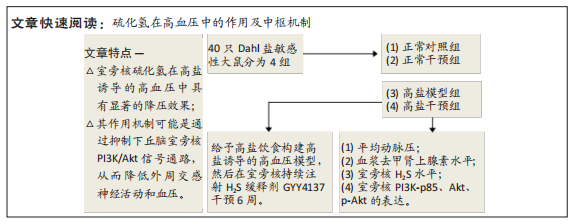
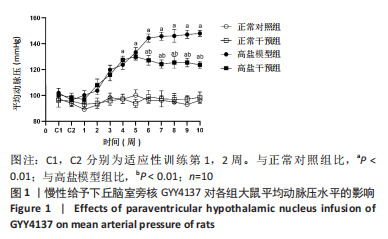
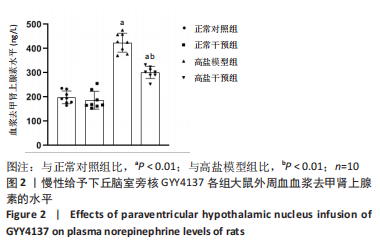
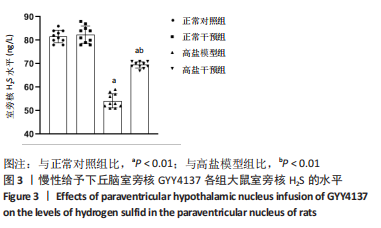
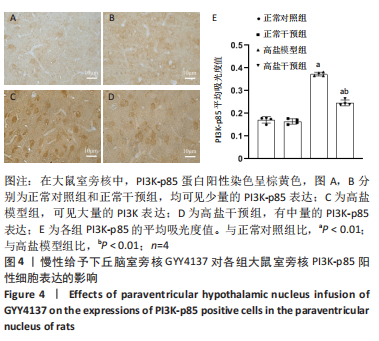
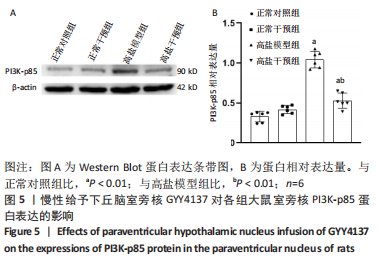
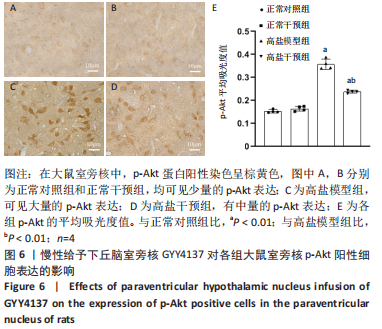
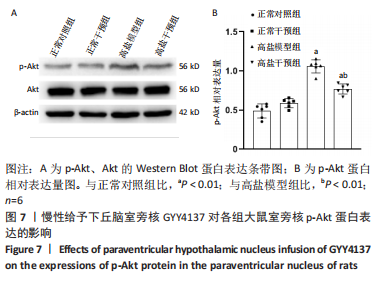
[1]《中国心血管健康与疾病报告 2019》编写组. 《中国心血管健康与疾病报告 2019》[J]. 中华高血压杂志,2021,29(3):203-214.
[2] ZHOU JJ, MA HJ, SHAO JY, et al. Impaired Hypothalamic Regulation of Sympathetic Outflow in Primary Hypertension.Neurosci Bull. 2019; 35(1):124-132.
[3] ZAORSKA E, TOMASOVA L, KOSZELEWSKI D, et al. Hydrogen Sulfide in Pharmacotherapy, Beyond the Hydrogen Sulfide-Donors. Biomolecules. 2020;10(2):323.
[4] LIANG YF, ZHANG DD, YU XJ, et al. Hydrogen sulfide in paraventricular nucleus attenuates blood pressure by regulating oxidative stress and inflammatory cytokines in high salt-induced hypertension. Toxicology Letters. 2017;270:62-71.
[5] FATTAHI S, AMJADI-MOHEB F, TABARIPOUR R, et al. PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling in gastric cancer: Epigenetics and beyond. Life Sci. 2020;262: 118513.
[6] 邹连玉,郑丽维.PI3K/AKt信号通路在高血压疾病防治中的研究进展[J].中国医学创新,2021,18(34):176-179.
[7] 平海芹, 周晓阳. 盐敏感性高血压发病机制与治疗的研究进展[J]. 广西医学,2020,42(7):4.
[8] XUE B, ZHANG Z, BELTZ TG, et al. Estrogen receptor-beta in the paraventricular nucleus and rostroventrolateral medulla plays an essential protective role in aldosterone/salt-induced hypertension in female rats. Hypertension. 2013;61(6):1255-1262.
[9] GEERLING JC, SEQUEIRA SM, LOEWY AD.Increased number of aldosterone-sensitive NTS neurons in Dahl salt-sensitive rats. Brain Res. 2005;1065(1-2):142-146.
[10] SU Q, YU XJ, WANG XM, et al. Bilateral Paraventricular Nucleus Upregulation of Extracellular Superoxide Dismutase Decreases Blood Pressure by Regulation of the NLRP3 and Neurotransmitters in Salt-Induced Hypertensive Rats. Front Pharmacol. 2021;12:756671.
[11] YU XJ, ZHAO YN, HOU YK, et al. Chronic Intracerebroventricular Infusion of Metformin Inhibits Salt-Sensitive Hypertension via Attenuation of Oxidative Stress and Neurohormonal Excitation in Rat Paraventricular Nucleus. Neurosci Bull. 2019;35(1):57-66.
[12] 徐明星,刘文秀,梁雨亭,等. 硫化氢在心血管疾病中的研究进展[J]. 中国现代医学杂志,2020,30(21):40-44.
[13] DUAN XC, LIU SY, GUO R, et al. Cystathionine-β-Synthase Gene Transfer Into Rostral Ventrolateral Medulla Exacerbates Hypertension via Nitric Oxide in Spontaneously Hypertensive Rats. Am J Hypertens. 2015;28: 1106-1113.
[14] SIKORA M, DRAPALA A, UFNAL M. Exogenous hydrogen sulfide causes different hemodynamic effects in normotensive and hypertensive rats via neurogenic mechanisms. Pharmacological Reports. 2014;66(5):751-758.
[15] WANG QS, LIANG C, JIANG S, et al. NaHS or Lovastatin Attenuates Cyclosporine A–Induced Hypertension in Rats by Inhibiting Epithelial Sodium Channels. Front Pharmacol. 2021;12:665111.
[16] GUO Q, JIN S, WANG XL, et al. Hydrogen Sulfide in the Rostral Ventrolateral Medulla Inhibits Sympathetic Vasomotor Tone through ATP-Sensitive K+ Channels. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2011;338(2):458-465.
[17] 杜幸. 硫化氢抑制中枢NLRP3炎症小体的激活调控交感神经紧张性[D]. 石家庄:河北医科大学,2018.
[18] NOOROLYAI S, SHAJARI N, BAGHBANI E, et al. The relation between PI3K/AKT signalling pathway and cancer. Gene. 2019;698:120-128.
[19] GENG Z, YE C, TONG Y, et al. Exacerbated pressor and sympathoexcitatory effects of central Elabela in spontaneously hypertensive rats. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2020;318(1): H124-H134.
[20] SUN HJ, CHEN D, HAN Y, et al. Relaxin in paraventricular nucleus contributes to sympathetic overdrive and hypertension via PI3K-Akt pathway. Neuropharmacology. 2016;103:247-256.
[21] SHI Y, YIN J, HU H, et al. Targeted regulation of sympathetic activity in paraventricular nucleus reduces inducible ventricular arrhythmias in rats after myocardial infarction. J Cardiol. 2019;73(1):81-88.
[22] TAN X, JIAO PL, WANG YK, et al. The phosphoinositide-3 kinase signaling is involved in neuroinflammation in hypertensive rats. CNS Neurosci Ther. 2017;23(4):350-359.
[23] NIE L, LIU M, CHEN J, et al. Hydrogen sulfide ameliorates doxorubicin-induced myocardial fibrosis in rats via the PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway. Mol Med Rep. 2021;23(4):299.
[24] XIAO Q, YING J, QIAO Z,et al. Exogenous hydrogen sulfide inhibits human melanoma cell development via suppression of the PI3K/AKT/ mTOR pathway. J Dermatol Sci. 2020;98(1):26-34.
[25] TAMIZHSELVI R, SUN J, KOH YH, et al. Effect of hydrogen sulfide on the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase-protein kinase B pathway and on caerulein-induced cytokine production in isolated mouse pancreatic acinar cells. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2009;329(3):1166-1177.
[26] HE XL, YAN N, CHEN XS, et al. Hydrogen sulfide down-regulates BACE1 and PS1 via activating PI3K/Akt pathway in the brain of APP/PS1 transgenic mouse. Pharmacol Rep. 2016;68(5):975-982.
[27] LI CX, ZHAO B, LIN CZ, et al. TREM2 inhibits inflammatory responses in mouse microglia by suppressing the PI3K/NF-κB signaling. Cell Biol Int. 2019;43(4):360-372.
[28] WU XY, PU LJ, CHEN W, et al. LY294002 attenuates inflammatory response in endotoxin-induced uveitis by downregulating JAK3 and inactivating the PI3K/Akt signaling. Immunopharmacol Immunotoxicol. 2022;44(4):510-518.
[29] YUE JZ, ZHAO X. GPR174 suppression attenuates retinopathy in angiotensin II (Ang II)-treated mice by reducing inflammation via PI3K/AKT signaling. Biomed Pharmacother. 2020;122:109701.
[30] PENDERGRASS KD, GWATHMEY TM, MICHALEK RD, et al. The angiotensin II-AT1 receptor stimulates reactive oxygen species within the cell nucleus. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2009;384(2):149-154. |