中国组织工程研究 ›› 2022, Vol. 26 ›› Issue (29): 4699-4703.doi: 10.12307/2022.908
• 骨组织构建 bone tissue construction • 上一篇 下一篇
Akt激活剂SC79抑制地塞米松诱导成骨细胞凋亡和程序性坏死的作用机制
宋建治,徐礼森,张 晨,涂 峰,牛 飞
- 武汉市第一医院(武汉市中西医结合医院)骨科,湖北省武汉市 430022
Mechanism by which SC79, an Akt activator, inhibits dexamethasone-induced apoptosis and programmed necrosis of osteoblasts
Song Jianzhi, Xu Lisen, Zhang Chen, Tu Feng, Niu Fei
- Department of Orthopaedics, Wuhan First Hospital (Wuhan Hospital of Integrated Traditional Chinese and Western Medicine), Wuhan 430022, Hubei Province, China
摘要:

文题释义:
SC79:是一种Akt激活剂,能够在各种生理及病理情况下增强Akt活性,具有一定的细胞保护作用。
地塞米松:作为一种糖皮质激素,为临床上常用的免疫抑制药及抗炎药,但其可能会诱导骨质疏松症甚至并发骨折,该不良作用可能与抑制成骨细胞形成、促进成骨细胞凋亡有关。
背景:有研究发现SC79(一种Akt激活剂)具有一定的细胞保护作用,其不仅能够抑制兴奋性中毒,还能够减轻由于脑卒中等原因引起的神经元细胞死亡。
目的:探究SC79抑制地塞米松诱导成骨细胞凋亡和程序性坏死的作用机制。
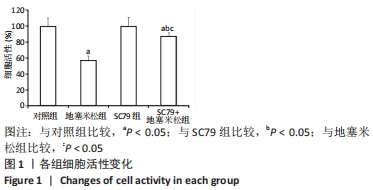
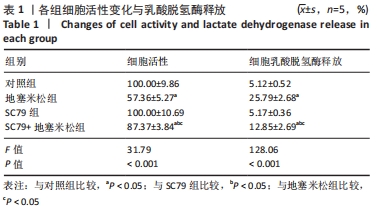
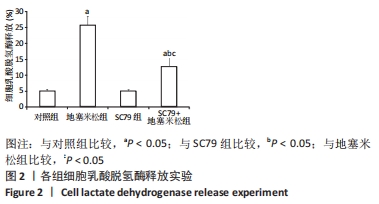
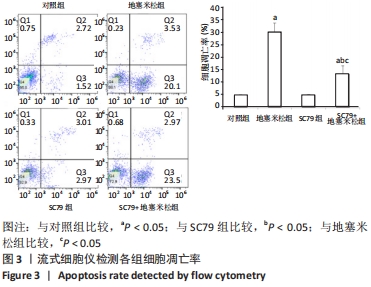
方法:取对数生长期的人成骨细胞株OB-6,分4组处理:对照组常规培养,地塞米松组加入2 μmol/L地塞米松处理24 h;SC79组加入
20 μmol/L SC79处理24 h;SC79+地塞米松组首先加入20 μmol/L SC79处理2 h,再加入2 μmol/L地塞米松处理24 h。检测细胞活性、乳酸脱氢酶释放、凋亡率、凋亡相关因子Caspase-3、Bax、Bcl-2的活性,以及氧化应激相关因子亲环蛋白D、细胞色素C的蛋白表达。
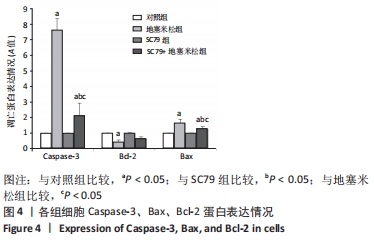
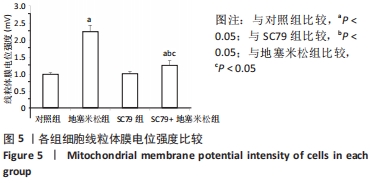
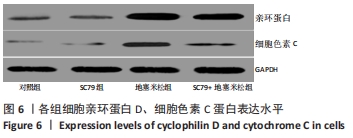
结果与结论:①与对照组比较,地塞米松组细胞活性降低(P < 0.05);与地塞米松组比较,SC79+地塞米松组细胞活性升高(P < 0.05);②与对照组比较,地塞米松组细胞乳酸脱氢酶释放、线粒体膜电位升高(P < 0.05);与地塞米松组比较,SC79+地塞米松组细胞乳酸脱氢酶释放、线粒体膜电位强度降低(P < 0.05);③与对照组比较,地塞米松组Caspase-3、Bax的活性及细胞凋亡率升高(P < 0.05),Bcl-2蛋白表达降低(P < 0.05);与地塞米松组比较,SC79+地塞米松组Caspase-3、Bax的活性及细胞凋亡率降低(P < 0.05),Bcl-2蛋白表达升高(P < 0.05);④与对照组比较,地塞米松组亲环蛋白D、细胞色素C蛋白表达升高(P < 0.05);与地塞米松组比较,SC79+地塞米松组亲环蛋白D、细胞色素C蛋白表达降低(P < 0.05);⑤结果表明,SC79可以通过增强细胞活性及抑制细胞凋亡、线粒体膜电位强度及氧化应激水平抑制地塞米松诱导的成骨细胞凋亡和程序性坏死。
https://orcid.org/0000-0001-9879-925X (宋建治)
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:组织构建;骨细胞;软骨细胞;细胞培养;成纤维细胞;血管内皮细胞;骨质疏松;组织工程
中图分类号: