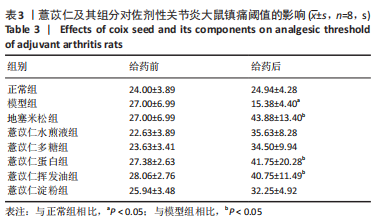
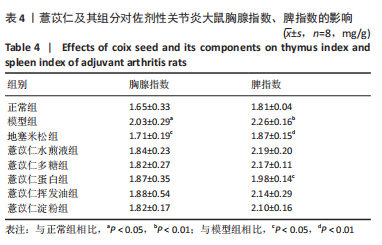
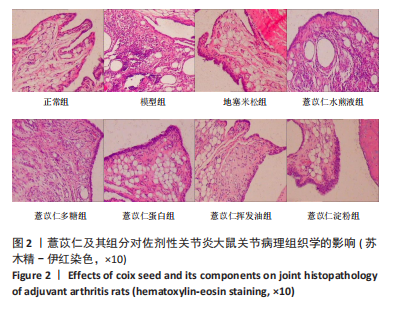
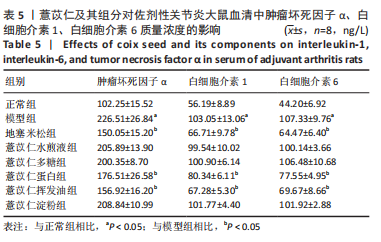
[1] ALETAHA D, SMOLEN JS. Diagnosis and Management of Rheumatoid Arthritis: A Review. JAMA. 2018;320(13):1360-1372.
[2] ALMUTAIRI K, NOSSENT J, PREEN D, et al. The global prevalence of rheumatoid arthritis: a meta-analysis based on a systematic review. Rheumatol Int. 2021;41(5):863-877.
[3] HUNTER TM, BOYTSOV NN, ZHANG X, et al. Prevalence of rheumatoid arthritis in the United States adult population in healthcare claims databases,2004-2014. Rheumatol Int. 2017;37(9):1551-1557.
[4] 朱丽芳, 俸一然, 许东云. 类风湿关节炎患者生存质量的研究进展[J]. 风湿病与关节炎,2018,7(4):76-80.
[5] ROSA-GONÇALVES D, BERNARDES M, COSTA L. Quality of life and functional capacity in patients with rheumatoid arthritis - Cross-sectional study. Reumatologia Clinica. 2018;14(6):360-366.
[6] 王月娇, 张宁. 国际类风湿关节炎病因学研究热点探析[J]. 中华风湿病学杂志,2017,21(12):800-806.
[7] 展俊平, 孟庆良, 孟婉婷, 等. 补阳还五汤对类风湿关节炎小鼠MPO, NE mRNA表达及TNF-α,IL-1β,IL-6,IL-17的影响[J]. 中国实验方剂学杂志,2018,24(24):158-163.
[8] LIN YJ, ANZAGHE M, SCHÜLKE S. Update on the Pathomechanism, Diagnosis, and Treatment Options for Rheumatoid Arthritis. Cells. 2020; 9(4):E880.
[9] 胡晓敏, 宗英, 余珊珊, 等. 类风湿关节炎治疗药物的研发进展及趋势[J]. 中国新药杂志,2017,26(1):36-43.
[10] BURMESTER GR, POPE JE. Novel treatment strategies in rheumatoid arthritis. Lancet (London, England). 2017;389(10086):2338-2348.
[11] 张图门. 类风湿关节炎药物治疗的规范化及临床实践探析[J]. 中国标准化,2021(18):173-175.
[12] 尹柏坤, 左军, 李冀. 类风湿关节炎的中医药治疗进展[J]. 中医药信息,2022,39(1):84-88.
[13] 梁金梅. 薏苡仁汤治疗类风湿关节炎的临床研究[D]. 武汉:湖北中医药大学, 2012.
[14] 赵斌勇. 重用薏苡仁治疗类风湿关节炎[J]. 内蒙古中医药,2013, 32(7):79-80.
[15] 王金丹. 薏苡仁中有效成分提取工艺的研究发展[J]. 农业科技与装备,2021(2):43-45.
[16] 朱蔚芊, 殷鑫, 周英, 等. 薏苡仁的化学成分研究[J].中药材, 2021(12):2835-2840.
[17] 刘帆, 侯林, 张晓平, 等. 薏苡仁多糖抗肿瘤作用及免疫作用研究进展[J]. 辽宁中医药大学学报,2019,21(3):123-126.
[18] 张敏娜. 类风湿关节炎的实验动物模型及其评价[J]. 实验动物科学, 2011,28(4):57-59.
[19] 韩晓春, 季旭明, 王彦芳, 等. 薏苡仁不同组分干预脾虚水湿不化大鼠细胞间隙基因变化[J]. 中华中医药杂志,2016,31(5):1955-1958.
[20] 崔媛, 容蓉, 杨勇, 等. 超声波辅助酸提薏苡仁多糖工艺优化[J]. 中华中医药学刊,2015,33(9):2143-2145.
[21] 武皓, 巩丽丽, 杨勇, 等. 薏苡仁水溶性蛋白提取工艺的优化[J]. 中药材,2015,38(2):376-380.
[22] 崔媛, 王小明, 杨勇, 等. 薏苡仁油融合指纹图谱研究[J]. 中草药, 2014,45(12):1698-1701.
[23] 范紫微, 古虹, 邹天琪, 等. 五味子木脂素对佐剂性关节炎大鼠的抗炎作用及对自噬相关通路的影响[J]. 中国药理学与毒理学杂志, 2020,34(6):442-450.
[24] 叶蕾, 宫健伟. 调肝脾方对佐剂性关节炎大鼠红细胞免疫功能的影响[J]. 时珍国医国药,2007,17(4):869-870.
[25] 陈旭, 杨邦祥, 刘慧, 等. 鞘内氯诺昔康对正常大鼠痛阈的影响[J]. 四川大学学报(医学版),2007,38(4):667-670.
[26] WANG X, HE X, ZHANG CF, et al. Anti-arthritic effect of berberine on adjuvant-induced rheumatoid arthritis in rats. Biomed Pharmacother. 2017;89:887-893.
[27] 张伊锐. 马文辉主任运用桂枝芍药知母汤加减治疗类风湿关节炎的经验总结[D].太原:山西中医药大学,2021.
[28] 孙广瀚, 许霞, 万磊, 等. 类风湿关节炎病证结合动物模型的研究进展[J]. 河南大学学报(医学版),2021,40(6):464-468.
[29] 熊丽, 杜肖, 陈宝忠, 等. 脊痛宁胶囊对风寒湿痹型类风湿关节炎大鼠的治疗作用[J]. 中国实验方剂学杂志,2017,23(1):140-145.
[30] 霍易飞, 吴彬, 杨宇峰, 等. 论明清时期对痹证病因病机认识[J]. 辽宁中医药大学学报,2019,21(8):79-81.
[31] 刘星, 王正武. 薏仁的化学成分及其应用研究[J]. 食品与药品, 2014,16(2):129-133.
[32] 杜成成, 谭余庆, 沈建英, 等. 双氢青蒿素对两种类风湿关节炎模型的影响及机制[J]. 中国实验方剂学杂志,2019,25(10):48-56.
[33] 许冰馨, 王琪珊, 范凯健, 等. 地塞米松改善胶原性关节炎大鼠免疫功能与其血药浓度的相关性研究[J]. 实用药物与临床,2021, 24(3):198-203.
[34] 李策力格, 黄健. 关于炎性细胞因子与类风湿关节炎的相关性研究[J]. 名医,2020(4):80.
[35] 李巧霞. CCK-8调节树突状细胞及其对胶原诱导型关节炎小鼠发病的影响[D]. 石家庄:河北医科大学,2010.
[36] 朱晓琴. IL-1β、IL-6与癫痫发病机制关系的研究[D]. 武汉:华中科技大学,2006.
[37] 陈絮蒙. DDAH/ADMA在类风湿关节炎中的作用及BTM-0512治疗机制研究[D]. 长沙:中南大学,2013.
[38] OGATA A, KATO Y, HIGA S, et al. IL-6 inhibitor for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis: A comprehensive review. Mod Rheumatol. 2019; 29(2):258-267.
[39] YAO X, HUANG J, ZHONG H, et al. Targeting interleukin-6 in inflammatory autoimmune diseases and cancers. Pharmacol Ther. 2014;141(2):125-139.
[40] NAVRÁTILOVÁ A, BEČVÁŘ V, BALOUN J, et al. S100A11 (calgizzarin) is released via NETosis in rheumatoid arthritis (RA) and stimulates IL-6 and TNF secretion by neutrophils. Sci Rep. 2021;11(1):6063.
[41] YOKOTA K, SATO K, MIYAZAKI T, et al Characterization and Function of Tumor Necrosis Factor and Interleukin-6-Induced Osteoclasts in Rheumatoid Arthritis. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2021;73(7):1145-1154.
[42] KIM GW, LEE NR, PI RH, et al. IL-6 inhibitors for treatment of rheumatoid arthritis: past, present, and future. Arch Pharm Res. 2015; 38(5):575-584.
[43] 冯玉才,邹瑞,李艳,等. IL-6、抗CCP抗体在类风湿性关节炎中的诊断价值[J]. 湖南师范大学学报(医学版),2022,19(2):199-202.
[44] 王伟东,陈如平,肖鲁伟,等. 雷公藤甲素对类风湿关节炎滑膜新生血管中血管内皮生长因子、白细胞介素-6抑制机理的探讨[J].中医正骨,2012,24(2):3-5.
[45] 陈英,张文玲,黄涛,等. 炎症因子TNF-α、IL-6、IL-17与类风湿关节炎并发动脉粥样硬化的关系[J].免疫学杂志,2017,33(3):268-272.
[46] 邓毅凡,张晶,周玮. 类风湿关节炎合并冠心病患者冠状动脉病变程度与白细胞介素-6、白细胞介素-17水平的相关性[J].实用临床医药杂志,2022,26(3):55-58.
[47] 谭晴心,肖琴. 雷公藤多甙联合甲氨蝶呤治疗类风湿关节炎疗效评价及对TNF-α、IL-6的影响[J]. 中国中医药信息杂志,2010,17(9):7-9.
|