[1] SINGH P, TYAGI M, KUMAR Y, et al. Ocular chemical injuries and their management. Oman J Ophthalmol. 2013;6(2):83-86.
[2] SHAYAN ASL N, NEJAT F, MOHAMMADI P, et al. Amniotic membrane extract eye drop promotes limbal stem cell proliferation and corneal epithelium healing. Cell J. 2019;20(4):459-468.
[3] SHAHRIARY A, SABZEVARI M, JADIDI K, et al. The role of inflammatory cytokines in neovascularization of chemical ocular injury. Ocul Immunol Inflamm. 2022;30(5):1149-1161.
[4] SHARMA N, KAUR M, AGARWAL T, et al. Treatment of acute ocular chemical burns. Surv Ophthalmol. 2018;63(2):214-235.
[5] YUAN X, MARCANO DC, SHIN CS, et al. Ocular drug delivery nanowafer with enhanced therapeutic efficacy. ACS Nano. 2015;9(2):1749-1758.
[6] CHAUHAN A, FITZHENRY L, SERRO AP. Recent advances in ophthalmic drug delivery. Pharmaceutics. 2022;14(10):2075.
[7] GAIN P, JULLIENNE R, HE Z G, et al. Global survey of corneal transplantation and eye banking. JAMA Ophthalmol. 2016;134(2):167-173.
[8] AHEARNE M, FERNANDEZ-PEREZ J, MASTERTON S, et al. Designing scaffolds for corneal regeneration. Adv Funct Mater. 2020;30(44):1908996.
[9] BIZRAH M, YUSUF A, AHMAD S. An update on chemical eye burns. Eye (Lond). 2019;33(9):1362-1377.
[10] OGUIDO A, HOHMANN M S N, PINHO-RIBEIRO F A, et al. Naringenin eye drops inhibit corneal neovascularization by anti-inflammatory and antioxidant mechanisms. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2017;58(13):5764-5776.
[11] WAN S, YANG W, PAN Y, et al. G9a Suppression alleviates corneal neovascularization through blocking Nox4-mediated oxidative stress. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2020;2020:6983268.
[12] KABE Y, ANDO K, HIRAO S, et al. Redox regulation of NF-kappaB activation: distinct redox regulation between the cytoplasm and the nucleus. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2005;7(3-4):395-403.
[13] CHOI H, PHILLIPS C, OH JY, et al. Comprehensive modeling of corneal alkali injury in the rat eye. Curr Eye Res. 2017;42(10):1348-1357.
[14] SPROGYTE L, PARK M, DI GIROLAMO N. Pathogenesis of alkali injury-induced limbal stem cell deficiency: a literature survey of animal models. Cells. 2023;12(9):1294.
[15] YAN D, YU F, CHEN L, et al. Subconjunctival injection of regulatory t cells potentiates corneal healing via orchestrating inflammation and tissue repair after acute alkali burn. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2020;61(14):22.
[16] JIANG L, HE W, TANG F, et al. Epigenetic landscape analysis of the long non-coding RNA and messenger RNA in a mouse model of corneal alkali burns. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2021;62(4):28.
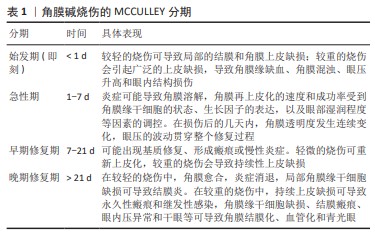
[17] WANG FY, CHENG J, ZHAI HL, et al. Correlation analysis of the clinical features and prognosis of acute ocular burns-exploration of a new classification scheme. Graef Arch Clin Exp. 2020;258(1):147-155.
[18] KUBOTA M, SHIMMURA S, KUBOTA S, et al. Hydrogen and N-acetyl-L-cysteine rescue oxidative stress-induced angiogenesis in a mouse corneal alkali-burn model. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2011;52(1):427-433.
[19] NICHOLAS MP, MYSORE N. Corneal neovascularization. Exp Eye Res. 2021; 202:108363.
[20] CUI N, HU M, KHALIL RA. Biochemical and biological attributes of matrix metalloproteinases. Prog Mol Biol Transl Sci. 2017;147:1-73.
[21] FUKUDA K. Corneal fibroblasts: function and markers. Exp Eye Res. 2020; 200:108229.
[22] WILSON SE. TGF beta -1, -2 and -3 in the modulation of fibrosis in the cornea and other organs. Exp Eye Res. 2021;207:108594.
[23] WILSON SE. The yin and yang of mesenchymal cells in the corneal stromal fibrosis response to injury: the cornea as a model of fibrosis in other organs. Biomolecules. 2022;13(1):87.
[24] KETHIRI AR, SINGH VK, DAMALA M, et al. Long term observation of ocular surface alkali burn in rabbit models: quantitative analysis of corneal haze, vascularity and self-recovery. Exp Eye Res. 2021;205:108526.
[25] KETHIRI AR, RAJU E, BOKARA KK, et al. Inflammation, vascularization and goblet cell differences in LSCD: validating animal models of corneal alkali burns. Exp Eye Res. 2019;185:107665.
[26] CLARE G, BUNCE C, TUFT S. Amniotic membrane transplantation for acute ocular burns. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022;9(9):Cd009379.
[27] YE J, SHI X, CHEN X, et al. Chitosan-modified, collagen-based biomimetic nanofibrous membranes as selective cell adhering wound dressings in the treatment of chemically burned corneas. J Mater Chem B. 2014;2(27): 4226-4236.
[28] THIA ZZ, HO YT, SHIH KC, et al. New developments in the management of persistent corneal epithelial defects. Surv Ophthalmol. 2023;68(6):1093-1114.
[29] PALCHESKO RN, CARRASQUILLA SD, FEINBERG AW. Natural biomaterials for corneal tissue engineering, repair, and regeneration. Adv Healthc Mater. 2018;7(16):e1701434.
[30] BOMFIM PEREIRA MG, PEREIRA GOMES JA, RIZZO LV, et al. Cytokine dosage in fresh and preserved human amniotic membrane. Cornea. 2016;35(1): 89-94.
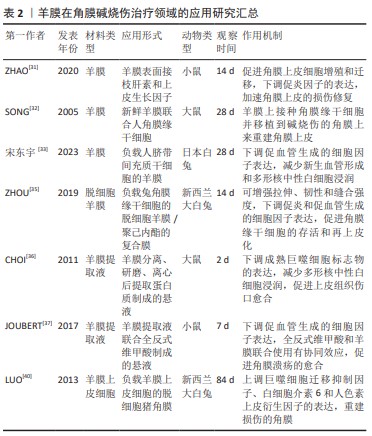
[31] ZHAO X, ZUO X, ZHONG J, et al. Heparin-modified amniotic membrane combined with growth factors for promoting corneal wound healing after alkali burn. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2020;8:599800.
[32] SONG E, YANG W, CUI ZH, et al. Transplantation of human limbal cells cultivated on amniotic membrane for reconstruction of rat corneal epithelium after alkaline burn. Chin Med J (Engl). 2005;118(11):927-935.
[33] 宋东宇,高明宏,李冬梅.人脐带间充质干细胞移植治疗角膜碱烧伤的实验研究[J].国际眼科杂志,2023,23(5):717-722.
[34] WANG MY, LI Y, WANG HQ, et al. Corneal regeneration strategies: from stem cell therapy to tissue engineered stem cell scaffolds. Biomed Pharmacother. 2023;165:115206.
[35] ZHOU Z, LONG D, HSU CC, et al. Nanofiber-reinforced decellularized amniotic membrane improves limbal stem cell transplantation in a rabbit model of corneal epithelial defect. Acta Biomaterialia. 2019;97:310-320.
[36] CHOI JA, CHOI JS, JOO CK. Effects of amniotic membrane suspension in the rat alkali burn model. Mol Vis. 2011;17:404-412.
[37] JOUBERT R, DANIEL E, BONNIN N, et al. Retinoic acid engineered amniotic membrane used as graft or homogenate: positive effects on corneal alkali burns. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2017;58(9):3513-3518.
[38] FATHI I, MIKI T. Human amniotic epithelial cells secretome: components, bioactivity, and challenges. Front Med (Lausanne). 2022;8:763141.
[39] YANG MB, WANG LQ, CHEN ZM, et al. Topical administration of the secretome derived from human amniotic epithelial cells ameliorates psoriasis-like skin lesions in mice. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2022;13(1):393.
[40] LUO H, LU Y, WU T, et al. Construction of tissue-engineered cornea composed of amniotic epithelial cells and acellular porcine cornea for treating corneal alkali burn. Biomaterials. 2013;34(28):6748-6759.
[41] GESTEIRA TF, SUN M, COULSON-THOMAS YM, et al. Hyaluronan rich microenvironment in the limbal stem cell niche regulates limbal stem cell differentiation. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2017;58(11):4407-4421.
[42] PAULOIN T, DUTOT M, WARNET JM, et al. In vitro modulation of preservative toxicity: high molecular weight hyaluronan decreases apoptosis and oxidative stress induced by benzalkonium chloride. Eur J Pharm Sci. 2008; 34(4):263-273.
[43] BOLLYKY PL, BOGDANI M, BOLLYKY JB, et al. The role of hyaluronan and the extracellular matrix in islet inflammation and immune regulation. Curr Diab Rep. 2012;12(5):471-480.
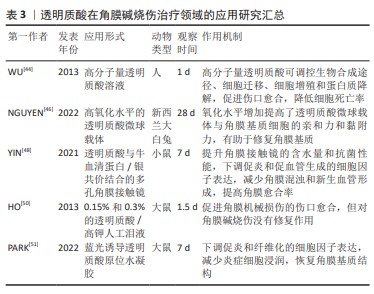
[44] WU CL, CHOU HC, LI JM, et al. Hyaluronic acid-dependent protection against alkali-burned human corneal cells. Electrophoresis. 2013;34(3):388-396.
[45] GUPTA RC, LALL R, SRIVASTAVA A, et al. Hyaluronic Acid: Molecular Mechanisms and Therapeutic Trajectory. Front Vet Sci. 2019;6:192.
[46] NGUYEN DD, YAO CH, LUO LJ, et al. Oxidation-mediated scaffold engineering of hyaluronic acid-based microcarriers enhances corneal stromal regeneration. Carbohydr Polym. 2022;292:119668.
[47] WEEKS A, MORRISON D, ALAUZUN JG, et al. Photocrosslinkable hyaluronic acid as an internal wetting agent in model conventional and silicone hydrogel contact lenses. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2012;100(8):1972-1982.
[48] YIN C, QI X, WU J, et al. Therapeutic contact lenses fabricated by hyaluronic acid and silver incorporated bovine serum albumin porous films for the treatment of alkali-burned corneal wound. Int J Biol Macromol. 2021;184:713-720.
[49] JOHNSON ME, MURPHY PJ, BOULTON M. Effectiveness of sodium hyaluronate eyedrops in the treatment of dry eye. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 2006;244(1):109-112.
[50] HO WT, CHIANG TH, CHANG SW, et al. Enhanced corneal wound healing with hyaluronic acid and high-potassium artificial tears. Clin Exp Optom. 2013;96(6):536-541.
[51] PARK SK, HA M, KIM EJ, et al. Hyaluronic acid hydrogels crosslinked via blue light-induced thiol-ene reaction for the treatment of rat corneal alkali burn. Regen Ther. 2022;20:51-60.
[52] BARATTA RO, SCHLUMPF E, BUONO BJD, et al. Corneal collagen as a potential therapeutic target in dry eye disease. Surv Ophthalmol. 2022;67(1):60-67.
[53] SKLENÁROVÁ R, AKLA N, LATORRE MJ, et al. Collagen as a biomaterial for skin and corneal wound healing. J Funct Biomater. 2022;13(4):249.
[54] NA KS, FERNANDES-CUNHA GM, VARELA IB, et al. Effect of mesenchymal stromal cells encapsulated within polyethylene glycol-collagen hydrogels formed in situ on alkali-burned corneas in an ex vivo organ culture model. Cytotherapy. 2021;23(6):500-509.
[55] LIU J, XU Y, HUANG Y, et al. Collagen membrane loaded with doxycycline through hydroxypropyl chitosan microspheres for the early reconstruction of alkali-burned cornea. Int J Biol Macromol. 2023;244:125188.
[56] SIMPSON FC, MCTIERNAN CD, ISLAM MM, et al. Collagen analogs with phosphorylcholine are inflammation-suppressing scaffolds for corneal regeneration from alkali burns in mini-pigs. Commun Biol. 2021;4(1):608.
[57] GAO XW, ZHAO XD, LI WJ, et al. Experimental study on the treatment of rabbit corneal melting after alkali burn with Collagen cross-linking. Int J Ophthalmol. 2012;5(2):147-150.
[58] KARTI O, ZENGIN MO, CINAR E, et al. Effect of 1- and 6-hour-delayed corneal collagen cross-linking on corneal healing in a rabbit alkali-burn model: clinical and histological observations. Cornea. 2016;35(12):1644-1649.
[59] XU X, LIU T, LI H. Effect of collagen cross-linking on alkali burn-induced corneal neovascularization in rabbits. J Ophthalmol. 2018;2018:7325483.
[60] SUBASI S, ALTINTAS O, YARDIMOGLU M, et al. Comparison of collagen cross-linking and amniotic membrane transplantation in an experimental Alkali burn rabbit model. Cornea. 2017;36(9):1106-1115.
[61] TANG Q, LUO C, LU B, et al. Thermosensitive chitosan-based hydrogels releasing stromal cell derived factor-1 alpha recruit MSC for corneal epithelium regeneration. Acta Biomater. 2017;61:101-113.
[62] FU J, YANG F, GUO Z. The chitosan hydrogels: from structure to function. New J Chem. 2018;42(21):17162-17180.
[63] XU W, LIU K, LI T, et al. An in situ hydrogel based on carboxymethyl chitosan and sodium alginate dialdehyde for corneal wound healing after alkali burn. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2019;107(4):742-754.
[64] ZHOU Y, ZHAI Z, YAO Y, et al. Oxidized hydroxypropyl cellulose/carboxymethyl chitosan hydrogels permit pH-responsive, targeted drug release. Carbohydr Polym. 2023;300:120213.
[65] KWON YS, KU SK, LEE DG, et al. Effect of carboxymethyl chitosan on the corneal alkali burn injury in dogs. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2014;55(13):5165-5165.
[66] XU W, WANG Z, LIU Y, et al. Carboxymethyl chitosan/gelatin/hyaluronic acid blended-membranes as epithelia transplanting scaffold for corneal wound healing. Carbohydr Polym. 2018;192:240-250.
[67] YEE KUEN C, MASARUDIN MJ. Chitosan nanoparticle-based system: a new insight into the promising controlled release system for lung cancer treatment. Molecules. 2022;27(2):473.
[68] 马高阳,蔡岩,李文静,等.替加环素/壳聚糖纳米粒对碱烧伤角膜新生血管的作用[J].眼科新进展,2020,40(9):831-836.
[69] 鲁静,武士科,陈光,等.玻璃酸钠壳聚糖纳米粒对烧伤角膜新生血管生长的影响[J].中国组织工程研究,2016,20(52):7803-7808.
[70] 邬桂玉,赵敏,计岩.溴芬酸钠/壳聚糖纳米粒蛋白胶胶联羊膜的制备及其对兔角膜新生血管的影响[J].第三军医大学学报,2013,35(6):495-499.
[71] FEIG VR, TRAN H, BAO ZN. Biodegradable polymeric materials in degradable electronic devices. ACS Cent Sci. 2018;4(3):337-348.
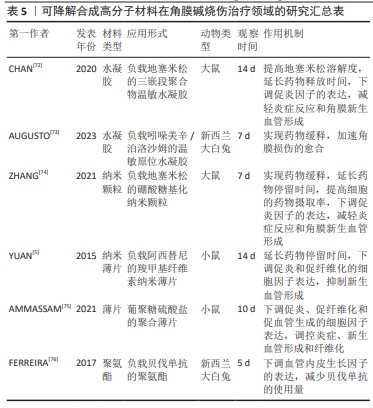
[72] CHAN PS, LI Q, ZHANG B, et al. In vivo biocompatibility and efficacy of dexamethasone-loaded PLGA-PEG-PLGA thermogel in an alkali-burn induced corneal neovascularization disease model. Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 2020;155:190-198.
[73] AUGUSTO DE CASTRO M, HENRIQUE REIS P, FERNANDES C, et al. Thermoresponsive in-situ gel containing hyaluronic acid and indomethacin for the treatment of corneal chemical burn. Int J Pharm. 2023;631:122468.
[74] ZHANG Y, YU Y, LI G, et al. Bioadhesive glycosylated nanoformulations for extended trans-corneal drug delivery to suppress corneal neovascularization. J Mater Chem B. 2021;9(20):4190-4200.
[75] AMMASSAM VEETTIL R, MARCANO DC, YUAN X, et al. Dextran sulfate polymer wafer promotes corneal wound healing. Pharmaceutics. 2021;13(10):1628.
[76] FERREIRA AE, CASTRO BF, VIEIRA LC, et al. Antiangiogenic activity of a bevacizumab-loaded polyurethane device in animal neovascularization models. J Fr Ophtalmol. 2017;40(3):202-208. |