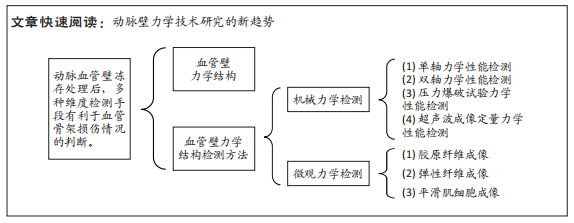
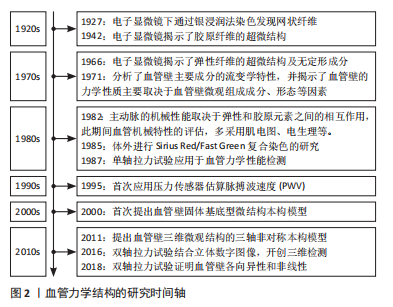
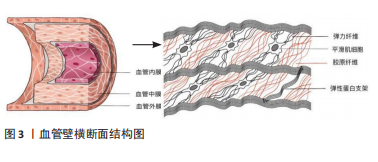
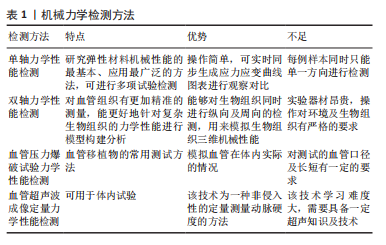
[1] CHEN H, KASSAB GS. Microstructure-based constitutive model of coronary artery with active smooth muscle contraction. Sci Rep. 2017; 7(1):9339.
[2] HOLZAPFEL GA, OGDEN RW. Biomechanical relevance of the microstructure in artery walls with a focus on passive and active components. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2018;315(3):H540-H549.
[3] CHEN H, KASSAB GS. Microstructure-based biomechanics of coronary arteries in health and disease. J Biomech. 2016;49(12):2548-2559.
[4] CAVINATO C, HELFENSTEIN-DIDIER C, OLIVIER T, et al. Biaxial loading of arterial tissues with 3D in situ observations of adventitia fibrous microstructure: A method coupling multi-photon confocal microscopy and bulge inflation test. J Mech Behav Biomed Mater. 2017;74:488-498.
[5] SUGITA S, MATSUMOTO T. Multiphoton microscopy observations of 3D elastin and collagen fiber microstructure changes during pressurization in aortic media. Biomech Model Mechanobiol. 2017;16(3):763-773.
[6] 王静,李逸明,刘丹,等.人主动脉平滑肌细胞体外分离及培养[J].临床军医杂志,2021,49(10):1117-1121,1126.
[7] LUO T, CHEN H, KASSAB GS. Resliced image space construction for coronary artery collagen fibers. PLoS One. 2017;12(9):e0184972.
[8] GIUDICI A, KHIR AW, SZAFRON JM, et al. From Uniaxial Testing of Isolated Layers to a Tri-Layered Arterial Wall: A Novel Constitutive Modelling Framework. Ann Biomed Eng. 2021;49(9):2454-2467.
[9] SHERIFOVA S, HOLZAPFEL GA. Biomechanics of aortic wall failure with a focus on dissection and aneurysm: A review. Acta Biomater. 2019;99:1-17.
[10] MOSTACO-GUIDOLIN LB, SMITH MSD, HEWKO M, et al. Fractal dimension and directional analysis of elastic and collagen fiber arrangement in unsectioned arterial tissues affected by atherosclerosis and aging. J Appl Physiol (1985). 2019;126(3):638-646.
[11] JADIDI M, HABIBNEZHAD M, ANTTILA E, et al. Mechanical and structural changes in human thoracic aortas with age. Acta Biomater. 2020;103:172-188.
[12] PENA JA, CORRAL V, MARTINEZ MA, et al. Over length quantification of the multiaxial mechanical properties of the ascending, descending and abdominal aorta using Digital Image Correlation. J Mech Behav Biomed Mater. 2018;77:434-445.
[13] MYNENI M, RAO A, JIANG M, et al. Segmental Variations in the Peel Characteristics of the Porcine Thoracic Aorta. Ann Biomed Eng. 2020; 48(6):1751-1767.
[14] FERRUZZI J, MADZIVA D, CAULK AW, et al. Compromised mechanical homeostasis in arterial aging and associated cardiovascular consequences. Biomech Model Mechanobiol. 2018;17(5):1281-1295.
[15] DIAZ C, PENA JA, MARTINEZ MA, et al. Unraveling the multilayer mechanical response of aorta using layer-specific residual stresses and experimental properties. J Mech Behav Biomed Mater. 2021;113: 104070.
[16] BOGUNOVIC N, MEEKEL JP, MICHA D, et al. Impaired smooth muscle cell contractility as a novel concept of abdominal aortic aneurysm pathophysiology. Sci Rep. 2019;9(1):6837.
[17] EICHINGER JF, HAEUSEL LJ, PAUKNER D, et al. Mechanical homeostasis in tissue equivalents: a review. Biomech Model Mechanobiol. 2021; 20(3):833-850.
[18] HUMPHREY JD, SCHWARTZ MA. Vascular Mechanobiology: Homeostasis, Adaptation, and Disease. Annu Rev Biomed Eng. 2021;23:1-27.
[19] 孟鑫,王小峰,黄敏杰,等.猪动脉血管的力学性能分析[J].医用生物力学,2019,34(4):411-416.
[20] 冯韵迪,吴昊,霍云龙.动脉血管壁主动和被动力学性能实验测量和建模分析[J].生物医学工程学杂志,2020,37(6):939-947.
[21] KORENCZUK CE, DHUME RY, LIAO K, et al. Ex Vivo Mechanical Tests and Multiscale Computational Modeling Highlight the Importance of Intramural Shear Stress in Ascending Thoracic Aortic Aneurysms. J Biomech Eng. 2019;141(12):121010-121010-11.
[22] SCHROEDER F, POLZER S, SLAZANSKY M, et al. Predictive capabilities of various constitutive models for arterial tissue. J Mech Behav Biomed Mater. 2018;78:369-380.
[23] JIA Y, QIAO Y, RICARDO ARGUETA-MORALES I, et al. Experimental Study of Anisotropic Stress/Strain Relationships of Aortic and Pulmonary Artery Homografts and Synthetic Vascular Grafts. J Biomech Eng. 2017; 139(10). doi: 10.1115/1.4037400.
[24] DEPLANO V, BOUFI M, BOIRON O, et al. Biaxial tensile tests of the porcine ascending aorta. J Biomech. 2016;49(10):2031-2037.
[25] NIESTRAWSKA JA, REGITNIG P, VIERTLER C, et al. The role of tissue remodeling in mechanics and pathogenesis of abdominal aortic aneurysms. Acta Biomater. 2019;88:149-161.
[26] CASTILLO-CRUZ O, PEREZ-ARANDA C, GAMBOA F, et al. Prediction of circumferential compliance and burst strength of polymeric vascular grafts. J Mech Behav Biomed Mater. 2018;79:332-340.
[27] SYEDAIN ZH, PRUNTY A, LI J, et al. Evaluation of the probe burst test as a measure of strength for a biologically-engineered vascular graft. J Mech Behav Biomed Mater. 2021;119:104527.
[28] PALMERI ML, MILKOWSKI A, BARR R, et al. Radiological Society of North America/Quantitative Imaging Biomarker Alliance Shear Wave Speed Bias Quantification in Elastic and Viscoelastic Phantoms. J Ultrasound Med. 2021;40(3):569-581.
[29] LOU Z, YANG J, TANG L, et al. Shear Wave Elastography Imaging for the Features of Symptomatic Carotid Plaques: A Feasibility Study. J Ultrasound Med. 2017;36(6):1213-1223.
[30] ARGANDA-CARRERAS I, ANDREY P. Designing Image Analysis Pipelines in Light Microscopy: A Rational Approach. Methods Mol Biol. 2017; 1563:185-207.
[31] JACKSON N, ASSAD M, VOLLMER D, et al. Histopathological Evaluation of Orthopedic Medical Devices: The State-of-the-art in Animal Models, Imaging, and Histomorphometry Techniques. Toxicologic Pathology. 2019;47(3):280-296.
[32] PIERCE GL, COUTINHO TA, DUBOSE LE, et al. Is It Good to Have a Stiff Aorta with Aging? Causes and Consequences. Physiology (Bethesda). 2022;37(3):154-173.
[33] SÁEZ P, GARCÍA A, PEÑA E, et al. Microstructural quantification of collagen fiber orientations and its integration in constitutive modeling of the porcine carotid artery. Acta Biomater. 2016;33:183-193.
[34] CAVINATO C, MURTADA SI, ROJAS A, et al. Evolving structure-function relations during aortic maturation and aging revealed by multiphoton microscopy. Mech Ageing Dev. 2021;196:111471.
[35] BIANCHI F, HOFMANN F, SMITH AJ, et al. Probing multi-scale mechanical damage in connective tissues using X-ray diffraction. Acta Biomater. 2016;45:321-327.
[36] GREINER C, GRAINGER S, FARROW S, et al. Robust quantitative assessment of collagen fibers with picrosirius red stain and linearly polarized light as demonstrated on atherosclerotic plaque samples. PLoS One. 2021;16(3):e0248068.
[37] BLOKSGAARD M, LEURGANS TM, SPRONCK B, et al. Imaging and modeling of acute pressure-induced changes of collagen and elastin microarchitectures in pig and human resistance arteries. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2017;313(1):H164-H178.
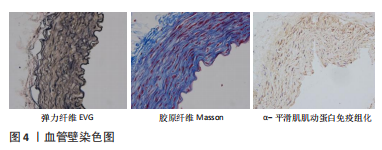
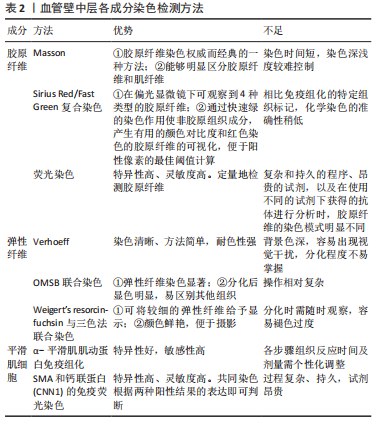
[38] CHEN SH, GAN L, ZHUANG M, et al. Overwork Affects Extracellular Matrix of Arterial Vessel Wall in Rats. Zhongguo Yi Xue Ke Xue Yuan Xue Bao. 2022;44(2):262-269.
[39] CAO S, DENG Q, TAN T, et al. Transthoracic ultrasound-guided percutaneous intramyocardial injection combined with ultrasound-targeted microbubble destruction-mediated angiogenin 1 gene therapy in canine myocardial infarction model. Cardiovasc Diagn Ther. 2021;11(6):1190-1205.
[40] SEGNANI C, IPPOLITO C, ANTONIOLI L, et al. Histochemical Detection of Collagen Fibers by Sirius Red/Fast Green Is More Sensitive than van Gieson or Sirius Red Alone in Normal and Inflamed Rat Colon. PLoS One. 2015;10(12):e0144630.
[41] MOHAMMADKHAH M, SIMMS CK, MURPHY P. Visualisation of Collagen in fixed skeletal muscle tissue using fluorescently tagged Collagen binding protein CNA35. J Mech Behav Biomed Mater. 2017;66: 37-44.
[42] XIAO Y, LING S, PEI Y. Structure of Elastin. Methods Mol Biol. 2021;2347: 27-33.
[43] HEDTKE T, SCHRADER CU, HEINZ A, et al. A comprehensive map of human elastin cross-linking during elastogenesis. FEBS J. 2019;286(18): 3594-3610.
[44] REICHHELD SE, MUIZNIEKS LD, KEELEY FW, et al. Direct observation of structure and dynamics during phase separation of an elastomeric protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2017;114(22):E4408-E4415.
[45] HERNANDEZ-MORERA P, TRAVIESO-GONZALEZ CM, CASTANO-GONZALEZ I, et al. Segmentation of elastic fibres in images of vessel wall sections stained with Weigert’s resorcin-fuchsin. Comput Methods Programs Biomed. 2017;142:43-54.
[46] GAJDA M, JASZTAL A, BANASIK T, et al. Combined orcein and martius scarlet blue (OMSB) staining for qualitative and quantitative analyses of atherosclerotic plaques in brachiocephalic arteries in apoE/LDLR(-/-) mice. Histochem Cell Biol. 2017;147(6):671-681.
[47] GIUDICI A, WILKINSON I B, KHIR AW. Review of the Techniques Used for Investigating the Role Elastin and Collagen Play in Arterial Wall Mechanics. IEEE Rev Biomed Eng. 2021;14:256-269.
[48] LU H, DU W, REN L, et al. Vascular Smooth Muscle Cells in Aortic Aneurysm: From Genetics to Mechanisms. J Am Heart Assoc. 2021; 10(24):e023601.
[49] CAI Z, HUANG J, YANG J, et al. LncRNA SENCR suppresses abdominal aortic aneurysm formation by inhibiting smooth muscle cells apoptosis and extracellular matrix degradation. Bosn J Basic Med Sci. 2021;21(3):323-330.
[50] LU W, ZHOU Y, ZENG S, et al. Loss of FoxO3a prevents aortic aneurysm formation through maintenance of VSMC homeostasis. Cell Death Dis. 2021;12(4):378.
[51] GUO Y, ZHU F, ZHANG X, et al. Extracellular signal-regulated kinase inhibition prevents venous adaptive remodeling via regulation of Eph-B4. Vascular. 2022;30(1):120-129.
[52] KIRKTON RD, SANTIAGO-MAYSONET M, LAWSON JH, et al. Bioengineered human acellular vessels recellularize and evolve into living blood vessels after human implantation. Sci Transl Med. 2019;11(485):eaau6934.
[53] DE BEAUFORT HWL, FERRARA A, CONTI M, et al. Comparative Analysis of Porcine and Human Thoracic Aortic Stiffness. Eur J Vasc Endovasc Surg. 2018;55(4):560-566.
[54] RAFUSE M, XU X, STENMARK K, et al. Layer-specific arterial micromechanics and microstructure: Influences of age, anatomical location, and processing technique. J Biomech. 2019;88:113-121. |