中国组织工程研究 ›› 2023, Vol. 27 ›› Issue (26): 4175-4180.doi: 10.12307/2023.407
• 骨组织构建 bone tissue construction • 上一篇 下一篇
miR-23b对风湿关节炎大鼠滑膜组织转化生长因子β1及破骨细胞的影响
宋建辉,穆继宏,黎士文
- 南部战区海军第二医院,海南省三亚市 572000
miR-23b effects on transforming growth factor beta1 and osteoclast activity in synovial tissue of rats with rheumatoid arthritis
Song Jianhui, Mu Jihong, Li Shiwen
- The Second Naval Hospital of Southern Theater Command, Sanya 572000, Hainan Province, China
摘要:
文题释义:
miR-23b:作为一种非编码miRNA,是一种可在不同器官发挥多效性调节功能的miRNA,其可通过与下游靶基因结合来调节信号转导通路,影响细胞炎性因子的分泌及细胞的增殖、分化等生命进程,同时在免疫炎症反应中扮演着重要角色。转化生长因子β1(transforming growth factor-β1,TGF-β1):属于一组新近发现的调节细胞生长和分化的TGF-β超家族,其在炎症、组织修复和胚胎发育等方面发挥重要作用,同时近年来发现其对细胞的生长、分化和免疫功能都有重要的调节作用。
背景:研究表明,miR-23b水平升高与风湿关节炎的发生发展密切相关,故抑制miR-23b的表达可作为治疗该病的一个新靶点。
目的:探究miR-23b对风湿关节炎大鼠滑膜组织转化生长因子β1调节及对破骨细胞活性的抑制作用。
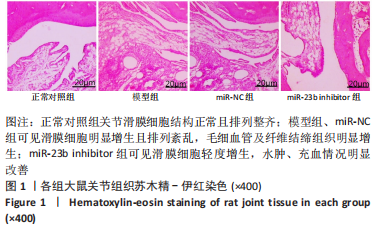
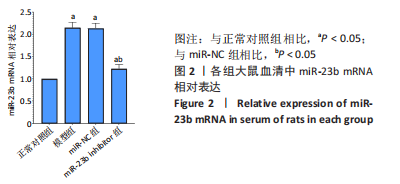
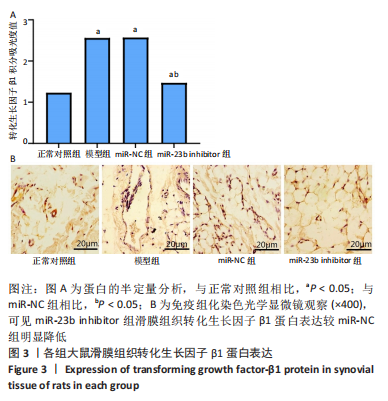
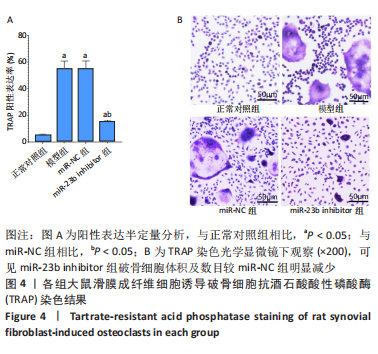
方法:选取60只SPF级SD雄性大鼠,随机分为正常对照组、模型组、miR-NC组、miR-23b inhibitor组。除正常对照组外,其他3组大鼠采用弗氏完全佐剂法进行风湿关节炎建模,建模成功后,对miR-NC组尾静脉注射20 μL 1×108 L-1的miR-NC,miR-23b inhibitor组尾静脉注射20 μL 1×108 L-1的miR-23b inhibitor,正常对照组、模型组同期尾静脉注射同体积生理盐水。21 d后,苏木精-伊红染色法检测大鼠关节组织病理形态;Real-time PCR 法检测大鼠血清中miR-23b的mRNA相对表达;免疫组化法检测大鼠滑膜组织中转化生长因子β1蛋白表达;抗酒石酸酸性磷酸酶染色法及鬼笔环肽染色法检测破骨细胞活性。
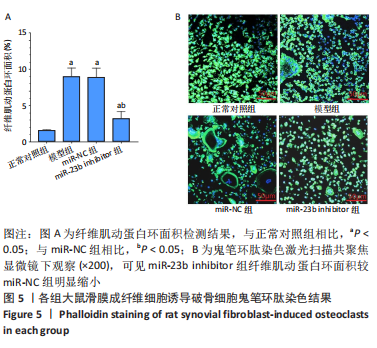
结果与结论:①正常对照组大鼠关节滑膜细胞结构正常且排列整齐,模型组、miR-NC组出现明显滑膜细胞增生且排列紊乱,同时可见毛细血管及纤维结缔组织明显增生,且出现大量炎性细胞浸润现象,miR-23b inhibitor组可见滑膜细胞轻度增生及少量炎性细胞浸润,水肿、充血情况明显改善;②与正常对照组比较,模型组大鼠血清中miR-23b 相对表达明显升高(P < 0.05),模型组与miR-NC组相比无明显差异(P > 0.05),miR-23b inhibitor组血清中miR-23b 相对表达较miR-NC组明显降低(P < 0.05);③与正常对照组比较,模型组大鼠滑膜组织转化生长因子β1蛋白表达显著升高(P < 0.05),模型组与miR-NC组相比无明显差异(P > 0.05),miR-23b inhibitor组滑膜组织转化生长因子β1蛋白表达较miR-NC组明显降低(P < 0.05);④与正常对照组比较,模型组大鼠滑膜成纤维细胞抗酒石酸酸性磷酸酶染色可见大量阳性表达的典型多核破骨细胞(P < 0.05),模型组与miR-NC组相比无明显差异(P > 0.05),miR-23b inhibitor组破骨细胞体积及数目较miR-NC组明显减少(P < 0.05);⑤与正常对照组比较,模型组大鼠破骨细胞鬼笔环肽染色可见明显纤维肌动蛋白环形成(P < 0.05),模型组与miR-NC组相比无明显差异(P > 0.05),miR-23b inhibitor组纤维肌动蛋白环面积较miR-NC组明显缩小(P < 0.05);⑥上述结果说明,降低miR-23b表达可对风湿关节炎起到治疗作用,其可有效抑制大鼠滑膜组织转化生长因子β1表达,降低破骨细胞活性。
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-2358-1165(宋建辉)
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:组织构建;骨细胞;软骨细胞;细胞培养;成纤维细胞;血管内皮细胞;骨质疏松;组织工程
中图分类号: