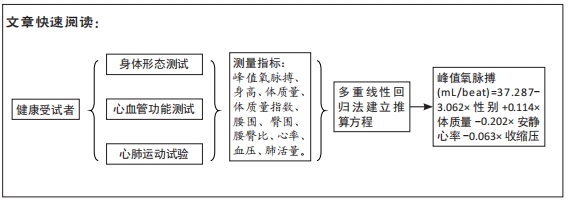
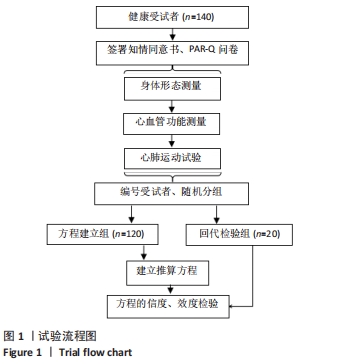
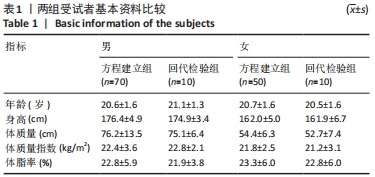
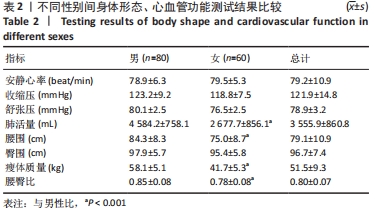
[1] FINGER JD, KRUG S, GÖßWALD A, et al. [Cardiorespiratory fitness among adults in Germany: results of the German Health Interview and Examination Survey for Adults (DEGS1)]. Bundesgesundheitsblatt Gesundheitsforschung Gesundheitsschutz. 2013;56(5-6):772-778.
[2] WASSERMAN K, HANSEN JE, SUE DY, et al. Principles of exercise testing and interpretation: including pathophysiology and clinical applications. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, 2011.
[3] ROSSI NETO JM, TEBEXRENI AS, ALVES ANF, et al. Cardiorespiratory fitness data from 18,189 participants who underwent treadmill cardiopulmonary exercise testing in a Brazilian population. PLoS One. 2019;14(1):178-185.
[4] 刘晓丽, 刘超能, 王人卫.心肺功能在健康风险预测中的应用[J]. 中国运动医学杂志,2018,37(2):158-165.
[5] SCHARHAG-ROSENBERGER F, CARLSOHN A, CASSEL M, et al. How to test maximal oxygen uptake: a study on timing and testing procedure of a supramaximal verification test. Appl Physiol Nutr Metab. 2011;36(1): 153-160.
[6] KWON SB, AHN JW, LEE SM, et al. Estimating Maximal Oxygen Uptake From Daily Activity Data Measured by a Watch-Type Fitness Tracker: Cross-Sectional Study. JMIR Mhealth Uhealth. 2019;7(6):123-135.
[7] ACCALAI E, VIGNATI C, SALVIONI E, et al. Non-invasive estimation of stroke volume during exercise from oxygen in heart failure patients. Eur J Prev Cardiol. 2019;18(3):168-176.
[8] ASTRAND I. Aerobic work capacity in men and women with special reference to age. Acta Physiol Scand Suppl. 1959;49(169):1-92.
[9] GMADA N, ALY B. Relationship between oxygen pulse and arteriovenous oxygen difference in healthy subjects: Effect of exercise intensity. Sci Sports. 2019;34(6):297-306.
[10] 王瑞元,苏全生. 运动生理学[M]. 北京:人民体育出版社, 2010: 234-256.
[11] SPEE RF, NIEMEIJER VM, THIJSSEN CGE, et al. The utility of the oxygen pulse recovery as a marker of the cardiac output response to exercise in patients with chronic heart failure. Clin Physiol Funct Imaging. 2020; 40(5):328-335.
[12] NETO GM, OLIVEIRA RB, MYERS JN, et al. Prediction of peak oxygen pulse (O2Ppeak) without exercise testing in older adults. Arch Gerontol Geriatr. 2014;59(3):562-567.
[13] LAUKKANEN JA, ARAÚJO CGS, KURL S, et al. Relative peak exercise oxygen pulse is related to sudden cardiac death, cardiovascular and all-cause mortality in middle-aged men. Eur J Prev Cardiol. 2018;25(7): 772-782.
[14] OLIVEIRA RB, MYERS JS, ARAÚJO CG, et al. Maximal exercise oxygen pulse as a predictor of mortality among male veterans referred for exercise testing. Eur J Cardiovasc Prev Rehabil. 2009;16(3):358-364.
[15] MUNHOZ EC, HOLLANDA R, VARGAS JP, et al. Flattening of Oxygen Pulse during Exercise May Detect Extensive Myocardial Ischemia. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2007;39(8):1221-1226.
[16] ARENA R, MYERS J, HARBER M, et al. Peak oxygen pulse responses during maximal cardiopulmonary exercise testing: Reference standards from FRIEND (Fitness Registry and the Importance of Exercise: an International Database) - ScienceDirect. Int J Cardiol. 2020;301:180-182.
[17] ZHANG W, HE K, ZHAO H, et al. Association of body mass index and waist circumference with high blood pressure in older adults. BMC Geriatr. 2021;21(1):260.
[18] MURATA M, ADACHI H, OSHIMA S, et al. Influence of stroke volume and exercise tolerance on peak oxygen pulse in patients with and without beta-adrenergic receptor blockers in patients with heart disease. J Cardiol. 2017;69(1):176-181.
[19] SHASTRI L, ALKHALIL M, FORBES C, et al. Skeletal muscle oxygenation during cycling at different power output and cadence. Physiol Rep. 2019;7(3):e13963.
[20] NITIN YM, SUCHARITA S, MADHURA M, et al. VO2 max in an Indian population: a study to understand the role of factors determining VO2 max. Indian J Physiol Pharmacol. 2013;57(2):87-94.
[21] LIM JG, MCAVENEY TJ, FLEG JL, et al. Oxygen pulse during exercise is related to resting systolic and diastolic left ventricular function in older persons with mild hypertension. Am Heart J. 2005;150(5):941-946.
[22] 米欢, 王正珍. 步行试验推测40-49岁人群最大摄氧量回归方程的研究[J]. 北京体育大学学报,2012,54(5): 50-54.
[23] DEGANI-COSTA LH, NERY LE, RODRIGUES MT, et al. Does oxygen pulse trajectory during incremental exercise discriminate impaired oxygen delivery from poor muscle oxygen utilisation? ERJ Open Res. 2019;5(2):00108-2018.
[24] 杨锡让. 实用运动生理学[M]. 北京:北京体育大学出版社,2007.
[25] PETERMAN JE, HARBER MP, CHAUDHRY S, et al. Peak oxygen pulse and mortality risk in healthy women and men: The Ball State Adult Fitness Longitudinal Lifestyle Study (BALL ST). Prog Cardiovasc Dis. 2021;68:19-24.
[26] BHAMBHANI Y, NORRIS S, BELL G. Prediction of stroke volume from oxygen pulse measurements in untrained and trained men. Can J Appl Physiol. 1994;19(1):49-59.
[27] CHAUDHRY S, ARENA R, WASSERMAN K, et al. Exercise-induced myocardial ischaemia detected by cardiopulmonary exercise testing. Am J Cardiol. 2009;103(5):615-619.
[28] OLIVEIRA RB, MYERS J, ARAÚJO C, et al. Does peak oxygen pulse complement peak oxygen uptake in risk stratifying patients with heart failure? Am J Cardiol. 2009;104(4):554-558.
[29] DELSART P, DELAHAYE C, DEVOS P, et al. Prognostic value of aerobic capacity and exercise oxygen pulse in postaortic dissection patients. Clin Cardiol. 2021;44(2):252-260.
[30] 王念辉, 洪平, 苏中军. 基于身高、体重及肺活量的大学一年级男生最大摄氧量推算方法研究[J]. 中国运动医学杂志,2018,37(3): 202-207.
[31] 潘棱, 何彤榕. 运动心肺功能的主要指标及其影响因素的探讨[J]. 中国运动医学杂志,1997,16(4):297-299.
[32] SIMONE GD, DEVEREUX RB, DANIELS SR, et al. Stroke Volume and Cardiac Output in Normotensive Children and Adults : Assessment of Relations With Body Size and Impact of Overweight. Circulation. 1997;95(7):1837-1843.
[33] 韩延柏. 腰围身高比结合体质指数预测心血管病危险因素效果评价[J]. 中国公共卫生,2015,31(10):1342-1346.
[34] VELLA CA, ONTIVEROS D, ZUBIA RY. Cardiac function and arteriovenous oxygen difference during exercise in obese adults. Eur J Appl Physiol. 2011;111(6):915-923.
[35] SANDVIK L, ERIKSSEN J, ELLESTAD M, et al. Heart rate increase and maximal heart rate during exercise as predictors of cardiovascular mortality: a 16-year follow-up study of 1960 healthy men. Coron Artery Dis. 1995;6(8):667-679.
[36] 常芸, 高晓嶙, 熊正英. 中国不同项目优秀运动员安静心率研究[J]. 中国运动医学杂志,2007,26(1):34-38.
[37] 王国军, 刘亚, 刘石军. 高中男生“阳光长跑”个体无氧阈心率回归方程的建立[J]. 体育学刊,2019,63(6):137-143.
[38] KOHL HW, NICHAMAN MZ, FRANKOWSKI RF, et al. Maximal exercise hemodynamics and risk of mortality in apparently healthy men and women. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 1996;28(5):601.
[39] BOO SH, JOO MC, LEE JM, et al. Association between skeletal muscle mass and cardiorespiratory fitness in community-dwelling elderly men. Aging Clin Exp Res. 2019;31(1):49-57.
[40] 方积乾. 现代医学统计学[M]. 北京:人民卫生出版社,2002:189-203.
|