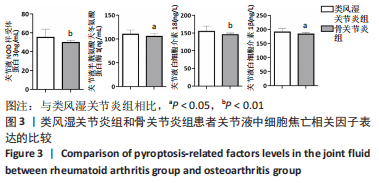
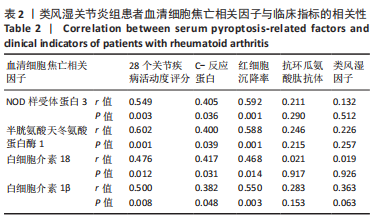
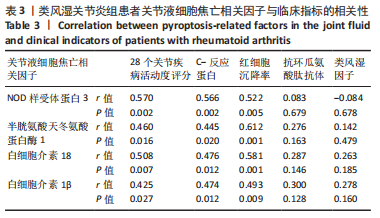
[1] MCINNES IB, SCHETT G. The pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis. New Engl J Med. 2011;365:2205-2219.
[2] SMOLEN JS, ALETAHA D, Barton A, et al. Rheumatoid arthritis. Nat Rev Dis Primers. 2018;4:18001.
[3] LIU X, ZHANG Z, RUAN J, et al. Inflammasomeactivated gasdermin D causes pyroptosis by forming membrane pores. Nature. 2016;535(7610):153-158.
[4] VANDE WALLE L, LAMKANFI M. Pyroptosis. Curr Biol. 2016;26(13):R568-R572.
[5] WU XY, LI KT, YANG HX, et al. Complement C1q synergizes with PTX3 in promoting NLRP3 inflammasome over-activation and pyroptosis in rheumatoid arthritis. J Autoimmun. 2020;106:102336.
[6] GUO C, FU R, WANG S, et al. NLRP3 inflammasome activation contributes to the pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis. Clin Exp Immunol. 2018;194(2):231-243.
[7] ALETAHA D, NEOGI T, SILMAN AJ, et al. 2010 rheumatoid arthritis classification criteria: an American College of Rheumatology/European League Against Rheumatism collaborative initiative. Ann Rheum Dis. 2010;69(9):1580-1588.
[8] FRANSEN J, VAN RIEL PL. The Disease Activity Score and the EULAR response criteria. Rheum Dis Clin North Am. 2009;35(4):745-757.
[9] 中华医学会骨科学分会关节外科学组, 中国医师协会骨科医师分会骨关节炎学组, 国家老年疾病临床医学研究中心(湘雅医院), 等.中国骨关节炎诊疗指南(2021年版)[J].中华骨科杂志,2021,41(18):1291-1314.
[10] 苏芮,赵向聪,穆艳飞,等.细胞焦亡在类风湿关节炎发病机制中的研究进展[J].中华风湿病学杂志,2019,23(5):341-344.
[11] MAN SM, KARKI R, KANNEGANTI TD. Molecular mechanisms and functions of pyroptosis, inflammatory caspases and inflammasomes in infectious diseases. Immunol Rev. 2017;277(1):61-75.
[12] MIAO EA, LEAF IA, TREUTING PM, et al. Caspase-1-induced pyroptosis is an innate immune effector mechanism against intracellular bacteria. Nat Immunol. 2010;11(12):1136-1142.
[13] CHADHA S, BEHL T, BUNGAU S, et al. Mechanistic insights into the role of pyroptosis in rheumatoid arthritis. Curr Res Transl Med. 2020;68(4):151-158.
[14] DEETS KA, VANCE RE. Inflammasomes and adaptive immune responses. Nat Immunol. 2021;22(4):412-422.
[15] BROZ P, DIXIT VM. Inflammasomes: mechanism of assembly, regulation and signalling. Nat Rev Immunol. 2016;16(7):407-420.
[16] BARKER BR, TAXMAN DJ, TING JP. Cross-regulation between the IL-1β/IL-18 processing inflammasome and other inflammatory cytokines. Curr Opin Immunol. 2011;23(5):591-597.
[17] SPEL L, MARTINON F. Inflammasomes contributing to inflammation in arthritis. Immunol Rev. 2020;294(1):48-62.
[18] ZENG C, WANG R, TAN H. Role of Pyroptosis in Cardiovascular Diseases and its Therapeutic Implications. Int J Biol Sci. 2019;15(7):1345-1357.
[19] DEANE KD, O’DONNELL CI, HUEBER W, et al. The number of elevated cytokines and chemokines in preclinical seropositive rheumatoid arthritis predicts time to diagnosis in an age-dependent manner. Arthritis Rheum. 2010;62(11):3161-3172.
[20] KOKKONEN H, SÖDERSTRÖM I, ROCKLÖV J, et al. Up-regulation of cytokines and chemokines predates the onset of rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 2010;62(2):383-391.
[21] HUGHES-AUSTIN JM, DEANE KD, DERBER LA, et al. Multiple cytokines and chemokines are associated with rheumatoid arthritis-related autoimmunity in first-degree relatives without rheumatoid arthritis: Studies of the Aetiology of Rheumatoid Arthritis (SERA). Ann Rheum Dis. 2013;72(6):901-907.
[22] YUAN S, LI X, LIN A, et al. Interleukins and rheumatoid arthritis: bi-directional Mendelian randomization investigation. Semin Arthritis Rheum. 2022;53:151958.
[23] HAREL M, FAUTEUX-DANIEL S, GIRARD-GUYONVARC’H C, et al. Balance between Interleukin-18 and Interleukin-18 binding protein in auto-inflammatory diseases. Cytokine. 2022;150:155781.
[24] CHOULAKI C, PAPADAKI G, REPA A, et al. Enhanced activity of NLRP3 inflammasome in peripheral blood cells of patients with active rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Res Ther. 2015;17(1):257.
[25] MATHEWS RJ, ROBINSON JI, BATTELLINO M, et al. Evidence of NLRP3-inflammasome activation in rheumatoid arthritis (RA); genetic variants within the NLRP3-inflammasome complex in relation to susceptibility to RA and response to anti-TNF treatment. Ann Rheum Dis. 2014;73(6):1202-1210.
[26] ADDOBBATI C, DA CRUZ HLA, ADELINO JE, et al. Polymorphisms and expression of inflammasome genes are associated with the development and severity of rheumatoid arthritis in Brazilian patients. Inflamm Res. 2018;67(3):255-264.
[27] XIE Q, WEI M, ZHANG B, et al. MicroRNA33 regulates the NLRP3 inflammasome signaling pathway in macrophages. Mol Med Rep. 2018;17(2):3318-3327.
[28] KIM HW, KWON YJ, PARK BW, et al. Differential expressions of NOD-like receptors and their associations with inflammatory responses in rheumatoid arthritis. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2017;35(4):630-637.
[29] ZHAO J, JIANG P, GUO S, et al. Apoptosis, Autophagy, NETosis, Necroptosis, and Pyroptosis Mediated Programmed Cell Death as Targets for Innovative Therapy in Rheumatoid Arthritis. Front Immunol. 2021;24;12:809806.
[30] YOU R, HE X, ZENG Z, et al. Pyroptosis and Its Role in Autoimmune Disease: A Potential Therapeutic Target. Front Immunol. 2022;25;13:841732.
[31] ZHANG Y, ZHENG Y, LI H. NLRP3 inflammasome plays an important role in the pathogenesis of collagen-induced arthritis. Mediators Inflamm. 2016;2016:9656270.
[32] JENKO B, PRAPROTNIK S, TOMŠIC M, et al. NLRP3 and CARD8 polymorphisms influence higher disease activity in rheumatoid arthritis. J Med Biochem. 2016; 35(3):319-323.
[33] YANG Z, CAO J, YU C, et al. Caspase-1 mediated interleukin-18 activation in neutrophils promotes the activity of rheumatoid arthritis in a NLRP3 inflammasome independent manner. Joint Bone Spine. 2016;83(3):282-289.
[34] WAWROCKI S, DRUSZCZYNSKA M, KOWALEWICZ-KULBAT M, et al. Interleukin 18 (IL-18) as a target for immune intervention. Acta Biochim Pol. 2016;63(1):59-63.
[35] JUNG SM, KIM KW, YANG CW, et al. Cytokine-mediated bone destruction in rheumatoid arthritis. J Immunol Res. 2014;2014:263625.
|