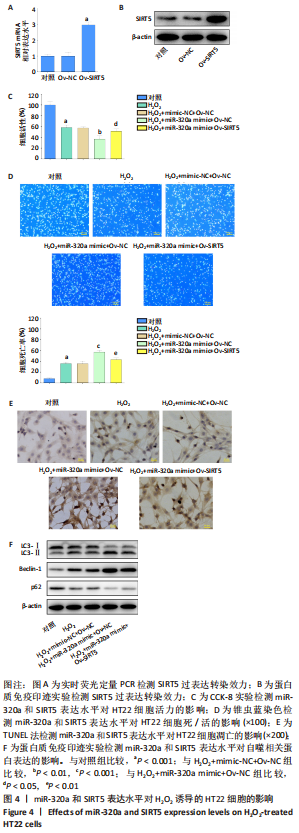
[1] AL MAMUN A, WU Y, MONALISA I, et al. Role of pyroptosis in spinal cord injury and its therapeutic implications. J Adv Res. 2020;28:97-109.
[2] 杜燕宣,李金波.可穿戴设备在脊髓损伤康复中的应用及发展现状[J].中国康复,2022,37(3):183-188.
[3] FAN B, WEI Z, YAO X, et al. Microenvironment Imbalance of Spinal Cord Injury. Cell Transplant. 2018;27(6):853-866.
[4] HUANG Y, LIN J, CHEN X, et al. Pannexin-1 Contributes to the Apoptosis of Spinal Neurocytes in Spinal Cord Injury. Front Physiol. 2021;12:656647.
[5] YANG S, LIAN G. ROS and diseases: role in metabolism and energy supply. Mol Cell Biochem. 2020;467(1-2):1-12.
[6] LUO W, WANG Y, LIN F, et al. Selenium-Doped Carbon Quantum Dots Efficiently Ameliorate Secondary Spinal Cord Injury via Scavenging Reactive Oxygen Species. Int J Nanomedicine. 2020;15:10113-10125.
[7] WU C, CHEN H, ZHUANG R, et al. Betulinic acid inhibits pyroptosis in spinal cord injury by augmenting autophagy via the AMPK-mTOR-TFEB signaling pathway. Int J Biol Sci. 2021;17(4):1138-1152.
[8] HUTSON TH, DI GIOVANNI S. The translational landscape in spinal cord injury: focus on neuroplasticity and regeneration. Nat Rev Neurol. 2019;15(12):732-745.
[9] AHUJA CS, MOTHE A, KHAZAEI M, et al. The leading edge: Emerging neuroprotective and neuroregenerative cell-based therapies for spinal cord injury. Stem Cells Transl Med. 2020;9(12):1509-1530.
[10] OKADA S. The pathophysiological role of acute inflammation after spinal cord injury. Inflamm Regen. 2016;36:20.
[11] TONG D, ZHAO Y, TANG Y, et al. Circ-Usp10 promotes microglial activation and induces neuronal death by targeting miRNA-152-5p/CD84. Bioengineered. 2021;12(2):10812-10822.
[12] LIU X, ZHANG Y, WANG Y, et al. Inflammatory Response to Spinal Cord Injury and Its Treatment. World Neurosurg. 2021;155:19-31.
[13] MA N, TIE C, YU B, et al. Identifying lncRNA-miRNA-mRNA networks to investigate Alzheimer’s disease pathogenesis and therapy strategy. Aging (Albany NY). 2020;12(3):2897-2920.
[14] RUAN W, WANG P, FENG S, et al. Long non-coding RNA small nucleolar RNA host gene 12 (SNHG12) promotes cell proliferation and migration by upregulating angiomotin gene expression in human osteosarcoma cells. Tumour Biol. 2016;37(3):4065-4073.
[15] WANG X, JIANG Q, ZHANG C, et al. Long noncoding RNA SNHG12 is a potential diagnostic and prognostic biomarker in various tumors. Chin Neurosurg J. 2021;7(1):37.
[16] CAI P, LI G, WU M, et al. ZIC2 upregulates lncRNA SNHG12 expression to promote endometrial cancer cell proliferation and migration by activating the Notch signaling pathway. Mol Med Rep. 2021;24(3):632.
[17] YAO X, YAO R, HUANG F, et al. LncRNA SNHG12 as a potent autophagy inducer exerts neuroprotective effects against cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2019;514(2): 490-496.
[18] YIN WL, YIN WG, HUANG BS, et al. LncRNA SNHG12 inhibits miR-199a to upregulate SIRT1 to attenuate cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury through activating AMPK signaling pathway. Neurosci Lett. 2019; 690:188-195.
[19] CHENG Y, JIANG Y, SUN Y, et al. The role of long non-coding RNA SNHG12 in neuroprotection following cerebral ischemic injury. Neuroreport. 2019;30(14):945-952.
[20] ZHAO M, WANG J, XI X, et al. SNHG12 Promotes Angiogenesis Following Ischemic Stroke via Regulating miR-150/VEGF Pathway. Neuroscience. 2018;390:231-240.
[21] LEE DS, CHEONG SH. Taurine Have Neuroprotective Activity against Oxidative Damage-Induced HT22 Cell Death through Heme Oxygenase-1 Pathway. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2017;975 Pt 1:159-171.
[22] PANG QM, CHEN SY, FU SP, et al. Regulatory Role of Mesenchymal Stem Cells on Secondary Inflammation in Spinal Cord Injury. J Inflamm Res. 2022;15:573-593.
[23] 朱强,胡国良,李全春,等.鼠神经生长因子、亚低温联合甲强龙在急性脊髓损伤中的应用及对氧化应激水平的影响[J].中国现代医学杂志,2021,31(23):79-83.
[24] ORR MB, GENSEL JC. Spinal Cord Injury Scarring and Inflammation: Therapies Targeting Glial and Inflammatory Responses. Neurotherapeutics. 2018;15(3):541-553.
[25] HELLENBRAND DJ, QUINN CM, PIPER ZJ, et al. Inflammation after spinal cord injury: a review of the critical timeline of signaling cues and cellular infiltration. J Neuroinflammation. 2021;18(1):284.
[26] LIN J, XIONG Z, GU J, et al. Sirtuins: Potential Therapeutic Targets for Defense against Oxidative Stress in Spinal Cord Injury. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2021;2021:7207692.
[27] ANJUM A, YAZID MD, FAUZI DAUD M, et al. Spinal Cord Injury: Pathophysiology, Multimolecular Interactions, and Underlying Recovery Mechanisms. Int J Mol Sci. 2020;21(20):7533.
[28] LUO C, TAO L. The Function and Mechanisms of Autophagy in Spinal Cord Injury. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2020;1207:649-654.
[29] 赵琳,许圣琳,贾鲲鹏,等.番茄红素对大鼠脊髓损伤后神经元自噬的影响[J].中国临床药理学杂志,2021,37(5):552-555.
[30] DU S, WU S, FENG X, et al. A nerve injury-specific long noncoding RNA promotes neuropathic pain by increasing Ccl2 expression. J Clin Invest. 2022;132(13):e153563.
[31] YAO C, YU B. Role of Long Noncoding RNAs and Circular RNAs in Nerve Regeneration. Front Mol Neurosci. 2019;12:165.
[32] LIU W, TAO JC, ZHU SZ, et al. Expression and regulatory network of long noncoding RNA in rats after spinal cord hemisection injury. Neural Regen Res. 2022;17(10):2300-2304.
[33] XIAO Z, QIU Y, LIN Y, et al. Blocking lncRNA H19-miR-19a-Id2 axis attenuates hypoxia/ischemia induced neuronal injury. Aging (Albany NY). 2019;11(11):3585-3600.
[34] XU S, LI Y, CHEN JP, et al. Oxygen glucose deprivation/re-oxygenation-induced neuronal cell death is associated with Lnc-D63785 m6A methylation and miR-422a accumulation. Cell Death Dis. 2020;11(9): 816.
[35] JIANG Y, ZHAO Y, ZHU X, et al. Effects of autophagy on macrophage adhesion and migration in diabetic nephropathy. Ren Fail. 2019;41(1): 682-690.
[36] WU Y, HUANG Y, CAI J, et al. LncRNA SNHG12 Improves Cerebral Ischemic-reperfusion Injury by Activating SIRT1/FOXO3a Pathway through I nhibition of Autophagy and Oxidative Stress. Curr Neurovasc Res. 2020;17(4):394-401.
[37] YAN L, LI L, LEI J. Long noncoding RNA small nucleolar RNA host gene 12/microRNA-138-5p/nuclear factor I/B regulates neuronal apoptosis, inflammatory response, and oxidative stress in Parkinson’s disease. Bioengineered. 2021;12(2):12867-12879.
[38] SEPRAMANIAM S, ARMUGAM A, LIM KY, et al. MicroRNA 320a functions as a novel endogenous modulator of aquaporins 1 and 4 as well as a potential therapeutic target in cerebral ischemia. J Biol Chem. 2010;285(38):29223-29230.
[39] MUNIATEGUI A, NOGALES-CADENAS R, VÁZQUEZ M, et al. Quantification of miRNA-mRNA interactions. PLoS One. 2012;7(2): e30766.
[40] MASUD KARIM SM, LIU L, LE TD, et al. Identification of miRNA-mRNA regulatory modules by exploring collective group relationships. BMC Genomics. 2016;17 Suppl 1(Suppl 1):7.
[41] CHEN XF, TIAN MX, SUN RQ, et al. SIRT5 inhibits peroxisomal ACOX1 to prevent oxidative damage and is downregulated in liver cancer. EMBO Rep. 2018;19(5):e45124.
[42] LIANG F, WANG X, OW SH, et al. Sirtuin 5 is Anti-apoptotic and Anti-oxidative in Cultured SH-EP Neuroblastoma Cells. Neurotox Res. 2017; 31(1):63-76.
[43] LIU L, PERITORE C, GINSBERG J, et al. Protective role of SIRT5 against motor deficit and dopaminergic degeneration in MPTP-induced mice model of Parkinson’s disease. Behav Brain Res. 2015;281:215-221.
|