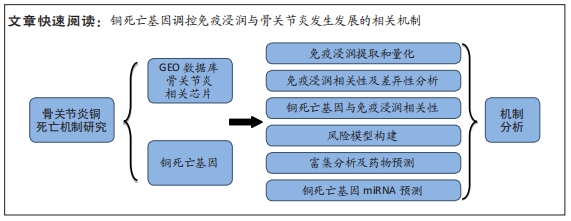
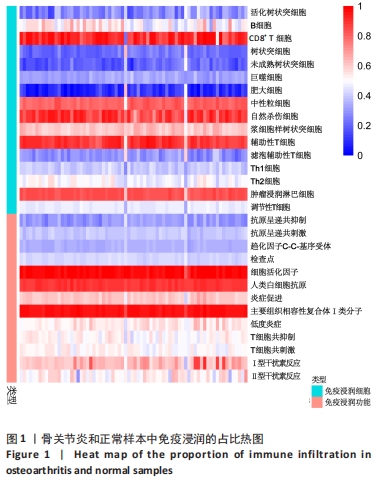
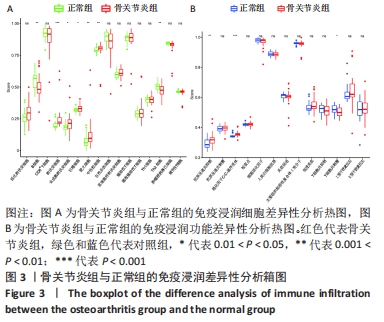
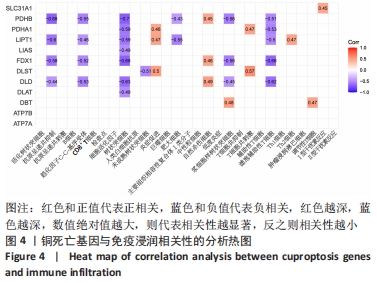
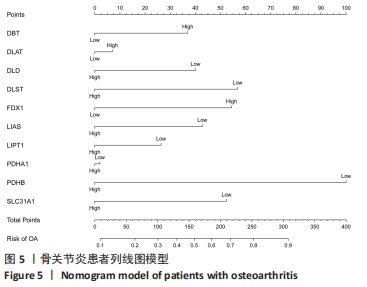
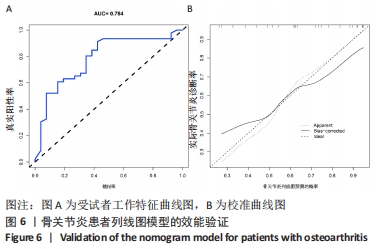
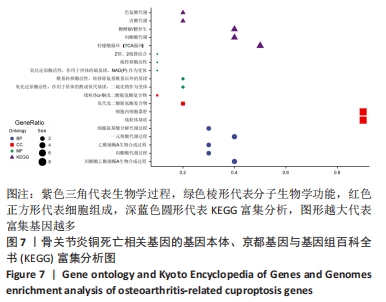
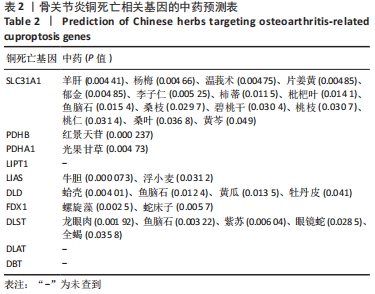
[1] BERENBAUM F. Osteoarthritis as an inflammatory disease (osteoarthritis is not osteoarthrosis!). Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2013;21(1):16-21.
[2] LO J, CHAN L, FLYNN S. A Systematic Review of the Incidence, Prevalence, Costs, and Activity and Work Limitations of Amputation, Osteoarthritis, Rheumatoid Arthritis, Back Pain, Multiple Sclerosis, Spinal Cord Injury, Stroke, and Traumatic Brain Injury in the United States: A 2019 Update. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 2021;102(1):115-131.
[3] GOLDRING SR, GOLDRING MB. Changes in the osteochondral unit during osteoarthritis: structure, function and cartilage-bone crosstalk. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2016;12(11):632-644.
[4] KATZ JN, ARANT KR, LOESER RF. Diagnosis and Treatment of Hip and Knee Osteoarthritis: A Review. JAMA. 2021;325(6):568-578.
[5] FAUST HJ, ZHANG H, HAN J, et al. IL-17 and immunologically induced senescence regulate response to injury in osteoarthritis. J Clin Invest. 2020;130(10):5493-5507.
[6] MA Y, YANG H, ZONG X, et al. Artificial M2 macrophages for disease-modifying osteoarthritis therapeutics. Biomaterials. 2021;274:120865.
[7] CHEN Z, MA Y, LI X, et al. The Immune Cell Landscape in Different Anatomical Structures of Knee in Osteoarthritis: A Gene Expression-Based Study. Biomed Res Int. 2020;2020:9647072.
[8] RAJANDRAN SN, MA CA, TAN JR, et al. Exploring the Association of Innate Immunity Biomarkers With MRI Features in Both Early and Late Stages Osteoarthritis. Front Med (Lausanne). 2020;7:554669.
[9] KRIEGOVA E, MANUKYAN G, MIKULKOVA Z, et al. Gender-related differences observed among immune cells in synovial fluid in knee osteoarthritis. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2018;26(9):1247-1256.
[10] LOHMANN N, SCHIRMER L, ATALLAH P, et al. Glycosaminoglycan-based hydrogels capture inflammatory chemokines and rescue defective wound healing in mice. Sci Transl Med. 2017;9(386):eaai9044.
[11] KIM BE, NEVITT T, THIELE DJ. Mechanisms for copper acquisition, distribution and regulation. Nat Chem Biol. 2008;4(3):176-185.
[12] GE EJ, BUSH AI, CASINI A, et al. Connecting copper and cancer: from transition metal signalling to metalloplasia. Nat Rev Cancer. 2022;22(2): 102-113.
[13] LUTSENKO S. Human copper homeostasis: a network of interconnected pathways. Curr Opin Chem Biol. 2010;14(2):211-217.
[14] TSVETKOV P, COY S, PETROVA B, et al. Copper induces cell death by targeting lipoylated TCA cycle proteins. Science. 2022;375(6586):1254-1261.
[15] TAN HY, WANG N, ZHANG C, et al. Lysyl Oxidase-Like 4 Fosters an Immunosuppressive Microenvironment During Hepatocarcinogenesis. Hepatology. 2021;73(6):2326-2341.
[16] CHOI BY, JANG BG, KIM JH, et al. Copper/zinc chelation by clioquinol reduces spinal cord white matter damage and behavioral deficits in a murine MOG-induced multiple sclerosis model. Neurobiol Dis. 2013;54: 382-391.
[17] ZHU Y, WU G, YAN W, et al. miR-146b-5p regulates cell growth, invasion, and metabolism by targeting PDHB in colorectal cancer. Am J Cancer Res. 2017;7(5):1136-1150.
[18] SAUNIER E, BENELLI C, BORTOLI S. The pyruvate dehydrogenase complex in cancer: An old metabolic gatekeeper regulated by new pathways and pharmacological agents. Int J Cancer. 2016;138(4):809-817.
[19] SMOLLE M, LINDSAY JG. Molecular architecture of the pyruvate dehydrogenase complex: bridging the gap. Biochem Soc Trans. 2006; 34(Pt 5):815-818.
[20] LANGSTON PK, NAMBU A, JUNG J, et al. Glycerol phosphate shuttle enzyme GPD2 regulates macrophage inflammatory responses. Nat Immunol. 2019;20(9):1186-1195.
[21] PARK S, BAEK IJ, RYU JH, et al. PPARα-ACOT12 axis is responsible for maintaining cartilage homeostasis through modulating de novo lipogenesis. Nat Commun. 2022;13(1):3.
[22] ECHEVERRI RNP, MOHAN V, WU J, et al. Dynamic regulation of mitochondrial pyruvate metabolism is necessary for orthotopic pancreatic tumor growth. Cancer Metab. 2021;9(1):39.
[23] FENG X, ZHANG L, XU S, et al. ATP-citrate lyase (ACLY) in lipid metabolism and atherosclerosis: An updated review. Prog Lipid Res. 2020;77:101006.
[24] PATEL MS, NEMERIA NS, FUREY W, et al. The pyruvate dehydrogenase complexes: structure-based function and regulation. J Biol Chem. 2014; 289(24):16615-16623.
[25] STIFEL U, WOLFSCHMITT EM, VOGT J, et al. Glucocorticoids coordinate macrophage metabolism through the regulation of the tricarboxylic acid cycle. Mol Metab. 2022;57:101424.
[26] MICHELUCCI A, CORDES T, GHELFI J, et al. Immune-responsive gene 1 protein links metabolism to immunity by catalyzing itaconic acid production. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2013;110(19):7820-7825.
[27] CORDES T, WALLACE M, MICHELUCCI A, et al. Immunoresponsive Gene 1 and Itaconate Inhibit Succinate Dehydrogenase to Modulate Intracellular Succinate Levels. J Biol Chem. 2016;291(27):14274-14284.
[28] LAMPROPOULOU V, SERGUSHICHEV A, BAMBOUSKOVA M, et al. Itaconate Links Inhibition of Succinate Dehydrogenase with Macrophage Metabolic Remodeling and Regulation of Inflammation. Cell Metab. 2016;24(1):158-166.
[29] MILLS EL, RYAN DG, PRAG HA, et al. Itaconate is an anti-inflammatory metabolite that activates Nrf2 via alkylation of KEAP1. Nature. 2018; 556(7699):113-117.
[30] LEE J, PROHASKA JR, DAGENAIS SL, et al. Isolation of a murine copper transporter gene, tissue specific expression and functional complementation of a yeast copper transport mutant. Gene. 2000; 254(1-2):87-96.
[31] HODGKINSON V, PETRIS MJ. Copper homeostasis at the host-pathogen interface. J Biol Chem. 2012;287(17):13549-13555.
[32] ABDUL SZ, CERO C, PIERCE AE, et al. Combining a β3 adrenergic receptor agonist with alpha-lipoic acid reduces inflammation in male mice with diet-induced obesity. Obesity (Silver Spring). 2022;30(1): 153-164.
[33] MAYR JA, FEICHTINGER RG, TORT F, et al. Lipoic acid biosynthesis defects. J Inherit Metab Dis. 2014;37(4):553-563.
[34] FROMMER KW, HASSELI R, SCHAFFLER A, et al. Free Fatty Acids in Bone Pathophysiology of Rheumatic Diseases. Front Immunol. 2019;10:2757.
[35] STRUSHKEVICH N, MACKENZIE F, CHERKESOVA T, et al. Structural basis for pregnenolone biosynthesis by the mitochondrial monooxygenase system. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2011;108(25):10139-10143.
[36] ZHANG Z, MA Y, GUO X, et al. FDX1 can Impact the Prognosis and Mediate the Metabolism of Lung Adenocarcinoma. Front Pharmacol. 2021;12:749134.
[37] UDUMULA MP, SAKR S, DAR S, et al. Ovarian cancer modulates the immunosuppressive function of CD11b+Gr1+ myeloid cells via glutamine metabolism. Mol Metab. 2021;53:101272.
[38] COLLIOU N, GE Y, SAHAY B, et al. Commensal Propionibacterium strain UF1 mitigates intestinal inflammation via Th17 cell regulation. J Clin Invest. 2017;127(11):3970-3986.
[39] AHN SH, YANG HY, TRAN GB, et al. Interaction of peroxiredoxin V with dihydrolipoamide branched chain transacylase E2 (DBT) in mouse kidney under hypoxia. Proteome Sci. 2015;13:4.
[40] ALAHDAL M, ZHANG H, HUANG R, et al. Potential efficacy of dendritic cell immunomodulation in the treatment of osteoarthritis. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2021;60(2):507-517.
[41] GUO W, WEI B, SUN J, et al. Suppressive oligodeoxynucleotide-induced dendritic cells rein the aggravation of osteoarthritis in mice. Immunopharmacol Immunotoxicol. 2018;40(5):430-436.
[42] BISCHOFF SC. Role of mast cells in allergic and non-allergic immune responses: comparison of human and murine data. Nat Rev Immunol. 2007;7(2):93-104.
[43] FARINELLI L, AQUILI A, MATTIOLI BM, et al. Synovial mast cells from knee and hip osteoarthritis: histological study and clinical correlations. J Exp Orthop. 2022;9(1):13.
[44] LI Y, GAO H, BRUNNER TM, et al. Menstrual blood-derived mesenchymal stromal cells efficiently ameliorate experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis by inhibiting T cell activation in mice. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2022;13(1):155.
[45] WANG Z, WANG B, ZHANG J, et al. Chemokine (C-C Motif) Ligand 2/Chemokine Receptor 2 (CCR2) Axis Blockade to Delay Chondrocyte Hypertrophy as a Therapeutic Strategy for Osteoarthritis. Med Sci Monit. 2021;27:e930053.
[46] 张尚霞,王宇红,龙红萍,等.基于UPLC-Q-TOF-MS法的郁金水提物的化学成分研究[J].中南药学,2021,19(5):820-826.
[47] AGGARWAL BB, Gupta SC, Sung B. Curcumin: an orally bioavailable blocker of TNF and other pro-inflammatory biomarkers. Br J Pharmacol. 2013;169(8):1672-1692.
[48] HENROTIN Y, CLUTTERBUCK AL, ALLAWAY D, et al. Biological actions of curcumin on articular chondrocytes. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2010; 18(2):141-149.
[49] 常青,王伟,杨增华,等.黄芩苷对IL-1β诱导大鼠软骨细胞凋亡和炎症反应的抑制作用及相关机制研究[J].中国免疫学杂志,2020, 36(21):2603-2607+2618.
[50] 丁童,周彦鹏,冯立平.红景天苷对骨关节炎大鼠软组织损伤和免疫失衡的调节作用[J].沈阳药科大学学报,2020,37(3):268-274.
[51] ZHANG L, LIU T, CHEN H, et al. Predicting lncRNA-miRNA interactions based on interactome network and graphlet interaction. Genomics. 2021;113(3):874-880.
[52] CHEN X, XIE D, ZHAO Q, et al. MicroRNAs and complex diseases: from experimental results to computational models. Brief Bioinform. 2019;20(2):515-539.
|