中国组织工程研究 ›› 2023, Vol. 27 ›› Issue (32): 5219-5226.doi: 10.12307/2023.827
• 组织构建综述 tissue construction review • 上一篇 下一篇
运动干预肠道菌群对自身免疫性疾病的作用
冷思逸1,蒲 锐1,2,陈子扬1,2,杨启航1,宋永晶1,刘 辉3
- 长江大学,1教育与体育学院,2运动人体科学实验室,3医学部,湖北省荆州市 434023
-
收稿日期:2022-11-03接受日期:2022-12-09出版日期:2023-11-18发布日期:2023-03-23 -
通讯作者:宋永晶,博士,副教授,硕士研究生导师,长江大学教育与体育学院,湖北省荆州市 434023 蒲锐,男,硕士,讲师,长江大学教育与体育学院,湖北省荆州市 434023 -
作者简介:冷思逸,女,1999年生,湖北省武汉市人,汉族,在读硕士,主要从事运动健康促进研究。 -
基金资助:国家自然科学基金项目(82271514),项目负责人:刘辉;2021湖北省教育厅项目(BXLBX0337),项目负责人:宋永晶
Roles of exercise intervention in intestinal flora in autoimmune diseases
Leng Siyi1, Pu Rui1, 2, Chen Ziyang1, 2, Yang Qihang1, Song Yongjing1, Liu Hui3
- 1College of Education and Sports Sciences, 2Human Science Laboratory of Exercise, 3Health Science Center, Yangtze University, Jingzhou 434023, Hubei Province, China
-
Received:2022-11-03Accepted:2022-12-09Online:2023-11-18Published:2023-03-23 -
Contact:Song Yongjing, MD, Associate professor, Master’s supervisor, College of Education and Sports Sciences, Yangtze University, Jingzhou 434023, Hubei Province, China Pu Rui, Master, Lecturer, College of Education and Sports Sciences, Yangtze University, Jingzhou 434023, Hubei Province, China; Human Science Laboratory of Exercise, Yangtze University, Jingzhou 434023, Hubei Province, China -
About author:Leng Siyi, Master candidate, College of Education and Sports Sciences, Yangtze University, Jingzhou 434023, Hubei Province, China -
Supported by:National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 82271514 (to LH); 2021 Hubei Provincial Education Department Project, No. BXLBX0337 (to SYJ)
摘要:
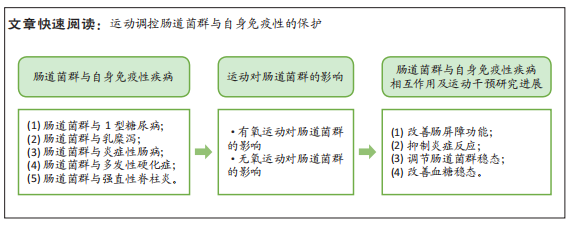
文题释义:
肠道菌群:是人体内最复杂和种群数量最高的共生微生物生态系统,对机体的代谢、营养和调节等发挥着重要作用,是近年来防治自身免疫性疾病相关研究的热点之一。
肠道菌群对自身免疫性疾病的作用及运动干预:运动可通过调节肠道菌群改善肠道屏障功能、抑制炎症反应、调节肠道菌群稳态和改善血糖稳态,进而在1型糖尿病、乳糜泻、炎症性肠病、多发性硬化症和强直性脊柱炎等自身免疫性疾病的预防与治疗中发挥免疫系统的保护作用。
背景:肠道菌群主要负责维持宿主防御和免疫耐受之间的平衡。此外,肠道菌群与自身免疫性疾病关系密切,且运动可对肠道菌群具有重要调控作用,进而影响着各类自身免疫性疾病的发生发展。
目的:总结肠道菌群对1型糖尿病、乳糜泻、炎症性肠病、多发性硬化症和强直性脊柱炎等不同自身免疫性疾病的作用,并围绕运动对肠道菌群的影响以及运动调控肠道菌群对自身免疫性保护的作用进行分析,旨在为自身免疫性疾病的防治提供新的参考与依据。
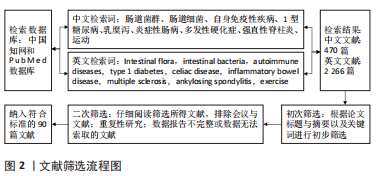
方法:以“Intestinal flora,intestinal bacteria,autoimmune diseases,type 1 diabetes,celiac disease,inflammatory bowel disease,multiple sclerosis,ankylosing spondylitis,exercise”和“肠道菌群、肠道细菌、自身免疫性疾病、1型糖尿病、乳糜泻、炎症性肠病、多发性硬化症、强直性脊柱炎、运动”为关键词,检索PubMed和CNKI数据库1996-2022年间相关文献。根据纳入排除标准选择90篇文献进行综述。
结果与结论:①1型糖尿病、乳糜泻、炎症性肠病、多发性硬化症和强直性脊柱炎等自身免疫性疾病受到肠道菌群的影响,且肠道菌群在自身免疫性疾病的调控中发挥关键作用。②不同运动方式对肠道菌群的影响不同,有氧运动可增加机体中肠道菌群多样性和菌群丰度,改善肠道黏膜免疫屏障功能,降低机体代谢性炎症反应,从而促进健康增强机体抵抗力。但有氧运动调控肠道菌群促进机体健康的途径和具体机制需要进一步研究。无氧运动对机体肠道菌群的影响研究尚存争议,可能与研究对象、研究方法、运动干预的时间强度异质性有关,需要进一步深层次挖掘,但研究均表明无氧运动可通过减轻机体炎症反应、提高胰岛素耐受能力和改善糖脂代谢紊乱,进而改善机体健康。③运动可通过调控肠道菌群改善肠道屏障功能、抑制炎症反应、调节肠道菌群稳态和改善血糖稳态等在自身免疫性疾病的防治中发挥重要作用,为运动促进机体健康及自身免疫性疾病的防治提供了新的思路与策略。
https://orcid.org/0000-0001-5097-5445(冷思逸)
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:组织构建;骨细胞;软骨细胞;细胞培养;成纤维细胞;血管内皮细胞;骨质疏松;组织工程
中图分类号:
引用本文
冷思逸, 蒲 锐, 陈子扬, 杨启航, 宋永晶, 刘 辉. 运动干预肠道菌群对自身免疫性疾病的作用[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2023, 27(32): 5219-5226.
Leng Siyi, Pu Rui, Chen Ziyang, Yang Qihang, Song Yongjing, Liu Hui. Roles of exercise intervention in intestinal flora in autoimmune diseases[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(32): 5219-5226.
2.2 肠道菌群与自身免疫性疾病 研究表明,肠道菌群在各类自身免疫性疾病中发挥关键诊疗作用,如1型糖尿病、乳糜泻、炎症性肠病、多发性硬化症和强直性脊柱炎。下文就以肠道菌群与各类自身免疫性疾病间的关系做出归纳总结。
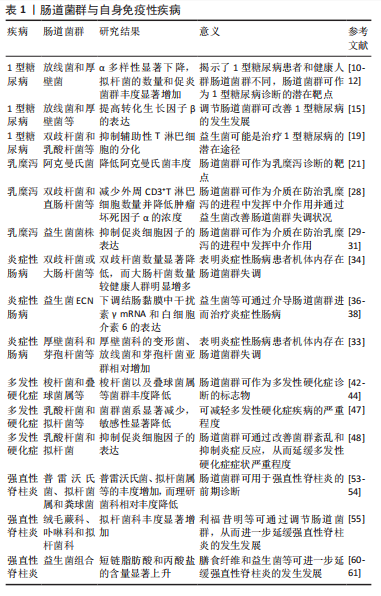
2.2.1 1型糖尿病 1型糖尿病是由免疫机制破坏产生胰岛素的β细胞引起血糖升高从而引发的疾病[7-8]。研究发现,肠道菌群通过改变肠道通透性诱发1型糖尿病,而肠道菌群的稳态和维持肠黏膜通透性可抑制炎症反应并减缓1型糖尿病的发生发展,从而维持机体健康[9]。此外,1型糖尿病患者和健康人群的肠道菌群组成存在显著差异,1型糖尿病儿童患者中,放线菌与厚壁菌的细菌数量以及厚壁菌与拟杆菌的比例均显著降低,与健康儿童相比,拟杆菌的数量和促炎菌群丰度显著增加[10-12]。上述研究表明,肠道菌群可作为1型糖尿病诊断的潜在靶点。
肠道菌群失调可能与1型糖尿病的发生有关,改善肠道菌群失调为1型糖尿病治疗提供了新的策略。研究者们发现1型糖尿病患者肠道菌群多样性显著降低,并伴随肠道通透性增加和肠菌结构的改变,并引起肠道菌群失衡,从而诱发宿主免疫炎症反应,最终导致糖尿病和自身免疫性疾病的发生发展[13]。而肠道菌群稳态可改善肠屏障功能进而减轻炎症反应及代谢紊乱,从而维持1型糖尿病患者健康,进一步发现其机制可能与肠道菌群稳态可上调内源性血清胰高血糖素样肽2的表达,并加强依赖内源性血清胰高血糖素样肽2的屏障作用有关[14]。此外,建立非肥胖糖尿病小鼠模型发现,通过肠道菌群移植可调控免疫反应,增加转化生长因子β表达,改善肠黏膜屏障功能障碍,进而保护非肥胖糖尿病小鼠免于发生1型糖尿病[15]。而丁酸盐诱导黏蛋白合成可维持肠道上皮完整性,从而维持肠屏障功能[16]。上述研究提示,通过改善肠道菌群稳态可调节肠黏膜屏障功能障碍和减轻炎症反应,进而延缓1型糖尿病发展。另有研究表明,丁酸盐、丙酸盐和烟酸都可通过以依赖性方式调节结肠巨噬细胞和树突状细胞来发挥其抗炎作用[17]。使用焦磷酸测序对有无1型糖尿病抗体的儿童进行比较,发现双歧杆菌和丁酸盐产生物种的低丰度可能对肠上皮屏障功能和炎症产生不利影响[18]。同时,补充双歧杆菌和乳酸杆菌等可改善肠道菌群失调,抑制辅助性 T 淋巴细胞分化,降低血糖减轻胰岛炎症,改善肠道免疫状态,从而延缓1型糖尿病的发展[19]。由此可见,益生菌可能是治疗1型糖尿病的潜在途径,且上述研究为1型糖尿病临床试验提供了坚实的基础和前瞻性的治疗选择。
综上所述,肠道菌群失调可能与1型糖尿病的发生密切关联,肠道菌群可作为其诊断的生物标记物。通过改善肠道菌群稳态可调节肠黏膜屏障功能障碍和减轻炎症反应,进而延缓1型糖尿病发展。此外,益生菌是治疗1型糖尿病的潜在途径,可改善肠道菌群失调,抑制辅助性 T 淋巴细胞分化,降低血糖减轻胰岛炎症,改善肠道免疫状态,从而有效控制1型糖尿病发展。而1型糖尿病患者中炎症细胞因子升高刺激血糖的机制值得进一步研究,也为1型糖尿病的治疗提供了新的方向。
2.2.2 乳糜泻(celiac disease,CD) 乳糜泻是由基因遗传易感人群摄入麸质而诱发的免疫性肠道疾病[20]。研究发现,乳糜泻疾病的发生与肠道菌群失调有密切联系,肠道菌群及其代谢物在乳糜泻的诊断中发挥重要作用。有研究发现乳糜泻患者患病前后的特定扩增子序列变异发生变化,十二指肠活检发现特殊CD-Nf菌株增加,且乳糜泻患者阿克曼氏菌的丰度降低[21]。此外,乳糜泻患者肠道内以革兰阴性杆菌为主的有害细菌大量增加,肠屏障功能遭到破坏,激发免疫炎症反应并导致肠道菌群生态失调,从而诱发乳糜泻[22]。另有研究发现,乳糜泻儿童与健康儿童相比,双歧杆菌菌群丰度降低[23]。上述研究提示,肠道菌群可作为乳糜泻诊断的潜在靶点。
乳糜泻可能与肠道菌群失调有关,改善肠道菌群失调可能是乳糜泻治疗的新靶点。有研究表明,乳糜泻患者摄入醇溶蛋白(麸质)会破坏菌群结构导致肠道菌群失调、激活炎症反应、破坏肠上皮组织功能和增大肠道黏膜通透性,进而诱发乳糜泻[24]。CHENG等[25]发现Toll样受体9(Toll-like receptor 9,TLR9)信号的高表达会引发肠道菌群和黏膜受体失衡,从而对乳糜泻产生不利影响。而厚壁菌群及其代谢的麸质降解酶在麸质水解中起重要作用,可帮助改善乳糜泻患者的生活质量[26]。同时,肠道菌群可通过激活先天免疫系统,调节肠上皮屏障功能和驱动黏膜炎症来影响乳糜泻的进展[27]。另有研究表明,双歧杆菌和直肠杆菌会导致外周CD3?T淋巴细胞减少和肿瘤坏死因子α浓度降低、长双歧杆菌CT 7347和粪便分泌物sIgA减少,且对患有乳糜泻的儿童使用长双歧杆菌可通过靶向调控其先天免疫系统,从而改善乳糜泻患儿消化不良和胃肠道反流等问题[28]。此外,复杂膳食纤维的缺乏会破坏结肠黏液屏障并促进病原体易感性增加,益生菌在降低乳糜泻患者IBS型症状的严重程度方面优于安慰剂,治疗成功率显著提高,且未有不良反应,服用含有益生菌菌株的小麦面包可减缓乳糜泻患者的症状,从而显著提高麸质耐受性,而通过对乳糜泻患儿施加益生菌干预能够减少血清促炎细胞因子白细胞介素10和肿瘤坏死因子α的产生[29-31]。 上述研究提示,肠道菌群可作为介质在防治乳糜泻的进程中发挥中介作用通过益生菌改善肠道菌群失调状况。
综上所述,肠道菌群及其代谢物与乳糜泻发展关系密切,肠道菌群可作为其诊断的标志物。同时肠道菌群失调可诱发炎症反应,并导致肠上皮组织破坏,进而增加肠黏膜的通透性,加重乳糜泻发生发展。肠道菌群可作为介质在防治乳糜泻的进程中发挥中介作用,并通过改变饮食和益生菌等改善肠道菌群失调、提高麸质耐受性提高、调控先天免疫系统改善乳糜泻患者胃肠道反流、减少促炎细胞因子,从而改善乳糜泻患者的健康状况。
2.2.3 炎症性肠病(inflammatory bowel disease,IBD) 炎症性肠病是以复发性胃肠道炎症为特征的慢性疾病,其发病机制复杂、影响因素众多,且炎症性肠病变化与肠道菌群失调和宿主免疫系统扰动有关。FRANK等[32]发现炎症性肠病受试者厚壁菌科和拟杆菌科的毛螺菌科减少,厚壁菌科的变形菌、放线菌和芽孢杆菌亚群相对增加,表明其机体内存在肠道菌群失调。炎症性肠病患者肠道菌群失调主要体现在致病菌数量的增加和肠道菌群正常比例的改变[33]。另有研究表明,活动期炎症性肠病患者肠道中丁酸盐、双歧杆菌和乳酸杆菌数量显著降低,而大肠杆菌与肠球菌数量较健康人群明显增多[34]。由此可见,厚壁菌科、双歧杆菌、大肠杆菌和丁酸盐等肠道菌群及其代谢产物的变化可作为诊断炎症性肠病的新方向。
益生菌、抗生素和饮食等可通过介导肠道菌群进而治疗炎症性肠病。有研究发现,炎症性肠病患者机体内大肠杆菌代谢增加可降低炎症反应,而多房杆菌感染的C57小鼠可通过减轻Th1/Th17介导的免疫反应保护硫酸葡聚糖诱导炎症性肠病的结肠损伤[35]。此外,益生菌ECN(大肠埃希菌Nissle1917)可用于治疗炎症性肠病,调节体内免疫因子,增强宿主免疫力,且益生菌ECN口服治疗可下调结肠黏膜中IFN-γ mRNA和白细胞介素6的表达,减缓黏膜损伤和黏蛋白细胞的进一步消耗,从而保持肠道屏障功能[36-38]。另有研究发现,平淡饮食、地中海式饮食和半素食饮食通过调节肠道菌群减轻肠道炎症、促进黏膜愈合和组织功能,有效预防炎症性肠病复发[39]。此外,使用抗生素治疗可改善肠道生态系统,对促进炎症的细菌定植提供抵抗力[40]。由此可见,益生菌、抗生素和饮食等可通过介导肠道菌群进而治疗炎症性肠病。
综上所述,炎症性肠病的变化与肠道菌群失调有关。肠道菌群的变化可作为炎症性肠病诊断的靶点。以肠道菌群为靶点调节炎症性肠病可能成为临床常用治疗手段。益生菌、抗生素和饮食等通过介导肠道菌群从而降低炎症反应和改善黏膜屏障功能,进而预防和延缓炎症性肠病的发展。但现阶段仍缺乏肠道菌群在发挥防治炎症性肠病中的有效机制,需进一步深入探讨。
2.2.4 多发性硬化症(multiple Sclerosis,MS) 多发性硬化症为中枢神经系统的脱髓鞘性神经炎和神经退化性疾病,是以青少年群体为主的神经性疾病之一[41]。研究发现,与健康受试者相比,多发性硬化症患者肠道菌群中嗜血杆菌属、蓝藻属、多莉亚属、厚壁菌属、古生菌属、甲烷短杆菌和艾克曼菌属的丰度增加 ,而梭杆菌以及叠球菌属的缺乏会导致多发性硬化症病情加重[42-44]。 此外,分段丝状细菌可促进小鼠脊髓中的Th17水平上升,诱导多发性硬化症的发展[45]。上述研究提示,肠道菌群可作为多发性硬化症诊断的标志物。
肠道菌群失调可能与多发性硬化症的发生有关,调节肠道菌群可作为多发性硬化症治疗的潜在方向。LEE等[46]通过建立多发性硬化症小鼠模型,发现无菌条件下多发性硬化症小鼠肠道和脊髓中促炎细胞因子IFN-γ和白细胞介素17A水平降低,CD49(+)、CD25(+)和调节性T细胞(Tregs)增加,并发现肠道菌群可影响多发性硬化症期间促炎和抗炎免疫反应之间的平衡,表明调节肠道细菌可在多发性硬化症的治疗中发挥关键作用。同时,口服抗生素后肠道菌群菌系显著减少,与对照组相比,小鼠对多发性硬化症诱导的敏感性显著降低,并减轻多发性硬化症疾病的严重程度[47]。此外,乳酸杆菌和拟杆菌可改变肠道菌群发挥抑制炎症作用,从而减少多发性硬化症患者临床疾病的复发[48]。而益生菌ECN连接肠道蛋白mRNA和抗菌肽可加强肠道屏障功能及改善肠道菌群稳态,调节自身免疫能力,从而延缓多发性硬化症症状中自身免疫性脑脊髓炎的严重程度[49-50]。由此可见,肠道菌群可通过改善菌群紊乱、加强肠道屏障功能和调节自身免疫能力,从而延缓多发性硬化症的进程。
综上所述,肠道菌群失调可能与多发性硬化症的发生有关,调节肠道菌群可作为多发性硬化症治疗的潜在靶点。口服抗生素、益生菌处理、肠道蛋白mRNA等通过介导肠道菌群从而加强肠道屏障功能、调节肠道炎症反应并维持肠道菌群稳态平衡,进而预防和延缓多发性硬化症的发展。调节肠道菌群可作为多发性硬化症治疗的新方向,并有助于了解肠道菌群在许多疾病中的作用。
2.2.5 强直性脊柱炎(ankylosing spondylitis,AS) 强直性脊柱炎是以骶髂关节和脊柱附着点炎症为主要症状的慢性免疫性疾病[51]。有研究认为肠道菌群可用于强直性脊柱炎的前期诊断,并发现肠道菌群失衡可引发机体炎症反应[52]。肠道内普雷沃氏菌、拟杆菌属、胃链球菌、粪球菌和拟杆菌的丰度增加,而理研菌科相对丰度降低[53-54]。此外,强直性脊柱炎患者机体内栉水母科、绒毛蕨科、卟啉科和拟杆菌科的丰度显著增加,而茜草科和瑞克氏菌科的丰度显著降低[55]。上述研究提示,肠道菌群可用于强直性脊柱炎的前期诊断。
WU等[56]研究发现,强直性脊柱炎患者外周血中存在肠道菌群失衡,并会导致机体免疫耐受性遭到破坏。而口服利福昔明可通过调节肠道菌群、改善肠屏障功能和减轻炎症反应,进而延缓强直性脊柱炎的发生发展[57-58]。同时,口服干酪乳杆菌可显著减少促炎细胞因子的表达,发挥有效抗炎作用[59]。此外,通过建立HLA-B27转基因大鼠模型发现,膳食纤维和益生菌组合可改善强直性脊柱炎大鼠肠道菌群失调,增强免疫抵抗力和降低机体炎症反应,且短链脂肪酸和丙酸盐的水平提高可减缓炎症性肠病和强直性脊柱炎的发生,其具体分子机制仍有待进一步深入探究[60-61]。
综上所述,肠道菌群可用于强直性脊柱炎的前期诊断,肠道菌群失调可作为诊断和治疗强直性脊柱炎的潜在靶点。利福昔明、膳食纤维、益生菌、短链脂肪酸等可调节肠道菌群、降低炎症反应和增强免疫抵抗力,从而进一步延缓强直性脊柱炎的发生发展。后续的研究可深入探讨肠道菌群发挥治疗强直性脊柱炎的具体分子机制,从而为强直性脊柱炎的防治提供科学依据和理论基础。
肠道菌群与自身免疫性疾病的关系,见表1。
2.3 运动与肠道菌群 运动对肠道菌群的研究尚处于起步阶段,研究表明不同运动方式对肠道菌群的作用不同。下文就有氧运动和无氧运动对肠道菌群作用的最新研究进行归纳总结。
2.3.1 有氧运动与肠道菌群 美国运动医学学院(ACSM)将有氧运动定义为任何使用大肌肉群的活动,可以连续保持并且本质上是有节奏的运动,依靠有氧代谢从氨基酸、碳水化合物和脂肪酸中提取三磷酸腺苷(ATP)形式的能量,而骑自行车、跳舞、太极、远足、慢跑/长跑、游泳等通常被认为是有氧运动[62-63]。
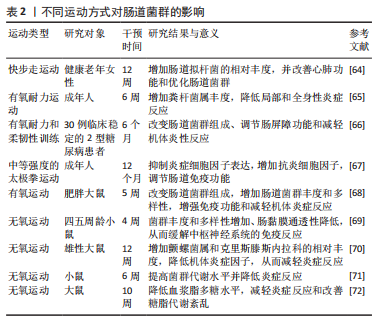
在探究有氧运动对肠道菌群作用的研究中,人体试验表明,对健康老年女性实施12周快步走运动干预,发现长时间快步走运动可增加健康老年女性肠道拟杆菌的相对丰度,从而改善心肺功能和优化肠道菌群[64]。而对成年人进行6周有氧耐力运动干预,发现有氧运动使得粪杆菌属丰度增加,可进一步降低局部和全身性炎症[65]。对30例临床稳定的2型糖尿病患者进行6个月的有氧耐力和柔韧性训练,运动后改变肠道菌群组成、改善肠屏障功能和减轻机体炎性反应[66]。同时,在研究太极拳运动对肠道菌群的影响时,认为太极拳作为一种中等强度运动可能在影响肠道菌群中发挥关键作用,也有可能是通过迷走神经调节和介导下丘脑-垂体-肾上腺轴来影响肠道菌群,改善肠道的免疫功能和炎症[67]。此外,对80只雄性肥胖大鼠模型进行5周有氧运动干预,发现可改变肠道菌群组成,增强大鼠免疫功能、减轻机体炎症、降低体脂率、增加肠道菌群丰度和多样性[68]。上述研究提示,有氧运动能调节肠道菌群,减轻机体炎症反应、增加肠道菌群丰度和改善免疫功能。
综上所述,有氧运动可增加机体中肠道菌群多样性和菌属丰度,改善肠道黏膜免疫屏障功能,降低机体代谢性炎症反应,但有氧运动调控肠道菌群促进机体健康的途径和具体机制需要进一步研究。
2.3.2 无氧运动与肠道菌群 ACSM将无氧运动定义为持续时间非常短的剧烈体力活动,由收缩肌肉内的能量源提供动力,通过糖酵解和发酵恢复ATP的形成,而短跑、高强度间歇训练(HIIT)、举重等持续的无氧代谢通常被认为是无氧运动[62]。
在探究不同无氧运动对肠道菌群作用的研究中,动物实验表明,对四五周龄小鼠进行无氧运动干预发现小鼠菌群丰度和多样性增加,肠黏膜的通透性降低,可缓解自身免疫性脑脊髓炎疾病中枢神经系统的免疫反应[69]。对雄性大鼠、小鼠进行12周和6周的无氧运动训练和补充α-亚麻酸干预后发现,无氧运动可增加小鼠肠道菌群丰度,提高肠道菌群代谢并减轻炎性反应,而大鼠肠道菌群内克里斯滕斯内拉科、螺旋体菌株和α多样性相对丰度增加 [70-71]。此外,10周的无氧运动干预可降低大鼠血浆脂多糖水平,减轻炎症反应和改善糖脂代谢紊乱,但肠道菌群区系组成未受影响[72]。以上研究表明,无氧运动对机体肠道菌群的影响研究尚存争议,但均表明可通过减轻机体炎症反应来改善机体健康。
综上所述,与有氧运动相比,无氧运动并未改变肠道菌群组成。无氧运动对机体肠道菌群的影响研究尚存争议,可能与研究对象、研究方法、运动干预的时间强度异质性有关,需要进一步深入研究。
运动与肠道菌群关系,见表2。
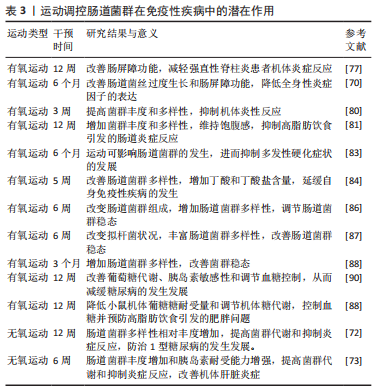
2.4 运动调控肠道菌群在自身免疫性疾病中的潜在作用 已有研究证明,运动可以介导肠道菌群对其组成、结构、功能及多样性进行有效调控,从而影响机体健康状况[73]。同时,肠道菌群通过免疫应答、免疫交流和黏膜免疫系统等功能影响免疫性疾病的发生,且肠道菌群可成为多种免疫性疾病治疗的新方向[74]。研究表明:运动主要通过调节肠道菌群改善肠道屏障功能、抑制炎症反应、调节肠道菌群稳态和改善血糖稳态,再进一步发挥免疫系统的保护作用。
2.4.1 运动调控肠道菌群改善肠道屏障功能 肠道屏障功能失调时常伴随自身免疫性疾病的发生。研究发现,益生菌治疗可加强肠道屏障功能,从而延缓多发性硬化症状中自身免疫性脑脊髓炎的严重程度[50-51]。药物干预可通过调节肠道菌群改善肠屏障功能,进而降低强直性脊柱炎的严重程度[59,75]。上述两项研究表明,可通过调节肠道菌群改善肠屏障功能达到防治自身免疫性疾病的作用。
炎症性肠病和免疫性疾病其特征都是肠道内稳态失调,肠道屏障完整性、血脑脊液屏障被破坏等多种因素相互影响导致的免疫系统失调[76]。COOK等[77]发现12周的有氧运动可通过增加黏膜层中的乳酸杆菌数量,改善肠屏障功能,进而减轻强直性脊柱炎患者机体炎症反应。2型糖尿病与免疫性疾病都有相同终末器官损害的症状表现,两者均通过多种病理生理机制相互影响。有研究发现,6个月的有氧运动可改善由2型糖尿病引起的肠道菌丝过度生长、肠道通透性增加和全身性低度炎症,表明有氧运动可通过改变肠道菌群组成和肠道屏障功能来控制2型糖尿病[70]。
由此可见,通过适度运动干预肠道菌群在维持肠道屏障完整性方面具有重要意义,但目前缺乏对不同运动负荷调控肠道菌群改善肠屏障功能来达到缓解自身免疫性疾病的系统性研究。因此,需要进一步探讨不同类型运动负荷对肠道菌群的影响,这些问题的揭示将有助于更好地理解运动调节肠道菌群发挥自身免疫性功能的途径。
2.4.2 运动调控肠道菌群抑制炎症反应 炎症反应的发生与自身免疫性疾病密切相关。乳糜泻患者机体内形成易引发炎症的肠道菌群结构可能导致肠道黏膜通透性的增大进而诱发乳糜泻[11]。肠道菌群通过改变肠道通透性诱发1型糖尿病,而肠道菌群的稳态和维持肠黏膜通透性可调节炎症反应,并抑制1型糖尿病进而维持机体健康[78]。上述研究提示,调控肠道菌群减轻炎症反应可在防治自身免疫性疾病中发挥有益效应。适度运动可调控肠道菌群抑制炎症反应、改善免疫功能和预防炎症性疾病的发生[79]。DING等[80]通过建立大鼠模型,发现3周的有氧运动可提高大鼠的菌群丰度和多样性并减少炎症递质的表达,从而抑制炎症反应和减轻大鼠炎症性脑损伤。另有研究表明,12周的有氧运动干预可增加肠道菌群的多样化,维持饱腹感,减少高脂肪饮食所引起的肠道炎症反应[81]。终身体力活动可显著改善肠道菌群的组成结构,如嗜粘菌阿克曼菌、普雷沃氏菌和拟杆菌的增加,导致机体炎症降低,从而改善多发性硬化症疾病[82]。MOKHTARZADE等[83]对42例多发性硬化症患者进行为期6个月的家庭运动(每周5次)干预,结果发现运动导致肠道菌群改变,嗜粘菌阿克曼菌、普雷沃氏菌增加,白细胞介素10和肿瘤坏死因子α表示下降,从而减轻机体炎症,抑制多发性硬化症疾病的发展。
由此可见,可通过运动调节肠道菌群减轻炎症反应来达到防治免疫性疾病的目的。但现阶段缺乏对具体炎性细胞因子的研究。因此,探讨运动调控肠道菌群抑制炎性因子表达在防治自身免疫性疾病中具有重要作用。
2.4.3 运动调控肠道菌群调节肠道菌群稳态 肠道菌群稳态与自身免疫性疾病密切相关。1型糖尿病患者肠道菌群多样性显著降低,肠道菌群结构发生改变,肠道菌群失衡,机体内促炎细胞因子和脂多糖增加[24]。LEE等[39]发现平淡饮食通过改善肠道菌群,减轻肠道炎症、促进黏膜愈合和组织功能,进而延缓炎症性肠病发展。此外,研究发现肠道蛋白mRNA可加强肠道屏障及肠道菌群稳态平衡,从而延缓强直性脊柱炎的发生[51]。上述研究提示,改善肠道菌群多样性可作为治疗自身免疫性疾病的潜在靶点。
有氧运动干预5周可改善肠道菌群多样性,增加丁酸和丁酸盐含量,从而延缓自身免疫性疾病的发生发展[84]。且有氧运动干预6周可增加人类的肠道微生物多样性,进而调控肠道菌群稳态[85]。MONDA等[86]也发现通过6周有氧运动干预可改善拟杆菌状况,并丰富肠道菌群的多样性,从而改善肠道菌群稳态。在动物实验中,发现对大鼠进行6周的持续体力活动前后蛋白激酶活性的增加从而导致菌群丰度增加,进而改善肠道菌群稳态[87]。同时,对肥胖小鼠模型施加多氯联苯再进行3个月运动干预后小鼠肠道菌群多样性增加[88]。上述研究表明,有氧运动干预可通过调控肠道菌群多样性、改善肠道菌群稳态,作为防治自身免疫性疾病的潜在方式之一。
2.4.4 运动调控肠道菌群改善血糖稳态 1型糖尿病是由免疫机制破坏产生胰岛素的β细胞大量凋亡引起血糖升高,使机体胰岛素相对不足和血糖摄取利用减少,而导致常见的自身免疫性疾病[18]。肠道菌群可通过调节血糖改善自身免疫性疾病。此外,有研究表明,补充益生菌可改善肠道菌群失调,抑制辅助性 T 淋巴细胞分化,降低血糖减轻胰岛炎症,从而延缓1型糖尿病的发展[30-31]。上述研究提示,肠道菌群可通过改善胰岛细胞自身免疫和减轻胰岛炎症进而调节血糖,起到防治自身免疫性疾病的作用。
运动可通过调控肠道菌群来改善血糖稳态,进而延缓1型糖尿病的发生发展。研究表明不同运动方式通过介导肠道菌群的组成和代谢来调节菌群多样性,从而改善2型糖尿病小鼠的血糖稳态,且不同运动方式在改善血糖控制的效果上可能与运动时间、强度和频率不同相关[89]。另有研究发现,对糖尿病患者实施12周的有氧运动干预来调节肠道菌群,可改善葡萄糖代谢、胰岛素敏感性和调节血糖控制,从而减缓糖尿病的发生发展[90]。同时,12周有氧运动可降低小鼠机体葡萄糖耐受量和调节机体糖代谢,从而诱导肠道菌群发生转变,控制血糖并预防高脂肪饮食引发的肥胖问题[88]。此外,对大鼠和小鼠分别实施为期12周和6周的无氧运动干预,发现大鼠肠道菌群α多样性相对丰度增加,而小鼠肠道菌群丰度和胰岛素耐受能力增加,并提高肠道菌群代谢和抑制炎症反应,进而改善机体肝脏炎症,防治1型糖尿病的发生发展[72-73]。由此可见,通过运动干预调控肠道菌群改善血糖稳态、胰岛素敏感性和葡萄糖代谢,进而调节血糖控制,可作为改善自身免疫性疾病潜在方式之一。
运动调控肠道菌群在免疫性疾病中的潜在作用,见表3。
| [1] MILLER FW. Environmental agents and autoimmune diseases. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2011;711:61-81. [2] 王宇恒.自身免疫性疾病药物市场潜力巨大[N]. 中国医药报,2021-11-19(004). [3] PASCALE A, MARCHESI N, MARELLI C, et al. Microbiota and metabolic diseases. Endocrine. 2018;61(3):357-371. [4] KAU AL, AHERN PP, GRIFFIN NW, et al. Human nutrition, the gut microbiome and the immune system. Nature. 2011;474(7351):327-336. [5] YATSUNENKO T, REY FE, MANARY MJ, et al. Human gut microbiome viewed across age and geography. Nature. 2012;486(7402):222-227. [6] GOMAA EZ. Human gut microbiota/microbiome in health and diseases: a review. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek. 2020;113(12):2019-2040. [7] SIMS EK, BESSER REJ, DAYAN C, et al. Screening for Type 1 Diabetes in the General Population: A Status Report and Perspective. Diabetes. 2022;71(4):610-623. [8] DEDRICK S, SUNDARESH B, HUANG Q, et al. The Role of Gut Microbiota and Environmental Factors in Type 1 Diabetes Pathogenesis. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2020;11:78. [9] 于莹莹,张小莉,宋超杰,等.肠道菌群对1型糖尿病肠道通透性及免疫作用机制研究进展[J].微生物学杂志,2019,39(4):115-121. [10] MURRI M, LEIVA I, GOMEZ-ZUMAQUERO JM, et al. Gut microbiota in children with type 1 diabetes differs from that in healthy children: a case-control study. BMC Med. 2013;11:46. [11] KOSTIC AD, GEVERS D, SILJANDER H, et al. The dynamics of the human infant gut microbiome in development and in progression toward type 1 diabetes. Cell Host Microbe. 2015;17(2):260-273. [12] GIONGO A, GANO KA, CRABB DB, et al. Toward defining the autoimmune microbiome for type 1 diabetes. Isme J. 2011;5(1):82-91. [13] LEIVA-GEA I, SáNCHEZ-ALCOHOLADO L, MARTíN-TEJEDOR B, et al. Gut Microbiota Differs in Composition and Functionality Between Children With Type 1 Diabetes and MODY2 and Healthy Control Subjects: A Case-Control Study. Diabetes Care. 2018;41(11):2385-2395. [14] CANI PD, BIBILONI R, KNAUF C, et al. Changes in gut microbiota control metabolic endotoxemia-induced inflammation in high-fat diet-induced obesity and diabetes in mice. Diabetes. 2008;57(6):1470-1481. [15] MACPHERSON AJ, UHR T. Induction of protective IgA by intestinal dendritic cells carrying commensal bacteria. Science. 2004;303(5664):1662-1665. [16] HARBISON JE, ROTH-SCHULZE AJ, GILES LC, et al. Gut microbiome dysbiosis and increased intestinal permeability in children with islet autoimmunity and type 1 diabetes: A prospective cohort study. Pediatr Diabetes. 2019;20(5):574-583. [17] LUO A, LEACH ST, BARRES R, et al. The Microbiota and Epigenetic Regulation of T Helper 17/Regulatory T Cells: In Search of a Balanced Immune System. Front Immunol. 2017;8:417. [18] DE GOFFAU MC, LUOPAJäRVI K, KNIP M, et al. Fecal microbiota composition differs between children with β-cell autoimmunity and those without. Diabetes. 2013;62(4):1238-1244. [19] 刘艳,李科.肠道菌群与糖尿病的相关研究进展[J].中国微生态学杂志,2021, 33(11):1354-1357. [20] DE RE V, MAGRIS R, CANNIZZARO R. New Insights into the Pathogenesis of Celiac Disease. Front Med (Lausanne). 2017;4:137. [21] BODKHE R, SHETTY SA, DHOTRE DP, et al. Comparison of Small Gut and Whole Gut Microbiota of First-Degree Relatives With Adult Celiac Disease Patients and Controls. Front Microbiol. 2019;10:164. [22] 郑德开,张绍衡,陈烨.肠道菌群失衡与乳糜泻:重要性及可能机制[J].微生物学报,2021,61(2):292-299. [23] SANZ Y, SÁNCHEZ E, MARZOTTO M, et al. Differences in faecal bacterial communities in coeliac and healthy children as detected by PCR and denaturing gradient gel electrophoresis. FEMS Immunol Med Microbiol. 2007;51(3):562-568. [24] OLIVARES M, BENíTEZ-PáEZ A, DE PALMA G, et al. Increased prevalence of pathogenic bacteria in the gut microbiota of infants at risk of developing celiac disease: The PROFICEL study. Gut Microbes. 2018;9(6):551-558. [25] CHENG J, KALLIOMäKI M, HEILIG HG, et al. Duodenal microbiota composition and mucosal homeostasis in pediatric celiac disease. BMC Gastroenterol. 2013;13:113. [26] HERRÁN AR, PÉREZ-ANDRÉS J, CAMINERO A, et al. Gluten-degrading bacteria are present in the human small intestine of healthy volunteers and celiac patients. Res Microbiol. 2017;168(7):673-684. [27] AKOBENG AK, SINGH P, KUMAR M, et al. Role of the gut microbiota in the pathogenesis of coeliac disease and potential therapeutic implications. Eur J Nutr. 2020;59(8):3369-3390. [28] MARIETTA E, MANGALAM AK, TANEJA V, et al. Intestinal Dysbiosis in, and Enteral Bacterial Therapies for, Systemic Autoimmune Diseases. Front Immunol. 2020;11: 573079. [29] DESAI MS, SEEKATZ AM, KOROPATKIN NM, et al. A Dietary Fiber-Deprived Gut Microbiota Degrades the Colonic Mucus Barrier and Enhances Pathogen Susceptibility. Cell. 2016;167(5):1339-1353.e21. [30] KLEMENAK M, DOLINŠEK J, LANGERHOLC T, et al. Administration of Bifidobacterium breve Decreases the Production of TNF-α in Children with Celiac Disease. Dig Dis Sci. 2015;60(11):3386-3392. [31] FRANCAVILLA R, PICCOLO M, FRANCAVILLA A, et al. Clinical and Microbiological Effect of a Multispecies Probiotic Supplementation in Celiac Patients With Persistent IBS-type Symptoms: A Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-controlled, Multicenter Trial. J Clin Gastroenterol. 2019;53(3):e117-e125. [32] FRANK DN, ST AMAND AL, FELDMAN RA, et al. Molecular-phylogenetic characterization of microbial community imbalances in human inflammatory bowel diseases. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2007;104(34):13780-13785. [33] 刘乐恒,张茜,薛庆节,等.肠道菌群及其在炎症性肠病中的作用[J].中国免疫学杂志,2020,36(16):2036-2041. [34] WANG W, CHEN L, ZHOU R, et al. Increased proportions of Bifidobacterium and the Lactobacillus group and loss of butyrate-producing bacteria in inflammatory bowel disease. J Clin Microbiol. 2014;52(2):398-406. [35] ORMSBY MJ, LOGAN M, JOHNSON SA, et al. Inflammation associated ethanolamine facilitates infection by Crohn’s disease-linked adherent-invasive Escherichia coli. EBioMedicine. 2019;43:325-332. [36] ZHAO Z, XU S, ZHANG W, et al. Probiotic Escherichia coli NISSLE 1917 for inflammatory bowel disease applications . Food Funct. 2022;13(11):5914-5924. [37] WANG J, GOEPFERT C, MUELLER N, et al. Larval Echinococcus multilocularis infection reduces dextran sulphate sodium-induced colitis in mice by attenuating T helper type 1/type 17-mediated immune reactions. Immunology. 2018;154(1): 76-88. [38] KANAUCHI O, OSHIMA T, ANDOH A, et al. Germinated barley foodstuff ameliorates inflammation in mice with colitis through modulation of mucosal immune system. Scand J Gastroenterol. 2008;43(11):1346-1352. [39] LEE D, ALBENBERG L, COMPHER C, et al. Diet in the pathogenesis and treatment of inflammatory bowel diseases. Gastroenterology, 2015;148(6):1087-1106. [40] DUBINSKY V, RESHEF L, BAR N, et al. Predominantly Antibiotic-resistant Intestinal Microbiome Persists in Patients With Pouchitis Who Respond to Antibiotic Therapy. Gastroenterology. 2020;158(3):610-624.e13. [41] 陈虎,丁国梁.间充质干细胞在多发性硬化症治疗中的应用:全球研究探索与展望[J].解放军医学杂志,2016,41(2):87-93. [42] TREMLETT H, FADROSH DW, FARUQI AA, et al. Gut microbiota composition and relapse risk in pediatric MS: A pilot study. J Neurol Sci. 2016;363:153-157. [43] JANGI S, GANDHI R, COX LM, et al. Alterations of the human gut microbiome in multiple sclerosis. Nat Commun. 2016;7:12015. [44] CHEN J, CHIA N, KALARI KR, et al. Multiple sclerosis patients have a distinct gut microbiota compared to healthy controls. Sci Rep. 2016;6:28484. [45] IVANOV II, ATARASHI K, MANEL N, et al. Induction of intestinal Th17 cells by segmented filamentous bacteria. Cell. 2009;139(3):485-498. [46] LEE YK, MENEZES JS, UMESAKI Y, et al. Proinflammatory T-cell responses to gut microbiota promote experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2011;108 Suppl 1(Suppl 1):4615-4622. [47] OCHOA-REPáRAZ J, MIELCARZ DW, DITRIO LE, et al. Role of gut commensal microflora in the development of experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. J Immunol. 2009;183(10):6041-6050. [48] SCHEPICI G, SILVESTRO S, BRAMANTI P, et al. The Gut Microbiota in Multiple Sclerosis: An Overview of Clinical Trials. Cell Transplant. 2019;28(12):1507-1527. [49] SECHER T, KASSEM S, BENAMAR M, et al. Oral Administration of the Probiotic Strain Escherichia coli Nissle 1917 Reduces Susceptibility to Neuroinflammation and Repairs Experimental Autoimmune Encephalomyelitis-Induced Intestinal Barrier Dysfunction. Front Immunol. 2017;8:1096. [50] KRUIS W, FRIC P, POKROTNIEKS J, et al. Maintaining remission of ulcerative colitis with the probiotic Escherichia coli Nissle 1917 is as effective as with standard mesalazine. Gut. 2004;53(11):1617-1623. [51] 闫婷婷,李军霞.肠道菌群与强直性脊柱炎的关系[J].现代免疫学,2021, 41(1):84-87. [52] 蒋光明.肠道菌群及FUT2/3基因多态性与强直性脊柱炎的相关性研究[D].合肥:安徽医科大学,2021. [53] LIN P, BACH M, ASQUITH M, et al. HLA-B27 and human β2-microglobulin affect the gut microbiota of transgenic rats. PLoS One. 2014;9(8):e105684. [54] RATH HC, HERFARTH HH, IKEDA JS, et al. Normal luminal bacteria, especially Bacteroides species, mediate chronic colitis, gastritis, and arthritis in HLA-B27/human beta2 microglobulin transgenic rats. J Clin Invest. 1996;98(4):945-953. [55] STEBBINGS S, MUNRO K, SIMON MA, et al. Comparison of the faecal microflora of patients with ankylosing spondylitis and controls using molecular methods of analysis. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2002;41(12):1395-1401. [56] WU Y, REN M, YANG R, et al. Reduced immunomodulation potential of bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells induced CCR4+CCR6+ Th/Treg cell subset imbalance in ankylosing spondylitis. Arthritis Res Ther. 2011;13(1):R29. [57] PONZIANI FR, ZOCCO MA, D’AVERSA F, et al. Eubiotic properties of rifaximin: Disruption of the traditional concepts in gut microbiota modulation. World J Gastroenterol. 2017;23(25):4491-4499. [58] YANG L, WANG L, WANG X, et al. A Possible Role of Intestinal Microbiota in the Pathogenesis of Ankylosing Spondylitis. Int J Mol Sci. 2016;17(12):2126. [59] AMDEKAR S, SINGH V, SINGH R, et al. Lactobacillus casei reduces the inflammatory joint damage associated with collagen-induced arthritis (CIA) by reducing the pro-inflammatory cytokines: Lactobacillus casei: COX-2 inhibitor. J Clin Immunol. 2011;31(2):147-154. [60] HOENTJEN F, WELLING GW, HARMSEN HJ, et al. Reduction of colitis by prebiotics in HLA-B27 transgenic rats is associated with microflora changes and immunomodulation. Inflamm Bowel Dis. 2005;11(11):977-985. [61] ASQUITH M, DAVIN S, STAUFFER P, et al. Intestinal Metabolites Are Profoundly Altered in the Context of HLA-B27 Expression and Functionally Modulate Disease in a Rat Model of Spondyloarthritis. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2017;69(10):1984-1995. [62] THOMPSON PD, ARENA R, RIEBE D, et al. ACSM’s new preparticipation health screening recommendations from ACSM’s guidelines for exercise testing and prescription, ninth edition. Curr Sports Med Rep. 2013;12(4):215-217. [63] PATEL H, ALKHAWAM H, MADANIEH R, et al. Aerobic vs anaerobic exercise training effects on the cardiovascular system. World J Cardiol. 2017;9(2):134-138. [64] MORITA E, YOKOYAMA H, IMAI D, et al. Aerobic Exercise Training with Brisk Walking Increases Intestinal Bacteroides in Healthy Elderly Women. Nutrients. 2019;11(4):868. [65] ALLEN JM, MAILING LJ, NIEMIRO GM, et al. Exercise Alters Gut Microbiota Composition and Function in Lean and Obese Humans. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2018;50(4):747-757. [66] PASINI E, CORSETTI G, ASSANELLI D, et al. Effects of chronic exercise on gut microbiota and intestinal barrier in human with type 2 diabetes. Minerva Med. 2019;110(1):3-11. [67] HAMASAKI H. Exercise and gut microbiota: clinical implications for the feasibility of Tai Chi. J Integr Med. 2017;15(4):270-281. [68] 林旺.低氧运动对食源性肥胖大鼠肠道菌群及免疫功能的影响[D].南昌:江西师范大学,2020. [69] CHEN H, SHEN L, LIU Y, et al. Strength Exercise Confers Protection in Central Nervous System Autoimmunity by Altering the Gut Microbiota. Front Immunol. 2021;12:628629. [70] DUPUIT M, CHAVANELLE V, CHASSAING B, et al. The TOTUM-63 Supplement and High-Intensity Interval Training Combination Limits Weight Gain, Improves Glycemic Control, and Influences the Composition of Gut Mucosa-Associated Bacteria in Rats on a High Fat Diet. Nutrients. 2021;13(5):1569. [71] FREDRICKSON G, BARROW F, DIETSCHE K, et al. Exercise of high intensity ameliorates hepatic inflammation and the progression of NASH. Mol Metab. 2021;53:101270. [72] MAILLARD F, VAZEILLE E, SAUVANET P, et al. High intensity interval training promotes total and visceral fat mass loss in obese Zucker rats without modulating gut microbiota. PLoS One. 2019;14(4):e0214660. [73] 梁家琪,刘恒旭,阳金鑫,等.运动与肠道菌健康效益的关系[J].中国组织工程研究,2023,27(8):1292-1299. [74] 沈茜,田继裕.肠道菌群构成及其对免疫性疾病的影响[J].世界最新医学信息文摘,2019,19(16):82+84. [75] YANG L, LIU B, ZHENG J, et al. Rifaximin Alters Intestinal Microbiota and Prevents Progression of Ankylosing Spondylitis in Mice. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2019; 9:44. [76] KASIMAY O, GüZEL E, GEMICI A, et al. Colitis-induced oxidative damage of the colon and skeletal muscle is ameliorated by regular exercise in rats: the anxiolytic role of exercise. Exp Physiol. 2006;91(5):897-906. [77] COOK MD, ALLEN JM, PENCE BD, et al. Exercise and gut immune function: evidence of alterations in colon immune cell homeostasis and microbiome characteristics with exercise training. Immunol Cell Biol. 2016;94(2):158-163. [78] YOU S, THIEBLEMONT N, ALYANAKIAN MA, et al. Transforming growth factor-beta and T-cell-mediated immunoregulation in the control of autoimmune diabetes. Immunol Rev. 2006;212:185-202. [79] VIEIRA VJ, VALENTINE RJ, WILUND KR, et al. Effects of exercise and low-fat diet on adipose tissue inflammation and metabolic complications in obese mice. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2009;296(5):E1164-E1171. [80] DING YH, YOUNG CN, LUAN X, et al. Exercise preconditioning ameliorates inflammatory injury in ischemic rats during reperfusion. Acta Neuropathol. 2005; 109(3):237-246. [81] CAMPBELL SC, WISNIEWSKI PJ, NOJI M, et al. The Effect of Diet and Exercise on Intestinal Integrity and Microbial Diversity in Mice. PLoS One. 2016;11(3): e0150502. [82] MOKHTARZADE M, MOLANOURI SHAMSI M, ABOLHASANI M, et al. Lifetime physical activity is associated with gut bacteria and brain health in people with multiple sclerosis: Focus on physical activity intensity. Mult Scler Relat Disord. 2022;59:103639. [83] MOKHTARZADE M, MOLANOURI SHAMSI M, ABOLHASANI M, et al. Home-based exercise training influences gut bacterial levels in multiple sclerosis. Complement Ther Clin Pract. 2021;45:101463. [84] BARCELO A, CLAUSTRE J, MORO F, et al. Mucin secretion is modulated by luminal factors in the isolated vascularly perfused rat colon. Gut. 2000;46(2):218-224. [85] ALLEN JM, BERG MILLER ME, PENCE BD, et al. Voluntary and forced exercise differentially alters the gut microbiome in C57BL/6J mice. J Appl Physiol (1985). 2015;118(8):1059-1066. [86] MONDA V, VILLANO I, MESSINA A, et al. Exercise Modifies the Gut Microbiota with Positive Health Effects [J]. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2017;2017:3831972. [87] KELLY M, KELLER C, AVILUCEA PR, et al. AMPK activity is diminished in tissues of IL-6 knockout mice: the effect of exercise. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2004;320(2):449-454. [88] EVANS CC, LEPARD KJ, KWAK JW, et al. Exercise prevents weight gain and alters the gut microbiota in a mouse model of high fat diet-induced obesity. PLoS One. 2014;9(3):e92193. [89] 韦薇,张秋,黄燕凤,等.不同运动方式对2型糖尿病小鼠肠道菌群及短链脂肪酸的影响[J].广西医科大学学报,2022,39(4):643-648. [90] LIU Y, WANG Y, NI Y, et al. Gut Microbiome Fermentation Determines the Efficacy of Exercise for Diabetes Prevention. Cell Metab. 2020;31(1):77-91.e5. |
| [1] | 农复香, 蒋志雄, 李英豪, 许文聪, 施智兰, 罗 慧, 张晴朗, 钟 爽, 唐梅文. 外泌体调控铁死亡在疾病诊断治疗中的应用与作用[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2023, 27(在线): 1-10. |
| [2] | 刘金玉, 张晗硕, 崔洪鹏, 潘灵之, 赵博然, 李 菲, 丁 宇. 脊柱微创治疗脊髓型颈椎病的有限元生物力学分析及精准化运动康复方案[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2023, 27(9): 1359-1364. |
| [3] | 潘钟杰, 秦志鸿, 郑铁军, 丁晓飞, 廖世杰. 股骨头坏死发病机制中非编码RNA的靶标性[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2023, 27(9): 1441-1447. |
| [4] | 蔡志浩, 谢召勇. 股骨颈前倾角测量评估:如何建立统一的方法和标准[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2023, 27(9): 1448-1454. |
| [5] | 党 祎, 杜成砚, 姚红林, 袁能华, 曹 金, 熊 山, 张顶梅, 王 信. 激素型骨坏死与氧化应激[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2023, 27(9): 1469-1476. |
| [6] | 王 继, 张 敏, 杨中亚, 张 龙. 体力活动干预2型糖尿病肌少症的研究现状[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2023, 27(8): 1272-1277. |
| [7] | 聂晨晨, 苏凯奇, 高 静, 凡勇福, 阮晓迪, 袁 洁, 段昭远, 冯晓东. 环状RNA调控脑缺血发病的作用与机制[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2023, 27(8): 1286-1291. |
| [8] | 梁家琪, 刘恒旭, 阳金鑫, 杨 椅, 邓旭辉, 谭明健, 罗 炯. 运动与肠道菌健康效益的关系[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2023, 27(8): 1292-1299. |
| [9] | 高 煜, 韩佳慧, 葛 新. 脊髓缺血再灌注损伤后的免疫炎性微环境[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2023, 27(8): 1300-1305. |
| [10] | 黄林科, 韦林华, 蒋 捷, 刘 倩, 陈蔚蔚. 雌激素与跑台运动干预卵巢切除模型小鼠骨量和关节软骨的变化[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2023, 27(8): 1166-1171. |
| [11] | 毕耕超, 张彦龙, 李秋月, 胡龙威, 张 愉. 不同高度和间距下跳深动作中膝关节力学和周围肌肉的激活特征[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2023, 27(8): 1211-1218. |
| [12] | 阮 凌, 王光华, 吴荣平, 晋 战, 吕镇庆, 张 楠, 李寿邦. 运动强度与高脂饮食模型大鼠脂代谢紊乱和氧化应激的相关性[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2023, 27(8): 1149-1155. |
| [13] | 张 艳, 何瑞波, 王庆博, 皮亦华, 陆春敏, 徐传仪, 马 刚, 彭 朋. 不同负荷量有氧运动对肥胖大鼠骨骼肌炎症反应和胰岛素信号途径的影响及机制[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2023, 27(8): 1237-1244. |
| [14] | 吴东哲, 高晓嶙, 李闯涛, 王 昊. 根据心肺最佳点构建反向传播神经网络最大摄氧量预测模型[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2023, 27(8): 1224-1231. |
| [15] | 杨九杰, 李 治, 王树杰, 田 野, 赵 伟. 神经电生理监测硬脊膜切开减压治疗急性脊髓损伤过程中脊髓的功能变化[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2023, 27(8): 1232-1236. |
大量研究表明,自身免疫性疾病的发生常常伴随着肠道菌群生态系统的失调。早期关于肠道菌群的研究受到如体外检测等技术限制,无法进行全面的数据分析。近年来,随着宏基因组、宏转录组检测的发展,肠道菌群参与1型糖尿病、乳糜泻、炎症性肠病、多发性硬化症、强直性脊柱炎等自身免疫性疾病的发生发展,通过改善肠道菌群失调、维持肠屏障功能、调节免疫炎症反应等可调控自身免疫性疾病。而通过运动干预可改善肠道屏障功能、抑制炎症反应、调节肠道菌群稳态和改善血糖稳态进而在自身免疫性疾病中发挥重要作用。但现阶段关于运动与肠道菌群及运动干预肠道菌群在自身免疫性疾病的防治中的具体机制所知较少。因此,该文梳理了肠道菌群与1型糖尿病、乳糜泻、炎症性肠病、多发性硬化症、强直性脊柱炎等自身免疫性疾病的之间的关系,并总结了不同运动形式对肠道菌群的影响以及运动调控肠道菌群在自身免疫性疾病中的潜在作用,以期为肠道菌群在自身免疫性疾病的诊疗和通过运动干预作用于肠道菌群进而改善自身免疫性疾病的相关研究提供参考。
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:组织构建;骨细胞;软骨细胞;细胞培养;成纤维细胞;血管内皮细胞;骨质疏松;组织工程
1.1.1 检索人及检索时间 第一作者于2022年7-10月进行文献检索收集。
1.1.2 检索文献时限 检索1996年8月至2022年10月发表的相关文献。
1.1.3 检索数据库 中国知网和PubMed数据库。
1.1.4 检索词 中文检索词为“肠道菌群、肠道细菌、自身免疫性疾病、1型糖尿病、乳糜泻、炎症性肠病、多发性硬化症、强直性脊柱炎、运动”,英文检索词为“Intestinal flora,intestinal bacteria,autoimmune diseases,type 1 diabetes,celiac disease,inflammatory bowel disease,multiple sclerosis,ankylosing spondylitis,exercise”。
1.1.5 检索文献类型 综述、荟萃分析、期刊文章、学位论文。
1.1.6 检索策略 以PubMed数据库为例,见图1。
1.2 筛选标准
1.2.1 纳入标准 ①肠道菌群与自身免疫性疾病的相关研究;②运动与肠道菌群的相关研究;③运动干预肠道菌群改善自身免疫性疾病的相关研究。
1.2.2 排除标准 ①会议、讲座;②重复性研究;③数据报告不完整或数据无法索取。
1.3 筛选流程与文献质量评价 通过阅读标题、摘要及关键词对文献进行初步筛选,排除重复研究与纳入标准无关的中英文文献,查阅全文最终保留90篇文献,见图2。
3.2 作者综述区别于他人他篇的特点 该综述总结了目前学者关于不同运动干预对肠道菌群的影响以及运动调控肠道菌群防治自身免疫性疾病的相关研究结果,重点介绍了运动干预对肠道菌群的影响,如有氧运动可调节肠道菌群、减轻机体炎症反应、增加肠道菌群丰度和改善免疫功能;与有氧运动相比,无氧运动并未改变肠道菌群组成,无氧运动对机体肠道菌群的影响研究尚存争议,可能与研究对象、研究方法、运动干预的时间强度异质性有关,需要进一步深入研究。其次,运动在调控肠道菌群防治自身免疫性疾病中发挥关键作用,主要包括:①有氧运动可增加黏膜层中的乳酸杆菌数量、防治肠道菌丝过度生长和改善肠道通透性增加,进而改善肠屏障功能,缓解自身免疫性疾病的发生发展。②有氧运动可改善肠道菌群的组成结构,如嗜粘菌阿克曼菌、普雷沃氏菌和拟杆菌的增加,下调白细胞介素10和肿瘤坏死因子,从而减轻机体炎症,抑制多发性硬化症疾病的发展。③有氧运动可增加肠道菌群多样性,提高短链脂肪酸含量,调节肠道菌群稳态,从而延缓自身免疫性疾病的发生发展。④运动干预调控肠道菌群改善血糖稳态、胰岛素敏感性和葡萄糖代谢,进而调节血糖控制改善自身免疫性疾病。
3.3 综述的局限性 文章综述了运动调节肠道菌群对改善自身免疫性疾病的可能作用,但现阶段缺乏与运动调控肠道菌群相关的具体分子机制。运动对肠道菌群产生影响,运动调控肠道菌群受机体自身状态、饮食和锻炼方式等多种影响,运动对肠道菌群的影响仍需具体探索。此外,应进一步研究运动调控肠道菌群免疫保护的具体机制。
3.4 综述的重要意义 文章综述了肠道菌群在自身免疫性疾病中的作用以及运动对肠道菌群的影响,并分析运动调控在改善自身免疫性疾病中的具体作用,为肠道菌群在自身免疫性疾病中的诊疗和通过运动调控肠道菌群进而改善自身免疫性的相关研究提供参考依据。并发现运动可通过调节肠道菌群稳态、改善肠道屏障功能、抑制机体炎症反应、改善血糖稳态等不同方式为自身免疫性疾病的防治提供了新的思路和方案。此外,综述发现运动调控肠道菌群可能是促进机体健康的新靶点,且在防治免疫性疾病中发挥重要作用。随着对肠道菌群-运动-免疫性的深入研究探讨,相信这些研究可在未来的自身免疫性疾病防治中发挥关键作用。
3.5 课题组专家的建议 ①目前关于运动调控肠道菌群改善自身免疫性疾病的研究较少,缺乏更深层次具体研究,需进一步阐明其具体机制;②运动对肠道菌群可产生有益影响,但不同类型的运动方案对肠道菌群的影响存在差异,训练状态、训练环境、训练负荷、健康状况、患病状况以及运动习惯等也是影响运动和肠道菌群关系的重要因素;③目前运动调控肠道菌群改善自身免疫性疾病的这一治疗方法尚待深入研究,且临床运用较少,未来应进一步加强运动与生活方式、饮食结构、抗生素、益生菌等多维度、多元化、多视角的组合形式,提高其临床应用的质量,通过制定科学的运动处方,从而为自身免疫性疾病的防治中提供科学的理论基础。 中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:组织构建;骨细胞;软骨细胞;细胞培养;成纤维细胞;血管内皮细胞;骨质疏松;组织工程
 #br#
#br#
文题释义:#br# 肠道菌群:是人体内最复杂和种群数量最高的共生微生物生态系统,对机体的代谢、营养和调节等发挥着重要作用,是近年来防治自身免疫性疾病相关研究的热点之一。#br# 肠道菌群对自身免疫性疾病的作用及运动干预:运动可通过调节肠道菌群改善肠道屏障功能、抑制炎症反应、调节肠道菌群稳态和改善血糖稳态,进而在1型糖尿病、乳糜泻、炎症性肠病、多发性硬化症和强直性脊柱炎等自身免疫性疾病的预防与治疗中发挥免疫系统的保护作用。#br# 中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:组织构建;骨细胞;软骨细胞;细胞培养;成纤维细胞;血管内皮细胞;骨质疏松;组织工程
近年来,研究者们发现肠道菌群与自身免疫性疾病的发生发展存在密切联系,肠道菌群可通过饮食、抗生素、益生菌和菌群移植等不同方式调节肠道菌群改善自身免疫性疾病,且运动可有效改善肠道菌群的组成和多样性,进而改善肠屏障功能、抑制炎症反应等。然而,现阶段关于肠道菌群及其代谢产物对自身免疫性疾病作用的具体分子机制仍需完善;不同运动方式、运动时间、运动强度等对肠道菌群的影响及其差异需进一步深入研究;同时运动干预肠道菌群发挥防治自身免疫性疾病的相互作用机制等问题尚未阐明。该综述总结了目前学者关于不同运动干预对肠道菌群的影响以及运动调控肠道菌群防治自身免疫性疾病的相关研究结果。重点介绍了运动干预对肠道菌群的影响,如有氧运动可调节肠道菌群、减轻机体炎症反应、增加肠道菌群丰度和改善免疫功能;与有氧运动相比,无氧运动并未改变肠道菌群组成,无氧运动对机体肠道菌群的影响研究尚存争议,可能与研究对象、研究方法、运动干预的时间强度异质性有关。
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||