[1] JANMOHAMMADI M, NAZEMI Z, SALEHI AOM, et al. Cellulose-based composite scaffolds for bone tissue engineering and localized drug delivery. Bioact Mater. 2023;20:137-163.
[2] ZHANG Q, YAN S, YAN X, et al. Recent advances in metal-organic frameworks: synthesis, application and toxicity. Sci Total Environ. 2023; 902:165944.
[3] LI B, WEN HM, CUI Y, et al. Emerging multifunctional metal–organic framework materials. Adv Mater. 2016;28(40):8819-8860.
[4] BAI Y, DOU Y, XIE LH, et al. Zr-based metal–organic frameworks: design, synthesis, structure, and applications. Chem Soc Rev. 2016;45(8): 2327-2367.
[5] FURUKAWA H, CORDOVA KE, O’KEEFFE M, et al. The chemistry and applications of metal-organic frameworks. Science. 2013;341(6149): 1230444.
[6] DENG H, GRUNDER S, CORDOVA KE, et al. Large-pore apertures in a series of metal-organic frameworks. Science. 2012;336(6084):1018-1023.
[7] TAO SY, YU H, YOU T, et al. A Dual-targeted metal–organic framework based nanoplatform for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis by restoring the macrophage niche. ACS Nano. 2023;17(14):13917-13937.
[8] ZHANG SQ, CAI JH, YAO Y, et al. Mitochondrial-targeting Mn(3)O(4)/UIO-TPP nanozyme scavenge ROS to restore mitochondrial function for osteoarthritis therapy. Regen Biomater. 2023;10:rbad078.
[9] ALSAIKHAN F, MAHMOUD MZ, SULIMAN M. Synthesis and characterization of novel denosumab/magnesium-based metal organic frameworks nanocomposite prepared by ultrasonic route as drug delivery system for the treatment of osteoporosis. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2023;11:1153969.
[10] LIN S, LIU X, TAN L, et al.. Porous iron-carboxylate metal-organic framework: a novel bioplatform with sustained antibacterial efficacy and nontoxicity. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2017;9(22):19248-19257.
[11] TAO BL, LIN CC, HE Y, et al. Osteoimmunomodulation mediating improved osteointegration by OGP-loaded cobalt-metal organic framework on titanium implants with antibacterial property. Chem Eng J. 2021;423:130176.
[12] XU C, KANG Y, DONG X, et al. Integration exosomes with MOF-modified multifunctional scaffold for accelerating vascularized bone regeneration. Chin Chem Lett. 2022;34(2):107528.
[13] WANG B, CHEN H, PENG S, et al. Multifunctional magnesium-organic framework doped biodegradable bone cement for antibacterial growth, inflammatory regulation and osteogenic differentiation. J Mater Chem B. 2023;11(13):2872-2885.
[14] MOHAMMAD MEHDI S, MAHMOOD K. Microstructure and anti-corrosion properties of acrylic bone cement-based with MOF nanostructured hybrid coatings on AZ31 Mg alloy. Mater Chem Phys. 2023;307:128147.
[15] SHU CQ, QIN C, CHEN L, et al. Metal-organic framework functionalized bioceramic scaffolds with antioxidative activity for enhanced osteochondral regeneration. Adv Sci. 2023;10(13):e2206875.
[16] LIU J, TAN Y, SHEN E, et al. Highly water-stable bimetallic organic framework MgCu-MOF74 for inhibiting bacterial infection and promoting bone regeneration. Biomed Mater. 2022;17(6):065026.
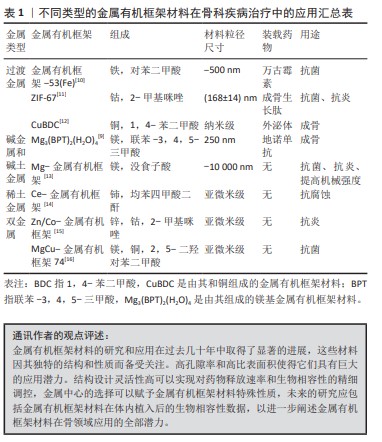
[17] MATLINSKA MA, HA M, HUGHTON B, et al. Alkaline earth metal-organic frameworks with tailorable ion release: a path for supporting biomineralization. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2019;11(36):32739-32745.
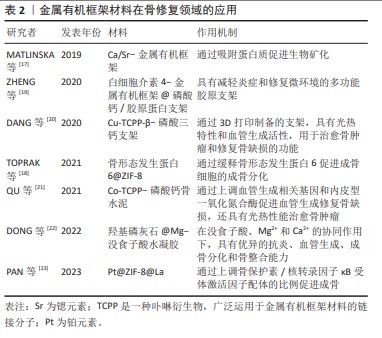
[18] TOPRAK Ö, TOPUZ B, MONSEF YA, et al. BMP-6 carrying metal organic framework-embedded in bioresorbable electrospun fibers for enhanced bone regeneration. Mater Sci Eng C. 2021;120:111738.
[19] ZHENG ZW, CHEN YH, GUO B, et al. Magnesium-organic framework-based stimuli-responsive systems that optimize the bone microenvironment for enhanced bone regeneration. Chem Eng J. 2020;396:125241.
[20] DANG WT, MA B, LI B, et al. 3D printing of metal-organic framework nanosheets-structured scaffolds with tumor therapy and bone construction. Biofabrication. 2020;12(2):025005.
[21] QU Y, ZHUANG H, ZHANG M, et al. Bone cements for therapy and regeneration for minimally invasive treatment of neoplastic bone defects. J Mater Chem B. 2021;9(21):4355-4364.
[22] DONG WY, ZHAO SS, WANG YL, et al. Stimuli-responsive metal–organic framework hydrogels endow long carbon fiber reinforced polyetheretherketone with enhanced anti-inflammatory and angiogenesis and osteogenesis. Mater Des. 2022;225:111485.
[23] PAN HJ, MIAO X, DENG J, et al. Bimetallic metal-organic framework for mitigating aseptic osteolysis. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2023; 15(4):4935-4946.
[24] WANG HF, CHEN S, HE Z, et al. Synthesis and potential osteogenic applications of Wnt3a‐loaded ZIF‐8 nanoparticles. Chin Chem Lett. 2023;35(3):108597.
[25] FAR BF, NAIMI-JAMAL MR, AHMADI S, et al. Enhancing bone tissue engineering with calcium and strontium nanoparticles immobilized on HKUST-1. Alex Eng J. 2023;76:221-235.
[26] XIAO TH, FAN L, LIU RT, et al. Fabrication of dexamethasone-loaded dual-metal-organic frameworks on polyetheretherketone implants with bacteriostasis and angiogenesis properties for promoting bone regeneration. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2021;13(43):50836-50850.
[27] XU C, KANG Y, GUAN S, et al. Iron-based metal–organic framework as a dual cooperative release system for enhanced vascularization and bone regeneration. Chin Chem Lett. 2022;34(5):107825.
[28] GUTOWSKA I, MACHOY Z, MACHALIŃSKI B. The role of bivalent metals in hydroxyapatite structures as revealed by molecular modeling with the HyperChem software. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2005;75(4):788-793.
[29] ZHANG YY, SHEN XK, MA. PP, et al. Composite coatings of Mg-MOF74 and Sr-substituted hydroxyapatite on titanium substrates for local antibacterial, anti-osteosarcoma and pro-osteogenesis applications. Mater Lett. 2019;241:18-22.
[30] LOU W, DONG Y, ZHANG H, et al. Preparation and characterization of lanthanum-Incorporated hydroxyapatite coatings on titanium substrates. Int J Mol Sci. 2015;16(9):21070-21086.
[31] YUAN Y, ZHANG Y. Enhanced biomimic bactericidal surfaces by coating with positively-charged ZIF nano-dagger arrays. Nanomedicine. 2017; 13(7):2199-2207.
[32] YU MF, YOU DQ, ZHUANG JJ, et al. Controlled release of naringin in metal-organic framework-loaded mineralized collagen coating to simultaneously enhance osseointegration and antibacterial activity. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces. 2017;9(23):19698-19705.
[33] KARAKEÇILI A, TOPUZ B, KORPAYEV S, et al. Metal-organic frameworks for on-demand pH controlled delivery of vancomycin from chitosan scaffolds. Mater Sci Eng C. 2019;105:110098.
[34] SHEN XK, ZHANG Y, MA P, et al. Fabrication of magnesium/zinc-metal organic framework on titanium implants to inhibit bacterial infection and promote bone regeneration. Biomaterials. 2019;212:1-16.
[35] TAO BL, ZHAO WK, LIN CC, et al. Surface modification of titanium implants by ZIF-8@Levo/LBL coating for inhibition of bacterial-associated infection and enhancement of osseointegration. Chem Eng J. 2020;390:124621.
[36] LU S, REN X, GUO T, et al. Controlled release of iodine from cross-linked cyclodextrin metal-organic frameworks for prolonged periodontal pocket therapy. Carbohydr Polym. 2021;267:118187.
[37] KARAKEÇILI A, TOPUZ B, ERSOY FŞ, et al. UiO-66 metal-organic framework as a double actor in chitosan scaffolds: antibiotic carrier and osteogenesis promoter. Mater Sci Eng C. 2022;136:212757.
[38] ZHU Y, ZHI Q, ZHANG C, et al. Debridement of contaminated implants using air-polishing coupled with pH-responsive maximin H5-embedded metal-organic. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2023;11:1124107.
[39] PACHECO T, GOMES AÉI, SIQUEIRA NMG, et al. SdiA, a quorum-sensing regulator, suppresses fimbriae expression, biofilm formation, and quorum-sensing signaling molecules. Production in Klebsiella pneumoniae Front Microbiol. 2021;12:597735.
[40] SI YH, LIU HY, LI MS, et al. An efficient metal–organic framework-based drug delivery platform for synergistic antibacterial activity and osteogenesis J Colloid Interface Sci. 2023;640:521-539.
[41] CLAUDIO P, RICCARDO P, CORRADO DIN, et al. Antimicrobial MOFs Coord Chem Rev. 2021;446:214121.
[42] LIU YH, ZHU Z, PEI XB, et al. ZIF-8-modified multifunctional bone-adhesive hydrogels. promoting angiogenesis and osteogenesis for bone regeneration. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2020;12(33):36978-36995.
[43] KUNDU B, REIS RL, KUNDU SC. Biomimetic antibacterial pro-osteogenic cu-sericin mofs for osteomyelitis treatment. Biomimetics. 2022;7(2):64.
[44] DEHNAVI SM, BARJASTEH M, AHMADI SEYEDKHANI S, et al. A novel silver-based metal-organic framework incorporated into nanofibrous chitosan coatings for bone tissue implants. Int J Pharm. 2023;640:123047.
[45] MUTALIK C, HSIAO YC, CHANG YH, et al. High UV-Vis-NIR light-induced antibacterial activity by heterostructured TiO(2)-FeS(2) nanocomposites. Int J Nanomedicine. 2020;15:8911-8920.
[46] TENG WSY, ZHANG ZJ, WANG YK, et al. Iodine immobilized metal-organic framework for NIR-triggered antibacterial therapy on orthopedic implants. Small. 2021;17(35):e2102315.
[47] DENG Y, SHI J, CHAN YK, et al. Heterostructured metal-organic frameworks/polydopamine coating endows. Polyetheretherketone implants with multimodal osteogenicity and photoswitchable disinfection. Adv Healthc Mater. 2022;11(14):e2200641.
[48] KANG Y, XU C, MENG LA, et al. Exosome-functionalized magnesium-organic framework-based scaffolds with osteogenic, angiogenic and anti-inflammatory properties for accelerated bone regeneration. Bioact Mater. 2022;18:26-41.
[49] LAO A, WU J, LI D, et al. Functionalized metal–organic framework-modified hydrogel that breaks the vicious cycle of inflammation and ROS for repairing of diabetic bone defects. Small. 2023;19(36): e2206919.
[50] QIAN GW, MAO YQ, SHUAI Y, et al. Enhancing bone scaffold interfacial reinforcement through in situ growth of metal-organic frameworks (MOFs) on strontium carbonate: achieving high strength and osteoimmunomodulation. J Colloid Interface Sci. 2023;655:43-57.
[51] CHEN M, WANG D, LI M, et al. Nanocatalytic biofunctional MOF coating on titanium implants promotes osteoporotic bone regeneration through cooperative pro-osteoblastogenesis MSC reprogramming. ACS Nano. 2022;16(9):15397-15412.
[52] YAN BC, TAN J, ZHANG HF, et al. Constructing fluorine-doped Zr-MOF films on titanium for antibacteria, anti-inflammation, and osteogenesis. Mater Sci Eng C. 2022;134:112699.
[53] GE Y, WANG K, LI H, et al. An Mg-MOFs based multifunctional medicine for the treatment of osteoporotic pain. Mater Sci Eng C. 2021;129:112386.
[54] JIANG YN, LIAO HX, YAN LW, et al. A metal–organic framework-incorporated hydrogel for delivery of immunomodulatory neobavaisoflavone to promote cartilage regeneration in osteoarthritis. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2023;15(40):46598-46612.
[55] XUE S, ZHOU X, SANG W, et al. Cartilage-targeting peptide-modified dual-drug delivery nanoplatform with NIR laser response for osteoarthritis therapy. Bioact Mater. 2021;6(8):2372-2389.
[56] ZHAO X, WU Q, GONG X, et al. Osteosarcoma:a review of current and future therapeutic approaches. Biomed Eng Online. 2021;20(1):24.
[57] GAO P, CHEN Y, PAN W, et al. Antitumor agents based on metal-organic frameworks angew. Chem Int Ed Engl. 2021;60(31):16763-16776.
[58] XU WF, LOU Y, CHEN WSJ, et al. Folic acid decorated metal-organic frameworks loaded with doxorubicin for tumor-targeted chemotherapy of osteosarcoma. Biomed Tech (Berl). 2020;65(2):229-236.
[59] MA YQ, CHEN L, LI XL, et al. Rationally integrating peptide-induced targeting and multimodal therapies in a dual-shell theranostic platform for orthotopic metastatic spinal tumors. Biomaterials. 2021; 275:120917.
[60] DENG XY, GUO Y, ZHANG XD, et al. Film-facilitated formation of ferrocenecarboxylic acid-embedded metal-organic framework nanoparticles for sonodynamic osteosarcoma treatment. Mater Today Chem. 2022;24:100842.
[61] LI W, YANG Y, WANG J, et al. Establishment of bone-targeted nano-platform and the study of its combination with 2-deoxy-d-glucose enhanced photodynamic therapy to inhibit bone metastasis J Mech Behav Biomed Mater. 2024;150:106306.
[62] WANG Y, WILLIAMS GR, ZHENG Y, et al. Polydopamine-cloaked Fe-based metal organic frameworks enable synergistic multidimensional treatment of osteosarcoma. J Colloid Interface Sci. 2023;651:76-92.
[63] DENG XT, ZHAO RL, TANG YF, et al. NIR laser-activated multifunctional nanocomposites for cascade low-temperature photothermal and oxygen-irrelevant thermodynamic therapy. Mater Des. 2023;233: 112206.
[64] DU CC, ZHOU MX, JIA F, et al. D-arginine-loaded metal-organic frameworks nanoparticles sensitize osteosarcoma to radiotherapy. Biomaterials. 2021;269:120642.
[65] LI T, GAO MQ, WU ZF, et al. Tantalum–zirconium co-doped metal–organic frameworks sequentially sensitize radio–radiodynamic–immunotherapy for metastatic osteosarcoma. Adv Sci. 2023;10(10): e2206779.
[66] TAN LL, SONG N, ZHANG SX, et al. Ca(2+), pH and thermo triple-responsive mechanized Zr-based MOFs for on-command drug release in bone diseases. J Mater Chem B. 2016;4(1):135-140.
[67] CHEN J, ZHANG X, HUANG C, et al. Osteogenic activity and antibacterial effect of porous titanium modified with metal-organic framework films. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2017;105(3):834-846.
[68] ZHONG L, CHEN J, MA Z, et al. 3D printing of metal-organic framework incorporated porous scaffolds to promote osteogenic differentiation and bone regeneration. Nanoscale. 2020;12(48):24437-24449.
[69] LIU W, YAN Z, MA X, et al. Mg-MOF-74/MgF₂ Composite coating for improving the. properties of magnesium alloy implants: hydrophilicity and corrosion resistance. Materials. 2018;11(3):396.
[70] JIANG Y, PAN X, YAO M, et al. Bioinspired adhesive and tumor microenvironment responsive nanoMOFs assembled 3D-printed scaffold for anti-tumor therapy and bone regeneration. Nano Today. 2021;39:101182.
[71] NIU Y, YANG H, YU Z, et al. Intervention with the bone-associated tumor vicious cycle through dual-protein therapeutics for treatment of skeletal-related events and bone metastases. ACS nano. 2022;16(2): 2209-2223.
[72] LI S, XU F, REN X, et al. H(2)S-reactivating antitumor immune response after microwave thermal therapy for long-term tumor suppression. ACS Nano. 2023;17(19):19242-19253. |