中国组织工程研究 ›› 2023, Vol. 27 ›› Issue (19): 3108-3116.doi: 10.12307/2023.655
• 干细胞综述 stem cell review • 上一篇
组织工程技术治疗缺血性心脏病的新方向
强勇嘉,曾 宽,张 彬,关睿聪,刘竹轩,许浩华,张心一,杨艳旗
- 中山大学附属第二医院(中山大学孙逸仙纪念医院)心血管外科,广东省广州市 510030
A new direction in tissue engineering technology for the treatment of ischemic heart disease
Qiang Yongjia, Zeng Kuan, Zhang Bin, Guan Ruicong, Liu Zhuxuan, Xu Haohua, Zhang Xinyi, Yang Yanqi
- Department of Cardiovascular Surgery, The Second Affiliated Hospital of Sun Yat-sen University (Sun Yat-sen Memorial Hospital of Sun Yat-sen University), Guangzhou 510030, Guangdong Province, China
摘要:
文题释义:
缺血性心脏病:由冠状动脉粥样硬化引起的心肌长期缺血缺氧和心肌细胞凋亡,造成大片心肌梗死,导致心脏收缩舒张功能障碍,从而引起心绞痛、胸痛、心律失常等一系列临床表现的心脏病。组织工程支架材料:人为构建的细胞外基质,为种子细胞的定点迁移、黏附、增殖、分化,保持生物学活性,发挥生理功能保驾护航。是组织工程领域中不可或缺的一环。
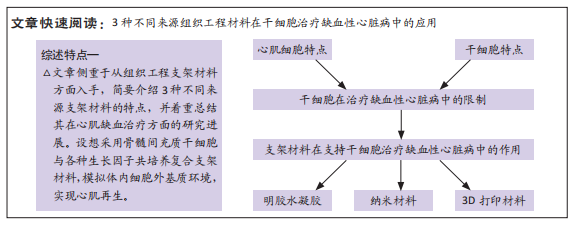
背景:干细胞疗法是目前研究的热点,已经在各种临床学科中得到应用,但在治疗缺血性心脏病方面收效甚微,主要是因为移植到缺血心肌部位的干细胞存活率较低,新型组织工程材料的发现和应用使人间充质干细胞在心肌缺血区域的存活率得到了提高,这让人们看到了人间充质干细胞在治疗缺血心肌中的广阔应用前景。
目的:归纳并总结目前常见的3种不同来源组织工程材料在干细胞治疗缺血性心脏病的研究进展,提出未来的应用展望。
方法:应用英文检索词“mesenchymal stem cells, biological hydrogel nanometer material, 3D printing, nanostructured material”检索PubMed、Web of Science数据库,应用中文检索词“干细胞,缺血性心脏病,组织工程,水凝胶,3D打印,纳米材料”检索CNKI、万方、维普数据库;检索2010-2021年期间有关组织工程技术治疗缺血性心肌病的相关文献,排除重复研究、个案报告或Meta分析类文章,纳入符合标准的74篇文献进行综述。
结果与结论:①可供选择的明胶水凝胶基底材料和制备技术多种多样,同时也是目前研究最成熟的支架材料,是未来最有望率先成为搭载干细胞治疗缺血性心脏病的支架材料。②纳米材料有着独特的理化性质,借助纳米材料构建的支架,不但能促进人间充质干细胞在缺血心肌处的存活和增殖,并且能使其更好地发挥旁分泌作用,从而起到治疗心肌缺血的效果。③新兴的3D打印技术,可以以水凝胶、纳米材料、干细胞为原材料,打印出所需要的细胞、血管、心肌、心室和心房甚至是“完整”心脏,但是距离临床的应用还需进一步发展。④在未来展望方面,大量的体外组织细胞实验有助于建立更加完善的支架体系,寻找最适合人间充质干细胞生存的细胞外基质环境;其次,构建标准化的心肌缺血动物模型有助于在基础研究方面深入了解干细胞在不同支架材料中的生理学表现,而临床应用需要未来多中心大样本的动物实验数据支撑。
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-0966-890X (强勇嘉)
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:干细胞;骨髓干细胞;造血干细胞;脂肪干细胞;肿瘤干细胞;胚胎干细胞;脐带脐血干细胞;干细胞诱导;干细胞分化;组织工程
中图分类号: