中国组织工程研究 ›› 2023, Vol. 27 ›› Issue (24): 3901-3909.doi: 10.12307/2023.476
• 干细胞综述 stem cell review • 上一篇 下一篇
库普弗细胞在肝移植免疫耐受中的机制
王耀权,轩娟娟,张继翔,陈凯歌,陈国勇,魏思东
- 河南大学人民医院,河南省郑州市 450003
-
收稿日期:2022-06-22接受日期:2022-08-09出版日期:2023-08-28发布日期:2023-01-19 -
通讯作者:陈国勇,主任医师,河南大学人民医院,河南省郑州市 450003 魏思东,主任医师,河南大学人民医院,河南省郑州市 450003 -
作者简介:王耀权,男,1994年生,河南省南阳市人,蒙古族,河南大学在读硕士,主要从事肝移植与排斥反应的研究。 -
基金资助:国家自然科学基金资助项目(U2004124),项目负责人:陈国勇;河南省医学科技攻关计划项目(SBGJ2018071),项目负责人:陈国勇;河南省医学科技攻关计划项目(SB201903020),项目负责人:魏思东;河南省科技攻关计划项目(212102310717),项目负责人:魏思东
Mechanism of Kupffer cells in immune tolerance after liver transplantation
Wang Yaoquan, Xuan Juanjuan, Zhang Jixiang, Chen Kaige, Chen Guoyong, Wei Sidong
- People’s Hospital of Henan University, Zhengzhou 450003, Henan Province, China
-
Received:2022-06-22Accepted:2022-08-09Online:2023-08-28Published:2023-01-19 -
Contact:Chen Guoyong, Chief physician, People’s Hospital of Henan University, Zhengzhou 450003, Henan Province, China Wei Sidong, Chief physician, People’s Hospital of Henan University, Zhengzhou 450003, Henan Province, China -
About author:Wang Yaoquan, Master candidate, People’s Hospital of Henan University, Zhengzhou 450003, Henan Province, China -
Supported by:the National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. U2004124 (to CGY); the Henan Medical Science and Technology Program, No. SBGJ2018071 (to CGY); Henan Provincial Medical Science and Technology Program, No. SB201903020 (to WSD); Henan Provincial Science and Technology Program, No. 212102310717 (to WSD)
摘要:
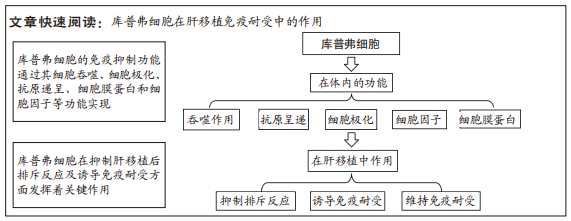
文题释义:
库普弗细胞:是在肝窦中发现的巨噬细胞,是宿主免疫系统的组成部分,参与各种化合物的代谢。其不但具有吞噬功能,还表达受体组织相容性复合体和共刺激分子以提呈抗原和特异性的免疫应答,在免疫调节和组织损伤修复中起主要作用。免疫耐受:指机体免疫系统接受供体抗原后产生的特异性的免疫无应答状态。耐受性通常分为完全免疫耐受性、操作耐受性和支撑耐受性,肝移植后免疫耐受主要是操作耐受性。
背景:肝移植后的免疫排斥反应严重影响患者的生存质量,长期免疫耐受的建立仍然面临着许多问题,而库普弗细胞在抑制肝移植排斥反应及促进免疫耐受方面发挥着重要作用。
目的:综述库普弗细胞在肝移植免疫耐受中的作用及其机制的研究进展,旨在为建立肝移植免疫耐受提供参考思路。
方法:第一作者于2021年12月应用计算机在PubMed和中国知网数据库检索1970年1月至2021年12月相关文献,以“kupffer cells,liver transplantation”为英文检索词,以“库普弗细胞、肝移植”为中文检索词,最终纳入73篇文献进行分析。
结果与结论:①库普弗细胞是驻留在肝脏内的巨噬细胞,其表面存在包括补体受体、Toll样受体和其他病原体识别受体在内的多种特异性受体和结合位点,能够快速响应组织环境的变化,根据需要呈现不同的细胞表型,即M1型和M2型库普弗细胞,而肝移植免疫耐受与M2型库普弗细胞关系密切。②库普弗细胞通过细胞吞噬、细胞极化、抗原呈递、细胞膜蛋白和细胞因子的作用等机制在移植后免疫耐受的建立中发挥重要作用,但是目前尚缺乏高质量的基础和临床研究。③目前已有的库普弗细胞的研究中,研究者们已发现多种库普弗细胞中的细胞因子和非特异性因子可能与移植后免疫耐受关联,主要包括T细胞免疫球蛋白结构域和黏蛋白结构域4、F1型清道夫受体、抗原钙网蛋白、蛋白二硫键异构酶、抑制组蛋白脱乙酰酶11、热休克蛋白、X-box结合蛋白1、骨髓间充质干细胞、白细胞介素2、白细胞介素4、白细胞介素6、白细胞介素10、白细胞介素17、白细胞介素23、白细胞介素34、补体、凋亡因子Fas-FasL、Toll样受体、前列腺素、转化生长因子β和干扰素γ。④在基础研究方面,通过构建原位肝移植动物模型有助于深入探究库普弗细胞不同功能对肝移植后免疫耐受建立的影响。⑤在临床应用方面,通过对移植物病理分析、移植物中库普弗细胞因子表达、基因检测及供者输注骨髓间充质干细胞的方式,可预测及促进免疫耐受的建立,但未来还需要多中心大样本的临床研究来证实。
https://orcid.org/0000-0003-4486-9077(王耀权)
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:干细胞;骨髓干细胞;造血干细胞;脂肪干细胞;肿瘤干细胞;胚胎干细胞;脐带脐血干细胞;干细胞诱导;干细胞分化;组织工程
中图分类号:
引用本文
王耀权, 轩娟娟, 张继翔, 陈凯歌, 陈国勇, 魏思东. 库普弗细胞在肝移植免疫耐受中的机制[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2023, 27(24): 3901-3909.
Wang Yaoquan, Xuan Juanjuan, Zhang Jixiang, Chen Kaige, Chen Guoyong, Wei Sidong. Mechanism of Kupffer cells in immune tolerance after liver transplantation[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(24): 3901-3909.
2.2 库普弗细胞的功能分类 库普弗细胞作为体内最大的巨噬细胞群,具有很强的可塑性,能够快速响应组织环境的变化,并根据需要呈现不同的细胞表型,即M1型库普弗细胞和M2型库普弗细胞[13-14]。M2型细胞又分为M2a(白细胞介素4或白细胞介素13)诱导、M2b(免疫复合物和脂多糖或白细胞介素1受体联合诱导)、M2c(糖皮质激素或白细胞介素10诱导)及M2d(腺苷或白细胞介素6诱导),见表1。
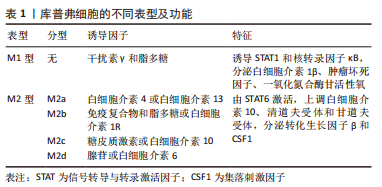
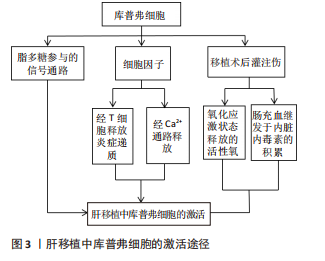
从各自功能角度来看,M1型由干扰素γ和脂多糖诱导,特征是诱导STAT1和核转录因子κB转录因子,分泌炎性递质(如白细胞介素1β、肿瘤坏死因子)和细胞毒性因子(如一氧化氮合酶和活性氧);M2型的特征是转录因子STAT6激活,上调抗炎因子白细胞介素10、清道夫受体(scavenger receptor,SR)、甘露糖受体(mannose receptor,MR)和各种组织重塑因子(如转化生长因子β和集落刺激因子1)[15-18]。目前研究表明库普弗细胞的激活与脂多糖、细胞因子及移植后灌注伤等因素有关。库普弗细胞经脂多糖参与的信号转导通路、T细胞释放炎症递质激活和缺血再灌注损伤状态下激活钙离子通路释放细胞因子等损害肝脏[19-21];同时氧化应激也可激活库普弗细胞,释放活性氧对肝脏造成急性损害;长时间的肠充血继发于内脏内毒素积累也会导致库普弗细胞活化[22],见表1和图3。
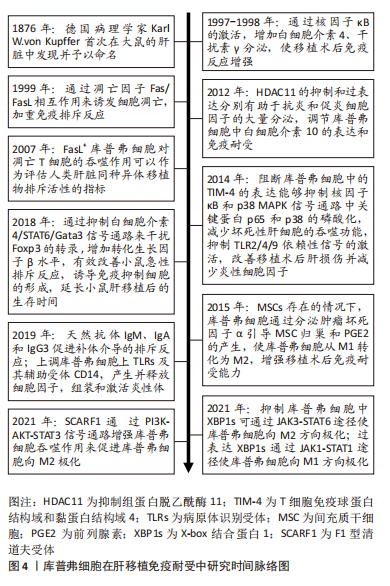
2.3 库普弗细胞在肝移植免疫耐受中的机制 免疫耐受是指机体免疫系统接受供体抗原后产生的特异性的免疫无应答状态[23]。肝脏作为“免疫特惠器官”与其他器官移植相比,在移植后更容易到达免疫耐受状态,而库普弗细胞在肝移植免疫耐受中占有举足轻重的地位[24]。根据纳入文献,库普弗细胞自19世纪首次发现以来,其表型、功能及作用的研究一直是研究者关注的热点。近年来关于库普弗细胞不同功能及其相关因子在肝移植免疫耐受中作用的机制研究也不断取得进展,见图4。
2.3.1 库普弗细胞的吞噬功能可诱导免疫耐受 吞噬作用是一种基本的细胞过程,在免疫中具有多种功能。肝脏是处理凋亡细胞的主要场所,对凋亡细胞处理的特定吞噬途径性质的不同决定了炎症反应的相对程度,同样影响移植后免疫反应的程度。因为吞噬活动中无新的蛋白产物合成参与,吞噬消化潜在有免疫原性的大颗粒(如微生物病原体、凋亡和坏死的尸体)释放出具有抗原递呈功能的吞噬体并促使其成熟,从而促使机体通过其受体激活信号通路而产生免疫耐受,所以把以吞噬作用来消除凋亡细胞以递呈抗原诱导耐受的方式可以认为是一种先天免疫反应[25-26]。
库普弗细胞对凋亡细胞的吞噬处理不仅是迅速吞噬以阻止凋亡细胞进一步发展而出现溶解和胞内免疫原性物质外泄,防止机体对其发生免疫反应[27],而且在吞噬后能分泌抑制性因子如转化生长因子β、白细胞介素10和前列腺素2等[28],使局部造成一个免疫抑制的微环境,进而降低该处淋巴细胞的功能,完成由异体凋亡细胞诱导受体产生特异性免疫耐受。在肝移植后排斥反应伴随的肝损害中,肝损伤导致固有巨噬细胞激活,分泌多种促炎细胞因子和趋化因子引起无菌性炎症和单核细胞、中性粒细胞等炎症细胞浸润,进一步加重肝损害及免疫排斥反应[29];另一方面,在移植后肝损伤及炎症发生情况下,巨噬细胞能及时有效清除凋亡细胞,增加如上所述抗炎因子的分泌或诱导调节性T淋巴细胞(Regulatory cells,Tregs)的产生,负向调控免疫反应,利于免疫耐受微环境形成。研究表明,库普弗细胞上表达T细胞免疫球蛋白结构域和黏蛋白结构域4(T-cell immunogloblin domain and mucin domain 4,TIM-4)介导共刺激信号并诱导对凋亡细胞的吞噬作用。阻断库普弗细胞上TIM-4信号会抑制巨噬细胞和中性粒细胞的迁移和功能,减少对坏死性肝细胞的吞噬功能,并抑制TLR2/4/9依赖性信号的激活,有助于改善移植后肝损伤并减少炎性细胞因子(如肿瘤坏死因子α、干扰素γ、CCL2和CXCL2)的释放,从而减轻肝移植后免疫排斥反应的发生[30-31];XU等[32]研究表明,F1型清道夫受体(Scavenger receptor class F,member 1,SCARF1)通过钙依赖性 PI3K-AKT-STAT3信号通路增强库普弗细胞吞噬作用来促进库普弗细胞向M2极化,库普弗细胞中过表达F1型清道夫受体可有效降低肝移植后急性排斥反应程度,增加凋亡细胞的清除率,改善肝功能,并促进肝移植免疫耐受功能。此外BRENNER等[33]研究表明,细胞死亡释放出3种免疫抗原钙网蛋白、ERp57和GP96,库普弗细胞吞噬死亡细胞以消除这些抗原同样有助于防止同种异体肝移植的排斥反应,见表2。
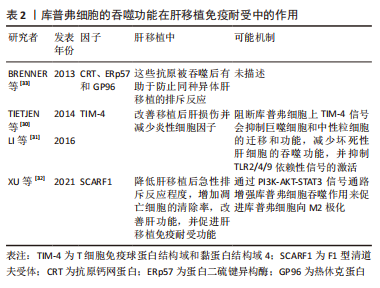
上述研究提示,在肝移植后库普弗细胞可通过其吞噬功能,一方面迅速清除凋亡细胞并分泌抑制性因子,作为防止免疫反应发生的第一道防线;另一方面,库普弗细胞分泌抗炎因子或诱导Tregs产生可负向调控免疫反应,作为第二道防线共同促使免疫耐受的建立。在免疫耐受建立的过程中,TIM-4、F1型清道夫受体与抗原钙网蛋白、ERp57和GP96蛋白的改变也会影响库普弗细胞吞噬功能,进而影响术后免疫耐受的建立,但具体机制仍需进一步详细研究。
2.3.2 库普弗细胞的抗原递呈功能与免疫耐受 在肝移植中导致排斥反应的主要抗原是MHC。库普弗细胞不仅可以表达MHC-Ⅰ/Ⅱ类抗原、共刺激分子和黏附分子,而且还是一类很有效的抗原递呈细胞。研究表明,通过出血小鼠模型、库普弗细胞细胞共培养发现简单的出血可产生明显和长期库普弗细胞抗原递呈的抑制,其机制与MHCⅡ类抗原的丢失和前列腺素的释放有关[34],说明出血导致的局部缺氧所造成的细胞代谢改变可降低库普弗细胞抗原递呈能力。而肝移植后长期的炎症刺激会上调肝脏所有细胞中MHCⅠ类的表达,刺激包括库普弗细胞、内皮细胞、胆管上皮细胞和肝细胞中MHCⅡ类的表达,因此认为肝移植后的炎症刺激通过增强库普弗细胞等细胞的抗原递呈功能,引发排斥反应[35]。
通过抑制库普弗细胞中的信号通路来影响库普弗细胞抗原呈递功能,也对免疫耐受形成有一定的影响,同时释放慢性抗炎性递质(前列腺素2、转化生长因子β、白细胞介素10、白细胞介素4和一氧化氮等)。TIM-4的功能是介导凋亡小体的结合和吞噬、调节适应性免疫反应、抑制外周免疫耐受并激活T细胞,有研究表明肝移植后会导致激活的 库普弗细胞中TIM-4的表达增加,通过阻断库普弗细胞中的TIM-4的表达能够抑制核转录因子κB和p38 MAPK信号通路中关键蛋白p65和p38的磷酸化,可显著改善体内急性排斥反应损伤[30]。此外,阻断库普弗细胞中的TIM-4降低白细胞介素4 的表达并触发iTregs的转化,其原因是通过抑制白细胞介素4/STAT6/Gata3信号通路来干扰人叉头框蛋白P3(Foxp3)的转录,增加转化生长因子β水平,从而抑制Th2分化来促进iTregs转化。
在肝移植后联用抗TIM-4 mAb和外源性转化生长因子β治疗,对改善肝移植的急性排斥反应也表现出协同作用,WU等[36]通过外源性转化生长因子β注射阻断库普弗细胞表达TIM-4也证实上述观点,且有效地改善了小鼠急性排斥反应,并可能诱导免疫抑制细胞的形成,延长小鼠肝移植后的生存时间。研究表明,库普弗细胞中miR-155水平的升高与促炎症细胞因子的分泌和肝移植后的急性排斥反应有关,其靶基因细胞因子信号传导抑制蛋白1(Suppressor of cytokine signaling-1,SOCS1)被认为是免疫细胞功能和炎症反应的中心调节因子,可调节库普弗细胞和DC的激活、发育和分化[37]。在库普弗细胞中使用miR-155 mimic沉默SOCS1,结果表明增强了库普弗细胞抗原递呈功能,并增加其MHC-Ⅱ和共刺激分子的表达及通过JAK/STAT信号通路诱导了更强的Th1细胞因子谱。相反,用miR-155抑制剂过表达SOCS1可使库普弗细胞保持在稳定、未成熟的状态,减少共刺激分子和MHC-Ⅱ分子的表面表达,通过下调T细胞反应和促炎细胞因子的分泌,并减少同种异体T细胞的增殖,增加FasL的表达,从而诱导T细胞凋亡。该研究还提出miR-155可能是肝移植免疫学中的一个关键成分,也是开发诱导耐受的新药或基因疗法的一个有前途的靶点,见表3。
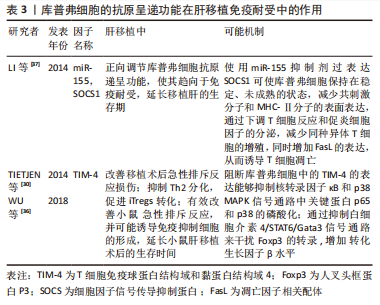
上述研究表明,在肝移植免疫排斥反应中,在受到各种刺激的因素下,库普弗细胞的抗原递呈能力改变进而影响MHC的表达,不仅与抗原的丢失和前列腺素的释放有关,同样与术后长期慢性炎症刺激有关,从而影响免疫耐受的建立。而通过对TIM-4、SOCS1的研究影响库普弗细胞抗原递呈功能来抑制免疫排斥反应的发生,促进免疫耐受的建立并延长移植后的生存期具有较好的前景,但仍需大量实验研究来验证。
2.3.3 库普弗细胞的表面分子与免疫耐受
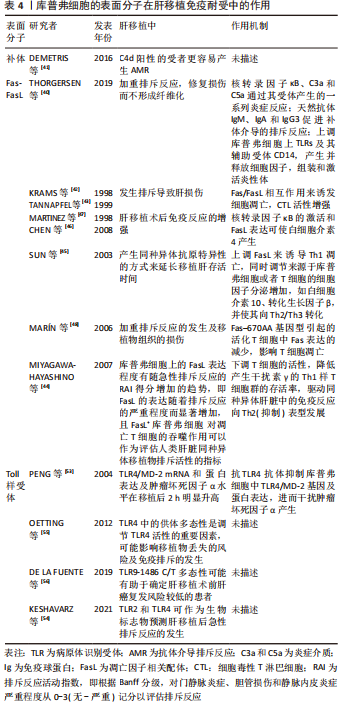
补体在肝移植免疫耐受中的作用:补体系统由几种补体蛋白组成,这些蛋白大部分由肝脏的库普弗细胞合成,在先天性免疫和适应性免疫中都是肝脏内稳态、免疫反应以及与其他效应系统相互作用的关键部分,还可通过大量可溶性病原体识别受体和补体成分的生物合成,来控制系统先天免疫[38-39]。
在肝移植中,补体是抗体介导排斥反应的主要免疫效应系统,供体特异性抗体会激活补体。首先供体特异性抗体通过经典途径启动激活补体,C3b结合到内皮细胞膜表面并作为调理素与C5b-9(MAC)插入膜中诱导核转录因子κB介导的炎症反应,此外C3a和C5a通过其受体产生的一系列炎症反应,均会导致免疫排斥的加剧。天然抗体如免疫球蛋白M(IgM)、IgA和IgG3同样会促进补体介导的排斥反应发生[40]。通过免疫组织病理学染色来检测肝移植受者肝组织,发现C4d阳性的受者更容易产生抗体介导排斥反应[41]。此外,补体系统还与其他效应系统经常相互关联,补体能够上调 库普弗细胞上Toll样受体(Toll-like receptor,TLRs)及其辅助受体CD14,二者共同作用产生并释放细胞因子,组装和激活炎性体,加重排斥反应。对于肝脏免疫耐受来说,补体在肝脏的再生潜能中起重要作用,可能会修复损伤而不形成纤维化[40]。
补体作为大部分由库普弗细胞合成的蛋白在调控免疫反应中起重要作用,但是在肝移植中研究较少,如何抑制补体介导的排斥反应是一个值得研究的方向;而通过免疫组织病理学染色来预测是否会发生急性排斥反应,尚需大量的实验及临床研究证实。
凋亡因子Fas-FasL(Fas/Fas ligand)在肝移植免疫耐受中的作用:Fas抗原是一种介导细胞凋亡的细胞表面蛋白,FasL或抗Fas抗体的结合会导致携带Fas的细胞发生凋亡,在肝移植后Fas表达的细胞(肝细胞、胆管上皮细胞、淋巴细胞和粒细胞)均会发生凋亡,在急性排斥反应中更为明显。研究表明FasL在大鼠肝移植后第3天表达显著增加并持续至第7天,同时细胞毒性T淋巴细胞活性增强,并观察到排斥组在术后第7天凋亡肝细胞及胆管细胞的数量最大,此外还可见大量浸润性T细胞的凋亡,说明Fas/FasL相互作用诱发细胞凋亡是移植后发生排斥导致肝损伤的重要机制[42-43]。
MIYAGAWA-HAYASHINO等[44]的研究证实FasL在库普弗细胞中同样高表达,急性排斥反应组门静脉区的凋亡片段、吞噬FasL+ 库普弗细胞的计数显著高于慢性排斥反应组及炎症对照组,且FasL+ 库普弗细胞吞噬的凋亡片段中主要为CD4+ 干扰素γ+T细胞,而加入免疫抑制剂或类固醇类药物后吞噬FasL+ 库普弗细胞计数减少,库普弗细胞还可以下调T细胞的活性,降低产生干扰素γ的Th1样T细胞群的存活率,从而导致门静脉系统的免疫抑制的发生,并可能驱动同种异体肝脏中的免疫反应向Th2(抑制)表型发展,进而影响移植后免疫耐受的建立。此外发现库普弗细胞上的FasL表达程度有随急性排斥反应的RAI得分增加的趋势,即FasL的表达随着排斥反应的严重程度而显著增加,因此认为FasL+库普弗细胞 对凋亡T细胞的吞噬作用可以作为评估人类肝脏同种异体移植物排斥活性的指标。
SUN等[45]将同种异体肝移植后长期存活大鼠的库普弗细胞输给急性排斥模型大鼠,发现可以诱导其产生同种异体抗原特异性的方式来延长移植肝存活时间,库普弗细胞通过上调FasL来诱导Th1凋亡,同时可以调节来源于库普弗细胞或者T细胞的细胞因子,使抗炎细胞因子分泌增加,如白细胞介素10、转化生长因子β,并使其向Th2/Th3转化。CHEN等[46]通过移植模型发现,与对照组相比移植组库普弗细胞中FasL mRNA和蛋白水平显著上调,说明核转录因子κB的激活和FasL表达与白细胞介素4的产生呈正相关,有数据也证实这一观点并表明FasL的过表达可能导致肝移植后免疫反应的增强[47]。而MARíN等[48]的研究表明Fas-670AA基因型会引起的活化T细胞中Fas表达的减少,将影响其T细胞凋亡,导致其在肝组织中的积聚,有利于移植物组织的损伤,加重排斥反应的发生,但这种效应只会发生在长期存活的同种异体移植物中,且在未突变型中则没有发现。
总之,库普弗细胞中核转录因子κB可促进其FasL及白细胞介素4的表达,并通过Fas/FasL途径诱导T细胞凋亡,调节辅助T细胞亚群分化来促进肝移植后免疫耐受的形成。上述研究表明,Fas/FasL途径在诱导肝移植后免疫耐受建立中起重要作用,一方面移植后急性排斥反应下FasL+ 库普弗细胞吞噬大量炎症细胞因子,同时下调T细胞活性,并驱动免疫反应向抑制表型发展来促进免疫耐受建立;而库普弗细胞中FasL的表达是否可应用以评估人类肝脏同种异体移植物排斥活性尚需大量临床数据支撑;另一方面,核转录因子κB及Fas-670AA基因型可影响移植后Tc凋亡,进而影响免疫耐受的形成,但其机制尚不明确,需进一步深入研究。
Toll样受体在肝移植免疫耐受中的作用:TLRs是病原体识别受体,属于跨膜蛋白家族,具有检测内源性和外源性分子的功能,在协调先天免疫反应和随后的获得性免疫反应中起关键作用。肝脏的正常生理环境是一种先天免疫耐受状态,人体经由门静脉循环把TLR2和TLR4配体从肠道带入肝实质,通过减少库普弗细胞表面TLR的表达和信号传导,来维持免疫处于稳态[49-50]。肝移植排斥反应中,TLRs 的种系编码模式识别受体(pattern recognition receptors,PRRs)亚组通过对病原体相关分子模式(pathogen-associated molecular patterns,PAMPs)和损伤相关分子模式(damage-associated molecule patterns,DAMPs)的识别,释放TLR刺激信号在树突细胞成熟、抗原呈递以及T和B细胞募集和激活中发挥作用,将先天与适应性免疫系统联系起来,这些过程在移植耐受和排斥中起重要作用。
通过PAMP刺激库普弗细胞上表达的TLR 2、3、4 和 9 会导致包括肿瘤坏死因子α、白细胞介素1β、白细胞介素6、白细胞介素12和白细胞介素10在内的多种细胞因子产生,进而诱导转化生长因子β、血小板衍生生长因子(platelet-derived growth factor,PDGF)、基质金属蛋白酶和活性氧的分泌来影响移植后免疫耐受的建立。而信号级联的启动则是通过4种主要衔接分子:髓样分化因子88(myeloid differentiation protein-88、MyD88)、含有TIR 结构域的衔接蛋白诱导干扰素β(Toll interleukin receptor domain-containing adaptor protein-inducing interferon β,TRIF)、TIR相关蛋白 (toll interleukin receptor-associated protein,TIRAP)和TRIF衔接蛋白诱导干扰素β相关蛋白(toll interleukin receptor domain-containing adaptor protein-inducing interferon β-related ,TRAM),TIR结构域与4种衔接分子其一连接,诱导免疫反应的发生[51-52]。
PENG等[53]研究表明,TLR4/MD-2mRNA和蛋白表达及肿瘤坏死因子α水平在移植后2 h明显升高,而抗TLR4抗体治疗后这些因子的表达明显降低,可能与抗TLR4抗体抑制库普弗细胞中TLR4/MD-2基因及蛋白表达,进而干扰肿瘤坏死因子α的产生有关。KESHAVARZ等[54]通过对肝移植患者术后急性排斥反应中TLR2和TLR4表达水平的观察,发现其均在术后1,7 d升高,认为其中TLR2和TLR4可作为生物标志物预测肝移植后急性排斥反应的发生。此外OETTING等[55]对738例不同人种的同种异体肝移植受者的TLR4基因进行分析,认为TLR4中的供体多态性可能是调节TLR4活性的重要因素,因此会影响移植物丢失的风险及免疫排斥的发生。DE LA FUENTE等[56]对159例患有肝细胞癌行肝移植的患者术后移植肝脏病理进行研究,发现TLR9-1486TT基因型与移植后肝癌复发率较低相关,因此认为TLR9-1486C/T多态性可能有助于确定肝移植术前肝癌复发风险较低的患者。上述研究表明,TLRs通过与衔接分子结合在移植后影响多种细胞因子产生,介导免疫排斥反应发生,其中以TLR2和TLR4在移植后的表达水平来预测急性排斥反应发生的可靠性尚待更多研究加以证实,TLR4表达及供体多态性均可作为研究移植后免疫排斥发生的方向;而TLR9-1486TT基因型与移植后肝癌复发率尚需更多临床数据及研究验证。
文章汇总了库普弗细胞的表面分子在肝移植免疫耐受中的作用相关研究进展,见表4。
2.3.4 库普弗细胞参与细胞因子的调控可诱导免疫耐受 细胞因子是由多种不同类型细胞产生的具有多种生物活性的蛋白质或肽类,通过与相应靶细胞表面表达的特定受体结合来介导产生免疫调节作用和某些效应功能。细胞因子可通过以下途径来介导肝移植后免疫耐受的建立:①白细胞介素是由多种细胞产生并作用于多种细胞的一类细胞因子,其在传递信息、激活与调节免疫细胞,介导T细胞和B细胞活化、增殖与分化及在炎症反应中起重要作用。白细胞介素10不仅能抑制巨噬细胞活化及继发的细胞免疫反应,而且能够减少炎症递质和细胞因子的释放,其作为一种负调因子,可对多种细胞因子产生抑制作用,在肝移植免疫耐受中起重要作用[57]。②由库普弗细胞所分泌的肿瘤坏死因子被认为是加重肝脏损伤的中心因素,主要通过诱导肝细胞凋亡、内皮细胞肿胀和活化、血小板窦状聚集和促进外周免疫细胞进入而使肝脏微循环恶化[58]。③转化生长因子β介导促炎或抗炎反应。受损的肝细胞和活化的库普弗细胞释放转化生长因子β,通过保护nTregs免受细胞凋亡以及通过诱导和维持iTregs中Foxp3的表达来抑制免疫反应,还可以抑制MHCⅡ类抗原表达,通过下调树突细胞与库普弗细胞的抗原递呈功能来介导各种免疫抑制效应,此外还可以通过其自身介导的信号通路来完成免疫耐受的建立,具体机制还尚待进一步研究[59]。④干扰素是一类糖蛋白,能上调淋巴细胞群的增殖和分化、主要由库普弗细胞产生的免疫调节蛋白诱导。所有这些过程均增强并维持炎症反应,这可能导致急性移植物的破坏和丧失[60]。
在排斥模型中Th1淋巴细胞可通过分泌白细胞介素2、干扰素γ等Th1细胞因子,Th17淋巴细胞可分泌白细胞介素17、白细胞介素6及白细胞介素23等Th17细胞因子,两者共同促使各亚型效应性T细胞的增殖、分化、成熟,从而促使细胞免疫应答的发生,致移植物中大量炎症因子浸润,最终导致移植物急性排斥的发生;而耐受模型中,Th2淋巴细胞通过分泌白细胞介素4、白细胞介素10等Th2细胞因子,同时抑制Th1细胞的表达,明显改善炎症细胞浸润程度及肝脏功能,从而有利于外周耐受的建立[61-63]。SAVIER等[64]的研究表明,移植耐受大鼠模型中库普弗细胞上的白细胞介素10和转化生长因子β表达明显上调,并促进Th细胞向Th2/Th3分化及Th1细胞凋亡。PAHLAVAN等[65]通过动物实验表明库普弗细胞可通过分泌除细胞因子外(白细胞介素4和白细胞介素10)的免疫受体和细胞黏附分子,它们可以抑制移植中的同种免疫反应来促进肝移植后肝细胞再生、修复及调控免疫反应,其分子机制可能与核转录因子κB的活化有关。有研究通过大鼠原位肝移植研究表明,抑制组蛋白脱乙酰酶11(Suppression of histone deacetylase 11,HDAC11)可调节库普弗细胞中白细胞介素10的表达和免疫耐受。HDAC11的抑制和过度表达分别有助于抗炎和促炎细胞因子的大量分泌,抑制其在库普弗细胞中的表达可通过上调白细胞介素10诱导免疫耐受的产生。此外,沉默HDAC11也能诱导大鼠原位肝移植后的耐受,并推测HDAC11可能是这移植后免疫调节系统中的一个关键成分,但具体机制尚待进一步研究,同时也表明HDAC11可以作为肝移植后免疫耐受及药物新的研究的方向[66]。TIAN等[67]通过心脏死亡后器官捐赠(Donation after cardiac death,DCD)建立了一种动脉化的小鼠非心脏跳动肝移植模型,研究表明骨髓间充质干细胞能抑制库普弗细胞的凋亡、Th1/Th17免疫反应、趋化因子的表达和炎性细胞的浸润,明显改善小鼠非心脏跳动肝移植损伤,提高移植后存活率。在体外,骨髓间充质干细胞分泌的前列腺素2通过调节TLR4-ERK1/2-caspase3通路抑制库普弗细胞的凋亡。并认为临床应用间充质干细胞输注保护心脏死亡后器官捐赠肝移植物,可为延长移植后存活时间提供了一种有前景的可行方案。上述研究表明,移植后库普弗细胞在细胞因子影响下促进Th细胞向Th2/Th3分化,并通过以分泌抑制性细胞因子同时抑制Th1细胞表达的方式促进免疫耐受的建立,但具体机制尚待进一步研究;核转录因子κB、HDAC11及间充质干细胞在移植后以通过影响库普弗细胞分泌细胞因子等方式来促进免疫耐受的建立,但均处于实验研究阶段,尚未有明确证据证实,而通过输注骨髓间充质干细胞的方式保护肝移植物似乎可行,需大量临床研究证实。
2.3.5 库普弗细胞的极化可诱导免疫耐受 肝移植后机体通过抑制M1型库普弗细胞细胞数量和功能,或者促使M2型库普弗细胞细胞数量增加和功能增强,有助于免疫耐受的建立。在库普弗细胞发生M1型极化后,MHCⅡ类分子和共刺激分子表达上调,抗原提呈能力提升,从而在免疫反应中发挥正向增强作用,导致急性排斥反应加重,其机制可能与肿瘤坏死因子α、核转录因子κB、白细胞介素、磷脂酰肌醇-3-激酶/蛋白激酶信号通路(PI3K/Akt)、α-酮戊二酸及衣康酸等因素有关,从而影响免疫耐受建立[68]。
YOU等 [69]通过库普弗细胞与骨髓间充质干细胞共培养后观察到库普弗细胞中促炎细胞因子的表达明显降低,如MHC-Ⅱ,CD40,CD80和CD86;而抗炎细胞因子的表达增加,如转化生长因子β、白细胞介素4、前列腺素2和白细胞介素10;通过大鼠肝移植模型观察到,在骨髓间充质干细胞存在的情况下,库普弗细胞从M1表型转变为M2表型,并增加其免疫耐受能力。此外,信号通路的改变也可以通过库普弗细胞的极化影响免疫耐受的形成。XU等[32]研究表明,通过上调库普弗细胞中的 F1型清道夫受体的表达,可以增强库普弗细胞对凋亡细胞的吞噬作用,并增加细胞内钙外流,进而上调 PI3K-AKT-STAT3信号活性,最终促进库普弗细胞的 M2 极化,同时减少促炎因子的分泌,增加抗炎因子的分泌,有利于肝移植后免疫耐受的形成。ZHAO等[70]研究表明,白细胞介素34可以在肝移植后的体内通过PI3K/Akt/mTOR通路信号的激活诱导库普弗细胞的M2极化,并可在体外将库普弗细胞的表型从M1转变为M2,以此来抑制急性免疫排斥反应,诱导免疫耐受。
HU等[71]通过研究,表明高血糖条件下肝组织和库普弗细胞中S1P/S1PR3 通路被激活,通过调节M1/M2极化使肝脏缺血/再灌注损伤加剧,从而影响移植后免疫耐受的建立。DENG等[72]通过白细胞介素4对供体大鼠肝脏的处理,发现白细胞介素4可诱导库普弗细胞M2极化,表明其机制与激活STAT6-JMJD3通路和抑制TLR-4-核转录因子κB通路有关,能够通过调节炎症反应和肝细胞凋亡来保护肝移植物免受缺血再灌注损伤,有利于移植后免疫耐受的建立。ZHANG等[73]发现,抑制活化库普弗细胞中X-box结合蛋白1(X-box Binding Protein 1,XBP1s)可以增加精氨酸酶1(Arginase-1,Arg-1)和CD204的表达,但也可以降低MHC-Ⅱ和CD40的表达水平,通过JAK3-STAT6途径使库普弗细胞向M2方向极化,并通过促进抗炎细胞因子的分泌和促进激活的T细胞的凋亡而发挥免疫抑制作用;而过表达的XBP1s则出现相反的表现,通过JAK1-STAT1途径使库普弗细胞向M1方向极化,并表现出强烈的促炎特性,说明XBP1对库普弗细胞具有较强的抑制其免疫功能的作用。
肝移植后细胞微环境发生变化,库普弗细胞在脂多糖、炎症介质激活和缺血再灌注损伤等因素下激活并极化,其M2 型极化对诱导肝移植免疫耐受的建立至关重要,极化机制主要与前文所述的不同刺激因素相关,也说明库普弗细胞的极化并非单一调控模式。骨髓间充质干细胞影响库普弗细胞的细胞因子表达及M2表型转化,但具体机制尚需进一步研究;此外在信号通路中,F1型清道夫受体通过PI3K-AKT-STAT3、白细胞介素34通过PI3K/Akt/mTOR、白细胞介素4通过激活STAT6-JMJD3与抑制TLR-4-核转录因子κB通路及XBP1s通过JAK3-STAT6途径均可以使库普弗细胞的表型从M1转变为M2,发挥促进免疫耐受的作用,但各因子通过其通路发挥作用的机制尚不明确,需要进一步深入研究。

| [1] 唐家琢,李满,王卫星,等.Treg在肝移植受者免疫耐受中的研究进展[J].中华肝脏外科手术学电子杂志,2021,10(3):337-339. [2] 泉余,蒋师放,夏仁培,等.肝移植临床免疫抑制剂及新药研究进展[J].器官移植,2020,11(6):663-670. [3] MERLIN S, BHARGAVA KK, RANALDO G, et al. Kupffer cell transplantation in mice for elucidating monocyte/macrophage biology and for potential in cell or gene therapy. Am J Pathol. 2016;186(3):539-551. [4] JIANG Y, QUE W, ZHU P, et al. The role of diverse liver cells in liver transplantation tolerance. Front Immunol. 2020;11:1203. [5] Kupffer CV. Ueber Sternzellen der Leber. Arch Mikrosk Anat. 1876; 12:353-358. [6] BILZER M, ROGGEL F, GERBES AL. Role of Kupffer cells in host defense and liver disease. Liver Int. 2006;26(10):1175-1186. [7] GOMEZ PERDIGUERO E, KLAPPROTH K, SCHULZ C, et al. Tissue-resident macrophages originate from yolk-sac-derived erythro-myeloid progenitors. Nature. 2015;518(7540):547-551. [8] KAZANKOV K, JØRGENSEN SMD, THOMSEN KL, et al. The role of macrophages in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2019;16(3):145-159. [9] 王茜,何浩,宋文刚.枯否细胞的负向免疫调节作用[J].细胞与分子免疫学杂志,2010,26(6):611-612. [10] NAITO M, HASEGAWA G, EBE Y, et al. Differentiation and function of Kupffer cells. Med Electron Microsc. 2004;37(1):16-28. [11] BENNETT H, TROUTMAN TD, SAKAI M, et al. Epigenetic regulation of Kupffer cell function in health and disease. Front Immunol. 2021; 11:609618. [12] WANG C, MA C, GONG L, et al. Macrophage polarization and its role in liver disease. Front Immunol. 2021;12:803037. [13] ZWICKER C, BUJKO A, SCOTT CL. Hepatic macrophage responses in inflammation, a function of plasticity, heterogeneity or both? Front Immunol. 2021;12:690813. [14] DIXON LJ, BARNES M, TANG H, et al. Kupffer cells in the liver. Compr Physiol. 2013;3(2):785-797. [15] MANTOVANI A, SICA A, SOZZANI S, et al. The chemokine system in diverse forms of macrophage activation and polarization. Trends Immunol. 2004;25(12):677-686. [16] KINARET PAS, SCALA G, FEDERICO A, et al. Carbon nanomaterials promote M1/M2 macrophage activation. Small. 2020;16(21):e1907609. [17] WANG Q, WEI S, ZHOU H, et al. Hyperglycemia exacerbates acetaminophen-induced acute liver injury by promoting liver-resident macrophage proinflammatory response via AMPK/PI3K/AKT-mediated oxidative stress. Cell Death Discov. 2019;5:119. [18] HUANG X, LI Y, FU M, et al. Polarizing macrophages in vitro. Methods Mol Biol. 2018;1784:119-126. [19] DOU L, SHI X, HE X, et al. Macrophage phenotype and function in liver disorder. Front Immunol. 2020;10:3112. [20] DOHERTY DG. Immunity, tolerance and autoimmunity in the liver: a comprehensive review. J Autoimmun. 2016;66:60-75. [21] 蔡佳晖,王经琳,任昊桢,等.枯否细胞在肝移植脂肪供肝的缺血再灌注损伤中的作用研究进展[J].肝胆胰外科杂志,2021,33(1):56-60. [22] URATA K, BRAULT A, ROCHELEAU B, et al. Role of Kupffer cells in the survival after rat liver transplantation with long portal vein clamping times. Transpl Int. 2000;13(6):420-427. [23] 张安元,刘一鸣,龚建平.Kupffer细胞与肝脏移植的研究进展[J].世界华人消化杂志,2015,23(12):1917-1923. [24] PEREZ R, JOHNSON J, WINKLER JD, et al. Kupffer cell-mediated lymphocyte apoptosis: a PGE2-dependent mechanism of portal venous transfusion-induced immunosuppression? J Surg Res. 1998;78(1):37-41. [25] GREENBERG S, GRINSTEIN S. Phagocytosis and innate immunity. Curr Opin Immunol. 2002;14(1):136-145. [26] GORDON S. Pattern recognition receptors: doubling up for the innate immune response. Cell. 2002;111(7):927-930. [27] RAVICHANDRAN KS. Beginnings of a good apoptotic meal: the find-me and eat-me signaling pathways. Immunity. 2011;35(4):445-455. [28] HOCHREITER-HUFFORD A, RAVICHANDRAN KS. Clearing the dead: apoptotic cell sensing, recognition, engulfment, and digestion. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2013;5(1):a008748. [29] 李静,季菊玲.肝脏巨噬细胞及其在肝损伤中的作用[J].世界华人消化杂志,2017,25(14):1223-1230. [30] TIETJEN GT, GONG Z, CHEN CH, et al.Molecular mechanism for differential recognition of membrane phosphatidylserine by the immune regulatory receptor Tim4. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2014;111(15):E1463-E1472. [31] LI XQ, LI XH, DUAN SG, et al. Effect of inhibiting TIM-4 function in Kupffer cells on liver graft rejection in mice. Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao. 2016;37(4):451-459. [32] XU XS, FENG ZH, CAO D, et al. SCARF1 promotes M2 polarization of Kupffer cells via calcium-dependent PI3K-AKT-STAT3 signalling to improve liver transplantation. Cell Prolif. 2021;54(4):e13022. [33] BRENNER C, GALLUZZI L, KEPP O, et al. Decoding cell death signals in liver inflammation. J Hepatol. 2013;59(3):583-594. [34] AYALA A, PERRIN MM, ERTEL W, et al. Differential effects of hemorrhage on Kupffer cells: decreased antigen presentation despite increased inflammatory cytokine (IL-1, IL-6 and TNF) release. Cytokine. 1992;4(1):66-75. [35] RONCA V, WOOTTON G, MILANI C, et al. The immunological basis of liver allograft rejection. Front Immunol. 2020;11:2155. [36] WU H, XU X, LI J, et al. TIM4 blockade of KCs combined with exogenous TGFβ injection helps to reverse acute rejection and prolong the survival rate of mice receiving liver allografts. Int J Mol Med. 2018;42(1):346-358. [37] LI J, GONG J, LI P, et al. Knockdown of microRNA-155 in Kupffer cells results in immunosuppressive effects and prolongs survival of mouse liver allografts. Transplantation. 2014;97(6):626-635. [38] GAO B, JEONG WI, TIAN Z. Liver: an organ with predominant innate immunity. Hepatology. 2008;47(2):729-736. [39] HADDAD A, WILSON AM. Biochemistry, Complement// StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing. 2020. [40] THORGERSEN EB, BARRATT-DUE A, HAUGAA H, et al. The role of complement in liver injury, regeneration, and transplantation. Hepatology. 2019;70(2):725-736. [41] DEMETRIS AJ, BELLAMY C, HÜBSCHER SG, et al. 2016 Comprehensive Update of the Banff Working Group on Liver Allograft Pathology: Introduction of Antibody-Mediated Rejection. Am J Transplant. 2016;16(10):2816-2835. [42] KRAMS SM, MARTINEZ OM. Apoptosis as a mechanism of tissue injury in liver allograft rejection. Semin Liver Dis. 1998;18(2):153-167. [43] TANNAPFEL A, KOHLHAW K, EBELT J, et al. Apoptosis and the expression of Fas and Fas ligand (FasL) antigen in rejection and reinfection in liver allograft specimens. Transplantation. 1999;67(7):1079-1083. [44] MIYAGAWA-HAYASHINO A, TSURUYAMA T, EGAWA H, et al. FasL expression in hepatic antigen-presenting cells and phagocytosis of apoptotic T cells by FasL+ Kupffer cells are indicators of rejection activity in human liver allografts. Am J Pathol. 2007;171(5):1499-1508. [45] SUN Z, WADA T, MAEMURA K, et al. Hepatic allograft-derived Kupffer cells regulate T cell response in rats. Liver Transpl. 2003;9(5):489-497. [46] CHEN Y, LIU Z, LIANG S, et al.Role of Kupffer cells in the induction of tolerance of orthotopic liver transplantation in rats. Liver Transpl. 2008; 14(6):823-836. [47] MARTINEZ OM, KRAMS SM. Involvement of Fas-Fas ligand interactions in graft rejection. Int Rev Immunol. 1999;18(5-6):527-546. [48] Marín LA, MURO M, MOYA-QUILES MR, et al. Study of Fas (CD95) and FasL (CD178) polymorphisms in liver transplant recipients. Tissue Antigens. 2006;67(2):117-126. [49] VIDYA MK, KUMAR VG, SEJIAN V, et al. Toll-like receptors: significance, ligands, signaling pathways, and functions in mammals. Int Rev Immunol. 2018;2;37(1):20-36. [50] HOWELL J, GOW P, ANGUS P, et al. Role of toll-like receptors in liver transplantation. Liver Transpl. 2014;20(3):270-280. [51] MENCIN A, KLUWE J, SCHWABE RF. Toll-like receptors as targets in chronic liver diseases. Gut. 2009;58(5):704-720. [52] EL-BENDARY M, NAEMATTALAH M, YASSEN A, et al. Interrelationship between Toll-like receptors and infection after orthotopic liver transplantation. World J Transplant. 2020;10(6):162-172. [53] PENG Y, GONG JP, LIU CA, et al.Expression of toll-like receptor 4 and MD-2 gene and protein in Kupffer cells after ischemia-reperfusion in rat liver graft. World J Gastroenterol. 2004;10(19):2890-2893. [54] KESHAVARZ Z, ZAREEI N, AFSHARI A, et al. TLR2 and TLR4 mRNA expression levels in liver transplant patients with acute rejection. Immunobiology. 2021;226(4):152107. [55] OETTING WS, GUAN W, SCHLADT DP, et al. Donor polymorphisms of toll-like receptor 4 associated with graft failure in liver transplant recipients. Liver Transpl. 2012;18(12):1399-1405. [56] DE LA FUENTE S, CITORES MJ, LUCENA JL, et al. TLR9-1486C/T polymorphism is associated with hepatocellular carcinoma recurrence after liver transplantation. Biomark Med. 2019;13(12):995-1004. [57] 陈凯,史政荣.肝移植免疫耐受的研究进展[J].重庆医学,2020, 49(2):310-314. [58] MARRA F, TACKE F. Roles for chemokines in liver disease. Gastroenterology. 2014;147(3):577-594.e1. [59] SCHON HT, WEISKIRCHEN R. Immunomodulatory effects of transforming growth factor-β in the liver. Hepatobiliary Surg Nutr. 2014;3(6):386-406. [60] GONG J, CAO D, CHEN Y, et al.Role of programmed death ligand 1 and Kupffer cell in immune regulation after orthotopic liver transplantation in rats. Int Immunopharmacol. 2017;48:8-16. [61] SIMPSON KJ, LUKACS NW, COLLETTI L, et al. Cytokines and the liver. J Hepatol. 1997;27(6):1120-1132. [62] DINARELLO CA. Historical insights into cytokines. Eur J Immunol. 2007;37 Suppl 1(Suppl 1):S34-S45. [63] 张安元,刘一鸣,龚建平.Kupffer细胞与肝脏移植的研究进展[J].世界华人消化杂志,2015,23(12):1917-1923. [64] SAVIER E, LEMASTERS JJ, THURMAN RG. Kupffer cells participate in rejection following liver transplantation in the rat. Transpl Int. 1994;7 Suppl 1:S183-S186. [65] PAHLAVAN PS, FELDMANN RE JR, ZAVOS C, et al. Prometheus’ challenge: molecular, cellular and systemic aspects of liver regeneration. J Surg Res. 2006;134(2):238-251. [66] LIAN ZR, XU YF, WANG XB, et al. Suppression of histone deacetylase 11 promotes expression of IL-10 in Kupffer cells and induces tolerance following orthotopic liver transplantation in rats. J Surg Res. 2012;174(2):359-368. [67] TIAN Y, WANG J, WANG W, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells improve mouse non-heart-beating liver graft survival by inhibiting Kupffer cell apoptosis via TLR4-ERK1/2-Fas/FasL-caspase3 pathway regulation. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2016;7(1):157. [68] 刘涛,李金政.枯否细胞极化状态在肝移植免疫耐受中的作用[J].器官移植,2021,12(6):687-691. [69] YOU Y, ZHANG J, GONG J, et al. Mesenchymal stromal cell-dependent reprogramming of Kupffer cells is mediated by TNF-α and PGE2 and is crucial for liver transplant tolerance. Immunol Res. 2015;62(3):292-305. [70] ZHAO Z, PAN G, TANG C, et al. IL-34 Inhibits acute rejection of rat liver transplantation by inducing Kupffer cell M2 polarization. Transplantation. 2018;102(6):e265-e274. [71] HU Y, YANG C, SHEN G, et al. Hyperglycemia-triggered sphingosine-1-phosphate and sphingosine-1-phosphate receptor 3 signaling worsens liver ischemia/reperfusion injury by regulating M1/M2 polarization. Liver Transpl. 2019;25(7):1074-1090. [72] DENG M, WANG J, WU H, et al. IL-4 alleviates ischaemia-reperfusion injury by inducing kupffer cells M2 polarization via STAT6-JMJD3 pathway after rat liver transplantation. Biomed Res Int. 2020;2020: 2953068. [73] ZHANG W, CAO D, WANG M, et al. XBP1s repression regulates Kupffer cell polarization leading to immune suppressive effects protecting liver allograft in rats. Int Immunopharmacol. 2021;91:107294. |
| [1] | 杨芷姗, 唐正龙. Hippo信号通路中的核心因子YAP/TAZ参与骨形成的作用与机制[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2023, 27(8): 1264-1271. |
| [2] | 高 煜, 韩佳慧, 葛 新. 脊髓缺血再灌注损伤后的免疫炎性微环境[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2023, 27(8): 1300-1305. |
| [3] | 杨怡天, 王 璐, 姚 蔚, 赵 彬. 生物支架与巨噬细胞在骨再生中的相互影响及应用[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2023, 27(7): 1071-1079. |
| [4] | 李文婕, 游艾佳, 周俊丽 , 方素娟, 李 春. 不同种类敷料治疗烧伤疗效的网状Meta分析[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2023, 27(7): 1141-1148. |
| [5] | 刘文涛, 冯兴超, 杨 毅, 白生宾. M2型巨噬细胞外泌体诱导骨髓间充质干细胞的成骨分化[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2023, 27(6): 840-845. |
| [6] | 张力宸, 陈 亮, 顾 勇. 无机离子仿生骨膜调控免疫微环境促进骨修复[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2023, 27(3): 346-353. |
| [7] | 田雨一, 刘立宏. 巨噬细胞的骨免疫学效应[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2023, 27(29): 4712-4722. |
| [8] | 邓墨渊, 彭 坤. 巨噬细胞及其特异性调控在生物材料纤维化形成中的作用[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2023, 27(25): 4085-4092. |
| [9] | 张 洁, 田 艾. M2巨噬细胞参与骨再生相关信号通路的作用与机制[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2023, 27(2): 314-321. |
| [10] | 黄贵才, 罗业浩, 江慧容, 李 媛, 毛德文, 官志杰. 干细胞对肝脏疾病的临床治疗前景与研究现状[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2023, 27(19): 3091-3098. |
| [11] | 苑舒月, 刘春艳, 刘 冰, 赵 菲. 巨噬细胞的极化与牙周炎[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2023, 27(17): 2699-2707. |
| [12] | 黄浩然, 卫杨文祥, 章家皓, 莫 亮, 刘予豪, 陈镇秋, 王海彬, 周 驰. Piezo1介导的机械应力刺激在抗骨质疏松中的作用[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2023, 27(17): 2716-2722. |
| [13] | 郑晓晗, 魏艳召, 黄 婷, 魏绪芳, 孙圣童, 王 埮, 赵振强. 巨噬细胞迁移抑制因子对干细胞的作用[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2023, 27(15): 2395-2403. |
| [14] | 徐明奎, 许日明, 林业武, 罗原泰, 张熙辉, 周 理, 袁仕国. 柚皮素调控巨噬细胞极化和肌卫星细胞增殖修复骨骼肌损伤[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2023, 27(14): 2133-2138. |
| [15] | 王钊鑫, 尼加提·吐尔逊, 代慧娟, 王俊祥, 霞黒达·依拉尔江, 李淑慧. 巨噬细胞炎性蛋白1α对人牙周膜干细胞生物学行为的影响[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2023, 27(10): 1521-1527. |
目前虽然已有一些研究者对库普弗细胞进行综述,但是主要局限在对库普弗细胞的不同表型、功能及其作用介绍,而对库普弗细胞在肝移植中的作用研究较少,如何诱导肝移植后免疫耐受的具体机制尚未明晰,关于库普弗细胞在抑制肝移植排斥反应的临床研究及应用的相关文献更少。
该综述在详细介绍库普弗细胞不同功能的基础上,着重对库普弗细胞在肝移植抑制排斥反应、诱导及维持免疫耐受作用机制的研究进展进行总结,为库普弗细胞在肝移植中进一步的研究及临床应用提供理论依据。
1.1.1 检索人及检索时间 第一作者于2021年12月应用计算机进行检索。
1.1.2 检索文献时限 1970年1月至2021年12月。
1.1.3 检索数据库 PubMed和中国知网数据库。
1.1.4 检索词 英文检索词为“Kupffer cells,liver transplantation”,中文检索词为“库普弗细胞、肝移植”。
1.1.5 检索文献类型 综述性论文、研究性论文及著作。
1.1.6 手工检索情况 对文献中高质量的参考文献,先阅读其文题,再以标题进行检索,阅读摘要或全文进行筛选。
1.1.7 检索策略 以中国知网数据库为例,见图1。
1.2 入组标准
1.2.1 纳入标准 通过文章标题及摘要进行初步筛选,通过精读及泛读筛选出与研究相关的文献。
1.2.2 排除标准 研究目的及内容与此综述无关的文献,重复性研究。
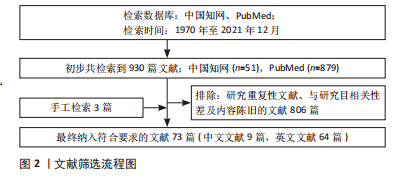
1.3 文献质量评估及数据的提取 在初步检索到的文献930篇文献中,中文文献51篇,英文文献879篇,排除与研究目的相关性差及内容陈旧、重复的文献806篇,纳入73篇符合标准的文献进行综述,见图2。
3.2 该综述区别于他人他篇的特点 目前已有大量文献对库普弗细胞进行综述,但是大部文献局限于库普弗细胞相关表型、功能及作用在不同领域的介绍,对肝移植的研究则以实验类较多,且大多机制尚不明确。而该综述重点则是详细介绍库普弗细胞近年来研究进展的同时,着眼于库普弗细胞在肝移植中抑制排斥反应,诱导及维持免疫耐受的机制研究进展。就库普弗细胞不同功能之间而言,研究广度与深度各异,临床中的应用及研究更少。文章将之列举出并指出问题所在,希望对今后开展深入研究有指引方向的作用。
3.3 综述的局限性 该综述在搜集大量基础实验文献的基础上,也致力于库普弗细胞在临床上的应用,但大多文献基于动物实验而未能开展临床试验加以验证,且具体关于库普弗细胞不同功能所影响免疫耐受建立的机制尚不完善,所得结论是否可以应用于临床尚需大量实验及临床研究证实。还由于文献筛选标准不同,可能存在一些偏倚及误差,同时也包含相对较早的文献,存在缺乏创新性、文献搜集不全面等问题,但仍然能够为库普弗细胞在肝移植中的进一步的研究提供一定的参考思路与方向。
3.4 综述的意义 器官移植后免疫耐受状态一直是医生与患者的最终梦想,不仅能够保证在安全的前提下使移植后患者的移植器官与自身融洽相处,还能够使移植后的患者摆脱终身使用免疫抑制剂的命运。如何抑制免疫排斥,达到免疫耐受目的,同样是研究的希望与努力的方向。而该综述是在一定时间段内对库普弗细胞在肝移植中所发表的高质量文献中提取自己认为有价值的信息,对其最新的研究现状、技术和观点等进行归纳、总结,从库普弗细胞的细胞吞噬、细胞极化、抗原递呈、细胞膜蛋白和细胞因子的不同角度加以论述,研究中可通过更为灵活的文本搜索方式节约大量时间,同时为研究者后续在该领域的科研选题、科研设计和实验实施等提供参考理论依据。此外,随着库普弗细胞及其相关细胞因子在肝移植免疫耐受中的作用逐渐被揭示,深入研究、探讨库普弗细胞的功能不仅有助于了解肝移植后免疫排斥反应的分子机制和发病机制,还助于了解通过调控库普弗细胞功能以达到免疫耐受状态具有重要意义。
3.5 课题专家组的建议 库普弗细胞作为人类体内最大的巨噬细胞群,在免疫调节和组织损伤修复中起重要作用,深入对其进行基础研究有助于发现、确认并利用新的靶点,把基础研究成果进一步应用于临床受益患者也是研究者最终的目的。但目前存在对库普弗细胞的研究大多为基础研究的限制,如何将研究成果转化到临床中仍是需要努力的方向与难题。使用基因检测的方法检测库普弗细胞中的免疫耐受基因,是否能预测肝移植后免疫排斥反应的发生可能在未来实验中得以验证,而相对于抑制T淋巴细胞的免疫抑制药物,通过影响巨噬细胞来抑制免疫排斥反应仍需深入研究,同时也希望此篇文章所总结出的机制可以进行深入研究或临床早期实验加以验证,为新药研制提供方向及帮助。
总之,库普弗细胞的细胞表型、功能、生物学特征及其在肝移植中的作用仍然需要进一步详细研究与探讨,对库普弗细胞功能的深入了解将有助于制定解决肝移植后相关问题的创新性治疗策略。

文题释义:
库普弗细胞:是在肝窦中发现的巨噬细胞,是宿主免疫系统的组成部分,参与各种化合物的代谢。其不但具有吞噬功能,还表达受体组织相容性复合体和共刺激分子以提呈抗原和特异性的免疫应答,在免疫调节和组织损伤修复中起主要作用。免疫耐受:指机体免疫系统接受供体抗原后产生的特异性的免疫无应答状态。耐受性通常分为完全免疫耐受性、操作耐受性和支撑耐受性,肝移植后免疫耐受主要是操作耐受性。#br#
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:干细胞;骨髓干细胞;造血干细胞;脂肪干细胞;肿瘤干细胞;胚胎干细胞;脐带脐血干细胞;干细胞诱导;干细胞分化;组织工程
目前虽然已有一些研究者对库普弗细胞进行综述,但是主要局限在对库普弗细胞的不同表型、功能及其作用介绍,而对库普弗细胞在肝移植中的作用研究较少,如何诱导肝移植后免疫耐受的具体机制尚未明晰,关于库普弗细胞在抑制肝移植排斥反应的临床研究及应用的相关文献更少。而该综述在详细介绍库普弗细胞不同功能的基础上,着重对库普弗细胞在肝移植抑制排斥反应、诱导及维持免疫耐受作用机制的研究进展,为库普弗细胞在肝移植中进一步的研究及临床应用提供理论依据。
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:干细胞;骨髓干细胞;造血干细胞;脂肪干细胞;肿瘤干细胞;胚胎干细胞;脐带脐血干细胞;干细胞诱导;干细胞分化;组织工程
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||