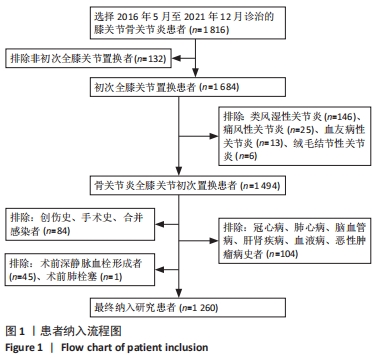
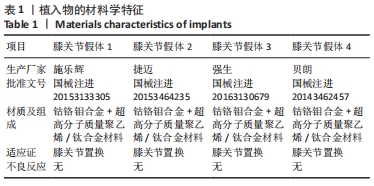
[1] TALMO CT, AGHAZADEH M, BONO JV. Perioperative complications following total joint replacement. Clin Geriatr Med. 2012;28(3):471-487.
[2] KURTZ S, ONG K, LAU E, et al. Projections of primary and revision hip and knee arthroplasty in the United States from 2005 to 2030. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2007;89(4):780-785.
[3] TANG X, WANG S, ZHAN S, et al. The Prevalence of Symptomatic Knee Osteoarthritis in China: Results From the China Health and Retirement Longitudinal Study. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2016;68(3):648-653.
[4] LONGO UG, CIUFFREDA M, MANNERING N, et al. Outcomes of Posterior-Stabilized Compared with Cruciate-Retaining Total Knee Arthroplasty. J Knee Surg. 2018;31(4):321-340.
[5] SALAFFI F, DI CARLO M, CAROTTI M, et al. Frailty prevalence according to the Survey of Health, Ageing and Retirement in Europe-Frailty Instrument (SHARE-FI) definition, and its variables associated, in patients with symptomatic knee osteoarthritis: findings from a cross-sectional study. Aging Clin Exp Res. 2021;33(6):1519-1527.
[6] MADALENO FO, SANTOS BA, ARAÚJO VL, et al. Prevalence of knee osteoarthritis in former athletes: a systematic review with meta-analysis. Braz J Phys Ther. 2018;22(6):437-451.
[7] BOURNE RB, CHESWORTH BM, DAVIS AM, et al. Patient satisfaction after total knee arthroplasty: who is satisfied and who is not? Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2010;468(1):57-63.
[8] DAI W L, LIN ZM, SHI ZJ, et al. Venous Thromboembolic Events after Total Knee Arthroplasty: Which Patients Are at a High Risk? J Knee Surg. 2020;33(10):947-957.
[9] ZHANG S, HTET KS, TAN XY, et al. Short-duration chemoprophylaxis might reduce incidence of deep vein thrombosis in Asian patients undergoing total knee arthroplasty. Knee Surg Relat Res. 2020;32(1): 58.
[10] GEERTS WH, PINEO GF, HEIT JA, et al. Prevention of venous thromboembolism: the Seventh ACCP Conference on Antithrombotic and Thrombolytic Therapy. Chest. 2004;126(3 Suppl):338-400.
[11] KLATSKY AL, ARMSTRONG MA, POGGI J. Risk of pulmonary embolism and/or deep venous thrombosis in Asian-Americans. Am J Cardiol. 2000;85(11):1334-1337.
[12] PIOVELLA F, WANG CJ, LU H, et al. Deep-vein thrombosis rates after major orthopedic surgery in Asia. An epidemiological study based on postoperative screening with centrally adjudicated bilateral venography. J Thromb Haemost. 2005;3(12):2664-2670.
[13] WANG S, LU H, LI S. Prevention of deep venous thrombosis in patients undergoing knee arthroplasty by intermittent pneumatic compression apparatus. Am J Transl Res. 2021;13(9):10765-10770.
[14] MENG B, MA J, LIU Z, et al. Efficacy and Safety of Tranexamic Acid Combined with Rivaroxaban in Primary Total Knee Arthroplasty: A Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. J Invest Surg. 2021; 34(7):728-737.
[15] 吴乾,郝跃峰,刘毅,等.全髋关节置换术后快速康复的研究进展[J].医学综述,2018,24(15):3023-3028.
[16] LIN HY, LIN CY, HUANG YC, et al. Deep vein thrombosis after major orthopedic surgery in Taiwan: A prospective cross-sectional study and literature review. J Formos Med Assoc. 2022;6646(21):594-595.
[17] LEE JK, LEE KB, KIM JI, et al. Risk factors for deep vein thrombosis even using low-molecular-weight heparin after total knee arthroplasty. Knee Surg Relat Res. 2021;33(1):29.
[18] DENG W, HUO L, YUAN Q, et al. Risk factors for venous thromboembolism in patients with diabetes undergoing joint arthroplasty. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2021;22(1):608.
[19] 中华医学会骨科分会关节外科学组,吴阶平医学基金会骨科学专家委员会.膝骨关节炎阶梯治疗专家共识(2018年版)[J].中华关节外科杂志(电子版),2019,13(1):124-130.
[20] OWENS WD, FELTS JA, SPITZNAGEL JR EL. ASA physical status classifications: a study of consistency of ratings. Anesthesiology. 1978; 49:239-243.
[21] SHIMOYAMA Y, SAWAI T, TATSUMI S, et al. Perioperative risk factors for deep vein thrombosis after total hip arthroplasty or total knee arthroplasty. J Clin Anesth. 2012;24(7):531-536.
[22] WAKABAYASHI H, HASEGAWA M, NIIMI R, et al. The risk factor of preoperative deep vein thrombosis in patients undergoing total knee arthroplasty. J Orthop Sci. 2017;22(4):698-702.
[23] ZHANG H, MAO P, WANG C, et al. Incidence and risk factors of deep vein thrombosis (DVT) after total hip or knee arthroplasty: a retrospective study with routinely applied venography. Blood Coagul Fibrinolysis. 2017;28(2):126-133.
[24] 姚尧,张成绩,戴小宇,等.关节置换术后下肢深静脉血栓形成的解剖分布[J].中华骨科杂志,2013,33(9):912-916.
[25] 邓立庆,冯品,甘彦峰,等.藏族人群关节置换术后下肢深静脉血栓发生率及解剖分布[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2019,27(16):1446-1450.
[26] CHAN WS, SPENCER FA, GINSBERG JS. Anatomic distribution of deep vein thrombosis in pregnancy. CMAJ. 2010;182(7):657-660.
[27] SASAKI K, MIURA H, TAKASUGI S, et al. Venous hemodynamic alterations in lower limbs undergoing total joint arthroplasty. Am J Orthop (Belle Mead NJ). 2009;38(8):137-140.
[28] FLEVAS DA, MEGALOIKONOMOS PD, DIMOPOULOS L, et al. Thromboembolism prophylaxis in orthopaedics: an update. EFORT Open Rev. 2018;3(4):136-148.
[29] ZÖLLER B, JI J, SUNDQUIST J, et al. Alcohol use disorders are associated with venous thromboembolism. J Thromb Thrombolysis. 2015;40(2): 167-173.
[30] FALL AO, PROULLE V, SALL A, et al. Risk factors for thrombosis in an african population. Clin Med Insights Blood Disord. 2014;7:1-6.
[31] ANDERSON FA JR, SPENCER FA. Risk factors for venous thromboembolism. Circulation. 2003;107(23 Suppl 1):9-16.
[32] BALA A, OLADEJI K, AMANATULLAH DF. Effect of Comorbidity Burden on the Risk of Venous Thromboembolic Events After Total Knee Arthroplasty. Geriatr Orthop Surg Rehabil. 2021;12: 21514593211043998.
[33] JIANG T, YAO Y, XU X, et al. Prevalence and Risk Factors of Preoperative Deep Vein Thrombosis in Patients with End-Stage Knee Osteoarthritis. Ann Vasc Sur. 2020;64:175-180.
[34] 刘其飞,钱玉英,张在清,等.全髋关节置换术后血清同型半胱氨酸、C反应蛋白、甘油三酯水平与深静脉血栓形成的相关性[J].海南医学,2020,31(12):1542-1544.
[35] 刘仁德,蔡广荣,张恒,等.术前D-二聚体升高对全膝关节置换术后深静脉血栓形成的影响[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2019,27(1):22-26.
[36] DAI X, DING W, LI H, et al. Associations of Serum Lipids and Deep Venous Thrombosis Risk After Total Knee Arthroplasty in Patients With Primary Knee Osteoarthritis. Int J Low Extrem Wounds. 2020;19(1):51-56.
|