| [1] Cassells W, Engler D, Willerson J, et al. Mechanism of restenosis. Tex Heart Inst J. 1994;21(1):68-77.
[2] Cortese B, Buccheri D, Piraino D, et al. Drug-coated balloon angioplasty for coronary chronic total occlusions. An OCT analysis for a “new” intriguing strategy. Int J Cardiol.2015; 189:257-258.
[3] Guan S, Tang Q, Liu W, et al. Nobiletin Inhibits PDGF-BB-induced vascular smooth muscle cell proliferation and migration and attenuates neointimal hyperplasia in a rat carotid artery injury model. Drug Dev Res. 2014;75(8):489-496.
[4] Guo X, Shi N, Cui XB, et al. Dedicator of cytokinesis 2, a novel regulator for smooth muscle phenotypic modulation and vascular remodeling. Circ Res. 2015; 116(10):e71-80.
[5] Wang J, Wang H, Guo C, et al. Mebendazole reduces vascular smooth muscle cell proliferation and neointimal formation following vascular injury in mice. 2014 27;9(2):e90146.
[6] Koniari I, Apostolakis E, Diamantopoulos A, et al. Transauricular balloon angioplasty in rabbit thoracic aorta: a novel model of experimental restenosis.Lipids. Health Dis. 2014;13:33.
[7] Indolfi C, Esposito G, Di Lorenzo E, et al. Smooth muscle cell proliferation is proportional to the degree of balloon injury in a rat model of angioplasty. Circulation. 1995;92(5):1230-1235.
[8] 温进坤,韩梅,杜玮南,等. 一种快速建立大鼠动脉粥样硬化模型的实验方法[J].中国老年学杂志,2001, 21(1):50-52.
[9] Li JM, Zhang X, Nelson PR, et al. Temporal evolution of gene expression in rat carotid artery following balloon angioplasty. J Cell Biochem. 2007;101(2): 399-410.
[10] Nicoll R, Howard JM, Henein MY. A review of the effect of diet on cardiovascular calcification. Int J Mol Sci. 2015;16(4):8861-8883.
[11] Eilat-Adar S, Sinai T, Yosefy C,et al. Nutritional recommendations for cardiovascular disease prevention. Nutrients. 2013;5(9):3646-3683.
[12] Holt AW, Tulis DA. Experimental Rat and Mouse Carotid Artery Surgery: Injury & Remodeling Studies. ISRN Minim Invasive Surg. 2013. pii:167407.
[13] Ojima A, Oda E, Higashimoto Y,et al. DNA aptamer raised against advanced glycation end products inhibits neointimal hyperplasia in balloon-injured rat carotid arteries. Int J Cardiol. 2014;171(3):443-446.
[14] Zhang J, Chen J, Xu C, et al. Resveratrol inhibits phenotypic switching of neointimal vascular smooth muscle cells after balloon injury through blockade of Notch pathway. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 2014;63(3): 233-239.
[15] Zhang J, Chen J, Yang J, et al. Sodium ferulate inhibits neointimal hyperplasia in rat balloon injury model. PLoS One. 2014;9(1):e87561.
[16] Eghbalieh SD, Chowdhary P, Muto A, et al. Age-related neointimal hyperplasia is associated with monocyte infiltration after balloon angioplasty.J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci. 2012;67(2):109-117.
[17] Horlitz M, Sigwart U, Niebauer J. Fighting restenosis after coronary angioplasty: contemporary and future treatment options. Int J Cardiol. 2002;83(3):199-205.
[18] Jiang B, Khandelwal AR, Rogers LK, et al. Antiretrovirals induce endothelial dysfunction via an oxidant-dependent pathway and promote neointimal hyperplasia. Toxicol Sci. 2010;117(2):524-536.
[19] Wu XJ, Huang L, Song DL, et al. Effects of endothelial cell growth states on the proliferation and migration of vascular smooth muscle cells in vitro.Sheng Li Xue Bao. 2003;55(5):554-559.
[20] Sheng J, Cai WW, Fang NY, et al. Role of stromal-derived factor-1<alpha>/CXCR4 in neo-intimal repair. Cardiovasc J Afr. 2011;22(6):313-318.
[21] Kundumani-Sridharan V, Singh NK, Kumar S, et al. Nuclear factor of activated T cells c1 mediates p21-activated kinase 1 activation in the modulation of chemokine-induced human aortic smooth muscle cell F-actin stress fiber formation, migration, and proliferation and injury-induced vascular wall remodeling. J Biol Chem. 2013;288(30):22150-22162.
[22] Yang X,Thomas DP,Zhang X,et al.Curcumin inhibits platelet-derived growth factor-stimulated vascular smooth muscle cell function and injury-induced neointima formation. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2006;26(1): 85-90.
[23] Davis BN, Hilyard AC, Nguyen PH, et al. Induction of microRNA-221 by platelet-derived growth factor signaling is critical for modulation of vascular smooth muscle phenotype. J Biol Chem. 2009;284(6):3728- 3738.
[24] Xu H, Shi D, Chen K. Inhibition of vascular remodelling in a porcine coronary injury model by herbal extract XS0601. Chin Med.2006;1: 2.
[25] Wang D, Wang Q, Yan G, et al. Phloretin Inhibits Platelet-derived Growth Factor-BB-induced Rat Aortic Smooth Muscle Cell Proliferation, Migration, and Neointimal Formation After Carotid Injury. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 2015;65(5):444-455. |
.jpg) 文题释义:
动脉粥样硬化血管损伤大鼠模型:选择Wistar大鼠,首先采用大剂量VitD3灌胃基础上饲高脂饲料的方法使大鼠形成血管动脉粥样硬化的病变,在这一基础上,再选用2F动脉取血栓导管损伤左侧颈总动脉,建立大鼠颈总动脉球囊损伤后狭窄模型。之后相应取损伤组大鼠动脉,分别进行血管组织学结构和超微结构的检测,以出现动脉粥样硬化改变及损伤后新生内膜增生为造模成功依据,从而成功模拟了人体血管成形术后再狭窄发生的病理过程。
再狭窄:是以管腔狭窄为特征的闭塞性血管反应,是在经皮冠状动脉腔内成形术(PTCA)术后几个月内发生的,通常指6个月内。其病理过程大致经历5个阶段:血栓形成期、炎症反应期、血管平滑肌细胞增殖期、细胞外基质形成期以及血管重塑期。
文题释义:
动脉粥样硬化血管损伤大鼠模型:选择Wistar大鼠,首先采用大剂量VitD3灌胃基础上饲高脂饲料的方法使大鼠形成血管动脉粥样硬化的病变,在这一基础上,再选用2F动脉取血栓导管损伤左侧颈总动脉,建立大鼠颈总动脉球囊损伤后狭窄模型。之后相应取损伤组大鼠动脉,分别进行血管组织学结构和超微结构的检测,以出现动脉粥样硬化改变及损伤后新生内膜增生为造模成功依据,从而成功模拟了人体血管成形术后再狭窄发生的病理过程。
再狭窄:是以管腔狭窄为特征的闭塞性血管反应,是在经皮冠状动脉腔内成形术(PTCA)术后几个月内发生的,通常指6个月内。其病理过程大致经历5个阶段:血栓形成期、炎症反应期、血管平滑肌细胞增殖期、细胞外基质形成期以及血管重塑期。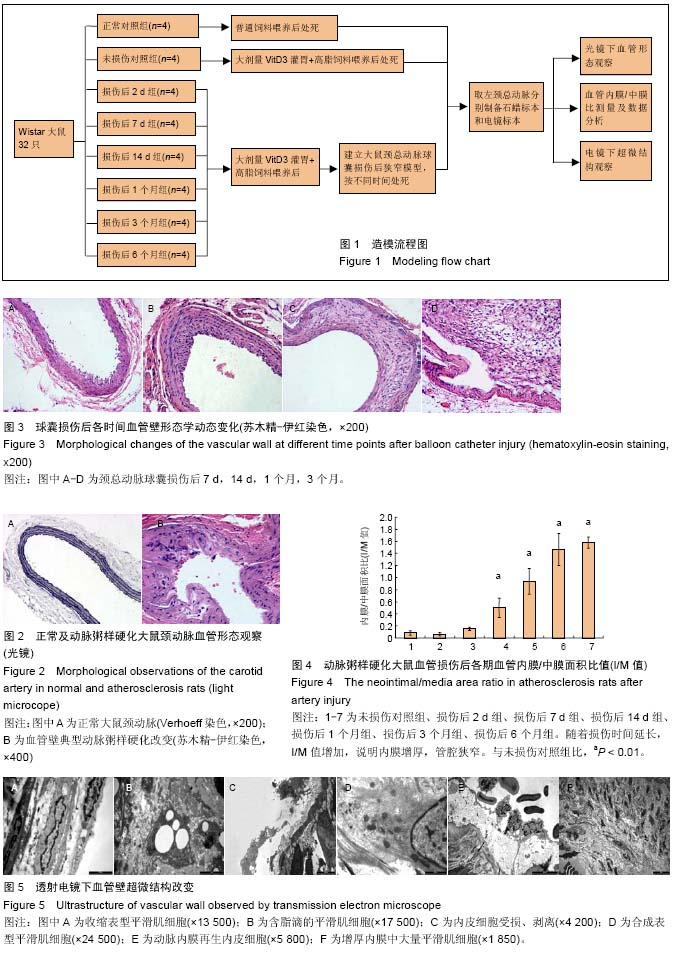
.jpg) 文题释义:
动脉粥样硬化血管损伤大鼠模型:选择Wistar大鼠,首先采用大剂量VitD3灌胃基础上饲高脂饲料的方法使大鼠形成血管动脉粥样硬化的病变,在这一基础上,再选用2F动脉取血栓导管损伤左侧颈总动脉,建立大鼠颈总动脉球囊损伤后狭窄模型。之后相应取损伤组大鼠动脉,分别进行血管组织学结构和超微结构的检测,以出现动脉粥样硬化改变及损伤后新生内膜增生为造模成功依据,从而成功模拟了人体血管成形术后再狭窄发生的病理过程。
再狭窄:是以管腔狭窄为特征的闭塞性血管反应,是在经皮冠状动脉腔内成形术(PTCA)术后几个月内发生的,通常指6个月内。其病理过程大致经历5个阶段:血栓形成期、炎症反应期、血管平滑肌细胞增殖期、细胞外基质形成期以及血管重塑期。
文题释义:
动脉粥样硬化血管损伤大鼠模型:选择Wistar大鼠,首先采用大剂量VitD3灌胃基础上饲高脂饲料的方法使大鼠形成血管动脉粥样硬化的病变,在这一基础上,再选用2F动脉取血栓导管损伤左侧颈总动脉,建立大鼠颈总动脉球囊损伤后狭窄模型。之后相应取损伤组大鼠动脉,分别进行血管组织学结构和超微结构的检测,以出现动脉粥样硬化改变及损伤后新生内膜增生为造模成功依据,从而成功模拟了人体血管成形术后再狭窄发生的病理过程。
再狭窄:是以管腔狭窄为特征的闭塞性血管反应,是在经皮冠状动脉腔内成形术(PTCA)术后几个月内发生的,通常指6个月内。其病理过程大致经历5个阶段:血栓形成期、炎症反应期、血管平滑肌细胞增殖期、细胞外基质形成期以及血管重塑期。