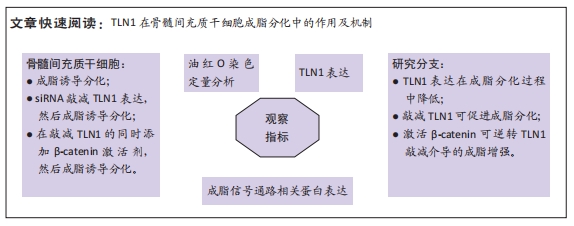
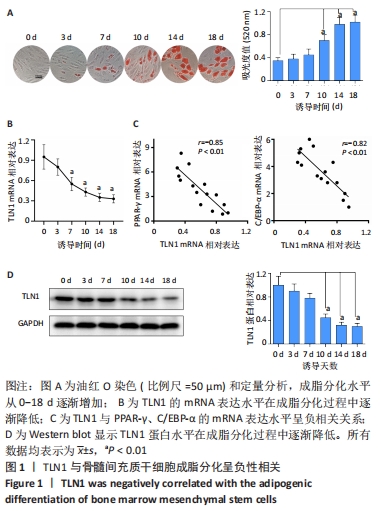
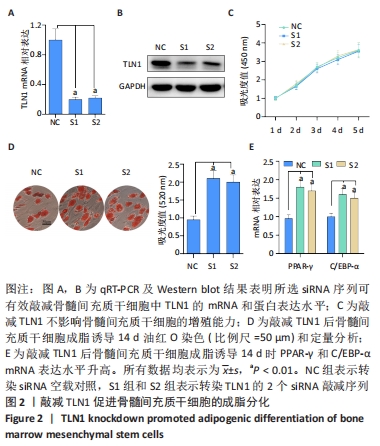
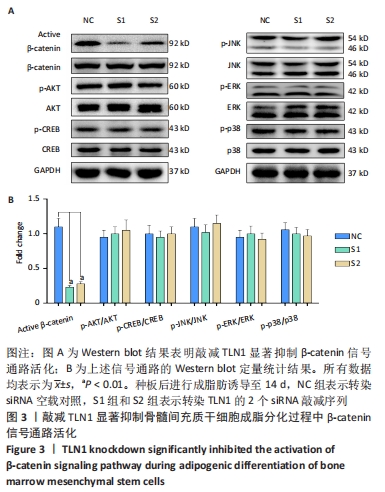
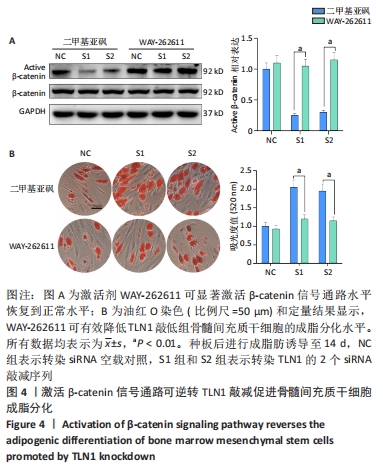
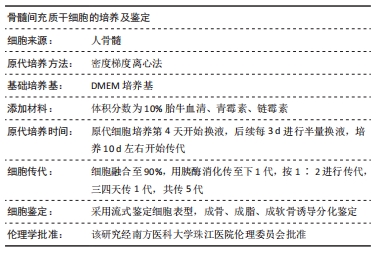
[1] CHEN Q, SHOU P, ZHENG C, et al. Fate decision of mesenchymal stem cells: adipocytes or osteoblasts? Cell Death Differ. 2016;23(7): 1128-1139.
[2] FAN J, LEE CS, KIM S, et al. Trb3 controls mesenchymal stem cell lineage fate and enhances bone regeneration by scaffold-mediated local gene delivery. Biomaterials. 2021;264:120445.
[3] RENDRA E, SCACCIA E, BIEBACK K. Recent advances in understanding mesenchymal stromal cells. F1000Res. 2020;9:F1000 Faculty Rev-156.
[4] ZHOU T, YUAN Z, WENG J, et al. Challenges and advances in clinical applications of mesenchymal stromal cells. J Hematol Oncol. 2021; 14(1):24.
[5] WOBMA H, SATWANI P. Mesenchymal stromal cells: Getting ready for clinical primetime. Transfus Apher Sci. 2021;60(1):103058.
[6] LIU J, HE X, QI Y, et al. Talin1 regulates integrin turnover to promote embryonic epithelial morphogenesis. Mol Cell Biol. 2011;31(16):3366-3377.
[7] ZHANG Y, SUN L, LI H, et al. Binding blockade between TLN1 and integrin beta1 represses triple-negative breast cancer. Elife. 2022;11: e68481.
[8] ZOU W, IZAWA T, ZHU T, et al. Talin1 and Rap1 are critical for osteoclast function. Mol Cell Biol. 2013;33(4):830-844.
[9] 李兆峰,王鹏,谢中瑜,等. TLN1-PI3K/AKT通路调控骨髓间充质干细胞成骨分化[J].岭南现代临床外科,2019,19(4):387-391.
[10] COLTER DC, CLASS R, DIGIROLAMO CM, et al. Rapid expansion of recycling stem cells in cultures of plastic-adherent cells from human bone marrow. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2000;97(7):3213-3218.
[11] XIE Z, WANG P, LI Y, et al. Imbalance Between Bone Morphogenetic Protein 2 and Noggin Induces Abnormal Osteogenic Differentiation of Mesenchymal Stem Cells in Ankylosing Spondylitis. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2016;68(2):430-440.
[12] CEN S, LI J, CAI Z, et al. TRAF4 acts as a fate checkpoint to regulate the adipogenic differentiation of MSCs by activating PKM2. EBioMedicine. 2020;54:102722.
[13] DOMINICI M, LE BLANC K, MUELLER I, et al. Minimal criteria for defining multipotent mesenchymal stromal cells. The International Society for Cellular Therapy position statement. Cytotherapy. 2006;8(4):315-317.
[14] GUO J, REN R, YAO X, et al. PKM2 suppresses osteogenesis and facilitates adipogenesis by regulating β-catenin signaling and mitochondrial fusion and fission. Aging (Albany NY). 2020;12(4):3976-3992.
[15] AMBELE MA, DHANRAJ P, GILES R, et al. Adipogenesis: A Complex Interplay of Multiple Molecular Determinants and Pathways. Int J Mol Sci. 2020;21(12):4283.
[16] JAMES AW. Review of Signaling Pathways Governing MSC Osteogenic and Adipogenic Differentiation. Scientifica (Cairo). 2013;2013:684736.
[17] CHAN JL, MILLER JG, ZHOU Y, et al. Intramyocardial Bone Marrow Stem Cells in Patients Undergoing Cardiac Surgical Revascularization. Ann Thorac Surg. 2020;109(4):1142-1149.
[18] CHUNG JW, CHANG WH, BANG OY, et al. Efficacy and Safety of Intravenous Mesenchymal Stem Cells for Ischemic Stroke. Neurology. 2021;96(7):e1012-e1023.
[19] CHAHAL J, GÓMEZ-ARISTIZÁBAL A, SHESTOPALOFF K, et al. Bone Marrow Mesenchymal Stromal Cell Treatment in Patients with Osteoarthritis Results in Overall Improvement in Pain and Symptoms and Reduces Synovial Inflammation. Stem Cells Transl Med. 2019;8(8): 746-757.
[20] GALIPEAU J, SENSÉBÉ L. Mesenchymal Stromal Cells: Clinical Challenges and Therapeutic Opportunities. Cell Stem Cell. 2018;22(6):824-833.
[21] JING H, LIAO L, AN Y, et al. Suppression of EZH2 Prevents the Shift of Osteoporotic MSC Fate to Adipocyte and Enhances Bone Formation During Osteoporosis. Mol Ther. 2016;24(2):217-229.
[22] ZHAO Y, LYKOV N, TZENG C. Talin‑1 interaction network in cellular mechanotransduction (Review). Int J Mol Med. 2022;49(5):60.
[23] TURLEY TN, THEIS JL, SUNDSBAK RS, et al. Rare Missense Variants in TLN1 Are Associated With Familial and Sporadic Spontaneous Coronary Artery Dissection. Circ Genom Precis Med. 2019;12(4):e002437.
[24] MALLA RR, VEMPATI RK. Talin: A Potential Drug Target for Cancer Therapy. Curr Drug Metab. 2020;21(1):25-32.
[25] BISIO V, ESPÉLI M, BALABANIAN K, et al. Culture, Expansion and Differentiation of Human Bone Marrow Stromal Cells. Methods Mol Biol. 2021;2308:3-20.
[26] STEWARD AJ, KELLY DJ. Mechanical regulation of mesenchymal stem cell differentiation. J Anat. 2015;227(6):717-731.
[27] DENG P, YUAN Q, CHENG Y, et al. Loss of KDM4B exacerbates bone-fat imbalance and mesenchymal stromal cell exhaustion in skeletal aging. Cell Stem Cell. 2021;28(6):1057-1073.e7.
[28] GRAFE I, ALEXANDER S, PETERSON JR, et al. TGF-β Family Signaling in Mesenchymal Differentiation. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2018; 10(5):a022202.
[29] XU Y, JIANG Y, JIA B, et al. Icariin stimulates osteogenesis and suppresses adipogenesis of human bone mesenchymal stem cells via miR-23a-mediated activation of the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway. Phytomedicine. 2021;85:153485.
[30] DE WINTER TJJ, NUSSE R. Running Against the Wnt: How Wnt/β-Catenin Suppresses Adipogenesis. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021;9:627429.
[31] SAFAROVA Y, UMBAYEV B, HORTELANO G, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells modifications for enhanced bone targeting and bone regeneration. Regen Med. 2020;15(4):1579-1594.
[32] COUSTRY F, POSEY KL, MAERZ T, et al. Mutant cartilage oligomeric matrix protein (COMP) compromises bone integrity, joint function and the balance between adipogenesis and osteogenesis. Matrix Biol. 2018;67:75-89.
[33] SUI BD, HU CH, LIU AQ, et al. Stem cell-based bone regeneration in diseased microenvironments: Challenges and solutions. Biomaterials. 2019;196:18-30.
|