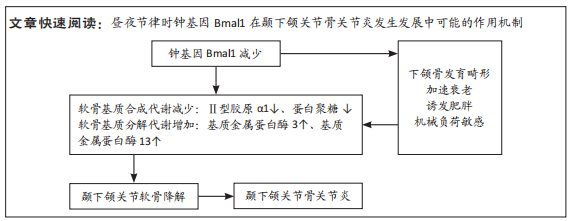
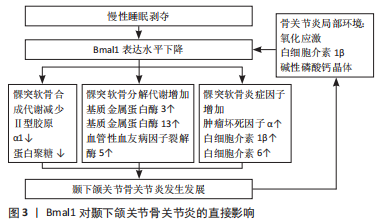
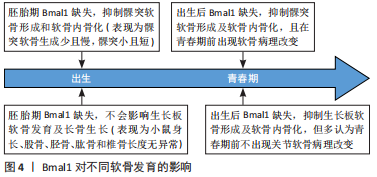
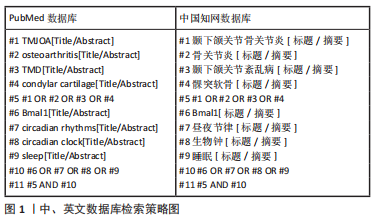
[1] HU Z, XIAO M, CAI H, et al. Glycyrrhizin regulates rat TMJOA progression by inhibiting the HMGB1-RAGE/TLR4-NF-κB/AKT pathway. J Cell Mol Med. 2022;26: 925-936.
[2] LI B, GUAN G, MEI L, et al. Pathological mechanism of chondrocytes and the surrounding environment during osteoarthritis of temporomandibular joint. Cell Mol Med. 2021;25:4902-4911.
[3] HE D, AN Y, LI Y, et al. RNA sequencing reveals target genes of temporomandibular joint osteoarthritis in rats after the treatment of low-intensity pulsed ultrasound. Gene. 2018;672:126-136.
[4] OUDET C, PETROVIC A. Growth rhythms of the cartilage of the mandibular condyle: effects of orthopaedic appliances. Int J Chronobiol. 1978;5:545-564.
[5] 周晓红,李柏村,李佳,等. 从肝论治取穴针灸治疗膝骨关节炎模型大鼠关节功能与昼夜节律的关系[J]. 中国组织工程研究,2021,25(14):2192-2198.
[6] ALBRECHT U. Timing to perfection: the biology of central and peripheral circadian clocks. Neuron. 2012;74:246-260.
[7] CHEN G, TANG Q, YU S, et al. The biological function of BMAL1 in skeleton development and disorders. Life Sci. 2020;253:117636.
[8] ZHU Q, BELDEN WJ. Molecular Regulation of Circadian Chromatin. J Mol Biol. 2020;432:3466-3482.
[9] DUDEK M, GOSSAN N, YANG N, et al. The chondrocyte clock gene Bmal1 controls cartilage homeostasis and integrity. J Clin Invest. 2016;126:365-376.
[10] SIMMONS DJ. Diurnal periodicity in epiphyseal growth cartilage. Nature. 1962; 195:82-83.
[11] STEVENSON S, HUNZIKER EB, HERRMANN W, et al. Is longitudinal bone growth influenced by diurnal variation in the mitotic activity of chondrocytes of the growth plate?. J Orthop Res. 1990;8:132-135.
[12] ALAGHA MA, VAGO J, KATONA É, et al. A Synchronized Circadian Clock Enhances Early Chondrogenesis. Cartilage. 2021;13:53S-67S.
[13] TAKARADA T, KODAMA A, HOTTA S, et al. Clock genes influence gene expression in growth plate and endochondral ossification in mice. J Biol Chem. 2012;287:36081-36095.
[14] ERENBAUM F, MENG QJ. The brain-joint axis in osteoarthritis: nerves, circadian clocks and beyond. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2016;12:508-516.
[15] GOSSAN N, ZEEF L, HENSMAN J, et al. The circadian clock in murine chondrocytes regulates genes controlling key aspects of cartilage homeostasis. Arthritis Rheum. 2013;65:2334-2345.
[16] POULSEN RC, HEARN JI, DALBETH N. The circadian clock: a central mediator of cartilage maintenance and osteoarthritis development?. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2021;60:3048-3057.
[17] LIANG C, YANG T, WU G, et al. Therapeutic effect of low-intensity pulsed ultrasound on temporomandibular joint injury induced by chronic sleep deprivation in rats. Am J Transl Res. 2019;11:3328-3340.
[18] DONG Y, WU G, ZHU T, et al. VEGF promotes cartilage angiogenesis by phospho-ERK1/2 activation of Dll4 signaling in temporomandibular joint osteoarthritis caused by chronic sleep disturbance in Wistar rats. Oncotarget. 2017;8:17849-17861.
[19] LIANG C, YANG T, WU G,et al. The Optimal Regimen for the Treatment of Temporomandibular Joint Injury Using Low-Intensity Pulsed Ultrasound in Rats with Chronic Sleep Deprivation. Biomed Res Int. 2020;2020:5468173.
[20] URSINI F, DE GIORGI A, D’ONGHIA M, et al. Chronobiology and Chronotherapy in Inflammatory Joint Diseases. Pharmaceutics. 2021;13:1832.
[21] RONG J, ZHU M, MUNRO J, et al. Altered expression of the core circadian clock component PERIOD2 contributes to osteoarthritis-like changes in chondrocyte activity. Chronobiol Int. 2019;36:319-331.
[22] CHEN G, ZHAO H, MA S, et al. Circadian Rhythm Protein Bmal1 Modulates Cartilage Gene Expression in Temporomandibular Joint Osteoarthritis via the MAPK/ERK Pathway. Front Pharmacol. 2022;11:527744.
[23] AKAGI R, AKATSU Y, FISCH KM, et al. Dysregulated circadian rhythm pathway in human osteoarthritis: NR1D1 and BMAL1 suppression alters TGF-β signaling in chondrocytes. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2017;25:943-951.
[24] ZHAO Y, LU X, WAN F, et al. Disruption of Circadian Rhythms by Shift Work Exacerbates Reperfusion Injury in Myocardial Infarction. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2022; 79:2097-2115.
[25] SANCHEZ EA, MARTINEA O, GARCIA M, et al. Association between Sleep Disorders and Sleep Quality in Patients with Temporomandibular Joint Osteoarthritis: A Systematic Review. Biomedicines. 2022;10:2143.
[26] NOJIMA K, NAGATA M, OOTAKE T, et al. Surgical Orthodontic Treatment Involving Mandibular Premolar Extraction in Patient with Mandibular Retrusion Associated with Temporomandibular Joint Osteoarthritis. Bull Tokyo Dent Coll. 2019;60:139-149.
[27] YU S, TANG Q, XIE M, et al. Circadian BMAL1 regulates mandibular condyle development by hedgehog pathway. Cell Prolif. 2020;53:e12727.
[28] KOSHI R, MATSUMOTO K, IMANISHI Y, et al. Morphological characteristics of interalveolar septum and mandible in BMAL1 gene knockout mice. J Oral Sci. 2020;63:83-86.
[29] ZHOU X, YU R, LONG Y, et al. BMAL1 deficiency promotes skeletal mandibular hypoplasia via OPG downregulation. Cell Prolif. 2018;51:e12470.
[30] ZHAO J, ZHOU X, TANG Q, et al. BMAL1 Deficiency Contributes to Mandibular Dysplasia by Upregulating MMP3. Stem Cell Reports. 2018;10:180-195.
[31] 熊国平,陈扬熙,罗颂椒. 功能矫形与大鼠髁突内源性甲状旁腺素昼夜节律变化的研究[J]. 中华口腔医学杂志,2000,35(5):394.
[32] MA Z, JIN X, QIAN Z, et al. Deletion of clock gene Bmal1 impaired the chondrocyte function due to disruption of the HIF1α-VEGF signaling pathway. Cell Cycle. 2019;18:1473-1489.
[33] SONG X, BAI H, MENG X, et al. Drivers of phenotypic variation in cartilage: Circadian clock genes. J Cell Mol Med. 2021;25:7593-7601.
[34] ROBERTS WE, STOCUM DL. Part II: Temporomandibular Joint (TMJ)-Regeneration, Degeneration, and Adaptation. Curr Osteoporos Rep. 2018;16:369-379.
[35] KONDRATOV RV, KONDRATOVA AA, GORBACHEVA VY, et al. Early aging and age-related pathologies in mice deficient in BMAL1, the core componentof the circadian clock. Genes Dev. 2006;20:1868-1873.
[36] FAN R, PENG X, XIE L, et al. Importance of Bmal1 in Alzheimer’s disease and associated aging-related diseases: Mechanisms and interventions. Aging Cell. 2022;21:e13704.
[37] BROWN SA, PAGANI L, CAJOCHEN C, et al. Systemic and cellular reflections on ageing and the circadian oscillator: a mini-review. Gerontology. 2011;57(5):427-434.
[38] CHA S, LEE SM, WANG J, et al. Enhanced Circadian Clock in MSCs-Based Cytotherapy Ameliorates Age-Related Temporomandibular Joint Condyle Degeneration. Int J Mol Sci. 2021;22:10632.
[39] YANG N, MENG QJ. Circadian Clocks in Articular Cartilage and Bone: A Compass in the Sea of Matrices. J Biol Rhythms. 2016;31:415-427.
[40] YANG W, KANG X, LIU J, et al. Clock Gene Bmal1 Modulates Human Cartilage Gene Expression by Crosstalk With Sirt1. Endocrinology. 2016;157:3096-3107.
[41] MORRIS H, GONCALVES CF, DUDEK M, et al. Tissue physiology revolving around the clock: circadian rhythms as exemplified by the intervertebral disc. Ann Rheum Dis. 2021;80:828-839.
[42] HASAN N, NAGATA N, MORISHIGE JI, et al. Brown adipocyte-specific knockout of Bmal1 causes mild but significant thermogenesis impairment in mice. Mol Metab. 2021;49:101202.
[43] SHIMBA S, ISHII N, OHTA Y, et al. Brain and muscle Arnt-like protein-1 (BMAL1), a component of the molecular clock, regulates adipogenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2005;102:12071-12076.
[44] JOUFFE C, WEGER BD, MARTIN E, et al. Disruption of the circadian clock component BMAL1 elicits an endocrine adaption impacting on insulin sensitivity and liver disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2022;119:e2200083119.
[45] TAKAOKA R, KUYAMA K, YATANI H, et al. Involvement of an FTO gene polymorphism in the temporomandibular joint osteoarthritis. Clin Oral Investig. 2022;2:2965-2973.
[46] DU J, JIANG Q, MEI L, et al. Effect of high fat diet and excessive compressive mechanical force on pathologic changes of temporomandibular joint. Sci Rep. 2020;10:17457.
[47] KC R, LI X, FORSYTH CB, et al. Osteoarthritis-like pathologic changes in the knee joint induced by environmental disruption of circadian rhythms is potentiated by a high-fat diet. Sci Rep. 2015;5:16896.
[48] KANBE K, INOUE K, XIANG C, et al. Identification of clock as a mechanosensitive gene by large-scale DNA microarray analysis: downregulation in osteoarthritic cartilage. Mod Rheumatol. 2006;16:131-136.
[49] LIANG C, LIU Z, SONG M, et al. Stabilization of heterochromatin by CLOCK promotes stem cell rejuvenation and cartilage regeneration. Cell Res. 2021;31:187-205.
[50] LU KH, LU PW, LU EW, et al. The potential remedy of melatonin on osteoarthritis. J Pineal Res. 2021;71:e12762. |