中国组织工程研究 ›› 2025, Vol. 29 ›› Issue (16): 3458-3468.doi: 10.12307/2025.421
• 生物材料综述 biomaterial review • 上一篇 下一篇
骨组织工程中传统与仿生支架结构设计的差异
赵 越,许 燕,周建平,张旭婧,陈宇彤,靳正阳,印治涛
- 新疆大学机械工程学院,新疆维吾尔自治区乌鲁木齐市 830047
-
收稿日期:2024-03-13接受日期:2024-04-19出版日期:2025-06-08发布日期:2024-09-05 -
通讯作者:许燕,教授,博士生导师,新疆大学机械工程学院,新疆维吾尔自治区乌鲁木齐市 830047 -
作者简介:赵越,女,2000年生,山西省大同市人,汉族,在读硕士,主要从事骨组织工程、骨支架的制备与性能研究。 -
基金资助:国家自然科学基金项目(52365053),课题名称:载三联药装配式骨支架制备及多激励源控释特性研究,项目负责人:许燕
Differences in structural design between traditional and bionic scaffolds in bone tissue engineering
Zhao Yue, Xu Yan, Zhou Jianping, Zhang Xujing, Chen Yutong, Jin Zhengyang, Yin Zhitao
- School of Mechanical Engineering, Xinjiang University, Urumqi 830047, Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, China
-
Received:2024-03-13Accepted:2024-04-19Online:2025-06-08Published:2024-09-05 -
Contact:Xu Yan, Professor, Doctoral supervisor, School of Mechanical Engineering, Xinjiang University, Urumqi 830047, Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, China -
About author:Zhao Yue, Master candidate, School of Mechanical Engineering, Xinjiang University, Urumqi 830047, Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, China -
Supported by:National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 52365053 (to XY)
摘要:
文题释义:
骨组织工程:是一门融合了生物学、工程学和材料科学等诸多领域的综合性学科,以“开发出与人体自然骨组织结合的功能性支架”为主要研究目标,以解决植入物无法与宿主骨融合的问题,从而达到骨缺损修复的目的。其中,支架材料、种子细胞及细胞因子是骨组织工程中的三大关键要素。
仿生支架:一种模仿天然组织复杂结构和微观生理环境及功能的多孔支架,或者用于模仿自然界生物系统某些特征的支架。这种多孔结构的支架有利于营养物质的流通与成骨细胞的长入,同时也可促进血管内皮细胞附着和增殖,以支持新生血管的形成和长入,在满足人体机械性能的同时又具备良好的生物活性和可降解性。
背景:多孔支架作为新骨生长的临时基质在骨修复过程中起着关键作用,其中多孔支架的结构设计是骨修复过程中的研究重点。
目的:综述传统支架(规则、均匀的支架)和仿生支架(不规则、不均匀的支架)在骨组织工程研究领域的应用。
方法:检索中国知网(CNKI)、维普、万方、Web of Science、Science Direct、PubMed、EI等数据库,选取2008年1月至2024年3月发表的文献,中文检索词为“骨组织工程,仿生支架,骨小梁,传统支架,骨修复,三周期极小曲面”,英文检索词为“bone tissue engineering,bionic scaffolds,bone trabeculae,traditional scaffolds, bone repair,TPMS”。最终纳入81篇文献进行综述。
结果与结论:骨支架的结构设计是实现骨修复和骨再生的关键,骨组织工程中的支架技术已取得显著进展。传统的规则多孔支架因简单的制造流程和良好的机械性能被广泛应用,然而这类支架往往缺乏生物活性,难以模拟自然骨组织的复杂微环境,限制了其在促进细胞增殖和骨再生方面的能力。相反,仿生支架通过模拟自然骨组织的结构特征,提供了更适宜的生理微环境,促进了成骨细胞的增殖、分化及新骨的形成,为骨缺损有效治疗提供了新的思路。尽管仿生支架在理论上具有巨大的潜力,但在实际应用中仍面临诸多挑战,支架的生物相容性、生物活性及长期稳定性等因素仍需通过临床试验进行进一步验证。
https://orcid.org/0009-0003-9720-253X (赵越)
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:生物材料;骨生物材料;口腔生物材料;纳米材料;缓释材料;材料相容性;组织工程
中图分类号:
引用本文
赵 越, 许 燕, 周建平, 张旭婧, 陈宇彤, 靳正阳, 印治涛. 骨组织工程中传统与仿生支架结构设计的差异[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2025, 29(16): 3458-3468.
Zhao Yue, Xu Yan, Zhou Jianping, Zhang Xujing, Chen Yutong, Jin Zhengyang, Yin Zhitao. Differences in structural design between traditional and bionic scaffolds in bone tissue engineering[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(16): 3458-3468.
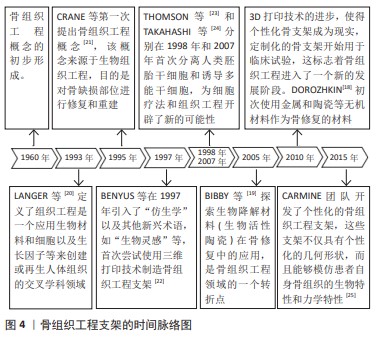
2.2 传统支架(规则多孔支架) 不少学者对多孔支架的结构和材料进行了广泛研究,其中多孔支架的结构设计是研究重点也是研究难点。目前,多孔支架的结构设计主要分为传统支架(规则多孔支架)和仿生支架(不规则多孔支架)[26]。传统的骨缺损修复支架大多是均匀、规则的几何体,拥有均匀、规则的孔径和孔隙率,具有周期性的结构,例如:单胞阵列法、拓扑优化法、三周期极小曲面法制备的多孔支架,这些支架往往由坚固的材料制成(如钛合金),以保证足够的机械强度来支撑缺损区域。
规则骨支架的孔径和孔隙率是这些支架设计中的关键参数,它们影响着细胞进入支架的能力、新骨形成的速率以及营养物质和代谢产物的运输。理想情况下这些孔隙应该是相互连通的,以模拟天然骨组织的三维网络结构,这样可以最大限度地增强生物活性和骨再生潜力。
孔隙率是影响支架力学性能的主要因素,孔隙率越低,支架的力学性能越好;相反,孔隙率越高,支架的力学性能越差。因此,在设计用于骨科植入物的支架时,必须在孔隙率(以促进生物相容性和骨组织生长)与足够的力学性能(以承受生物体内的负荷)之间找到平衡。对于支架的生物相容性和骨诱导性,既要关注支架的孔隙率,同时也需要对支架的渗透率、流速等进行测试。而上述研究仅对支架的孔隙率和力学性能进行了研究,缺乏对支架渗透率、流速的探究。下面这些研究发现关渗透率与流速会对支架产生一定的影响:XU等[30]设计出了圆柱形和球形2种支架结构,通过比较发现球形晶胞结构的支架在受压下能够更均匀地分散应力,并且孔隙率较高;而圆柱形晶胞结构则在机械稳定性和渗透性方面表现良好;HUANG等[31]采用选择性激光熔化技术制备了金刚石晶胞、菱形十二面体晶胞结构的多孔钛合金支架,通过机械测试和细胞实验发现该晶胞结构具有类似于骨小梁的机械强度,细胞染色实验则证明了骨支架具有成骨性能,可以在不同水平上调节整合素连接激酶/细胞外调节蛋白激酶1/2/Runx2信号通路,为细胞的增殖、分化提供适宜的生理环境。 在设计人工骨支架时除了考虑孔隙率之外,还需要考虑孔洞的大小、形状和分布。理想的支架孔洞大小通常在100-600 μm之间,这有利于细胞进入和营养物质的交换,而孔洞的三维网络结构有助于骨组织的生长和血管形成。PENG等[32]采用镁锶改性的羟基磷灰石为基底材料,设计了一种孔径分布在10-70 μm、通孔结构为300-500 μm的支架结构,对支架进行细胞染色实验、降解实验,发现孔径在300-500 μm范围内的支架可为营养物质的运输和细胞迁移提供通道,通过体外碱性磷酸酶活性检测发现该支架没有细胞毒性并具有良好的成骨活性。XIA等[33]采用激光粉末床熔融技术制备具有金刚石结构、孔径为600 μm的纯锌多孔支架,通过力学实验得出该支架的弹性模量满足人体骨小梁的弹性模量,可以为骨骼提供适当的机械支撑,避免了应力屏蔽效应;通过生物细胞实验发现该支架结构可从周围骨骼中募集细胞并促进营养扩散和血管化,表现出来良好的体外细胞相容性和促成骨能力。QIU等[34]采用渗透铸造法制备多孔锌-0.8锂(Zn-0.8Li)合金支架,不同孔径的支架均具有良好的孔隙连通性,大孔径(120-440 μm)支架孔的连通性相对较好,孔的结构更加均匀,有利于细胞和血管的正常生长以及氧气和营养物质的运输,最终促进新骨组织的生长。 2.2.2 拓扑优化法 拓扑优化法的主要思想是在满足给定范围的载荷约束情况、性能要求下,对材料在某一范围内的分布进行优化,是结构优化的一种[35]。实际上,多孔支架的拓扑优化是通过对单胞的拓扑优化来间接实现的,拓扑优化后的单胞结构就是最优的,再对其进行周期性的阵列或布尔运算,将其进行规律的排列和分布,从而形成结构均匀的三维结构。 岳怀俊等[36]采用各向同性材料惩罚模型,以保证髋关节植入体疲劳寿命且减小应力遮挡效应为优化目标,对植入假体进行结构优化,优化后的假体疲劳性能随孔径的增大而降低,应力遮挡随孔径的增加而减小,优化后假体的近端降低假体刚度,减小了整体应力遮挡,使假体的总体疲劳性能得到了提高。CHENG等[37]通过拓扑优化设计了一种具有复杂结构的聚醚醚酮下颌骨模拟物,以应力为优化目标,对载荷和边界进行约束,发现优化后模型的最大应力和位移远低于优化前的模型,创建了更多的正常应力-应变曲线,为外科下颌重建提供更好的功能和外观。SCHOTTEY等[38]基于对植入物在失效、稳定性和应力屏蔽方面的性能评估,对植入物进行了拓扑优化,获得了较高稳定性、利于骨向内生长的骨植入物,减小了潜在的应力屏蔽区域。LI等[39]采用选择性激光熔化技术,通过结构拓扑优化构建了一种基于面心立方晶胞的多孔结构,与传统方法设计的晶胞相比,该拓扑优化的晶胞具有更高的相对弹性模量,产生的位移和应力分布较均匀,优化后的晶胞节点更平滑,改善了细胞黏附和营养运输,降低了应力集中现象,提高了支架的生物相容性。LIU等[40]通过引入网格点密度对晶胞进行拓扑边界优化,分别将优化后的晶胞按周期性排列获得支架结构,以弹性模量和孔隙率为目标设计了一种与松质骨各向异性、弹性模量相匹配的骨支架结构,优化后的支架可以更均匀地将应力传递到松质骨上,并且晶胞边界清晰平滑,3个方向上都有相互连接的孔隙,这有利于营养物质的运输和代谢废物的清除,这种平稳的负荷转移可以减少骨吸收的高应力和低应力集中区域。LI等[41]以渗透率、力学性能为优化目标对三周期极小曲面晶格进行拓扑优化,在孔隙率特定的情况下,P晶格的弹性模量和渗透率提高了四五倍,G晶格的比表面积和孔径分别增加了7倍,优化后的支架在满足最小生物学性能的同时比表面积和孔径大小都具有很高的可调性。
以上研究发现,经过拓扑优化后能够确保骨支架具有最佳的力学性质,如强度、刚度和韧性,以承受体内的负载条件,这意味着支架能够更有效地支持受损骨骼的修复过程,同时减少因过度负载或不适当负载而导致支架失败的风险;经过拓扑优化后的支架具有促进骨生长的特殊表面特性和孔隙结构,这些特性能够加速成骨细胞在支架上的增殖和分化,优化后的孔隙率和孔径大小有助于血管生长和营养物质的传输,从而促进骨再生。 2.2.3 三周期极小曲面法 三周期极小曲面法的概念于1883年被SCHWARZ及其学生NEOVIUS提出[42]。三周期极小曲面法常被用于构建多孔支架,它在任意一点处的平均曲率均为零,孔洞连通度高且具有一定的周期性,可以通过改变表达式中的参数来调节支架的孔隙率与形状。其中常见的三周期极小曲面法类型包括P型、G型、D型(图5)。 KLADOVASILAKIS等[43]采用熔丝技术,使用聚乳酸材料制备G型、D型、P型单元的三周期极小曲面晶胞结构,在准静压缩下进行测试,发现D型结构表现出最高的机械强度,G型具有与D型结构相似的机械强度,而P型结构的机械强度最低。SUN等[44]采用选择性激光熔化技术制备了3种片状结构,通过压缩实验发现该结构的压缩力学性能与相对密度呈近似正相关关系,P型结构的应力波动较大,相比之下,G型和D型结构具有较低的应力波动。CUI等[45]采用选择性激光熔化技术制备互联孔梯度三周期极小曲面结构,压缩实验显示,与G型晶胞相比,D型晶胞表现出优越的力学性能,具有较高的抗弹性变形能力和极限压应力。CAO等[46]设计了2种具有均匀和渐变壁厚的Schwarz P(P)和Gyroid (G)结构,通过压缩和拉伸实验发现,G型结构的承载能力均优于P型结构,P型梯度结构的抗压强度均不如均匀结构;在拉伸载荷作用下,两种均匀的P型、G型结构均优于梯度结构。
以上研究仅关注了不同三周期极小曲面结构对支架生物力学环境及机械性能产生的影响,缺乏对支架的生物学性能评估。支架的结构参数(如孔径、孔隙率和表面粗糙度)会影响成骨性能和再生骨的结构,对细胞的增殖攀附、血管的长入也会存在一定的影响。
KARAMAN等[47]通过D型、G型和I-WP型三周期极小曲面结构分别设计了60%,70%和80%孔隙率的网状和片状结构,利用流体动力学对支架的渗透率、流体产生的壁面剪切应力和流速进行了探究,发现支架的渗透率值在(1.06-12.8)×10-9 m2之间,都与小梁骨结构相似,该支架能为黏附在表面的细胞生长提供足够的营养,具有良好的生物相容性和骨诱导性。ZHOU等[48]采用激光粉末床融合技术制备了3种固定孔隙率的G型、D型、P型结构,基于流体力学模拟仿真3种结构的渗透性和流动性能,实验发现G型结构具有良好的流动性,在满足人体骨细胞生长的方面可以作为骨科植入物。LI等[49]采用立体光刻技术制备了不同β-磷酸三钙含量的G型结构生物陶瓷支架,通过力学、生物实验发现,基于三周期极小曲面的G型结构具有良好的机械性能、降解性能和骨黏结能力。孙亚迪等[50]探究了具有三周期极小曲面结构支架的性能与微观结构之间的影响,发现P型结构拥有最大的孔隙率,展现出优异的稳定性和促进细胞增殖的能力;而D型结构则在刚度和屈服强度方面表现更为出色。

流速在三周期极小曲面结构用于骨修复中起着至关重要的作用,它通过促进营养物质的有效传输和代谢废物的及时排除直接影响细胞的黏附、增殖和分化,从而加速骨组织的再生。合理的流速还能通过机械刺激(如剪切力)促进血管生成和细胞的成骨活性,为新生骨组织提供充足的营养和氧气(图6)。因此,精确控制三周期极小曲面结构中的流速,不仅可以创造一个有利于细胞生长和分化的微环境,还可以通过力学刺激进一步促进骨修复和再生,显示出在骨组织工程中的巨大潜力和应用价值。
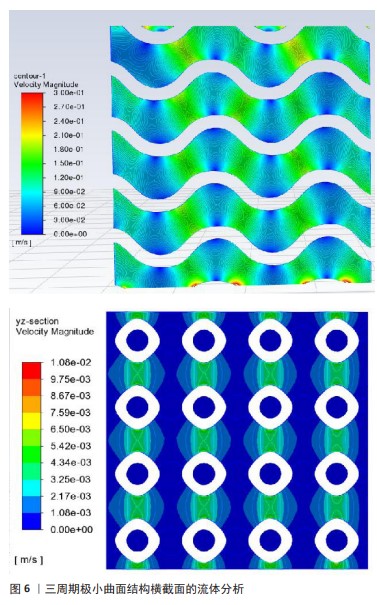
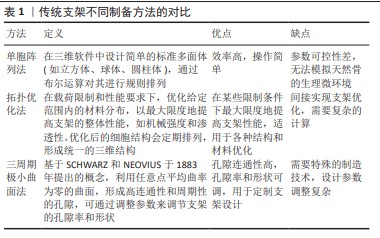
表1对传统支架的各种制备方法进行了清晰比较。由规则、均匀的晶胞构成的骨支架内部结构简单,易于控制,机械性能可预测,但边缘棱角尖锐,导致无法与人体原生骨紧密贴合,出现组织结合和互连失败的现象[50]。尽管确保了骨支架的孔径与孔隙率达到一定标准,但与真实骨结构及生理微环境之间仍存在显著差异,可能引发死腔现象,成为治疗过程中的新风险。 在临床应用中,尽管规则支架在机械性能上表现出色,但由于缺乏对患者骨解剖结构的适应性,可能会在生物相容性和功能性方面存在局限。因此,在设计这类规则支架时需要仔细考量植入后的细胞反应和组织融合效果,以保证修复效果和患者安全。
支架的力学性能(包括压缩应力、屈服应力和应力传导能力)直接受孔隙结构的影响。由于不同孔隙结构中的应力分布多样性,破坏方向也会受到孔隙几何形状的影响。梯度结构中的应力可以从上到下逐渐减小,但是均匀结构不能表现出这种特性,它在顶部和底部具有相同的应力水平,这表明应力屏蔽更有可能发生在均匀支架周围,因为应力可以很容易地在这种类型的多孔结构中传导。因此,传统的均匀多孔支架难以模仿天然骨骼的力学性能和生物相容性。基于这些证据,多孔支架结构设计的改进具有非常重要的意义,与此同时,仿生支架的设计理念——模仿自然界中的生物结构,在构建高性能骨组织工程方面备受关注,使得制造更复杂的多孔结构成为可能,为个性化医疗提供了更加复杂且功能化的解决方案。
2.3 仿生支架(不规则多孔支架) 大量错综复杂的多孔结构在自然界中随处可见,例如蜂窝、珊瑚、海绵、昆虫鞘翅、蜘蛛网、莲藕、天然丝瓜络、叶子,这些天然的多孔结构吸引着大量学者设计各类仿生多孔结构[51]。与规则多孔支架相比,随机形态产生的不规则晶胞结构增强了仿生学与生物医学的联系,改善了支架的应力分布,增强了生物整合[52-53]。
2.3.1 仿动植物、蜂窝结构 WANG等[54]使用自体移植材料(颞筋膜和气软骨)制备仿生蜘蛛网支架,通过创建壳耦合条件和强耦合边界条件来修复鼓膜穿孔,结合蜘蛛网在受载作用下具有优异的变形特性,植入后与天然骨膜具有相似的声传导能力,显著提高了耳骨修复效果。ZHAO等[55]受天然蜘蛛网的启发,采用双射流同步静电纺丝法制备了多尺度结构的聚乳酸纳米纤维膜,这种具有蜘蛛网状的纤维膜有更优异的过滤性能和良好透气性,层状结构的形成增强了纤维膜的疏水性和机械强度,能承载更大的载荷和抵抗弹性变形,具有良好的韧性。SHI等[56]采用生物3D打印技术制备了仿生莲藕结构支架,这种结构结合了空心薄壁多孔结构和横截面致密多孔结构的特点,引入等质量的空心圆管和空心方管,通过横向载荷和准静态力学模拟实验发现该支架具有优良的抗压抗弯性能,通过有限元分析发现该结构具有一种负泊松比特性,显著增强了承载特性。CHEN等[57]采用短切玄武岩纤维为增强材料和双酚A二缩水甘油醚(A-E51)环氧树脂为基体材料,提出了一种仿生全集成蜂窝板小梁结构的设计方法,该仿生结构具有良好的力学性能,并且质量和压缩强度都优于同类仿生结构;通过对仿生蜂窝板的结构进行优化,克服了小梁结构在抗压性能方面的弱点,在失效前表现出优异的完整性和抗压性能。CHEN等[58]受生物结构优化材料设计的启发,通过仿生甲虫前翅的结构发现,纤维交联形成的网状结构提高了二维强度;在层压层之间通过小梁结构提高了三维强度,这种层层堆叠的结构有利于加强支架的力学性能。FU等[59]设计了6种不同截面构型的仿生竹管结构,通过研究“X”形截面构型肋角、中心距和肋骨厚度的影响发现,仿生结构的能量吸收明显高于传统的多细胞管,竹竿的空心圆柱形分布相对均匀,使支架具有优越的结构稳定性和较强的抗弯曲变形能力。 ZHANG等[60]根据红耳龟壳背甲的结构和各层特征,考虑壳背甲的精细结构,将碳纤维和发泡硅橡胶材料制成了一种仿生龟壳背甲的夹层结构,通过低速冲击实验和有限元仿真分析发现:在受到低速冲击载荷时,大部分能量在切向方向上消散,一小部分能量在法向方向上消散,夹层结构的吸收能量和比能量吸收增加,这使得仿生夹层结构具有优异的抗冲击特性。
以上研究只关注了仿生结构对力学性能产生的影响,虽然支架的材料和结构对支架机械性能也会产生一定影响,但植入人体后的骨支架在满足力学性能的同时还需要具有一定的生物相容性和可降解性,而上述研究缺乏仿生支架结构对生物学性能的研究与探索。
YU等[61]设计了一款仿生叶脉的结构,对仿生系统进行肿瘤细胞培养和血栓裂解实验,结果发现该系统具有血管内营养物质流通的能力,这种仿生结构可以提供均匀稳定的液场,性能强劲,有利于细胞的生长和附着;叶脉上微小的孔隙通过控制相关物质的流入和流出来促进流体的运动,有利于后期营养物质的运输及新骨的长入;在微米和纳米尺度上制造叶脉形状可以增强仿生材料的力学性能。CHEN等[62]模仿具有高孔隙率和连通性的天然丝瓜络空间网状结构,通过立体光刻技术制备了多孔仿生松质骨结构支架,通过体内细胞实验发现,毛细血管均匀地分布在骨支架表面,支架有更高的比表面积,有利于成骨细胞的攀附和再生,具有良好的成骨性能;经过脱脂烧结工艺后得到了具有适当孔径和孔隙率的仿生支架,同时提升了支架的压缩性。HAYASHI 等[63]制造了碳酸盐磷灰石蜂窝支架,通过调整支柱厚度(100,200,300 μm)来控制支架的吸收率和机械强度,将支架植入兔颅骨后观察4周发现,蜂窝式支架在垂直方向有新骨生成;第8周时所有支架中新骨的高度和数量都有所增加,甚至支柱厚度越厚形成血管的直径越大,因此蜂窝式结构式天生适合垂直增骨。值得注意的是,具有300 μm厚支柱支架增强了新骨形成和血管生成,这种单轴通道有利于骨和血管的向内生长,具有骨诱导性和骨传导性。
WENG等[64]在兔模型中使用连续培养方法培养分离骨髓间充质干细胞以形成成骨细胞片,通过诱导轴向血管化将成骨细胞与天然珊瑚支架结合起来,通过动物实验发现术后12周血管生成更明显;骨髓间充质干细胞在成骨培养基培养2周后获得成骨能力并黏附在仿珊瑚支架上,使支架具有促进新骨再生和血管生成的能力。WANG 等[65]将自体脂肪干细胞成骨片与珊瑚支架相结合,通过碱性磷酸酶活性测定和茜素红染色发现形成了很多高密度的复合物组织、钙沉积物,具有一定的成骨能力。珊瑚支架的多孔结构不仅提供了较大的表面积来增加细胞附着、迁移和向内生长,而且还促进了细胞代谢活动和所需营养物质的运输。
ZENG等[66]将三维明胶海绵支架作为脊髓损伤治疗中细胞和营养因子的递送载体,发现损伤/植入界面处的α-平滑肌肌动蛋白阳性细胞显著减少,从而减轻了残余脊髓组织的纤维化压迫;支架中的再生组织显示许多细胞迁移到植入物中,分泌丰富的细胞外基质,从而形成有利于再生的微环境;支架植入也没有增加受伤部位已经存在的神经炎症或星形胶质细胞反应,表明支架具有良好的生物相容性,有助于损伤脊髓的结构修复。
通过上述研究发现,仿生结构设计来源于对高分子结构优异功能的深入理解,如材料的力学稳定性、支架的局部结构和化学组成,仿生支架不仅能模仿天然细胞外基质的物理和化学环境,促进细胞增殖和增殖,还可以通过设计其孔隙率和孔径大小来匹配骨组织修复的速度,从而进一步减少骨植入物长期滞留体内的风险。通过仿生原理设计的支架结构,能够在保证机械强度的同时优化生物相容性和促成骨能力,使其在骨修复方面产生巨大的潜力。2.3.2 仿生结构 骨质构成了骨骼的主要部分,依据其密集程度不同可分为致密的骨密质(又称皮质骨)和较为疏松的骨松质(也称为骨小梁)。
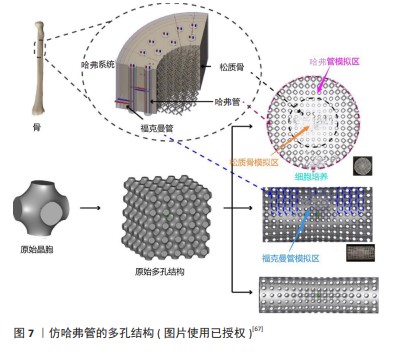
(1)仿哈弗管结构(仿Haversian结构):骨密质的结构特别复杂,主要由规律性强且紧凑排列的骨板层构成,这些层次相互交错形成的密集结构,从根本上赋予了骨密质出色的抗压、抗拉和抗扭能力。哈弗管结构通常位于长骨的骨干部分和不规则骨的外表层。
在骨骼中,所谓的“哈弗管”实际上指的是哈弗系统或骨质小管中的中心管道。哈弗系统是密质骨中的基本结构单元(图7),位于内外骨板之间,通过观察骨单位的横截面发现骨板同心排列形成了独特的圆柱形结构。哈弗管在哈弗氏系统的中心,它贯穿着重要的血管、淋巴管和神经纤维,可以确保骨组织得到充足的营养供应和有效的废物排出。哈弗系统对维持整个骨骼系统的功能和健康发挥着关键作用,对骨骼的修复和重塑过程也至关重要。
LI等[67]利用三周期极小曲面法设计了一种孔径从两端到中心部分逐渐减小且类似哈弗系统的梯度多孔支架,利用有限元分析技术、计算机模型和偏微分方程预测骨向内生长情况,通过力学测试发现仿哈弗管支架可以改善应力屏蔽现象,而在计算机流体动力学分析中表现出良好的渗透率和细胞迁移流动特性,表明该梯度结构较均匀支架表现出更明显的血管化、更好的生物相容性和更强的成骨特性,可以为血管形成和骨生长提供合适的微环境。ZHANG等[68]受到天然骨组织多层次结构的启发,制备了一种多细胞负载的仿哈弗管生物陶瓷支架,利用支架的分层结构将间充质干细胞和巨噬细胞分布在特定的空间位置,实现了物理结构和细胞分布的双向仿生构建,这种仿生构建激活了免疫细胞与成骨细胞的信号通路,表现出了相对较高的成骨潜力。BIAN等[69]通过巧妙地堆叠仿生哈弗管(层状圆柱形序列)制备了磷酸钙水泥/小肠黏膜下层复合支架,该序列可以形成类似于天然骨骼中哈弗管的微观结构,将其在模拟体液中浸泡6 h支架的抗压强度提高了3倍,它较大的比表面积和孔隙率以及100-400 μm的孔径结构,有利于细胞的附着、生长、迁移和血管的长入,适合体内植入和骨重塑。ZHANG等[70]利用数字激光处理技术成功打印了具有集成分层哈弗管骨结构的生物陶瓷支架,通过3D建模软件调整仿哈弗管结构参数控制支架的抗压强度和孔隙率,通过细胞共培养实验发现,该支架具有体外诱导成骨、血管生成和神经源性分化的能力,可以加速体内血管的向内生长和新骨形成。MAYYA等[71]的研究发现,仿哈弗管比非哈弗管骨具有更高的抗压强度,哈弗管密度较高的部位表现出较高的抗压强度;通过压缩实验获得的骨折微观表面发现,非哈弗管骨标本呈现棱柱形断裂表面,平面外碎片极少,而哈弗管骨标本的断裂表面具有三维外观。
通过以上研究发现,仿哈弗管支架是一种模仿天然骨组织中哈佛系统结构的生物支架,这种设计理念旨在模拟天然骨内部的微观结构,实现更接近自然骨骼的力学性质,包括强度和韧性。这种结构能够有效地改善支架力学性能和生物学性能,承载并分散施加于骨骼上的压力,减少断裂风险,从而促进骨组织的修复和再生。仿哈弗管支架的微管道结构为细胞提供了迁移通道,支持血管内皮细胞的吸附和增殖,促进了营养物质和代谢产物的有效交换,这对于维持植入区域的细胞活性和促进新骨形成至关重要。采用可降解生物活性材料设计的仿哈弗管支架通常具有良好的生物降解性,能够随着新骨组织的形成而逐渐降解,最终完全由自体骨组织替代,实现与周围组织的无缝整合。总体而言,仿哈弗管支架通过模仿天然骨骼的结构特征,不仅能满足人体缺损处的力学性能,而且在促进组织再生和修复等方面存在巨大的潜力。
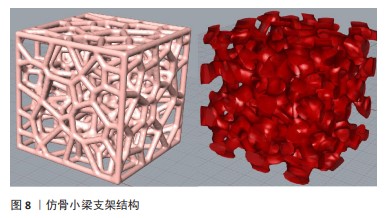
(2)仿骨小梁结构:骨松质由众多针状或片状骨板交织而成,形成了类似海绵或网络的骨小梁结构,这些结构的排列方向与骨承载的方向相匹配,使其能够承担较大的质量。因此,骨松质不仅起到支撑和减轻骨骼质量的作用,还具备缓冲冲击、容纳骨髓和适应形变的功能(图8)。由于骨松质较疏松的结构特点,常分布在长骨的端部、短骨、扁骨以及不规则骨的内部,尽管骨松质仅占人体骨量的20%,却构成了骨骼表面80%的面积。人体骨骼中的骨小梁部分有着不规则的孔径大小和孔隙、高度组织化的结构,因此不规则性是人体骨骼的天然特性[72]。
各研究团队通过不同技术和工艺来设计和评估仿骨小梁支架在骨修复和骨再生方面的力学性能和生物学性能。WANG等[73]利用沃罗诺伊图-泰森多边形,采用概率球法生成不规则形态但力学性能可控的多孔支架,探究了3个可变参数(孔隙率、不规则度、孔径)对支架力学性能的影响,通过压缩实验发现,支架的抗压强度与孔隙率呈幂函数关系,并且抗压强度随不规则度的增加呈现出较大波动,表观弹性模量与孔隙率呈强线性关系;通过不规则系数控制和表征多孔支架的不规则程度发现,仿骨小梁支架的孔隙率可达60%-85%,孔径在200-1 200 μm范围内,并且支架的压缩性能可以调整到皮质骨水平,抗压强度在不规则程度较强时增加,可以获得高强度、低刚度的多孔结构。徐淑波等[74]基于沃罗诺伊图-泰森多边形设计了一种仿骨小梁的多孔结构,对不同孔隙率下标准多孔结构和沃罗诺伊多孔结构进行静态模拟仿真,与标准结构相比,沃罗诺伊结构表现出更均匀的连杆分布,具有更好的抗压缩变形能力,可有效降低应力屏蔽效应,减少支架与骨组织之间的摩擦,并且沃罗诺伊结构的最大等效应力远低于标准结构,最大应力点位置较高,具有优异的抗压缩变形能力;经过应力分析最终得出,75%孔隙率的沃罗诺伊结构最适合作为人骨植入物。KONG等[75]提出了一种基于黏菌算法的仿生骨小梁支架,通过压缩实验、摩擦实验、流固耦合实验等发现,该支架有良好的承载能力和渗透性、耐磨性,弹性模量在天然松质骨的范围内,有利于后期营养物质的交换,为成骨细胞的生长和植入提供更高的服务可靠性。用作植入物的仿生支架不仅需要足够的机械性能和可靠的耐磨性,还需要适当的应力刺激和渗透性,以促进植入后成骨细胞的生长和分化,可靠的稳定性和更高的渗透性是有助于提高多孔植入物骨传导能力的重要因素。汤永锋及其团队[76]利用光固化技术和沃罗诺伊图设计出4种具有不同梯度的多孔结构,通过横向和纵向压缩测试发现,这些梯度多孔结构在横向压缩下的表现与均匀多孔结构类似,而在纵向压缩下则呈现出分层坍塌的特性;在相似孔隙率的条件下,梯度变化对纵向压缩的支架力学性能有所影响,但对横向压缩的支架力学性能影响不大,最终发现减小梯度多孔结构的平均孔隙率有助于增强支架的力学性能。WANG等[77]采用了激光熔融技术制造了孔径均匀的立方体和骨小梁结构的多孔钽支架,结果表明该仿生骨小梁结构对细胞增殖分化起促进作用,并且力学性能更接近人体松质骨,在相同孔隙率条件下骨小梁结构表现出较低的抗压屈服强度和弹性模量。这种包含大孔和小孔的不均匀结构是确保营养物质流通、成骨细胞黏附的关键。刘俭涛等[78]采用选择性激光熔融技术设计了相同孔隙率和孔径大小的钛合金(Ti6Al4V)仿生和规则多孔支架,通过吖啶橙和鬼笔环肽/DAPI染色法评估细胞附着情况,发现在同等的孔隙和孔径条件下,仿生结构相较于规则结构更能促进成骨细胞的附着、生长和分化;此外,仿生结构上的骨细胞展现出更密集的分布,小鼠胚胎成骨细胞前体细胞(MC3T3-E1)的伪足更长且钙盐沉积更为丰富。LIU等[79]利用挤出成型技术和水热法制备了具有微/纳米羟基磷灰石表层的仿生分层结构支架,这种具有互连孔隙的生物陶瓷支架具有更高的比表面积,有利于小鼠骨间充质干细胞的黏附和成骨分化以及人脐静脉内皮细胞的血管生成基因表达,可以诱导皮质骨形成新骨,促进骨整合。
上述研究采用3D打印技术(光固化成型、挤出成型和激光熔融技术)与结构性能优化,通过调控支架孔径大小和孔隙率制备表面微纳米结构来对支架进行仿生。在与规则均匀的多孔支架对比后发现,仿骨小梁支架在促进血管生成和成骨细胞增殖方面有着天然优势,这种不规则的孔径和孔隙率是影响支架流速和渗透率的2个关键因素,它们共同影响支架的渗透性能,进而影响后期营养物质的交换、成骨细胞的黏附和血管的长入。理想情况下的支架应该具有足够大的孔径以促进流体流动和细胞迁移,同时保持高孔隙率以确保良好的渗透性和足够的机械强度。
CHEN等[72]基于沃罗诺伊(Voronoi)方法使支架维持恒定孔隙率,通过改变支架直径在不规则支架中产生梯度并对其进行渗透性仿真,结果表明不规则支架的微观结构与皮质骨和松质骨相似,具有优异的渗透性和良好的可控性,支架的渗透率随孔隙的增加而增加,相比于常规支架具有较好的应力分布。WANG等[80]采用选择性激光熔化技术设计了2种不同平均孔径仿骨小梁结构和规则结构的多孔钛合金支架,研究了不同孔形、孔径和孔隙分布对多孔钛合金支架骨整合能力的影响,发现随着多孔支架孔隙率的增加,支架屈服强度和抗压能力逐步减小,从而有效降低了应力屏蔽效果;通过生物细胞实验、碱性磷酸酶活性和染色测定发现,仿骨小梁结构支架具有更高的细胞存活率和生物相容性以及良好的骨整合能力。LI等[81]通过对人类椎体松质骨组织结构进行力学性能、渗透率和流体剪切应力研究,发现仿生骨支架在孔隙率低于人类椎骨的情况下具有相似的渗透率,当孔隙率大于70%时仿生骨支架渗透率大于椎骨(孔隙率82%)的渗透率范围,侧面证明了该仿生支架有利于细胞的增殖和分化,在微观结构、机械和流体性能上与天然人体松质骨骼非常匹配。
仿生支架作为一种骨植入物,通过模拟天然骨骼微观结构来促进骨组织的修复和再生,这些支架的设计充分考虑了骨组织的独特生物学、力学和结构特性,使其在骨科植入物中具有诸多优势。仿生支架独特的微观结构为成骨细胞提供了理想的附着环境,有助于成骨细胞的增殖和分化,进而加速骨组织的再生和愈合过程;仿生支架的结构设计经过优化,以增强与周围天然骨骼界面的相互作用,提高骨整合效率,能有效承受生理负荷;仿生支架设计还减少了应力屏蔽效应,即避免因植入物与天然骨之间的弹性模量差异过大而导致周围骨组织负载降低和逐渐吸收的现象,确保植入物的稳定性和长期性能。通过多孔结构仿生支架还促进了血管生成,为骨组织再生提供了必要的营养和氧气,其中良好的血管渗透性对于维持植入区域的生物活性和支持新骨形成至关重要。
| [1] 刘凯,艾合买提江·玉素甫.可生物降解金属支架修复长骨严重骨缺损[J].临床骨科杂志,2024,27(1):142-146. [2] LIU K, LIU Y, CAI F, et al. Efficacy comparison of trifocal bone transport using unilateral external fixator for femoral and tibial bone defects caused by infection. BMC Surg. 2022;22(1):141-141. [3] LIU Y, YUSHAN M, LIU Z, et al. Complications of bone transport technique using the Ilizarov method in the lower extremity: a retrospective analysis of 282 consecutive cases over 10 years. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2020;21(1):354. [4] 陈澍东,林宗汉.大块骨缺损治疗研究进展[J].新乡医学院学报, 2023,40(7):691-695. [5] ARO HT, VÄLIMÄKI VV, STRANDBERG N, et al. Bioactive glass granules versus standard autologous and allogeneic bone grafts: a randomized trial of 49 adult bone tumor patients with a 10-year follow-up. Acta Orthop. 2022;93:519-527. [6] HOFMANN A, GORBULEV S, GUEHRING T, et al. Autologous Iliac Bone Graft Compared with Biphasic Hydroxyapatite and Calcium Sulfate Cement for the Treatment of Bone Defects in Tibial Plateau Fractures: A Prospective, Randomized, Open-Label, Multicenter Study. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2020;102(3):179-193. [7] LI P, HONDA Y, ARIMA Y, et al. Interferon-γ enhances the efficacy of autogenous bone grafts by inhibiting postoperative bone resorption in rat calvarial defects. J Prosthodont Res. 2016;60(3):167-176. [8] DE PONTE FS, FALZEA R, RUNCI M, et al. Histomorhological and clinical evaluation of maxillary alveolar ridge reconstruction after craniofacial trauma by applying combination of allogeneic and autogenous bone graft. Chin J Traumatol. 2017;20(1):14-17. [9] HERNIGOU P. Bone transplantation and tissue engineering, part III: allografts, bone grafting and bone banking in the twentieth century. Int Orthop. 2015;39(3):577-587. [10] SINGH R, SINGH D, SINGH A. Radiation sterilization of tissue allografts: A review.World J Radiol. 2016;8(4):355-369. [11] 王金孟,杨智宇,雷浪,等.同种异体骨与异种骨对牙周骨下袋缺损再生治疗的疗效对比[J].遵义医科大学学报,2024,47(2):152-158. [12] 蔡元庆,刘谟震,李忠海.同种异体骨移植材料在脊柱融合中的应用[J].中国组织工程研究,2023,27(16):2571-2579. [13] WINKLER T, SASS FA, DUDA GN, et al. A review of biomaterials in bone defect healing, remaining shortcomings and future opportunities for bone tissue engineering: The unsolved challenge. Bone Joint Res. 2018;7(3):232-243. [14] XIE L, CHEN C, ZHANG Y, et al. Three-dimensional printing assisted ORIF versus conventional ORIF for tibial plateau fractures: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Int J Surg. 2018;57:35-44. [15] 王晓康.骨组织工程仿生多孔支架设计及性能分析[D].秦皇岛:燕山大学,2023. [16] LEE MS, TALLERICO V. Distraction Arthrodesis of the Subtalar Joint Using Allogeneic Bone Graft: A Review of 15 Cases. J Foot Ankle Surg. 2010;49(4):369-374. [17] 皇磊,王晓丽,王思明,等.骨组织工程支架的制备方法研究进展[J].中国组织工程研究,2024,28(29):4710-47161. [18] DOROZHKIN SV. Bioceramics of calcium orthophosphates. Biomaterials. 2010;31(7):1465-1485. [19] BIBBY JK, BUBB NL, WOOD DJ, et al. Fluorapatite-mullite glass sputter coated Ti6Al4V for biomedical applications. J Mater Sci Mater Med. 2005;16(5):379-385. [20] LANGER R, VACANTI JP. Tissue Engineering. Science. 1993;260(5110): 920-926. [21] MEINEL L, KARAGEORGIOU V, FAJARDO R, et al. Bone tissue engineering using human mesenchymal stem cells: effects of scaffold material and medium flow. Ann Biomed Eng. 2004;32(1):112-122. [22] HAN Z, JIAO Z, NIU S, et al. Ascendant bioinspired antireflective materials: Opportunities and challenges coexist. Prog Mater Sci. 2019; 103:1-68. [23] THOMSON JA, ITSKOVITZ-ELDOR J, SHAPIRO SS, et al. Embryonic Stem Cell Lines Derived from Human Blastocysts. Science. 1998; 282(5391):1145-1147. [24] TAKAHASHI K, TANABE K, OHNUKI M, et al. Induction of pluripotent stem cells from adult human fibroblasts by defined factors. Cell. 2007; 131(5):861-872. [25] LI J, JIANG P, YANG J, et al. Self-Reinforced PTLG Copolymer with Shish Kebab Structures and a Bionic Surface as Bioimplant Materials for Tissue Engineering Applications. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2024; 16(8):11062-11075. [26] 汤永锋,路平,刘斌,等.不同梯度变化方式的不规则多孔结构设计与力学性能分析[J].中国机械工程,2022,33(23):2859-2866. [27] MOARREFZADEH A, MOROVVATI MR, ANGILI SN, et al. Fabrication and finite element simulation of 3D printed poly L-lactic acid scaffolds coated with alginate/carbon nanotubes for bone engineering applications. Int J Biol Macromol. 2023;224:1496-1508. [28] AHMADI SM, YAVARI SA, WAUTHLE R, et al. Additively Manufactured Open-Cell Porous Biomaterials Made from Six Different Space-Filling Unit Cells: The Mechanical and Morphological Properties. Materials (Basel). 2015;8(4):1871-1896. [29] 孙海波,徐淑波,张森,等.SLM成形不同孔隙结构骨支架的仿真与实验研究[J].精密成形工程,2022,14(2):123-128. [30] XU B, LEE KW, LI W, et al. A comparative study on cylindrical and spherical models in fabrication of bone tissue engineering scaffolds: Finite element simulation and experiments. Mater Design. 2021; 211:110150. [31] HUANG G, PAN ST, QIU JX. The osteogenic effects of porous Tantalum and Titanium alloy scaffolds with different unit cell structure. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2022;2101:12229. [32] PENG RH, ZHAO Q, XIAO T, et al. Preparation and properties of magnesium/strontium modified hydroxyapatite whisker bone tissue engineering scaffold. Mater Lett. 2024;361:135922. [33] XIA D, QIN Y, GUO H, et al. Additively manufactured pure zinc porous scaffolds for critical-sized bone defects of rabbit femur. Bioact Mater. 2023;19:12-23. [34] QIU S, SUN F, YOU C, et al. Preparation of porous Zn-Li alloy scaffolds for bone repair and its degradation behavior in vitro and in vivo. Mater Today Commun. 2023;35:105605. [35] AL-TAMIMI AA,FERNANDES ARP, PEACH C, et al. Metallic bone fixation implants: a novel design approach for reducing the stress shielding phenomenon. Virtual Phys Prototy. 2017;12(2):141-151. [36] 岳怀俊,蒋文涛,徐凯仁.3D打印髋关节植入体疲劳性能的拓扑优化[J].医用生物力学,2019,34(S1):70. [37] CHENG KJ, LIU YF, WANG R, et al. Topological optimization of 3D printed bone analog with PEKK for surgical mandibular reconstruction. J Mech Behav Biomed Mater. 2020;107:103758. [38] SCHOTTEY O, HUYS SEF, VAN LENTHE GH, et al. Development of a topologically optimized patient-specific mandibular reconstruction implant for a Brown class II defect. Ann Print Med. 2023;10:100107. [39] LI H, YAO B, LI ZH, et al. Compressive properties and deformation mechanism of selective laser melting of Ti6Al4V porous femoral implants based on topological optimization. Compos Struct. 2023; 321:117326. [40] LIU M, WANG Y, WEI Q, et al. Topology optimization for reducing stress shielding in cancellous bone scaffold. Compos Struct. 2023; 288:107132. [41] LI Z, CHEN Z, CHEN X, et al. Multi-objective optimization for designing porous scaffolds with controllable mechanics and permeability: A case study on triply periodic minimal surface scaffolds. Compos Struct. 2024;333:117923. [42] STRMBERG N. Optimal grading of TPMS-based lattice structures with transversely isotropic elastic bulk properties. Eng Optim. 2021; 53(11):1871-1883. [43] KLADOVASILAKIS N, TSONGAS K, TZETZIS D. Mechanical and FEAassisted characterization of fused filament fabricated triply periodic minimal surface structures. J Compos Sci. 2021;5(2):58. [44] SUN Q, SUN J, GUO K, et al. Compressive mechanical properties and energy absorption characteristics of SLM fabricated Ti6Al4V triply periodic minimal surface cellular structures. Mech Mater. 2022;166: 104241. [45] CUI Y, GAIN KA, ZHANG L, et al. Manufacture and property characterization of interconnected pore-gradient TPMS materials. Mate Sci Eng A. 2024;892:146100. [46] CAO Y, LAI S, WU W, et al. Design and mechanical evaluation of additively-manufactured graded TPMS lattices with biodegradable polymer composites. J Mater Res Technol. 2023;23:2868-2880. [47] KARAMAN D, GHAHRAMANZADEH ASL H. The effects of sheet and network solid structures of similar TPMS scaffold architectures on permeability, wall shear stress, and velocity: A CFD analysis. Med Eng Phys. 2023;118:104024. [48] ZHOU J, GUI Y, XU Q, et al. Investigation of permeability and biocompatibility of TPMS structures printed by laser powder bed fusion using Ti64-5Cu alloy for orthopedic implants. Mater Lett. 2024; 355:135552. [49] LI M, JIANG W, LIU W, et al. Bioadaptable bioactive glass-β-tricalcium phosphate scaffolds with TPMS-gyroid structure by stereolithography for bone regeneration. J Mater Sci Technol. 2023;155:54-65. [50] 孙亚迪,马剑雄,王岩,等.三周期极小曲面骨支架微观结构对支架性能的影响研究进展[J].中国修复重建外科杂志,2023,37(10): 1314-1318. [51] FENG J, FU J, YAO X, et al. Triply periodic minimal surface (TPMS) porous structures: from multi-scale design, precise additive manufacturing to multidisciplinary applications. Int J Extrem Manuf. 2022;4(2):022001. [52] OKUBO S, YAMAUCHI Y, KITAZONO K. Effects of random and controlled irregularity in strut lattice structure of PA12 on compression anisotropy. Addit Manuf. 2023;63:103385. [53] REZAPOURIAN M, HUSSAINOVA I. Optimal mechanical properties of Hydroxyapatite gradient Voronoi porous scaffolds for bone applications - A numerical study. J Mech Behav Biomed Mater. 2023;148: 106232-106232. [54] WANG L, HAN H, WANG J, et al. Finite element analysis of repairing tympanic membrane perforation using autologous graft material and biodegradable bionic cobweb scaffold. Comput Methods Programs Biomed. 2023;243:107868-107868. [55] ZHAO Y, MING J, CAI S, et al. One-step fabrication of polylactic acid (PLA) nanofibrous membranes with spider-web-like structure for high-efficiency PM0.3 capture. J Hazard Mater. 2024;465:133232. [56] SHI L, TU F, YANG J. Mechanical behaviors of porous bionic structure of lotus stem. Int J Solids Struct. 2024;290:112665. [57] CHEN J, TUO W, ZHANG X, et al. Compressive failure modes and parameter optimization of the trabecular structure of biomimetic fully integrated honeycomb plates. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2016;69:255-261. [58] CHEN J, DAI G, XU Y, et al. Basic study of biomimetic composite materials in the forewings of beetles. Mater Sci Eng A. 2006;483(C): 625-628. [59] FU J, LIU Q, LIUFU K, et al. Design of bionic-bamboo thin-walled structures for energy absorption. Thin Wall Struct. 2019;135:400-413. [60] ZHANG D, GUO D, WANG F, et al. Low-velocity impact response of a novel bionic turtle shell back armor sandwich structure. J Mater Res Technol. 2024;29:910-923. [61] YU H, ZHANG J, ZHANG S, et al. Bionic structures and materials inspired by plant leaves: A comprehensive review for innovative problem-solving. Prog Mater Sci. 2023;139:101181. [62] Chen Q, ZOU B, LAI Q, et al. 3D printing and osteogenesis of loofah-like hydroxyapatite bone scaffolds. Ceram Int. 2021;47(14):20352-20361. [63] HAYASHI K, SHIMABUKURO M, KISHIDA R, et al. Structurally optimized honeycomb scaffolds with outstanding ability for vertical bone augmentation. J Adv Res. 2022;41:101-112. [64] WENG Y, WANG Z, SUN J, et al. Engineering of axially vascularized bone tissue using natural coral scaffold and osteogenic bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell sheets. J Stomatol Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2021; 122(4):397-404. [65] WANG Z, HAN L, SUN T, et al. Construction of tissue-engineered bone with differentiated osteoblasts from adipose-derived stem cell and coral scaffolds at an ectopic site. Br J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2020;59(1):46-51. [66] ZENG X, WEI QS, YE JC, et al. A biocompatible gelatin sponge scaffold confers robust tissue remodeling after spinal cord injury in a non-human primate model. Biomaterials. 2023;299:122161-122161. [67] LI L, WANG P, LIANG H, et al. Design of a Haversian system-like gradient porous scaffold based on triply periodic minimal surfaces for promoting bone regeneration. J Adv Res. 2023;54:89-104. [68] ZHANG B, ZHANG M, SUN Y, et al. Haversian bone-mimicking bioceramic scaffolds enhancing MSC-macrophage osteo-imunomodulation. Prog Nat Sci Mater. 2021;31(6):883-890. [69] BIAN T, ZHAO K, MENG Q, et al. Preparation and properties of calcium phosphate cement/small intestinal submucosa composite scaffold mimicking bone components and Haversian microstructure. Mater Lett. 2018;212:73-77. [70] ZHANG M, LIN R, WANG X, et al. 3D printing of Haversian bone–mimicking scaffolds for multicellular delivery in bone regeneration. Sci Adv. 2020;6(12):eaaz6725. [71] MAYYA A, BANERJEE A, RAJESH R. Haversian microstructure in bovine femoral cortices: An adaptation for improved compressive strength. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2016;59:454-463. [72] CHEN H, LIU Y, WANG C, et al. Design and properties of biomimetic irregular scaffolds for bone tissue engineering. Comput Biol Med. 2021;130:104241. [73] WANG G, SHEN L, ZHAO J, et al. Design and Compressive Behavior of Controllable Irregular Porous Scaffolds: Based on Voronoi-Tessellation and for Additive Manufacturing. ACS Biomater Sci Eng. 2018;4(2): 719-727. [74] 徐淑波,赵晨浩,刘建营,等.高孔隙度可再生骨支架仿真与实验研究[J].精密成形工程,2023,15(1):120-127. [75] KONG D, KANG Z, JIANG C, et al. Reinforcement of bionic trabecular bone scaffolds for bone defect repair using the slime mould algorithm. Mater Design. 2023;233:112184. [76] 汤永锋,路平,刘斌,等.不同梯度变化方式的不规则多孔结构设计与力学性能分析[J].中国机械工程,2022,33(23):2859-2866. [77] WANG X, ZHANG D, PENG H, et al. Optimize the pore size-pore distribution-pore geometry-porosity of 3D-printed porous tantalum to obtain optimal critical bone defect repair capability. Biomater Adv. 2023;154:213638-213638. [78] 刘俭涛,任志伟,张淑媛,等.仿生骨小梁与规则多孔结构骨整合性能的体外细胞学对比研究[J].西安交通大学学报(医学版), 2023,44(6):983-989. [79] LIU X, MIAO Y, LIANG H, et al. 3D-printed bioactive ceramic scaffolds with biomimetic micro/nano-HAp surfaces mediated cell fate and promoted bone augmentation of the bone–implant interface in vivo. Bioact Mater. 2022;12:120-132. [80] WANG Z, ZHANG M, LIU Z, et al. Biomimetic design strategy of complex porous structure based on 3D printing Ti-6Al-4V scaffolds for enhanced osseointegration. Mater Design. 2022;218: 110721. [81] LI X, WANG Y, ZHANG B, et al. The design and evaluation of bionic porous bone scaffolds in fluid flow characteristics and mechanical properties. Comput Methods Programs Biomed. 2022;225:107059. |
| [1] | 肖 放, 黄 雷, 王 琳. 磁性纳米材料与磁场效应加速骨损伤修复[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2025, 29(4): 827-838. |
| [2] | 俞 磊, 张 巍, 秦 毅, 葛高然, 柏家祥, 耿德春. 贻贝启发接枝骨形态发生蛋白2成骨活性肽的介孔生物玻璃修复股骨髁缺损[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2025, 29(22): 4629-4638. |
| [3] | 陈家瀚, 奉 超, 黄晓夏, 牛明慧, 王 鑫, 滕 勇. 骨组织工程研究中的二维黑磷材料[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2025, 29(10): 2124-2131. |
| [4] | 吴尧昆, 刘成林, 付佳豪, 宋 伟, 陈 浩, 席洪钟, 刘 锌, 杜 斌, 孙光权. 中药有效成分结合骨组织工程材料用于骨修复[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2025, 29(10): 2141-2150. |
| [5] | 刘云翔, 张晓玉, 李 昊, 张 荣, 李利平, 陈崇伟. 金属有机框架材料在骨组织工程和骨科疾病治疗中的多重应用[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2025, 29(10): 2151-2161. |
| [6] | 伍志鑫, 蒋雯雯, 詹健辉, 李杨书润, 任文燕, 王一宇. 水凝胶:口腔颌面部组织缺损修复中的作用与问题[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2025, 29(10): 2178-2188. |
骨组织工程技术作为一种替代方法备受关注,展现出了促进骨愈合与骨再生的潜力,有望弥补当前技术的不足,成为修复骨缺损的新途径。骨组织工程技术的核心理念在于:在体外培养成骨细胞,再将其种植到具有良好生物相容性且随人体逐步降解吸收的天然或人工支架上,随后移植到骨缺损区域。随着生物材料的逐渐分解,植入的骨细胞会持续增殖,从而实现骨组织损伤的修复[15]。骨组织工程是由支架材料、种子细胞和细胞因子组成(图1)[16],其中多孔支架修复缺损的过程主要依靠其提供的细胞生长微环境,传导力学刺激实现成骨,同时复合生物材料的骨诱导性发挥积极作用。 多孔支架主要是为骨再生提供结构框架,促进细胞增殖并支持新骨的形成,这些微观构造(包括形状、尺寸及内部连通孔洞)直接影响支架在生物力学上的性能。与此同时,支架可以为成骨细胞、干细胞提供黏附和增殖场所,在支架材料上培养一段时间后进一步分化为骨细胞,随着支架材料在体内被逐渐降解吸收,从而达到成骨细胞长入和血管化形成的目的。支架的结构特性,如承载能力、孔隙的连通性及对细胞生长和营养物质运输的支持,是优化其功能性的关键因素。骨支架需要在缺损处具备良好的力学支撑能力,可以减少受力时的变形和应力集中现象。 追溯到20世纪80年代,在生物学、工程学、材料科学和纳米技术飞速发展的情况下,仿生支架和传统支架的研究取得了突破性进展。传统支架以简单的设计和稳定的支撑特性在骨组织工程中占据了一席之地,然而其在生物相容性、促进细胞增殖和分化等方面具有一定的局限性。与此同时,仿生支架的设计理念——模仿自然界中的生物结构,在构建高性能骨组织工程方面备受关注,可以提供更加复杂且功能化的解决方案。仿生支架通过模拟人体自然骨骼的微观结构,在提供物理支撑的同时促进细胞黏附、增殖及分化,甚至是血管化的形成,最终达到加速骨组织修复和再生的目的。由此可见,多孔支架不仅要提供机械支撑和生物活性,也要为细胞附着、增殖和分化提供合适的生理微环境[17]。
该文旨在深入探讨传统与仿生支架在结构设计方面的差异,以及这些结构设计对支架力学性能、生物学性能(生物相容性、骨诱导性)的影响,为骨缺损和骨再生的后续治疗设计出既有生物相容性和机械稳定性又能够模拟自然骨组织微环境的支架。
1.1.1 检索人及检索时间 由第一作者在 2024年1-2月进行检索。
1.1.2 检索文献时限 设置文献检索时限为2008年1月至2024年3月。
1.1.3 检索数据库 中国知网(CNKI)、维普、万方、Web of Science、Science Direct、PubMed、EI等数据库。
1.1.4 检索词 中文检索词为“骨组织工程,仿生支架,骨小梁,传统支架,骨修复,三周期极小曲面”,英文检索词为“bone tissue engineering,bionic scaffolds,bone trabeculae,traditional scaffolds, bone repair,TPMS”。
1.1.5 检索文献类型 综述、研究原著和学位论文,此外还对检索范围内文献的部分优质参考文献进行追踪收录,选择近10 年内的高质量文献。
1.1.6 手工检索情况 无。
1.1.7 检索策略 使用上述检索词依次组合,通过高级检索方式进行检索,中、英文数据库的检索策略见图2。
1.1.8 检索文献量 初步共检索596篇文献,其中英文文献354篇,中文文献242篇。1.2 入组标准
1.2.1 纳入标准 ①阐述骨支架在骨组织工程和再生医学中发展的高质量、高水平文献;②重点研究各类骨支架在医学领域应用的文献;③发表在影响因子较高期刊的骨支架相关文献;④论点论据清晰明了的高质量文献;⑤具有相关性强、代表性和权威性的生物骨支架文献。
1.2.2 排除标准 ①通过审查题目、摘要、关键词、引言等,排除了一些相关度低、参考价值有限和重复的文献;②影响因子较低的非核心期刊文献;③创新性不足、观点较单一且主题逻辑不清的文献。
1.3 文献质量评估和数据的提取 通过泛读和精读摘要及全文,依据纳入和排除标准,提取近5年内的文献,最后选入81篇文献进行综述。文献筛选流程见图3。
总之,传统和仿生支架都存在或多或少的不足(表2),传统支架虽然可为骨骼生长提供稳定的结构,但不能为骨细胞的黏附、增殖和分化提供生理微环境;而仿生支架的微观结构与人体骨骼的骨小梁结构相似,这种多孔网状结构不但可以很好地分散应力、应对形变、保证力学性能,而且为成骨细胞的长入、营养物质的流通提供了良好的孔隙结构。仿生支架的设计加强了植入支架与人体天然骨骼在结构上的紧密度,使其在自然骨骼愈合过程中起到至关重要的作用。
未来几年,相关研究人员可以利用仿生支架与天然骨骼相似的孔隙结构这一天然优势,结合一些与天然骨组成和结构接近的新材料以及干细胞(特别是间充质干细胞)、生长因子、药物或其他生物活性分子等,制备具有多功能的骨支架。仿生骨支架的未来是高度跨学科的,将材料科学、细胞和分子生物学及工程学的进步结合起来,为骨修复和骨再生创造更有效的解决方案。
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||