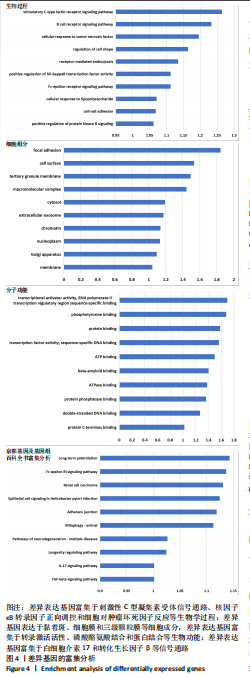
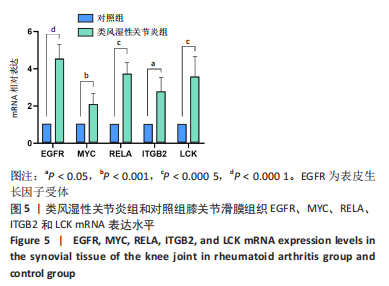
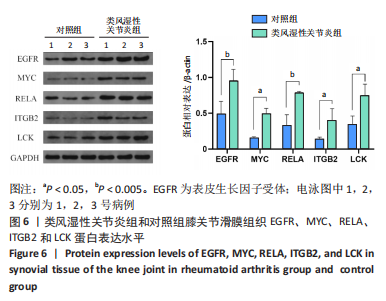
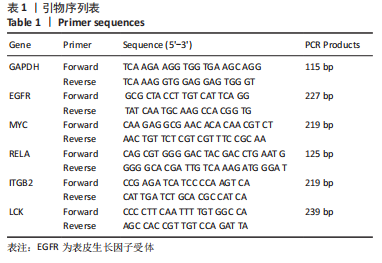
[1] TATEIWA D, YOSHIKAWA H, KAITO T. Cartilage and Bone Destruction in Arthritis: Pathogenesis and Treatment Strategy: A Literature Review. Cells. 2019;8(8):818.
[2] WANG T, HE C. TNF-alpha and IL-6: The Link between Immune and Bone System. Curr Drug Targets. 2020;21(3):213-227.
[3] 闫慧明, 于江锐, 张雪, 等. 凋亡抑制蛋白在类风湿关节炎发病机制中的研究进展[J]. 风湿病与关节炎,2021,10(5):69-72.
[4] 伍沙沙, 王延, 徐婷, 等. 成纤维样滑膜细胞在类风湿关节炎发病机制中的作用[J]. 风湿病与关节炎,2022,11(2):43-47.
[5] NOZAKI Y, RI J, SAKAI K, et al. Inhibition of the IL-18 Receptor Signaling Pathway Ameliorates Disease in a Murine Model of Rheumatoid Arthritis. Cells. 2020;9(1):11.
[6] TAKEUCHI Y, HIROTA K, SAKAGUCHI S. Impaired T cell receptor signaling and development of T cell–mediated autoimmune arthritis. Immunological Reviews. 2020;294(1):164-176.
[7] DEVAIAH BN, MU J, AKMAN B, et al. MYC protein stability is negatively regulated by BRD4. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2020;117(24): 13457-13467.
[8] LEE YZ, GUO HC, ZHAO GH, et al. Tylophorine-based compounds are therapeutic in rheumatoid arthritis by targeting the caprin-1 ribonucleoprotein complex and inhibiting expression of associated c-Myc and HIF-1alpha. Pharmacol Res. 2020;152:104581.
[9] SUN W, QIN R, WANG R, et al. Correction to: Sam68 Promotes Invasion, Migration, and Proliferation of Fibroblast-like Synoviocytes by Enhancing the NF-kappaB/P65 Pathway in Rheumatoid Arthritis. Inflammation. 2019;42(2):763.
[10] ELEMAM NM, HACHIM MY, HANNAWI S, et al. Differentially Expressed Genes of Natural Killer Cells Can Distinguish Rheumatoid Arthritis Patients from Healthy Controls. Genes (Basel). 2020;11(5):492.
[11] ZHANG X, DONG Y, ZHAO M, et al. ITGB2-mediated metabolic switch in CAFs promotes OSCC proliferation by oxidation of NADH in mitochondrial oxidative phosphorylation system. Theranostics. 2020;10(26):12044-12059.
[12] DMITRZAK-WEGLARZ M, SZCZEPANKIEWICZ A, RYBAKOWSKI J,
et al. Transcriptomic profiling as biological markers of depression - A pilot study in unipolar and bipolar women. World J Biol Psychiatry. 2021;22(10):744-756.
[13] KUMAR SP, KASHYAP A, SILAKARI O. Exploration of the therapeutic aspects of Lck: A kinase target in inflammatory mediated pathological conditions. Biomed Pharmacother. 2018;108:1565-1571.
[14] LI Z, XU M, LI R, et al. Identification of biomarkers associated with synovitis in rheumatoid arthritis by bioinformatics analyses. Biosci Rep. 2020;40(9):BSR20201713.
[15] YIN J, LI Z, YE L, et al. EphB2 represents an independent prognostic marker in patients with gastric cancer and promotes tumour cell aggressiveness. J Cancer. 2020;11(10):2778-2787.
[16] RODRIGUEZ-CARRIO J, LOPEZ P, ALPERI-LOPEZ M, et al. IRF4 and IRGs Delineate Clinically Relevant Gene Expression Signatures in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus and Rheumatoid Arthritis. Front Immunol. 2018; 9:3085.
[17] ALVISI G, BRUMMELMAN J, PUCCIO S, et al. IRF4 instructs effector Treg differentiation and immune suppression in human cancer. J Clin Invest. 2020;130(6):3137-3150.
[18] VALENCIA-SAMA I, LADUMOR Y, KEE L, et al. NRAS Status Determines Sensitivity to SHP2 Inhibitor Combination Therapies Targeting the RAS-MAPK Pathway in Neuroblastoma. Cancer Res. 2020;80(16):3413-3423.
[19] ZAYOUD M, MARCU-MALINA V, VAX E, et al. Ras Signaling Inhibitors Attenuate Disease in Adjuvant-Induced Arthritis via Targeting Pathogenic Antigen-Specific Th17-Type Cells. Front Immunol. 2017;8: 799.
[20] LIU X, MENG L, LI X, et al. Regulation of FN1 degradation by the p62/SQSTM1-dependent autophagy-lysosome pathway in HNSCC. Int J Oral Sci. 2020;12(1):34.
[21] WANG X, LIU B, WEN F, et al. MicroRNA-454 inhibits the malignant biological behaviours of gastric cancer cells by directly targeting mitogen-activated protein kinase 1. Oncol Rep. 2018;39(3):1494-1504.
[22] LUO M, LIANG C. LncRNA LINC00483 promotes gastric cancer development through regulating MAPK1 expression by sponging miR-490-3p. Biol Res. 2020;53(1):14.
[23] DENG R, ZHANG HL, HUANG JH, et al. MAPK1/3 kinase-dependent ULK1 degradation attenuates mitophagy and promotes breast cancer bone metastasis. Autophagy. 2021;17(10):3011-3029.
[24] BRAZ N, PINTO M, VIEIRA E, et al. Renin-angiotensin system molecules are associated with subclinical atherosclerosis and disease activity in rheumatoid arthritis. Mod Rheumatol. 2021;31(1):119-126.
[25] SHI W, ZHENG Y, LUO S, et al. METTL3 Promotes Activation and Inflammation of FLSs Through the NF-kappaB Signaling Pathway in Rheumatoid Arthritis. Front Med (Lausanne). 2021;8:607585.
[26] CHOE JY, HUN KJ, PARK KY, et al. Activation of dickkopf-1 and focal adhesion kinase pathway by tumour necrosis factor alpha induces enhanced migration of fibroblast-like synoviocytes in rheumatoid arthritis. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2016;55(5):928-938.
[27] LEGERSTEE K, HOUTSMULLER AB. A Layered View on Focal Adhesions. Biology (Basel). 2021;10(11):1189.
[28] TAAMS LS. Interleukin-17 in rheumatoid arthritis: Trials and tribulations. J Exp Med. 2020;217(3):e20192048.
[29] MCGEACHY MJ, CUA DJ, GAFFEN SL. The IL-17 Family of Cytokines in Health and Disease. Immunity. 2019;50(4):892-906.
[30] STEEL KJA, SRENATHAN U, RIDLEY M, et al. Polyfunctional, Proinflammatory, Tissue‐Resident Memory Phenotype and Function of Synovial Interleukin‐17A+CD 8+ T Cells in Psoriatic Arthritis. Arthritis & Rheumatology. 2020;72(3):435-447.
[31] WANG S, WANG S, LI H, et al. Inhibition of the TGF-beta/Smads signaling pathway attenuates pulmonary fibrosis and induces anti-proliferative effect on synovial fibroblasts in rheumatoid arthritis. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2019;12(5):1835-1845.
[32] PROUX-GILLARDEAUX V, ADVEDISSIAN T, PERIN C, et al. Identification of a new regulation pathway of EGFR and E-cadherin dynamics. Sci Rep. 2021;11(1):22705.
[33] SABBAH DA, HAJJO R, SWEIDAN K. Review on Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor (EGFR) Structure, Signaling Pathways, Interactions, and Recent Updates of EGFR Inhibitors. Curr Top Med Chem. 2020;20(10): 815-834.
[34] MANSOUR HM, FAWZY HM, EL-KHATIB AS, et al. Lapatinib ditosylate rescues memory impairment in D-galactose/ovariectomized rats: Potential repositioning of an anti-cancer drug for the treatment of Alzheimer’s disease. Exp Neurol. 2021;341:113697.
[35] KARGBO RB. Treatment of Cancer and Alzheimer’s Disease by PROTAC Degradation of EGFR. ACS Med Chem Lett. 2019;10(8):1098-1099.
[36] HU J, ZHANG H, CAO M, et al. Auranofin Enhances Ibrutinib’s Anticancer Activity in EGFR-Mutant Lung Adenocarcinoma. Mol Cancer Ther. 2018;17(10):2156-2163.
[37] 王康, 智晓东, 张玉强, 等. 人羊膜上皮细胞激活EGFR/ERK1信号轴调节关节软骨细胞增殖、凋亡和细胞外基质的合成[J]. 中国组织工程研究,2022,26(31):4967-4974.
[38] 曾文波, 兰生辉, 蔡贤华, 等. EGFR信号通路在骨性关节炎研究中进展[J]. 中华老年骨科与康复电子杂志,2019,5(2):109-113.
[39] HUANG CM, CHEN HH, CHEN DC, et al. Rheumatoid arthritis is associated with rs17337023 polymorphism and increased serum level of the EGFR protein. PLoS One. 2017;12(7):e180604.
[40] NIU J, LI C, JIN Y, et al. Identification and suppression of epidermal growth factor receptor variant III signaling in fibroblast-like synoviocytes from aggressive rheumatoid arthritis by the mimotope. Immunol Lett. 2018;198:74-80.
|