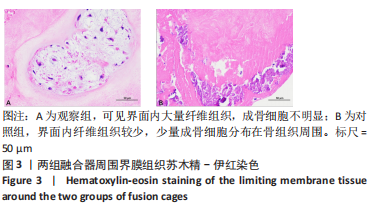
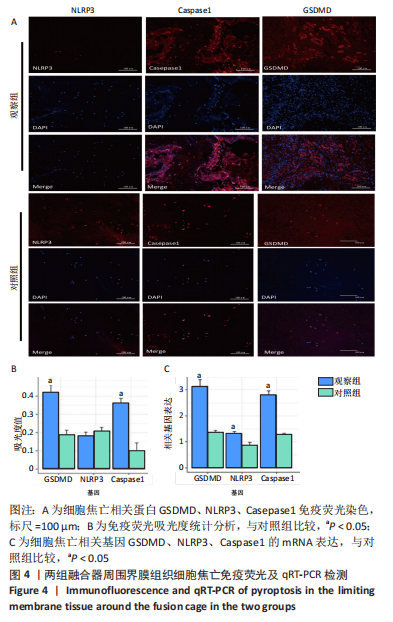
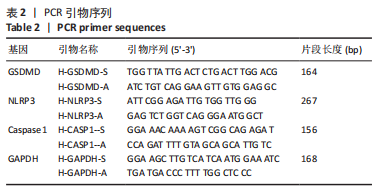
[1] KIENLE A, GRAF N, WILKE HJ. Does impaction of titanium-coated interbody fusion cages into the disc space cause wear debris or delamination? Spine J. 2016;16(2):235-242.
[2] QIAN H, LEI T, QIAN H, et al. Additively manufactured Tantalum implants for repairing bone defects : a systematic review. Tissue Eng Part B Rev. 2021;27(2):166-180.
[3] ZHU W, QIU J, YANG J, et al. Effect of titanium ions on the Hippo / YAP signaling pathway in regulating biological behaviors of MC3T3-E1 osteoblasts. J Appl Toxicol. 2018;38(6):824-833.
[4] 石晓岫,毛世龙,刘洋,等.钽与钛(合金)骨科材料的差异比较:理化指标及抗菌和成骨能力[J].中国组织工程研究,2021,25(4): 593-599.
[5] 马志杰,李京育,曹放,等.多孔碳化硅涂覆生物活性钽新型生物医用材料的影响因素及生物学性能[J].中国组织工程研究,2021, 25(4):558-563.
[6] HUANG G, PAN ST, QIU JX. The clinical application of porous tantalum and its new development for bone tissue engineering. Materials (Basel). 2021;14(10):2647.
[7] ZHANG L, HADDOUTI E M, WELLE K, et al. Local Cellular Responses to Metallic and Ceramic Nanoparticles from Orthopedic Joint Arthroplasty Implants. Int J Nanomedicine. 2020;15:6705-6720.
[8] PATEL MS, MCCORMICK JR, GHASEM A, et al. Tantalum: The next biomaterial in spine surgery? J Spine Surg. 2020;6(1):72-86.
[9] LÖFGREN H, ENGQUIST M, HOFFMANN P, et al. Clinical and radiological evaluation of Trabecular Metal and the Smith-Robinson technique in anterior cervical fusion for degenerative disease: A prospective, randomized, controlled study with 2-year follow-up. Eur Spine J. 2010; 19(3):464-473.
[10] KASLIWAL MK, BASKIN DS, TRAYNELIS VC. Failure of Porous Tantalum Cervical Interbody Fusion Devices. J Spinal Disord Tech. 2013;26(5): 239-245.
[11] ZHANG L, HADDOUTI EM, WELLE K, et al. Local cellular responses to metallic and ceramic nanoparticles from orthopedic joint arthroplasty implants. Int J Nanomedicine. 2020;15:6705-6720.
[12] ZHU Y, GU Y, QIAO S, et al. Bacterial and mammalian cells adhesion to tantalum-decorated micro-/nano-structured titanium. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2017;105(3):871-878.
[13] BONUTTI PM, PIVEC R, ISSA K, et al. Delamination of tantalum porous coating from a TKA due to regional dissemination of debris. Orthopedics. 2013;36(8):600-604.
[14] HALLAB NJ, SAMELKO L, HAMMOND D. The Inflammatory Effects of Breast Implant Particulate Shedding: Comparison with Orthopedic Implants. Aesthetic Surg J. 2019;39:S36-S48.
[15] HALLAB NJ. A review of the biologic effects of spine implant debris: Fact from fiction. SAS J. 2009;3(4):143-160.
[16] WANG JC, YU WD, SANDHU HS, et al. Metal debris from titanium spinal implants. Spine. 1999;24(9):899-903.
[17] DEVANT P, SHARPE AH, THIAGARAJAH JR, et al. Article Control of gasdermin D oligomerization and pyroptosis by the Ragulator-Rag-mTORC1 pathway Article Control of gasdermin D oligomerization and pyroptosis by the Ragulator-Rag-mTORC1 pathway. Cell. 2021:1-17.
[18] LIU X, XIA S, ZHANG Z, et al. Channelling inflammation : gasdermins. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2021;20(5):384-405.
[19] LIU Y, CHEN Q, ZHU Y, et al. Non-coding RNAs in necroptosis, pyroptosis and ferroptosis in cancer metastasis. Cell Death Discov. 2021;7(1:210.
[20] CHEN C, JIANG Z, JIANG Q, et al. Caspase-3 and gasdermin E detection in peri-implantitis. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis. 2021;1867(11): 166217.
[21] JUAN CX, MAO Y, CAO Q, et al. Exosome-mediated pyroptosis of miR-93-TXNIP-NLRP3 leads to functional difference between M1 and M2 macrophages in sepsis induced acute kidney injury. J Cell Mol Med. 2021;25(10):4786-4799.
[22] FAN C, ZHAO X, GUO X, et al. P2X4 promotes interleukin‑1β production in osteoarthritis via NLRP1. Mol Med Rep. 2014;9(1):340-344.
[23] ZHANG L, XING R, HUANG Z, et al. Inhibition of Synovial Macrophage Pyroptosis Alleviates Synovitis and Fibrosis in Knee Osteoarthritis. Mediators Inflamm. 2019;2019:2165918.
[24] TAO Z, WANG J, WEN K, et al. Pyroptosis in Osteoblasts: A Novel Hypothesis Underlying the Pathogenesis of Osteoporosis. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2021;11:1-11.
[25] PIERRE CA, CHAN M, IWAKURA Y, et al. Periprostheticosteolysis: characterizing the innate immune response to titanium wear-particles. J Orthop Res. 2010;28(11):1418-1424.
[26] BURTON L, PAGET D, BINDER NB, et al. Orthopedic wear debris mediated inflammatory osteolysis is mediated in part by NALP3 inflammasome activation. J Orthop Res. 2013;31(1):73-80.
[27] MA QL, FANG L, JIANG N, et al. Bone mesenchymal stem cell secretion of RANKL/OPG/M-CSF in response to macrophage-mediated inflammatory response influences osteogenesis on nanostructured Ti surfaces. Biomaterials. 2018;154:234-247.
[28] TSUKASAKI M, TAKAYANAGI H. Osteoimmunology: evolving concepts in bone–immune interactions in health and disease. Nat Rev Immunol. 2019;19(10):626-642.
[29] MINODA Y, KOBAYASHI A, IKEBUCHI M, et al. Periprosthetic Loss of Bone Mineral Density After Cementless Porous Tantalum and Cemented Total Knee Arthroplasties: A Mean of 11-Year Concise Follow-Up of a Previous Report. J Arthroplasty. 2020;35(11):3156-3160. |