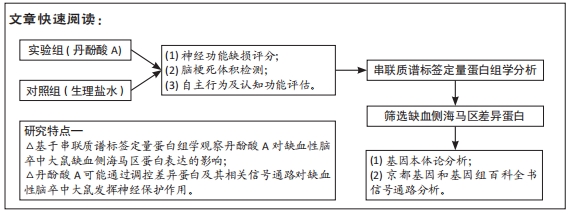
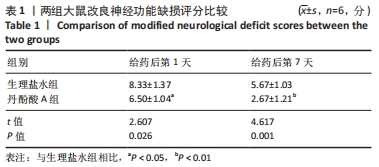
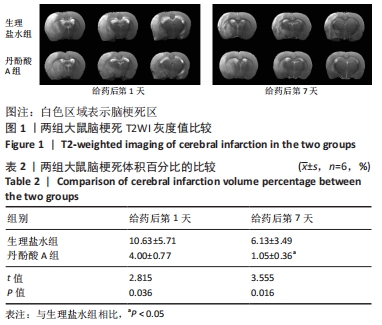
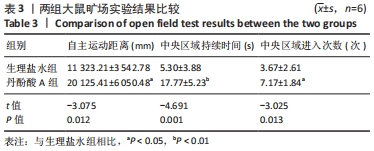
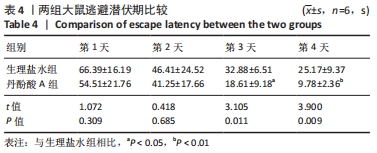
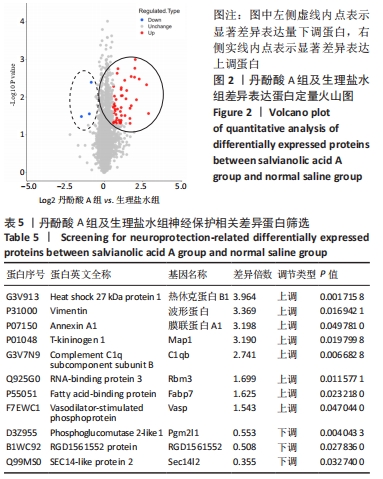
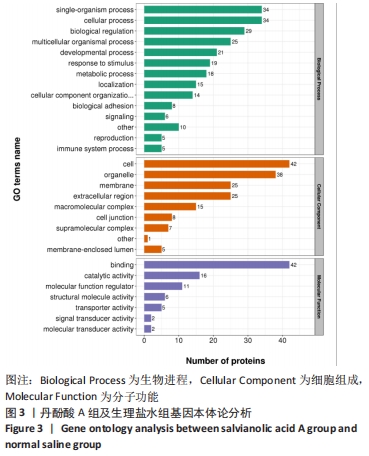
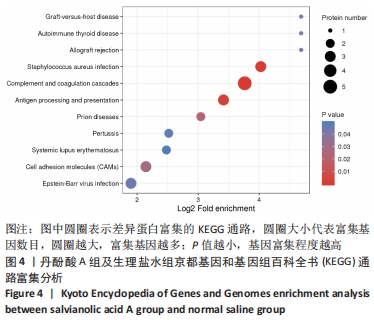
[1] CAMPBELL BCV, DE SILVA DA, MACLEOD MR, et al. Ischaemic stroke. Nat Rev Dis Primers. 2019;5(1):70.
[2] Qin T, Rasul A, Sarfraz A, et al. Salvianolic acid A & B: potential cytotoxic polyphenols in battle against cancer via targeting multiple signaling pathways. Int J Biol Sci. 2019;15(10):2256-2264.
[3] Wu Y, Xu S, Tian XY. The Effect of Salvianolic Acid on Vascular Protection and Possible Mechanisms. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2020:5472096.
[4] Kuriakose D, Xiao Z. Pathophysiology and Treatment of Stroke: Present Status and Future Perspectives. Int J Mol Sci. 2020;21(20):7609.
[5] Zhang W, Song JK, Zhang X, et al. Salvianolic acid A attenuates ischemia reperfusion induced rat brain damage by protecting the blood brain barrier through MMP-9 inhibition and anti-inflammation. Chin J Nat Med. 2018;16(3):184-193.
[6] Jiao CX, Zhou H, Yang CX, et al. Protective efficacy of a single salvianolic acid A treatment on photothrombosis-induced sustained spatial memory impairments. Neuropsychiatr Dis Treat. 2017;13:1181-1192.
[7] Zhang F, Wu Y, Jia J, et al. Pre-ischemic treadmill training induces tolerance to brain ischemia: involvement of glutamate and ERK1/2. Molecules. 2010;15(8):5246-5257.
[8] Chen J, Li Y, Wang L, et al. Therapeutic benefit of intravenous administration of bone marrow stromal cells after cerebral ischemia in rats. Stroke. 2001;32(4):1005-1011.
[9] Caliskan H, Akat F, Tatar Y, et al. Effects of exercise training on anxiety in diabetic rats. Behav Brain Res. 2019;376:112084.
[10] Yu L, Duan Y, Zhao Z, et al. Hydroxysafflor Yellow A (HSYA) Improves Learning and Memory in Cerebral Ischemia Reperfusion-Injured Rats via Recovering Synaptic Plasticity in the Hippocampus. Front Cell Neurosci. 2018;12:371.
[11] Elgendy IY, Mahmoud AN, Mansoor H, et al. Evolution of acute ischemic stroke therapy from lysis to thrombectomy: Similar or different to acute myocardial infarction? Int J Cardiol. 2016;222: 441-447.
[12] Yu KH, Cho SJ, Oh MS, et al. Cognitive impairment evaluated with Vascular Cognitive Impairment Harmonization Standards in a multicenter prospective stroke cohort in Korea. Stroke. 2013;44(3): 786-788.
[13] XU AH, SUN YX. Research hotspots and effectiveness of repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation in stroke rehabilitation. Neural Regen Res. 2020;15(11):2089-2097.
[14] Levine DA, Galecki AT, Langa KM, et al. Trajectory of Cognitive Decline After Incident Stroke. JAMA. 2015;314(1):41-51.
[15] Guo X, Yuan J, Wang J, et al. Calcitriol alleviates global cerebral ischemia-induced cognitive impairment by reducing apoptosis regulated by VDR/ERK signaling pathway in rat hippocampus. Brain Res. 2019;1724:146430.
[16] Lin R, Yu K, Li X, et al. Electroacupuncture ameliorates post-stroke learning and memory through minimizing ultrastructural brain damage and inhibiting the expression of MMP-2 and MMP-9 in cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injured rats. Mol Med Rep. 2016;14(1):225-233.
[17] Zhang X, Shen X, Dong J, et al. Inhibition of Reactive Astrocytes with Fluorocitrate Ameliorates Learning and Memory Impairment Through Upregulating CRTC1 and Synaptophysin in Ischemic Stroke Rats. Cell Mol Neurobiol. 2019;39(8):1151-1163.
[18] WANG WJ, ZHONG YB, ZHAO JJ, et al. Transcranial pulse current stimulation improves the locomotor function in a rat model of stroke. Neural Regen Res. 2021;16(7):1229-1234.
[19] Li ZM, Xu SW, Liu PQ. Salvia miltiorrhizaBurge (Danshen): a golden herbal medicine in cardiovascular therapeutics. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2018;39(5):802-824.
[20] Wang SB, Pang XB, Zhao Y, et al. Protection of salvianolic acid A on rat brain from ischemic damage via soluble epoxide hydrolase inhibition. J Asian Nat Prod Res. 2012;14(11):1084-1092.
[21] Chien MY, Chuang CH, Chern CM, et al. Salvianolic acid A alleviates ischemic brain injury through the inhibition of inflammation and apoptosis and the promotion of neurogenesis in mice. Free Radic Biol Med. 2016;99:508-519.
[22] Singh MK, Sharma B, Tiwari PK. The small heat shock protein Hsp27: Present understanding and future prospects. J Therm Biol. 2017;69:149-154.
[23] Behdarvandy M, Karimian M, Atlasi MA, et al. Heat shock protein 27 as a neuroprotective biomarker and a suitable target for stem cell therapy and pharmacotherapy in ischemic stroke. Cell Biol Int. 2020;44(2):356-367.
[24] Teramoto S, Shimura H, Tanaka R, et al. Human-derived physiological heat shock protein 27 complex protects brain after focal cerebral ischemia in mice. PLoS One. 2013;8(6):e66001.
[25] Tóth ME, Szegedi V, Varga E, et al. Overexpression of Hsp27 ameliorates symptoms of Alzheimer’s disease in APP/PS1 mice. Cell Stress Chaperones. 2013;18(6):759-771.
[26] Potokar M, Morita M, Wiche G, et al. The Diversity of Intermediate Filaments in Astrocytes. Cells. 2020;9(7):1604.
[27] Moon C, Ahn M, Kim S, et al. Temporal patterns of the embryonic intermediate filaments nestin and vimentin expression in the cerebral cortex of adult rats after cryoinjury. Brain Res. 2004;1028(2):238-242.
[28] Tao J, Zheng Y, Liu W, et al. Electro-acupuncture at LI11 and ST36 acupoints exerts neuroprotective effects via reactive astrocyte proliferation after ischemia and reperfusion injury in rats. Brain Res Bull. 2016;120:14-24.
[29] Wilhelmsson U, Pozo-Rodrigalvarez A, Kalm M, et al. The role of GFAP and vimentin in learning and memory. Biol Chem. 2019; 400(9):1147-1156.
30] Liu JH, Feng D, Zhang YF, et al. Chloral Hydrate Preconditioning Protects Against Ischemic Stroke via Upregulating Annexin A1. CNS Neurosci Ther. 2015;21(9):718-726.
[31] Ries M, Watts H, Mota BC, et al. Annexin A1 restores cerebrovascular integrity concomitant with reduced amyloid-β and tau pathology. Brain. 2021;144(5):1526-1541.
[32] Foley JH. Examining coagulation-complement crosstalk: complement activation and thrombosis. Thromb Res. 2016;141 Suppl 2:S50-S54.
[33] Wang Y, Guo W, Xie S, et al. Multi-omics analysis of brain tissue metabolome and proteome reveals the protective effect of gross saponins of Tribulus terrestris L. fruit against ischemic stroke in rat. J Ethnopharmacol. 2021;278:114280.
[34] Niu B, Zhang H, Li C, et al. Network pharmacology study on the active components of Pterocypsela elata and the mechanism of their effect against cerebral ischemia. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2019;13: 3009-3019.
[35] LIU CD, LIU NN, ZHANG S, et al. Salvianolic acid A prevented cerebrovascular endothelial injury caused by acute ischemic stroke through inhibiting the Src signaling pathway. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2021;42(3):370-381.
[36] LING Y, JIN L, MA Q, et al. Salvianolic acid A alleviated inflammatory response mediated by microglia through inhibiting the activation of TLR2/4 in acute cerebral ischemia-reperfusion. Phytomedicine. 2021;87:153569.
[37] JIANG M, WANG XY, ZHOU WY, et al. Cerebral protection of salvianolic acid A by the inhibition of granulocyte adherence. Am J Chin Med. 2011;39(1):111-120.
[38] FENG SQ, AA N, GENG JL, et al. Pharmacokinetic and metabolomic analyses of the neuroprotective effects of salvianolic acid A in a rat ischemic stroke model. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2017;38(11):1435-1444.
[39] PENG JW, LIU Y, MENG G, et al. Effects of salvianolic acid on cerebral perfusion in patients after acute stroke: A single-center randomized controlled trial. Exp Ther Med. 2018;16(3):2600-2614.
[40] MAHMOOD Q, WANG GF, WU G, et al. Salvianolic acid A inhibits calpain activation and eNOS uncoupling during focal cerebral ischemia in mice. Phytomedicine. 2017;25:8-14.
|