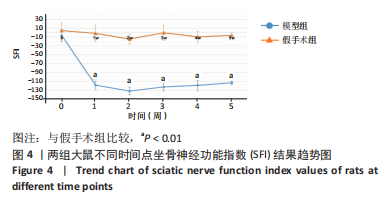
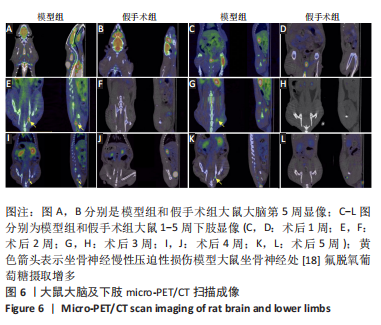
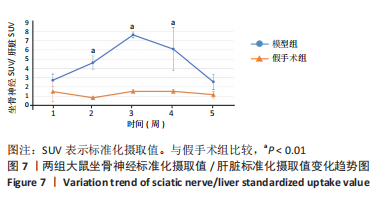
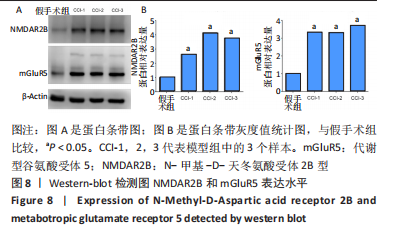
[1] MORI N, HOSOMI K, NISHI A, et al. Analgesic Effects of Repetitive Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation at Different Stimulus Parameters for Neuropathic Pain: A Randomized Study. Neuromodulation. 2022;25(4):520-527.
[2] ZHANG W, SUO M, YU G, et al. Antinociceptive and anti-inflammatory effects of cryptotanshinone through PI3K/Akt signaling pathway in a rat model of neuropathic pain. Chem Biol Interact. 2019;305:127-133.
[3] SAMPSON SM, KUNG S, MCALPINE DE, et al. The use of slow-frequency prefrontal repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation in refractory neuropathic pain. J ect. 2011;27(1):33-37.
[4] 郭铁成, 许惊飞. 低频和高频重复经颅磁刺激对大鼠神经病理性疼痛及背根神经节内nNOS的影响[J]. 中华物理医学与康复杂志,2014,36(11): 823-8273.
[5] BOUHASSIRA D. Neuropathic pain: Definition, assessment and epidemiology. Rev Neurol (Paris). 2019;175(1-2):16-25.
[6] HSU JH, DASKALAKIS ZJ, BLUMBERGER DM. An Update on Repetitive Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation for the Treatment of Co-morbid Pain and Depressive Symptoms. Curr Pain Headache Rep. 2018;22(7):51.
[7] LI J X. Pain and depression comorbidity: a preclinical perspective. Behav Brain Res. 2015;276:92-98.
[8] HUMO M, LU H, YALCIN I. The molecular neurobiology of chronic pain-induced depression. Cell Tissue Res. 2019;377(1):21-43.
[9] SEMINOWICZ DA, DE MARTINO E, SCHABRUN SM, et al. Left dorsolateral prefrontal cortex repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation reduces the development of long-term muscle pain. Pain. 2018;159(12):2486-2492.
[10] SEMINOWICZ D A, MOAYEDI M. The Dorsolateral Prefrontal Cortex in Acute and Chronic Pain. J Pain. 2017;18(9):1027-1035.
[11] LAUBACH M, AMARANTE L M, SWANSON K, et al. What, If Anything, Is Rodent Prefrontal Cortex? eNeuro. 2018;5(5):ENEURO.0315-18.2018.
[12] 祝建平. 束缚-浸水应激大鼠内侧前额叶皮质对胃机能的调控作用及机制的研究[D].济南:山东师范大学,2015.
[13] OBARA I, GOULDING SP, HU JH, et al. Nerve injury-induced changes in Homer/glutamate receptor signaling contribute to the development and maintenance of neuropathic pain. Pain. 2013;154(10):1932-1945.
[14] LARSSON M, BROMAN J. Synaptic plasticity and pain: role of ionotropic glutamate receptors. Neuroscientist. 2011;17(3):256-273.
[15] PEREIRA V, GOUDET C. Emerging Trends in Pain Modulation by Metabotropic Glutamate Receptors. Front Mol Neurosci. 2018;11:464.
[16] GONG K, KUNG L H, MAGNI G, et al. Increased response to glutamate in small diameter dorsal root ganglion neurons after sciatic nerve injury. PLoS One. 2014;9(4):e95491.
[17] GIORDANO C, CRISTINO L, LUONGO L, et al. TRPV1-dependent and -independent alterations in the limbic cortex of neuropathic mice: impact on glial caspases and pain perception. Cereb Cortex. 2012;22(11): 2495-2518.
[18] INQUIMBERT P, BARTELS K, BABANIYI OB, et al. Peripheral nerve injury produces a sustained shift in the balance between glutamate release and uptake in the dorsal horn of the spinal cord. Pain. 2012;153(12):2422-2431.
[19] XIE JD, CHEN SR, PAN HL. Presynaptic mGluR5 receptor controls glutamatergic input through protein kinase C-NMDA receptors in paclitaxel-induced neuropathic pain. J Biol Chem. 2017;292(50):20644-20654.
[20] FONSECA-RODRIGUES D, AMORIM D, ALMEIDA A, et al. Emotional and cognitive impairments in the peripheral nerve chronic constriction injury model (CCI) of neuropathic pain: A systematic review. Behav Brain Res. 2021;399:113008.
[21] AUSTIN PJ, WU A, MOALEM-TAYLOR G. Chronic constriction of the sciatic nerve and pain hypersensitivity testing in rats. J Vis Exp. 2012;(61):3393.
[22] MEDEIROS P, DOS SANTOS IR, JÚNIOR IM, et al. An Adapted Chronic Constriction Injury of the Sciatic Nerve Produces Sensory, Affective, and Cognitive Impairments: A Peripheral Mononeuropathy Model for the Study of Comorbid Neuropsychiatric Disorders Associated with Neuropathic Pain in Rats. Pain Med. 2021;22(2):338-351.
[23] IÑIGUEZ SD, FLORES-RAMIREZ FJ, RIGGS LM, et al. Vicarious Social Defeat Stress Induces Depression-Related Outcomes in Female Mice. Biol Psychiatry. 2018; 83(1):9-17.
[24] LIU M Y, YIN C Y, ZHU LJ, et al. Sucrose preference test for measurement of stress-induced anhedonia in mice. Nat Protoc. 2018;13(7):1686-1698.
[25] MORENO-SANTOS B, MARCHI-COELHO C, COSTA-FERREIRA W, et al. Angiotensinergic receptors in the medial amygdaloid nucleus differently modulate behavioral responses in the elevated plus-maze and forced swimming test in rats. Behav Brain Res. 2021;397:112947.
[26] CUI M, LIANG J, XU D, et al. NLRP3 inflammasome is involved in nerve recovery after sciatic nerve injury. Int Immunopharmacol. 2020;84:106492.
[27] TSUANG FY, CHEN MH, LIN FH, et al. Partial enzyme digestion facilitates regeneration of crushed nerve in rat. Transl Neurosci. 2020;11(1):251-263.
[28] KREMER M, BECKER LJ, BARROT M, et al. How to study anxiety and depression in rodent models of chronic pain?. Eur J Neurosci. 2021;53(1): 236-270.
[29] LI Q, YUE N, LIU SB, et al. Effects of chronic electroacupuncture on depression- and anxiety-like behaviors in rats with chronic neuropathic pain. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2014;2014:158987.
[30] LI Y, CHEN C, LI S, et al. Ginsenoside Rf relieves mechanical hypersensitivity, depression-like behavior, and inflammatory reactions in chronic constriction injury rats. Phytother Res. 2019;33(4):1095-1103.
[31] FUKUHARA K, ISHIKAWA K, YASUDA S, et al. Intracerebroventricular 4-methylcatechol (4-MC) ameliorates chronic pain associated with depression-like behavior via induction of brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF). Cell Mol Neurobiol. 2012;32(6):971-977.
[32] GARG S, DESHMUKH VR, PRASOON P. Possible modulation of PPAR-γ cascade against depression caused by neuropathic pain in rats. J Basic Clin Physiol Pharmacol. 2017;28(6):593-600.
[33] WANG C, CHEN P, LIN D, et al. Effects of varying degrees of ligation in a neuropathic pain model induced by chronic constriction injury. Life Sci. 2021;276:119441.
[34] CHERIF F, ZOUARI HG, CHERIF W, et al. Depression Prevalence in Neuropathic Pain and Its Impact on the Quality of Life. Pain Res Manag. 2020;2020:7408508.
[35] LEUNG A, METZGER-SMITH V, HE Y, et al. Left Dorsolateral Prefrontal Cortex rTMS in Alleviating MTBI Related Headaches and Depressive Symptoms. Neuromodulation. 2018;21(4):390-401.
[36] BRIGHINA F, DE TOMMASO M, GIGLIA F, et al. Modulation of pain perception by transcranial magnetic stimulation of left prefrontal cortex. J Headache Pain. 2011;12(2):185-191.
[37] DE MARTINO E, SEMINOWICZ DA, SCHABRUN SM, et al. High frequency repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation to the left dorsolateral prefrontal cortex modulates sensorimotor cortex function in the transition to sustained muscle pain. Neuroimage. 2019;186:93-102.
[38] ZHU CZ, WILSON SG, MIKUSA JP, et al. Assessing the role of metabotropic glutamate receptor 5 in multiple nociceptive modalities. Eur J Pharmacol. 2004;506(2):107-118.
[39] CHUNG G, KIM SJ, KIM SK. Metabotropic Glutamate Receptor 5 in the Medial Prefrontal Cortex as a Molecular Determinant of Pain and Ensuing Depression. Front Mol Neurosci. 2018;11:376.
[40] CHUNG G, KIM CY, YUN YC, et al. Upregulation of prefrontal metabotropic glutamate receptor 5 mediates neuropathic pain and negative mood symptoms after spinal nerve injury in rats. Sci Rep. 2017;7(1):9743.
[41] 车银伟, 蔡国洪, 王鑫,等. 神经病理性痛条件下前额叶皮质内代谢型谷氨酸受体第5亚型的表达及分布变化[J]. 神经解剖学杂志,2016, 32(3):301-306.
[42] 王云霞, 付淼, 罗芳. 脉冲射频对坐骨神经慢性压迫模型大鼠的痛觉过敏及脊髓背角NR2B亚基表达的作用[J]. 中国康复理论与实践,2016, 22(9):1020-1023.
[43] WANG XY, ZHOU HR, WANG S, et al. NR2B-Tyr phosphorylation regulates synaptic plasticity in central sensitization in a chronic migraine rat model. J Headache Pain. 2018;19(1):102.
[44] NIU Y, ZENG X, ZHAO L, et al. Metabotropic glutamate receptor 5 regulates synaptic plasticity in a chronic migraine rat model through the PKC/NR2B signal. J Headache Pain. 2020;21(1):139.
[45] 黄敏, 许涛, 江伟. 代谢型谷氨酸受体5与N-甲基-D-天冬氨酸受体的关系及其在疾病中的作用[J]. 上海交通大学学报(医学版),2018,38(7): 825-828.
[46] HOOKER JM, CARSON RE. Human Positron Emission Tomography Neuroimaging. Annu Rev Biomed Eng. 2019;21:551-581.
[47] KIM C E, KIM Y K, CHUNG G, et al. Large-scale plastic changes of the brain network in an animal model of neuropathic pain. Neuroimage. 2014; 98:203-215.
[48] BEHERA D, JACOBS KE, BEHERA S, et al. (18)F-FDG PET/MRI can be used to identify injured peripheral nerves in a model of neuropathic pain. J Nucl Med. 2011;52(8):1308-1312.
[49] LEE S H, SEO HG, OH BM, et al. (18)F-FDG positron emission tomography as a novel diagnostic tool for peripheral nerve injury. J Neurosci Methods. 2019;317:11-19. |