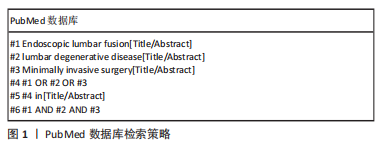
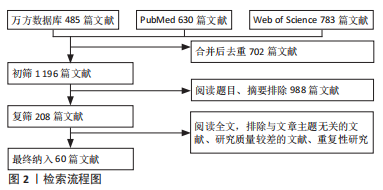
[1] KAISER MG, ECK JC, GROFF MW, et al. Guideline update for the performance of fusion procedures for degenerative disease of the lumbar spine. Part 1: introduction and methodology. J Neurosurg Spine. 2014;21(1):2-6.
[2] LI L, LIU Y, ZHANG P, et al. Comparison of posterior lumbar interbody fusion with transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion for treatment of recurrent lumbar disc herniation: A retrospective study. J Int Med Res. 2016;44(6):1424-1429.
[3] 陈培,戴春宏,彭和兵,等.椎间孔镜治疗退行性腰椎管狭窄的临床疗效及其对腰椎功能评分的影响[J]. 医学综述,2020,26(7):1402-1406.
[4] PRICE JP, DAWSON JM, SCHWENDER JD, et al. Clinical and Radiologic Comparison of Minimally Invasive Surgery With Traditional Open Transforaminal Lumbar Interbody Fusion: A Review of 452 Patients From a Single Center. Clin Spine Surg. 2018;31(2):E121-E126.
[5] 李佳奇,王林峰,高显达,等.MIS-TLIF治疗腰椎退变性疾病的研究进展[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2018,26(7):631-634.
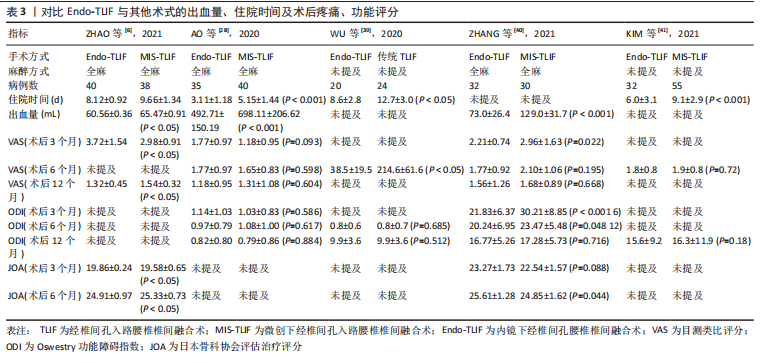
[6] ZHAO XB, MA HJ, GENG B, et al. Early Clinical Evaluation of Percutaneous Full-endoscopic Transforaminal Lumbar Interbody Fusion with Pedicle Screw Insertion for Treating Degenerative Lumbar Spinal Stenosis. Orthop Surg. 2021;13(1):328-337.
[7] JIN M, ZHANG J, SHAO H, et al. Percutaneous Transforaminal Endoscopic Lumbar Interbody Fusion for Degenerative Lumbar Diseases: A Consecutive Case Series with Mean 2-Year Follow-Up. Pain Physician. 2020;23(2):165-174.
[8] WANG MY, GROSSMAN J. Endoscopic minimally invasive transforaminal interbody fusion without general anesthesia: initial clinical experience with 1-year follow-up. Neurosurg Focus. 2016;40(2):E13.
[9] XU D, HAN S, WANG C, et al. The technical feasibility and preliminary results of minimally invasive endoscopic-TLIF based on electromagnetic navigation: a case series. BMC Surg. 2021;21(1):149.
[10] ATTIVISSIMO F, LANZOLLA A, CARLONE S, et al. A novel electromagnetic tracking system for surgery navigation. Comput Assist Surg (Abingdon). 2018;23(1):42-52.
[11] BRIGGS H, MILLIGAN PR. Chip fusion of the low back following exploration of the spinal canal. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1944;26:125-130.
[12] BAEESA SS, MEDRANO BG, NORIEGA DC. Long-Term Outcomes of Posterior Lumbar Interbody Fusion Using Stand-Alone Ray Threaded Cage for Degenerative Disk Disease: A 20-Year Follow-Up. Asian Spine J. 2016;10(6):1100-1105.
[13] HARMS J, ROLINGER H. A one-stager procedure in operative treatment of spondylolistheses: dorsal traction-reposition and anterior fusion (author’s transl). Z Orthop Ihre Grenzgeb. 1982;120(3):343-347.
[14] LOWERY GL, KULKARNI SS. Posterior percutaneous spine instrumentation. Eur Spine J. 2000;9 Suppl 1(Suppl 1):S126-S130.
[15] FOLEY KT, GUPTA SK. Percutaneous pedicle screw fixation of the lumbar spine: preliminary clinical results. J Neurosurg. 2002;97(1 Suppl):7-12.
[16] PARVIZ K, HARRIS G. Percutaneous Lateral Discectomy of the Lumbar Spine. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1983;174:127-132.
[17] YEUNG AT. Minimally Invasive Disc Surgery with the Yeung Endoscopic Spine System (YESS). Surg Technol Int. 1999;8:267-277.
[18] HOOGLAND T, SCHUBERT M, MIKLITZ B, et al. Transforaminal posterolateral endoscopic discectomy with or without the combination of a low-dose chymopapain: a prospective randomized study in 280 consecutive cases. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2006;31(24):E890-E897.
[19] CHOI G, LEE SH, RAITURKER PP, et al. Percutaneous endoscopic interlaminar discectomy for intracanalicular disc herniations at L5-S1 using a rigid working channel endoscope. Neurosurgery. 2006;58(1 Suppl):ONS59-68; discussion ONS59-68.
[20] RUETTEN S, KOMP M, GODOLIAS G. A New full-endoscopic technique for the interlaminar operation of lumbar disc herniations using 6-mm endoscopes: prospective 2-year results of 331 patients. Minim Invasive Neurosurg. 2006;49(2):80-87.
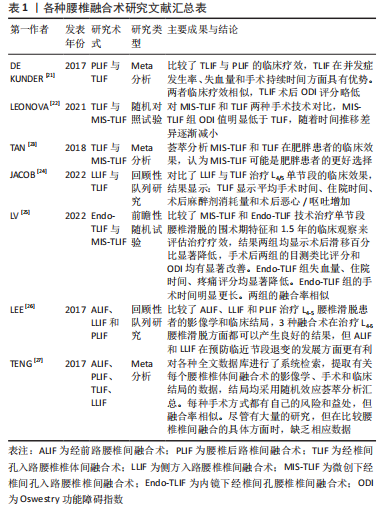
[21] DE KUNDER SL, VAN KUIJK S, RIJKERS K, et al. Transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion (TLIF) versus posterior lumbar interbody fusion (PLIF) in lumbar spondylolisthesis: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Spine J. 2017;17(11):1712-1721.
[22] LEONOVA ON, CHEREPANOV EA, KRUTKO AV. MIS-TLIF versus O-TLIF for single-level degenerative stenosis: study protocol for randomised controlled trial. BMJ Open. 2021;11(3):e041134.
[23] TAN JH, LIU G, NG R, et al. Is MIS-TLIF superior to open TLIF in obese patients?: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur Spine J. 2018; 27(8):1877-1886.
[24] JACOB KC, PATEL MR, RIBOT MA, et al. Single-level TLIF Versus LLIF at L4-5: A Comparison of Patient-reported Outcomes and Recovery Ratios. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2022;30(4):e495-e505.
[25] LV Y, CHEN M, WANG SL, et al. Endo-TLIF versus MIS-TLIF in 1-segment lumbar spondylolisthesis: A prospective randomized pilot study. Clin Neurol Neurosurg. 2022;212:107082.
[26] LEE CW, YOON KJ, HA SS. Which Approach Is Advantageous to Preventing Development of Adjacent Segment Disease? Comparative Analysis of 3 Different Lumbar Interbody Fusion Techniques (ALIF, LLIF, and PLIF) in L4-5 Spondylolisthesis. World Neurosurg. 2017;105:612-622.
[27] TENG I, HAN J, PHAN K, et al. A meta-analysis comparing ALIF, PLIF, TLIF and LLIF. J Clin Neurosci. 2017;44:11-17.
[28] AO S, ZHENG W, WU J, et al. Comparison of Preliminary clinical outcomes between percutaneous endoscopic and minimally invasive transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion for lumbar degenerative diseases in a tertiary hospital: Is percutaneous endoscopic procedure superior to MIS-TLIF? A prospective cohort study. Int J Surg. 2020;76: 136-143.
[29] WU J, LIU H, AO S, et al. Percutaneous Endoscopic Lumbar Interbody Fusion: Technical Note and Preliminary Clinical Experience with 2-Year Follow-Up. Biomed Res Int. 2018;2018:5806037.
[30] AHN Y, YOUN MS, HEO DH. Endoscopic transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion: a comprehensive review. Expert Rev Med Devices. 2019;16(5):373-380.
[31] SHEN J. Fully Endoscopic Lumbar Laminectomy and Transforaminal Lumbar Interbody Fusion Under Local Anesthesia with Conscious Sedation: A Case Series. World Neurosurg. 2019;127:e745-e750.
[32] QUILLO-OLVERA J, QUILLO-RESÉNDIZ J, QUILLO-OLVERA D, et al. Ten-Step Biportal Endoscopic Transforaminal Lumbar Interbody Fusion Under Computed Tomography-Based Intraoperative Navigation: Technical Report and Preliminary Outcomes in Mexico. Oper Neurosurg (Hagerstown). 2020;19(5):608-618.
[33] MORGENSTERN C, YUE JJ, MORGENSTERN R. Full Percutaneous Transforaminal Lumbar Interbody Fusion Using the Facet-sparing, Trans-Kambin Approach. Clin Spine Surg. 2020;33(1):40-45.
[34] HEO DH, SON SK, EUM JH, et al. Fully endoscopic lumbar interbody fusion using a percutaneous unilateral biportal endoscopic technique: technical note and preliminary clinical results. Neurosurg Focus. 2017; 43(2):E8.
[35] HEO DH, HONG YH, LEE DC, et al. Technique of Biportal Endoscopic Transforaminal Lumbar Interbody Fusion. Neurospine. 2020;17(Suppl 1): S129-S137.
[36] PARK MK, PARK SA, SON SK, et al. Clinical and radiological outcomes of unilateral biportal endoscopic lumbar interbody fusion (ULIF) compared with conventional posterior lumbar interbody fusion (PLIF): 1-year follow-up. Neurosurg Rev. 2019;42(3):753-761.
[37] HEO DH, PARK CK. Clinical results of percutaneous biportal endoscopic lumbar interbody fusion with application of enhanced recovery after surgery. Neurosurg Focus. 2019;46(4):E18.
[38] WU PH, KIM HS, LEE YJ, et al. Uniportal Full Endoscopic Posterolateral Transforaminal Lumbar Interbody Fusion with Endoscopic Disc Drilling Preparation Technique for Symptomatic Foraminal Stenosis Secondary to Severe Collapsed Disc Space: A Clinical and Computer Tomographic Study with Technical Note. Brain Sci. 2020;10(6):373.
[39] WU W, YANG S, DIAO W, et al. Analysis of clinical efficacy of endo-LIF in the treatment of single-segment lumbar degenerative diseases. J Clin Neurosci. 2020;71:51-57.
[40] ZHANG H, ZHOU C, WANG C, et al. Percutaneous Endoscopic Transforaminal Lumbar Interbody Fusion: Technique Note and Comparison of Early Outcomes with Minimally Invasive Transforaminal Lumbar Interbody Fusion for Lumbar Spondylolisthesis. Int J Gen Med. 2021;14:549-558.
[41] KIM JE, YOO HS, CHOI DJ, et al. Comparison of Minimal Invasive Versus Biportal Endoscopic Transforaminal Lumbar Interbody Fusion for Single-level Lumbar Disease. Clin Spine Surg. 2021;34(2):E64-E71.
[42] POSTACCHINI R, CINOTTI G, POSTACCHINI F. Injury to major abdominal vessels during posterior lumbar interbody fusion. A case report and review of the literature. Spine J. 2013;13(1):e7-e11.
[43] STONE CE, MYERS BL, GUPTA S, et al. Surgical Outcomes After Single-Level Endoscopic Transforaminal Lumbar Interbody Fusion: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Cureus. 2020;12(10):e11052.
[44] 赵志明,王玉召,钟浩,等.脊柱微创通道镜系统辅助下椎间孔腰椎椎体间融合术对腰椎退行性疾病患者血清氧化应激指标、疼痛介质及脊髓功能的影响[J].中国临床医生杂志,2019,47(1):72-76.
[45] 刘镠,李莹,吴从俊,等. 经皮内镜下腰椎间融合技术研究进展[J].中国中医骨伤科杂志,2019,27(11):85-88.
[46] CRIPTON PA, JAIN GM, WITTENBERG RH, et al. Load-sharing characteristics of stabilized lumbar spine segments. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2000;25(2):170-179.
[47] 姚楚亮,陈杰,杜杰明,等.脊柱微创通道镜下改良经椎间孔入路椎间植骨融合术治疗腰椎退行性疾病106例[J].中国中医骨伤科杂志,2022,30(1):74-77.
[48] HEO DH, LEE DC, KIM HS, et al. Clinical Results and Complications of Endoscopic Lumbar Interbody Fusion for Lumbar Degenerative Disease: A Meta-Analysis. World Neurosurg. 2021;145:396-404.
[49] 王放,王永虎,乔浩,等.脊柱内镜下融合技术治疗退行性腰椎疾病的早期疗效[J].西安交通大学学报(医学版),2022,43(1):143-148.
[50] 任伟剑,朱志勇,吴骏,等.脊柱内镜下融合术治疗腰椎滑脱症的疗效[J].局解手术学杂志,2021,30(12):1038-1042.
[51] KIM HS, RAORANE HD, WU PH, et al. Incidental Durotomy During Endoscopic Stenosis Lumbar Decompression: Incidence, Classification, and Proposed Management Strategies. World Neurosurg. 2020;139: e13-e22.
[52] CHOI DJ, CHOI CM, JUNG JT, et al. Learning Curve Associated with Complications in Biportal Endoscopic Spinal Surgery: Challenges and Strategies. Asian Spine J. 2016;10(4):624-629.
[53] 郭时空,高全有,周程沛,等.全内镜下腰椎椎间融合术治疗腰椎退行性病变伴腰椎失稳的早期临床疗效[J].西安交通大学学报(医学版),2022,43(1):149-153.
[54] HAHN P, OEZDEMIR S, KOMP M, et al. A New Electromagnetic Navigation System for Pedicle Screws Placement: A Human Cadaver Study at the Lumbar Spine. PLoS One. 2015;10(7):e0133708.
[55] USUDA J. Virtual Bronchoscopic Navigation( VBN) and Electromagnetic Navigation System. Kyobu Geka. 2018;71(10):843-849.
[56] The classic. The treatment of ruptured lumbar intervertebral discs by vertebral body fusion. I. Indications, operative technique, after care. By Ralph B. Cloward, 1953. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1985;(193):5-15.
[57] PHAN K, MOBBS RJ. Evolution of Design of Interbody Cages for Anterior Lumbar Interbody Fusion. Orthop Surg. 2016;8(3):270-277.
[58] 唐杰,汪洋,应放,等.经侧方入路腰椎融合术(LLIF)的研究进展[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2016,24(15):1399-1402.
[59] GAMMAL ID, SPIVAK JM, BENDO JA. Systematic Review of Thigh Symptoms after Lateral Transpsoas Interbody Fusion for Adult Patients with Degenerative Lumbar Spine Disease. Int J Spine Surg. 2015;9:62.
[60] 张蒂, 冯世庆. 斜外侧腰椎椎间融合术[J].中华骨科杂志,2017, 37(16):1029-1035. |