中国组织工程研究 ›› 2023, Vol. 27 ›› Issue (19): 3091-3098.doi: 10.12307/2023.633
• 干细胞综述 stem cell review • 上一篇
干细胞对肝脏疾病的临床治疗前景与研究现状
黄贵才1,罗业浩1,江慧容1,李 媛2,毛德文2,官志杰2
- 1广西中医药大学,广西壮族自治区南宁市 530200;2广西中医药大学第一附属医院肝病科,广西壮族自治区南宁市 530023
Clinical therapeutic prospect and current research status of stem cells for liver diseases
Huang Guicai1, Luo Yehao1, Jiang Huirong1, Li Yuan2, Mao Dewen2, Guan Zhijie2
- 1Guangxi University of Chinese Medicine, Nanning 530200, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China; 2Department of Hepatology, First Affiliated Hospital of Guangxi University of Chinese Medicine, Nanning 530023, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China
摘要:
文题释义:
干细胞:是具有多向分化潜能、自我更新能力的细胞,是处于细胞系起源顶端的最原始细胞,在体内能够分化产生某种特定组织类型的细胞。肝脏疾病:是发生在肝脏的所有疾病的总称,包括感染性疾病、肿瘤性疾病、血管性疾病、代谢性疾病、中毒性疾病、自身免疫性疾病及遗传性疾病等。
背景:干细胞在肝脏的再生与自我修复能力中发挥着重要的作用,对于肝脏疾病的临床诊断和治疗具有重要意义。
目的:总结目前国内外该领域的临床试验及基础研究,回顾以往治疗肝脏疾病的干细胞类型,各类干细胞对各类肝脏疾病的治疗方案,概述各类干细胞对肝脏疾病未来应用的临床应用前景,为其应用于临床肝脏疾病的治疗提供研究基础。
方法:应用计算机以“stem cells,mesenchymal stem cell,hepatic stem cell,embryonic stem cell,induced pluripotent stem cell,hematopoietic stem cell,hepatopathy,non-alcoholic fatty liver disease,liver cirrhosis,liver failure,autoimmune hepatitis,hepatocellular carcinoma”为检索词,检索PubMed、Web of Science及Wiley电子期刊数据库中的相关文献,根据纳入标准并筛选,最终选择71篇文献进行综述。
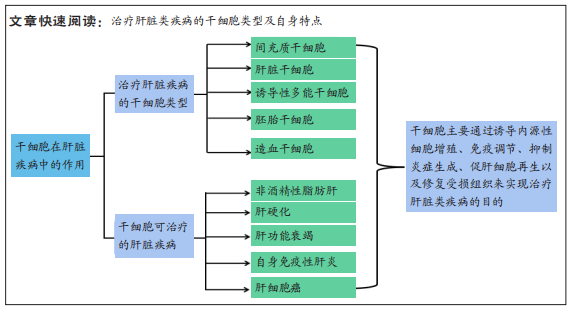
结果与结论:①对于治疗肝脏疾病的干细胞主要以间充质干细胞、肝脏干细胞、胚胎干细胞、诱导性多能干细胞及造血干细胞等为主,文章总结归纳了上述干细胞的特点、表达的时期以及在肝脏受损后分化的应用情况。②综合来看,间充质干细胞可通过外泌体、基质金属蛋白酶、抗炎症反应等修复肝脏;肝脏干细胞可通过分化肝卵圆细胞和小肝细胞样祖细胞最终形成成熟的肝细胞,促进肝脏损伤修复;诱导性多能干细胞、胚胎干细胞和造血干细胞可通过迅速的增殖与分化,转换为成熟的肝细胞。③干细胞对于各种肝脏疾病的治疗,主要通过诱导内源性细胞增殖、免疫调节、抑制炎症生成、促肝细胞再生以及修复受损组织来实现。④综合而言,目前间充质干细胞获取相对容易,应用前景最广,而且并不涉及伦理问题,正在实现由临床前研究到临床研究的转化。由于间充质干细胞可分化为各种成体干细胞、免疫原性低、自我增殖和分化能力强等优势,特别对于治疗免疫性肝炎、肝硬化及肝细胞癌等肝脏疾病效果最为理想。⑤诱导性多能干细胞因其可分化成特异性体细胞和肝细胞,且无免疫排斥反应,对于治疗终末期肝病效果更为显著。⑥然而,干细胞移植后可出现腹泻、黄疸及皮疹等急性排斥反应,供受者间的组织相容性差则容易导致移植物抗宿主反应等不良反应,所以干细胞移植后对于干细胞的应用及其临床安全性的评估,仍需要更多的临床试验以及循证医学数据的支持。
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-2959-7598 (黄贵才);https://orcid.org/0000-0003-1298-5022(官志杰)
中图分类号: