 技术相结合有望深入揭示疾病及其治疗的微观机制。关于外泌体在重建排尿反射的运用中主要集中在促进外泌体的释放,从而调整膀胱平滑肌功能。

| [1] TATE DG, WHEELER T, LANE GI, et al. Recommendations for evaluation of neurogenic bladder and bowel dysfunction after spinal cord injury and/or disease. J Spinal Cord Med. 2020;43(2):141-164. [2] QUADRI SA, FAROOQUI M, IKRAM A, et al. Recent update on basic mechanisms of spinal cord injury. Neurosurg Rev. 2020;43(2):425-441. [3] 胥少汀,郭世绂.脊髓损伤的基础与临床[M].北京:人民卫生出版社,2012. [4] DE GROAT WC, YOSHIMURA N. Mechanisms underlying the recovery of lower urinary tract function following spinal cord injury. Prog Brain Res. 2006;152:59-84. [5] MANACK A, MOTSKO SP, HAAG-MOLKENTELLER C, et al.Epidemiology and healthcare utilization of neurogenic bladder patients in a US claims database. Neurourol Urodyn. 2011;30(3):395-401. [6] DE GROAT WC. Integrative control of the lower urinary tract: preclinical perspective. Br J Pharmacol. 2006;147 Suppl 2:S25-40. [7] DE GROAT WC, WICKENS C. Organization of the neural switching circuitry underlying reflex micturition. Acta Physiol(Oxford, England). 2013;207(1):66-84. [8] 严振国,毛根金,严振国,等.正常人体解剖学[M].北京:中国中医药出版社,2000. [9] PANICKER JN, FOWLER CJ, KESSLER TM. Lower urinary tract dysfunction in the neurological patient: clinical assessment and management. Lancet Neurol. 2015;14(7):720-732. [10] SAKAKIBARA R, SHINOTOH H,UCHIYAMA T, et al. SPECT imaging of the dopamine transporter with [(123)I]-beta-CIT reveals marked decline of nigrostriatal dopaminergic function in Parkinson’s disease with urinary dysfunction. J Neurol Sci. 2001;187(1-2):55-59. [11] ZINCK ND. DOWNIE JW. Plasticity in the injured spinal cord: can we use it toadvantage to reestablish effective bladder voiding and continence? Prog Brain Res. 2006;152:147-162. [12] 王笑,刘卿,谷成旭,等.汉黄芩苷对大鼠脊髓损伤的修复效果[J].解剖学报,2022,53(2):173-182. [13] ALIZADEH A, DYCK SM, KARIMI-ABDOLREZAEE S. Traumatic Spinal Cord Injury:An Overview of Pathophysiology,Models and Acute Injury Mechanisms. Front Neurol. 2019;10:282. [14] AHUJA CS, NORI S, TETREAULT L, et al. Traumatic Spinal Cord Injury-Repair and Regeneration. Neurosurgery. 2017;80:S9-S22. [15] BROCKIE S, HONG J, FEHLINGS MG. The Role of Microglia in Modulating Neuroinflammation after Spinal Cord Injury. Int J Mol Sci. 2021;22:9706. [16] DE GROAT WC, YOSHIMURA N. Plasticity in reflex pathways to the lower urinary tract following spinal cord injury. Exp Neurol. 2012;235(1):123-132. [17] HALL A. Rho GTPases and the actin cytoskeleton. Science. 1998;279(5350): 509-514. [18] MUELLER BK, MACK H, TEUSCH N. Rho kinase, a promising drug target for neurological disorders. NatRev Drug Discov. 2005;4:387-398. [19] CONRAD S, SCHLUESENER HJ, TRAUTMANN K, et al. Prolonged lesional expression of RhoA and RhoB following spinal cord injury. J Comp Neurol. 2005;487(2):166-175. [20] LUO L. Rho GTPases in neuronal morphogenesis. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2000;1: 173-180. [21] CHEN XL, LIU L, WEN QQ, et al. Effect of acupuncture at different acupoints on RhoA/ ROCK signalinging pathway in gastric antral smooth muscle tissue of rats with diabetic gastroparesis. Shijie Huaren Xiaohua Zazhi. 2016;24(23):3508-3516. [22] WU XF, CHEN XL, ZHENG XN, et al. Effect of different stimulating strength of electroacupuncture on gastrointestinal motility and RhoA/ROCK signaling in gastric antral smooth muscle in diabetic gastroparesis rats. Zhen Ci Yan Jiu. 2018;43(3):169-174. [23] 李晓宁,吴磊,覃业校,等.夹脊电针对急性脊髓损伤大鼠运动功能及脊髓组织NogoA、RhoA、ROCK Ⅱ蛋白表达的影响[J].针灸临床杂志,2018, 34(1):63-67+81. [24] SUN X, ZHANG C, XU J, et al. Neurotrophin-3-loaded multichannel nanofibrous scaffolds promoted anti-inflammation,neuronal differentiation,and functional recovery after spinal cord injury. ACS Biomater Sci Eng. 2020;6(2):1228-1238. [25] SOBANI ZA, QUADRI SA, ENAM SA. Stem cells for spinal cord regeneration: current status.Surg Neurol Int. 2010;1:93. [26] KARIMI-ABDOLREZAEE S, BILLAKANTI R. Reactive astrogliosis after spinal cord injury-beneficial and detrimental effects. Mol Neurobiol. 2012;46(2):251-264. [27] LEAL-FILHO MB. Spinal cord injury:from inflammation to glial scar. Surg Neurol Int. 2011;2:112. [28] VERHOEVEN Y, TILBORGHS S, JACOBS J, et al. The potential and controversy of targeting STAT family members in cancer. Semin Cancer Biol. 2020;60:41-56. [29] HERRMANN JE, IMURA T, SONG B, et al. STAT3 is a critical regulator of astrogliosis and scar formation after spinal cord injury. J Neurosci. 2008;28(28): 7231-7243. [30] ZHOU ZL, TIAN XB, MO BL, et al. Adipose mesenchymal stem cell transplantation alleviates spinal cord injury-induced neuroinflammation partly by suppressing the Jagged1/Notch pathway. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2020; 11(1):212. [31] 许绍芬.神经生物学[M].上海:上海医科大学出版社,1990. [32] Cregg JM, DePaul MA, Filous AR, et al. Functional regeneration beyond the glial scar. Exp Neurol. 2014;253:197-207. [33] FAWCETT JW, SCHWAB ME, MONTANI L, et al. Defeating inhibition of regeneration by scar and myelin components. Handb Clin Neurol. 2012;109: 503-522. [34] MIN ZY, CHENG LH, MIN YJ. Effect of electroacupuncture on Nogo/NgR signaling pathway related factors in SCI rats. J Beijing Univ Tradit Chin Med. 2016;39(11):926-932. [35] 闵志云,程立红,闵友江.Nogo/NgR通路在脊髓神经再生中的研究进展[J].江西中医药大学学报,2016,28(3):103-105+109. [36] MIN YJ, DING LL, CHENG LH, et al. Effect of electroacupuncture on the mRNA and proteinexpression of Rho-A and Rho-associated kinase II in spinal cord injury rats. Neural Regen Res. 2017;12(2):276-282. [37] OCHODNICKÝ P, CRUZ CD, YOSHIMURA N, et al. Nerve growth factor in bladder dysfunction: contributing factor, biomarker, and therapeutic target. Neurourol Urodyn. 2011;30(7):1227-1241. [38] CACIALLI P. Neurotrophins Time Point Intervention after Traumatic Brain Injury: From Zebrafish to Human.Int J Mol Sci. 2021;22(4):1585. [39] ISAEV NK, STELMASHOOK EV, GENRIKHS EE. Role of Nerve Growth Factor in Plasticity of Forebrain Cholinergic Neurons. Biochemistry (Mosc). 2017;82(3): 291-300. [40] 石勇,霞晓燕.NGF过表达质粒修饰BMSCs移植促进大鼠急性脊髓损伤修复[J].实用骨科杂志,2020,26(8):707-711,715. [41] 邓明,谢萍,马永刚,等.慢病毒介导NGF过表达转染促进骨髓间充质干细胞向神经细胞转化的研究[J].中国临床研究,2019,32(2):145-149. [42] 范筱,汪今朝,刘宇,等.活血通督汤促进脊髓损伤大鼠肢体运动功能恢复的神经营养机制[J].中华中医药杂志,2017,32(10):4611-4615. [43] REN XD,WAN CX, NIU YL. Overexpression of lncRNA TCTN2 protects neurons from apoptosis by enhancing cell autophagy in spinal cord injury. FEBS Open Bio. 2019;9(7):1223-1231. [44] KAWABATA H, SETOGUCHI T, YONE K, et al. High mobility group box 1 is upregulated after spinal cord injury and is associated with neuronal cell apoptosis. Spine(Phila Pa1976). 2010;35(11):1109-1115. [45] ZHAO D, ZHANG M, YUAN H, et al. Ginsenoside Rb1protects against spinal cord ischemia-reperfusion injury in rats by downregulating the Bax/Bcl-2 ratio and caspase-3 and p-Ask-1 levels. Exp Mol Pathol. 2018;105(3):229-235. [46] YUAN B, PAN S, ZHANG WW. Effects of gangliosides on expressions of caspase-3 and NGF in rats with acute spinal cord injury. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2017;21(24):5843-5849. [47] GASHMARDI N, HOSSEINI SE, MEHRABANI D, et al. Impacts of Bone Marrow Stem Cells on Caspase-3 Levels after Spinal Cord Injury in Mice. Iran J Med Sci. 2017;42(6):593-598. [48] LIN HS, JI ZS, ZHENG LH, et al. Effect of methylprednisolone on the activities of caspase-3,-6,-8 and-9 in rabbits with acute spinal cord injury. Exp Ther Med. 2012;4(1):49-54. [49] CITRON BA, ARNOLD PM, HAYNES NG, et al. Neuroprotective effects of caspase-3 inhibition on functional recovery and tissue sparing after acute spinal cord injury. Spine(Phila Pa 1976). 2008;33(21):2269-2277. [50] SONG IS, JEONG YJ, JEONG SH, et al. Modulation of mitochondrial ERβ expression inhibits triple-negative breast cancer tumor progression by activating mitochondrial function. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2019;52(3):468-485. [51] GOLLIHUE JL, PATEL SP, RABCHEVSKY AG. Mitochondrial transplantation strategies as potential therapeutics for central nervous system trauma. Neural Regen Res. 2018;13(2):194-197. [52] YING Y, ZHANG Y, TU Y, et al. Hypoxia response element-directed expression of aFGF in neural stem cells promotes the recovery of spinal cord injury and attenuates SCI-induced apoptosis. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021;9:693694. [53] 缪鑫,林俊卿,郑宪友.线粒体功能障碍在脊髓损伤中的作用及相关治疗研究进展[J].中国修复重建外科杂志,2022,36(7):902-907. [54] GRAHAM SH, CHEN J, CLARK RS. Bcl-2 family gene products in cerebral ischemia and traumatic brain injury. J Neurotrauma. 2000;17(10):831-841. [55] SCHULMAN JJ, WRIGHT FA, KAUFMANN T, et al. The Bcl-2 family member Bok binds to the coupling domain of inositol 1,4,5-trisphate receptors and protects them from proteolytic cleavage. Biol Chem. 2013;288(35): 25340-25349. [56] CLARK RS, CHEN J, WATKINS SC, et al. Apoptosis suppressor gene Bcl-2 expression after traumatic brain injury in rats. J Neurosci. 1997;17(23):9172-9182. [57] 于荣华,侯春林,林浩东,等.大鼠脊髓圆锥损伤后大脑排尿功能区变化的实验研究[J].中国修复重建外科杂志,2018,32(1):75-79. [58] NA L, WANG S, LIU TT, et al. Ultrashort Wave Combined with Human Umbilical Cord Mesenchymal Stem Cell (HUC-MSC) Transplantation Inhibits NLRP3 Inflammasome and Improves Spinal Cord Injury via MK2/TTP Signalling Pathway. Biomed Res Int. 2020;2020:3021750. [59] 刘雯,郭文洁,徐强,等.NLRP3炎症小体调控机制研究进展[J].药学学报, 2016,51(10):1505-1512. [60] 周雨昕,马勇,吴承杰,等.基于NLRP3炎症小体途径探究脊髓康促进脊髓损伤大鼠修复的机制[J].中华中医药杂志,2022,37(9):5385-5389. [61] RAMAGE AG. The role of central 5-hydroxytryptamine (5-HT, serotonin) receptors in the control of micturition. Br J Pharmacol. 2006;147 Suppl 2 (Suppl 2):S120-131. [62] GU B, WU G, SI J, et al. Improving voiding efficiency in the diabetic rat by a 5-HT1A serotonin receptor agonist. Neurourol Urodyn. 2012;31(1):168-173. [63] CHEN J, GU B, WU G, et al. Andersson KE. The effect of the 5-HT2A/2C receptor agonist DOI on micturition in rats with chronic spinal cord injury. J Urol. 2013; 189(5):1982-1988. [64] 倪剑书.神经生长因子及5-羟色胺7受体在脊髓损伤后下尿路功能障碍中的作用研究[D].上海:上海交通大学,2019. [65] 乔原.脊髓内源性多巴胺能神经机制对脊髓损伤雄性大鼠排尿反射的调控[D].济南:山东大学,2019. [66] JIANG W, HE F, DING G, et al. Dopamine inhibits pyroptosis and attenuates secondary damage after spinal cord injury in female mice. Neurosci Lett. 2023; 792:136935. [67] 闵勇正.Cajal间质细胞在膀胱胆碱能神经传递中作用的研究[D].重庆:第三军医大学,2012. [68] 史晓东,胥少汀,刘智,等.兔脊髓不同平面损伤后尿流动力与膀胱AchE、α-SMA表达的研究[J].中国脊柱脊髓杂志,2002,12(5):39-42+83. [69] 闫晓,李在洺,冯晓东,等.隔姜灸对大鼠脊髓损伤后神经源性膀胱M2、M3乙酰胆碱mRNA及P2X3受体表达的影响[J].护理学杂志,2020,35(19): 1-3+17. [70] DE GROAT WC, ARAKI I, VIZZARD MA, et al. Developmental and injury induced plasticity in the micturition reflex pathway. Behav Brain Res. 1998;92(2):127-140. [71] GUARNERI L, POGGESI E, ANGELICO P, et al. Effect of selective antagonists of group I metabotropic glutamate receptors on the micturition reflex in rats. BJU Int. 2008;102(7):890-898. [72] SZOLLAR SM, DUNN KL, BRANDT S, et al. Nocturnal polyuria and antidiuretic hormone levels in spinal cord injury. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 1997;78:455-458. [73] SZOLLAR S, NORTH J, CHUNG J. Antidiuretic hor-mone levels and polyuria in spinal cord injury:A preliminary report. Paraplegia. 1995;33:94-97. [74] 王德成,于振山,张亚奎,等.脊髓损伤患者夜间尿量增多与抗利尿激素水平的关系[J].中华创伤杂志,2004,20(7):18-21. [75] SCHRIER RW, BERL T, ANDERSON RJ. Osmotic and nonosmotic control of vasopressin release. Am J Physiol. 1979;236:F321-F332. [76] DEGROAT WC, YOSHIMURA N. Afferent nerve regulation of bladderfunction in health and disease.Handb Exp Pharmacol. 2009;(194):91-138. [77] 李芮志,周谋望,曾凡硕大鼠脊髓损伤痉挛性膀胱中神经肽含量的观察[J].中华医学杂志,2012,92(15):1058-1061. [78] OGAWA T, SASATOMI K, HIRAGATA S, et al. Therapeutic effects of endo-thelin-a receptor antagonist on bladder overactivity in rats with chro-nic spinal cord injury.Urology. 2008;71(2):341-345. [79] KOSKINEN EA, HAKULINEN U, BRANDER AE, et al. Clinical correlates of cerebral diffusion tensor imaging findings in chronic traumatic spinal cord injury. Spinal Cord. 2014;52(3):202-208. [80] HENDERSON LA, GUSTIN SM, MACEY PM, et al. Functional reorganization of the brain in humans following spinal cord injury: evidence for underlying changes in cortical anatomy. J Neurosci. 2011;31(7):2630-2637. [81] GULERIA S, GUPTA RK, SAKSENA S, et al. Retrograde Wallerian degeneration of cranial corticospinal tracts in cervical spinal cord injury patients using diffusion tensor imaging. J Neurosci Res. 2008;86(10):2271-2280. [82] FREUND P, WEISKOPF N, WARD NS, et al. Disability, atrophy and cortical reorganization following spinal cord injury. Brain. 2011;134(Pt 6):1610-1622. [82] WRIGLEY PJ, GUSTIN SM, MACEY PM, et al. Anatomical changes in human motor cortex and motor pathways following complete thoracic spinal cord injury. Cereb Cortex. 2009;19(1):224-232. [83] 吴新红,肖传国.大鼠脑桥排尿中枢和脊髓交感中枢之间的形态学研究[J].神经解剖学杂志,2005,21(5):65-69. [84] BLOK BF, HOLSTEGE G. Ultrastructural evidence for a direct pathway from the pontine micturition center to the parasympathetic pregan-glionic motoneurons of the bladder of the cat. Neurosci Lett. 1997;222:195-198. [85] MATSUMOTO G, HISAMITSU T, DE GROAT WC. Role of glutamate and NMDA receptors in the descending limb of the spinobulbospinal micturition reflex pathway of the rat. Neurosci Lett. 1995;183:58-61. [86] BLOK BF, DE WEERD H, HOLSTEGE G. The pontine micturition center projects to sacral cord GABA immunoreactive neurons in the cat. Neurosci Lett. 1997; 233:109-112. [87] BLOK BF, VAN MAARSEVEEN JT, HOLSTEGE G. Electrical stimulation of the sacral dorsal gray commissure evokes relaxation of the external urethral sphincter in the cat. Neurosci Lett. 1998;249:68-70. [88] 廖利民,鞠彦合.下尿路功能的神经控制[J].中国康复理论与实践,2005, 11(11):16-17. [89] 冯鉴强,陈培熹.大脑皮层对C类神经纤维传入的电反应及其调制机理[J].中山医科大学学报,1991,12(2):81-85. [90] MAZIÈRES L, JIANG C, LINDSTRÖM S. The C fibre reflex of the cat urinary bladder. J Physiol. 1998;513(Pt 2):531-541. [91] SHARMA SK, VIJ AS, SHARMA M. Mechanisms and clinical uses of capsaicin. Eur J Pharmacol. 2013;720(1-3):55-62. [92] 王锋,龙志新.膀胱过度活动症的治疗研究进展[J].山东医药,2010, 50(22):115-116. [93] IMAMURA T, ISHIZUKA O, AIZAWA N, et al. Gosha-jinki-gan reduces transmitter proteins and sensory receptors associated with C fiber activation induced by acetic acid in rat urinary bladder. Neurourol Urodyn. 2008;27(8):832-837. [94] SHAKER H, WANG Y, LOUNG D, et al. Role of C-afferent fibres in the mechanism of action of sacral nerve root neuromodulation in chronic spinal cord injury. BJU international. 2000;85(7):905-910. [95] 陈忠,崔喆,双卫兵.神经源性膀胱[M].北京:人民卫生出版社,2009. [96] SANTIBANEZ JF, QUINTANILLA M, BERNABEU C. TGF-beta/TGF-beta receptor system and its Role in physiological and pathological conditions. Clin Sci (Lond). 2011;121(6):233-251. [97] 罗太阳,刘小慧.结缔组织生长因子及其在心肌纤维化中的作用[J].心血管病学进展,2009,30(z1):8-10. [98] HU HH, CHEND Q, WANG YN, et al. New insights into TGF-beta/Smad signaling in tissue fibrosis. Chem Biol Interact. 2018;292:76-83. [99] 邢栋.SB431542阻断TGF-β1/Smad信号通路延缓大鼠神经源性膀胱纤维化[D].郑州:郑州大学,2020. [100] LIU Z, LIU Y, XU H, et al. Effect of Electroacupuncture on Urinary Leakage Among Women With Stress Urinary Incontinence: A Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA. 2017;317(24):2493-2501. [101] JIANG YQ, ZAAIMI B, MARTIN JH. Competition with Primary Sensory Afferents Drives Remodeling of Corticospinal Axons in Mature Spinal Motor Circuits. J Neurosci. 2016;36(1):193-203. [102] WILLAND MP, HOLMES M, BAIN JR, et al. Sensory nerve crossanastomosis and electrical muscle stimulation synergistically enhance functional recovery of chronically denervated muscle. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2014;134(5):736e-745e. [103] ZHANG C, RONG W, ZHANG GH, et al. Early electrical field stimulation prevents the loss of spinal cord anterior horn motoneurons and muscle atrophy following spinal cord injury. Neural Regen Res. 2018;13(5):869-876. [104] 吕威,李冰,景泉凯,等.电针“大椎”“命门”对脊髓损伤大鼠神经元细胞凋亡及JNK信号通路相关蛋白表达的影响[J].针刺研究,2017,42(1):14-19. [105] 李晓宁,吴磊,迟蕾,等.不同治疗周期夹脊电针对急性脊髓损伤大鼠运动功能及细胞凋亡的影响[J].针刺研究,2016,41(6):492-496. [106] GENG X, SUN T, LI JH, et al. Electroacupuncture in the repair of spinal cord injury:inhibiting the Notch signaling pathway and promoting neural stem cell proliferation. Neural Regen Res. 2015;10(3):394-403. [107] 张志英,余安胜,严振国.电针对脊髓损伤早期caspase-3mRNA及蛋白表达的影响[J].解剖学杂志,2002,25(6):548-551. [108] 时素华,李志刚,宋金玲,等.电针对大鼠脊髓损伤caspase-3、calpastatin表达及髓鞘变化的影响[J].广州中医药大学学报,2011,28(2):149-154+158. [109] YANG YJ, KIM YS, SHIN MS, et al. Effects of acupuncture on the intrastriatal hemorrhage-induced caspase-3 expression and newly cell birth in rats. Neurol Res. 2007;29(S1):S65-S71. [110] 陈忠,周宁,蔡丹,喻澜,等.膀胱壁肌层肉毒素注射治疗高张力性神经源性膀胱初步临床报告[C].第十五届全国泌尿外科学术会议论文集,第十五届全国泌尿外科学术会议论文集,中华医学会泌尿外科学分会,2008:5616. [111] PARADELLA AC, MUSEGANTE AF, BRITES C. Comparison of different antibiotic protocols for asymptomatic bacteriuria in patients with neurogenic bladder treated with botulinum toxin A. Braz J Infect Dis. 2016;20(6):623-626. [112] QIAO Y, BRODNIK ZD, ZHAO S, et al. Spinal Dopaminergic Mechanisms Regulating the Micturition Reflex in Male Rats with Complete Spinal Cord Injury. J Neurotrauma. 2021;38(6):803-817. [113] 侯春林,衷鸿宾,张世民,等.建立人工膀胱反射弧恢复脊髓损伤患者排尿功能的初步报告[J].第二军医大学学报,2000,21(1):87-89. [114] 侯春林,钟贵彬,谢庆平,等.人工反射弧重建脊髓损伤后弛缓性膀胱排尿功能的临床初步报告[J].中华显微外科杂志,2006,29(2):92-94. [115] BARNABÉ-HEIDER F, GÖRITZ C, SABELSTRÖM H, et al. Origin of new glial cells in intact and injured adult spinal cord. Cell Stem Cell. 2010;7:470-482. [116] CAO QL, ZHANG YP, HOWARD RM, et al. Pluripotent stem cells engrafted into the normal or lesioned adult rat spinal cord are restricted to a glial lineage. Exp Neurol. 2001;167:48-58. [117] WANG B, XIAO Z, CHEN B, et al. Nogo-66 promotes the differentiation of neural progenitors into astroglial lineage cells through mTOR-STAT3pathway. PLoS One. 2008;3:e1856. [118] LIU W, YU M, CHEN F, et al. A novel delivery nanobiotechnology: engineered miR-181b exosomes improved osteointegration by regulating macrophage polarization. J Nanobiotechnol. 2021;19(1):269. [119] PARK C, YAN W, WARD SM, et al. MicroRNAs dynamically remodel gastrointestinal smooth muscle cells. PLoS One. 2011;6(4):e18628. [120] LIU W, YU M, CHEN F, et al. A novel delivery nanobiotechnology: engineered miR-181b exosomes improved osteointegration by regulating macrophage polarization. J Nanobiotechnol. 2021;19(1):269. |
| [1] | 余伟杰, 刘爱峰, 陈继鑫, 郭天赐, 贾易臻, 冯汇川, 杨家麟. 机器学习在腰椎间盘突出症诊治中的优势和应用策略[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2024, 28(9): 1426-1435. |
| [2] | 林泽玉, 徐 林. 痛风致骨破坏机制的研究与进展[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2024, 28(8): 1295-1300. |
| [3] | 周邦瑜, 李 杰, 阮玉山, 耿福能, 李绍波. 美洲大蠊研粉干预脊髓半横断大鼠运动功能和自噬蛋白Beclin-1的表达[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2024, 28(8): 1223-1228. |
| [4] | 曾凡卓, 李雨欣, 孙嘉晨, 谷欣阳, 文 山, 田 鹤, 梅晰凡. 脊髓损伤模型小胶质细胞的高效移植替换策略[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2024, 28(7): 1007-1014. |
| [5] | 刘 涛, 张文凯, 马子谦, 张 焱, 陈学明. 利鲁唑干预脊髓损伤大鼠小胶质细胞中NLRP3炎性小体的活化[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2024, 28(7): 1036-1042. |
| [6] | 张克凡, 石 辉. 细胞因子治疗骨关节炎的研究现状及应用前景[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2024, 28(6): 961-967. |
| [7] | 陈小芳, 郑国爽, 李茂源, 于炜婷. 可注射海藻酸钠水凝胶的制备及应用[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2024, 28(5): 789-794. |
| [8] | 刘 闯, 单 烁, 于腾波, 周 欢, 杨 磊. 骨科止血材料临床应用的优势、不适与面临的挑战[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2024, 28(5): 795-803. |
| [9] | 李佳琪, 黄元礼, 李 妍, 王春仁, 韩倩倩. 非交联透明质酸分子质量降解的机制及影响因素[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2024, 28(5): 747-752. |
| [10] | 徐 溶, 王豪杰, 耿梦想, 孟 凯, 王 卉, 张克勤, 赵荟菁. 多孔聚四氟乙烯人工血管制备及功能化改性研究的进展[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2024, 28(5): 759-765. |
| [11] | 陈泽鹏, 侯永辉, 陈树东, 侯 宇, 林定坤. 牛磺熊去氧胆酸干预缺糖缺氧条件下脊髓神经元的凋亡[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2024, 28(4): 528-534. |
| [12] | 张 明, 王 斌, 贾 凡, 陈 杰, 唐 玮. 基于脑电图的脑机接口技术在脑卒中患者上肢运动功能康复中的应用[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2024, 28(4): 581-586. |
| [13] | 何远杰, 陈宇恒, 赵永超, 王正龙. 表观遗传调控血管平滑肌细胞重塑在主动脉瘤发生发展中的作用[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2024, 28(4): 602-608. |
| [14] | 马思聪 , 陈 晶, 李云庆. 结缔组织生长因子在神经系统中的功能与作用[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2024, 28(4): 615-620. |
| [15] | 闫炳翰, 李志超, 苏 辉, 薛海鹏, 徐展望, 谭国庆. 中药单体靶向自噬治疗骨关节炎的作用机制[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2024, 28(4): 627-632. |
在神经源性膀胱的治疗理念上,国内外学者认为重建脊髓损伤后排尿反射是改善膀胱功能的重要立足点之一,脊髓损伤后膀胱反射活动的恢复依赖于脊髓中反射通路的重组及膀胱传入神经元特性的改变。而影响重建排尿反射的因素包括中枢、反射途径、作用物质及膀胱感受等。该文将对上述因素进行详细论述,以飨读者,并借以为重建膀胱排尿反射的思路及方法抛砖引玉。 中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:人工关节;骨植入物;脊柱;骨折;内固定;数字化骨科;组织工程
1.1.1 检索人及检索时间 由第一作者在2023年2月进行检索。
1.1.2 检索文献时限 1990年1月至2023年12月。
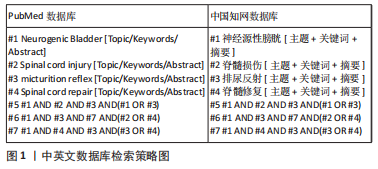
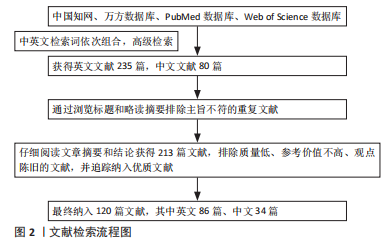
1.1.3 检索数据库 检索中国知网、万方数据库、PubMed数据库、Web of Science数据库。
1.1.4 检索词 中文检索词为“神经源性膀胱;脊髓损伤;排尿反射;脊髓修复”,英文检索词为“Neurogenic Bladder;Spinal cord injury;micturition reflex;Spinal cord repair”。
1.1.5 检索文献类型 研究原著、综述、病例报告、荟萃分析。
1.1.6 手工检索情况 无。
1.1.7 检索策略 以中国知网和PubMed数据库为例,检索策略见图1。
纳入标准:①与重建排尿反射机制相关的文献;②神经源性膀胱与排尿反射和脊髓修复有关的文献。
排除标准:①文献内容陈旧、重复性文献;②文献与该文研究目的不相符。
1.3 文献质量评估及数据提取 在中、英文数据库中检索出所有文献,共检索到文献315篇,根据纳入与排除标准实际纳入120篇文献,其中英文86篇、中文34篇,文献筛选流程图见图2。
综上所述,在重建膀胱排尿反射的过程中涉及较多的因素,包括脊髓受损区域的修复与重建、排尿中枢的重塑、膀胱组织及体内外物质激素的变化,在此过程中主要存在以下问题:①排尿作为一个复杂的过程,重建排尿反射中涉及位点较多,可选取主要作用位点进行深入研究,以突破重建排尿反射通路上存在的疑点,为改善脊髓损伤后排尿障碍提供新的治疗思路;②正常的排尿反射机制复杂,脊髓横断损伤后,中枢神经系统中控制或参与排尿反射的中枢核团是否发生了代偿及相应的代偿机制如何有待进一步探究;③脊髓横断损伤后中枢与膀胱的信息交流中断,中枢与膀胱是否存在直接的信息连接尚待进一步探究;④脊髓横断损伤后重建排尿反射与体液之间的关系尚待进一步研究。上述内容以期为未来研究脊髓损伤后神经源性膀胱的损伤机制、干预位点抛砖引玉。 中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:人工关节;骨植入物;脊柱;骨折;内固定;数字化骨科;组织工程
 #br#
#br#
文题释义:
神经源性膀胱:是一类由于神经系统病变导致的膀胱和尿道功能障碍,进而产生一系列下尿路症状的疾病总称,是脊髓损伤后严重的合并症。
脊髓修复:脊髓遭受内外源性损伤后会产生一系列损伤后表现,通过各种手段促进损伤脊髓修复可以有效改善脊髓损伤后并发症。
在神经源性膀胱的治疗理念上,国内外学者认为重建脊髓损伤后排尿反射是改善膀胱功能的重要立足点之一,脊髓损伤后膀胱反射活动的恢复依赖于脊髓中反射通路的重组及膀胱传入神经元特性的改变。影响重建排尿反射的因素包括中枢、反射途径、作用物质及膀胱感受等。该文通过文献综述,探讨脊髓横断损伤后促进脊髓修复、重建排尿反射在治疗神经源性膀胱中的运用,以期为神经源性膀胱的治疗提供新思路。
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||