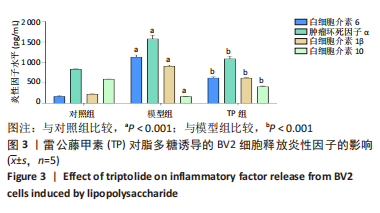
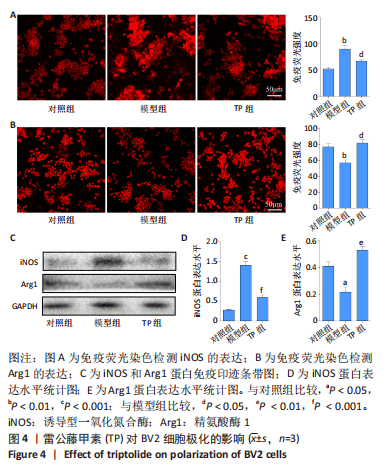
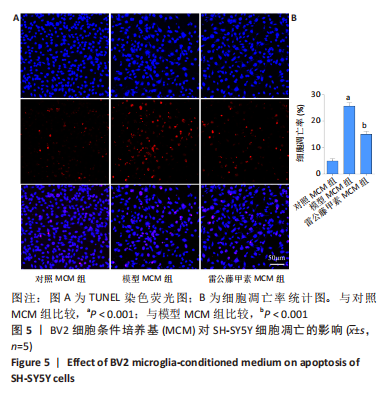
[1] STEPHENSON J, NUTMA E, VAN DER VALK P, et al. Inflammation in CNS neurodegenerative diseases. Immunology. 2018;154(2):204-219.
[2] SONG GJ, SUK K. Pharmacological Modulation of Functional Phenotypes of Microglia in Neurodegenerative Diseases. Front Aging Neurosci. 2017;9:139.
[3] GuO S, WANG H, YIN Y. Microglia Polarization From M1 to M2 in Neurodegenerative Diseases. Front Aging Neurosci. 2022;14:815347.
[4] 王贝,赵雨航,王乐伟,等.柚皮苷通过调节小胶质细胞极化对APPswe/PS1dE9双转基因小鼠的认知功能影响[J]. 中国比较医学杂志,2021,31(2): 1-7.
[5] BÉCHADE C, CANTAUT-BELARIF Y, BESSIS A. Microglial control of neuronal activity. Front Cell Neurosci. 2013;7:32.
[6] EYO UB, WU LJ. Bidirectional microglia-neuron communication in the healthy brain. Neural Plast. 2013;2013:456857.
[7] CSERÉP C, PÓSFAI B, DÉNES Á. Shaping Neuronal Fate: Functional Heterogeneity of Direct Microglia-Neuron Interactions. Neuron. 2021; 109(2):222-240.
[8] NOEL P, VON HOFF DD, SALUJA AK, et al. Triptolide and Its Derivatives as Cancer Therapies. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 2019;40(5):327-341.
[9] CUI YQ, WANG Q, ZHANG DM, et al. Triptolide Rescues Spatial Memory Deficits and Amyloid-β Aggregation Accompanied by Inhibition of Inflammatory Responses and MAPKs Activity in APP/PS1 Transgenic Mice. Curr Alzheimer Res. 2016;13(3):288-296.
[10] GAO JP, SUN S, LI WW, et al. Triptolide protects against 1-methyl-4-phenyl pyridinium-induced dopaminergic neurotoxicity in rats: implication for immunosuppressive therapy in Parkinson’s disease. Neurosci Bull. 2008;24(3):133-142.
[11] BAI S, HU Z, YANG Y, et al. Anti-Inflammatory and Neuroprotective Effects of Triptolide via the NF-κB Signaling Pathway in a Rat MCAO Model. Anat Rec (Hoboken). 2016;299(2):256-266.
[12] ZHANG T, GONG X, HU G, et al. EP2-PKA signaling is suppressed by triptolide in lipopolysaccharide-induced microglia activation. J Neuroinflammation. 2015;12:50.
[13] BAO X, CHEN C, YUAN L. Triptolide Attenuates Neuropathic Pain by Regulating Microglia Polarization through the CCL2/CCR2 Axis. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2021;2021:8985721.
[14] KWON HS, KOH SH. Neuroinflammation in neurodegenerative disorders: the roles of microglia and astrocytes. Transl Neurodegener. 2020;9(1):42.
[15] DELEGGE MH, SMOKE A. Neurodegeneration and inflammation. Nutr Clin Pract. 2008;23(1):35-41.
[16] BAJWA E, KLEGERIS A.Neuroinflammation as a mechanism linking hypertension with the increased risk of Alzheimer’s disease. Neural Regen Res. 2022;17(11):2342-2346.
[17] SUBHRAMANYAM CS, WANG C, HU Q, et al. Microglia-mediated neuroinflammation in neurodegenerative diseases. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2019;94:112-120.
[18] CAO CY, YANG YX, XIE Z, et al. Derivatives of sarcodonin A isolated from sarcodon scabrosus reversed LPS-induced M1 polarization in microglia through MAPK/NF-κB pathway. Bioorg Chem. 2022;125:105854.
[19] HE Y, GAO Y, ZHANG Q, et al. IL-4 Switches Microglia/macrophage M1/M2 Polarization and Alleviates Neurological Damage by Modulating the JAK1/STAT6 Pathway Following ICH. Neuroscience. 2020;437:161-171.
[20] 刘丽,李琦,杜欣珂,等.M2型小胶质细胞极化促进少突胶质祖细胞的分化-促进多发性硬化症髓鞘再生的有效途径[J].中国比较医学杂志,2022,32(2):126-132.
[21] WANG J, XING H, WAN L, et al. Treatment targets for M2 microglia polarization in ischemic stroke. Biomed Pharmacother. 2018;105: 518-525.
[22] YANG Y, GUO L, WANG J, et al. Arglabin regulates microglia polarization to relieve neuroinflammation in Alzheimer’s disease. J Biochem Mol Toxicol. 2022;36(6):e23045.
[23] LI J, DAI X, ZHOU L, et al. Edaravone plays protective effects on LPS-induced microglia by switching M1/M2 phenotypes and regulating NLRP3 Inflammasome Activation. Front Pharmacol. 2021;12:691773.
[24] YAO YY, LING EA, LU D. Microglia mediated neuroinflammation-signaling regulation and therapeutic considerations with special reference to some natural compounds. Histol Histopathol. 2020;35(11):1229-1250.
[25] 张诗雨,张静,高攀,等.雷公藤甲素对血管内皮细胞炎症反应的影响及机制研究[J].时珍国医国药,2021,32(7):1537-1541.
[26] TANG B, ZHU J, ZHANG B, et al. Therapeutic Potential of Triptolide as an Anti-Inflammatory Agent in Dextran Sulfate Sodium-Induced Murine Experimental Colitis. Front Immunol. 2020;11:592084.
[27] 宋海红,毕滢,何栾樱,等.雷公藤甲素与雷公藤红素对小胶质细胞炎症反应的影响机制[J].北京化工大学学报(自然科学版), 2020,47(5):83-88.
[28] HUANG Y, ZHU N, CHEN T, et al. Triptolide Suppressed the Microglia Activation to Improve Spinal Cord Injury Through miR-96/IKKβ/NF-κB Pathway. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2019;44(12):E707-E714.
[29] HUANG YY, ZHANG Q, ZHANG JN, et al. Triptolide up-regulates metabotropic glutamate receptor 5 to inhibit microglia activation in the lipopolysaccharide-induced model of Parkinson’s disease. Brain Behav Immun. 2018;71:93-107.
[30] XU P, WANG H, LI Z, et al. Triptolide attenuated injury via inhibiting oxidative stress in Amyloid-Beta25-35-treated differentiated PC12 cells. Life Sci. 2016;145:19-26.
[31] YAO XL, LIU J, LEE E, et al. Progesterone differentially regulates pro- and anti-apoptotic gene expression in cerebral cortex following traumatic brain injury in rats. J Neurotrauma. 2005;22(6):656-668.
[32] LI L, PENG L, ZUO Z. Isoflurane preconditioning increases B-cell lymphoma-2 expression and reduces cytochrome c release from the mitochondria in the ischemic penumbra of rat brain. Eur J Pharmacol. 2008;586(1-3):106-113.
|