| [1] Iwamoto S, Higashi A, Ueno T, et al. Protective effect of sivelestat sodium hydrate (ONO-5046) on ischemic spinal cord injury. Interact Cardiovasc Thorac Surg. 2009;8(6):606-609.
[2] Etz CD, Homann TM, Luehr M, et al. Spinal cord blood flow and ischemic injury after experimental sacrifice of thoracic and abdominal segmental arteries. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg. 2008;33(6):1030-1038.
[3] 金华,郭光琼,李江,等.脊髓缺血再灌注损伤模型的改进及对大鼠神经行为学的影响[J].中风与神经疾病杂志, 2012, 29(10):879-882.
[4] Margolis JM, Juneau P, Sadosky A, et al.Health care resource utilization and medical costs of spinal cord injury with neuropathic pain in a commercially insured population in the United States. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 2014;95(12): 2279-2287.
[5] Varma AK, Das A, Wallace GT, et al.Spinal cord injury: a review of current therapy, future treatments, and basic science frontiers. Neurochem Res. 2013;38(5): 895-905.
[6] Nagoshi N, Fehlings MG. Investigational drugs for the treatment of spinal cord injury: review of preclinical studies and evaluation of clinical trials from Phase I to II. Expert Opin Investig Drugs. 2015;24(5): 645-658.
[7] Zhang SX, Huang F, Gates M, et al. Tail nerve electrical stimulation combined with scar ablation and neural transplantation promotes locomotor recovery in rats with chronically contused spinal cord. Brain Res. 2012;1456: 22-35.
[8] Jones CF, Lee JH, Kwon BK, et al.Development of a large-animal model to measure dynamic cerebrospinal fluid pressure during spinal cord injury: Laboratory investigation. J Neurosurg Spine. 2012;16(6): 624-635.
[9] 张俐,张纪浩,陈凯,等.活血通督汤对脊髓缺血再灌注损伤NF-κB、VCAM-1表达的作用[J].中华中医药杂志, 2015, 30(4):1020-1023.
[10] Awad H, Ankeny DP, Guan Z, et al.A mouse model of ischemic spinal cord injury with delayed paralysis caused by aortic cross-clamping. Anesthesiology. 2010; 113(4): 880-891.
[11] Su YF, Lin CL, Lee KS, et al.A modified compression model of spinal cord injury in rats: functional assessment and the expression of nitric oxide synthases. Spinal Cord. 2015;53(6): 432-435.
[12] Nout YS, Ferguson AR, Strand SC, et al.Methods for functional assessment after C7 spinal cord hemisection in the rhesus monkey. Neurorehabil Neural Repair. 2012;6(6): 556-569.
[13] Xue F, Wei Y, Chen Y, et al.A rat model for chronic spinal nerve root compression. Eur Spine J. 2014; 23(2): 435-446.
[14] Zibly Z, Schlaff CD, Gordon I, et al.A novel rodent model of spinal metastasis and spinal cord compression. BMC Neurosci. 2012; 13: 137.
[15] Svensson E, Schillberg B, Kling AM, et al.Reliability of the balanced inventory for spinal disorders, a questionnaire for evaluation of outcomes in patients with various spinal disorders. J Spinal Disord Tech. 2012;25(4): 196-204.
[16] Seifert JL, Bell JE, Elmer BB, et al.Characterization of a novel bidirectional distraction spinal cord injury animal model. J Neurosci Methods. 2011;197(1): 97-103.
[17] Kandhare AD, Shivakumar V, Rajmane A, et al. Evaluation of the neuroprotective effect of chrysin via modulation of endogenous biomarkers in a rat model of spinal cord injury. J Nat Med. 2014;68(3): 586-603.
[18] Fehlings MG, Wilson JR, Frankowski RF, et al. Riluzole for the treatment of acute traumatic spinal cord injury: rationale for and design of the NACTN Phase I clinical trial. J Neurosurg Spine. 2012;17(1 Suppl): 151-156.
[19] Li H, Roy Choudhury G, Zhang N, et al.Photothrombosis- induced Focal Ischemia as a Model of Spinal Cord Injury in Mice. J Vis Exp. 2015;(101): e53161.
[20] Falowski S, Ooi YC, Sabesan A, et al.Spinal cord injury induced by a cervical spinal cord stimulator. Neuromodulation. 2011;14(1): 34-36; discussion 36-37.
[21] Alilain WJ, Horn KP, Hu H, et al.Functional regeneration of respiratory pathways after spinal cord injury. Nature. 2011;475(7355): 196-200.
[22] Rabchevsky AG, Patel SP, Duale H, et al.Gabapentin for spasticity and autonomic dysreflexia after severe spinal cord injury. Spinal Cord. 2011;49(1):99-105.
[23] Zheng Y, Zhang YP, Shields LB, et al.Effect of heparin following cervical spinal cord injuries in rats. Neurosurgery. 2011;69(4): 930-941; discussion 941.
[24] Gruner JA.A monitored contusion model of spinal cord injury in the rat. J Neurotrauma. 1992;9(2): 123-126; discussion 126-128.
[25] Huan W, Wu X, Zhang S, et al.Spatiotemporal patterns and essential role of TNF receptor-associated factor 5 expression after rat spinal cord Injury. J Mol Histol. 2012;43(5): 527-533.
[26] Rosas OR, Torrado AI, Santiago JM, et al.Long-term treatment with PP2 after spinal cord injury resulted in functional locomotor recovery and increased spared tissue. Neural Regen Res. 2014;9(24): 2164-2173.
[27] Basso DM, Beattie MS, Bresnahan JC. A sensitive and reliable locomotor rating scale for open field testing in rats. J Neurotrauma. 1995;12(1): 1-21.
[28] 吕静.大鼠脊髓损伤模型的建立及行为学评分[D].中南大学,2011.
[29] 李剑锋,冯世庆,夏润福,等.不同程度脊髓背侧压迫损伤模型大鼠脊髓损伤致伤器的设计[J].中国组织工程研究, 2015,19(18):2856-2861.
[30] 黄霖,唐勇,杨睿,等.通用型脊髓打击器的研制与脊髓损伤动物模型的建立[J].中国脊柱脊髓杂志,2008,18(9):688-693.
[31] 陈霄雷,林雷雷,邵璐斐,等.大鼠脊髓打击器研制及其制备的脊髓损伤模型稳定性评价[J]. 宁夏医科大学学报, 2014,36(7):716-719.
[32] 陈德英,程赛宇,肖艳,等.坐骨神经损伤后相应脊髓前角运动神经元的形态学变化[J].中国临床康复,2002,6(10): 1424-1425.
[33] 陈德英,程赛宇,肖燕,等. 神经元尼氏染色法在坐骨神经损伤研究中的应用[J]. 创伤外科杂志,2001,13(z1):35-37.
[34] 王力,孙丽,窦慧慧,等. 大鼠新型挫伤型脊髓损伤模型的建立及评价[J]. 神经解剖学杂志,2010,26(6):638-642.
[35] 熊春翔,宗少晖,曾高峰,等. 大鼠Allen’s脊髓损伤模型的建立及评价[J]. 广西医科大学学报,2011,28(2):215-217.
[36] 蔡文琴,阮怀珍,黎海蒂.医用神经生物学基础[M].重庆:西南师范大学出版社,2001: 41.
[37] 陈凯.活血通督汤对兔脊髓缺血再灌注损伤后肢运动功能及细胞凋亡的影响[D].福建中医药大学,2014.
[38] 陈向华,张俐,王和鸣,等.丹参酮及电针对脊髓缺血再灌注损伤细胞因子IL-1β、IL-1Ra、IL-8的影响[J].中华中医药杂志,2012,27(4):987-991.
[39] 张俐,林庆宾.丹参及丹参酮Ⅱ-A磺酸钠对脊髓缺血再灌注损伤IL-1β、ICAM-1及MPO表达的影响[J].中华中医药杂志,2012,27(8):2042-2047.
[40] 张俐,安国尧,张文光,等.丹参酮-ⅡA磺酸钠对脊髓缺血再灌注损伤NF-κB、VCAM-1和血液流变性的影响[J].中国骨伤,2012,28(12):1016-1020.
[41] 林庆宾,张俐.活血通督汤对脊髓缺血再灌注损伤神经细胞凋亡的影响[J]. 中国中医骨伤科杂志,2014,22(8):1-11. |
.jpg) 文题释义:
脊髓损伤:是是指外力直接或间接作用于脊髓,引起脊髓功能性或器质性损害,以及继发一系列病理改变进一步加重脊髓损伤,从而出现不可逆性的损伤平面以下感觉、运动、括约肌功能障碍、肌张力异常及病理反射。
脊髓损伤模型:建立与人类发病相近的动物模型,探其发病机制,寻找有效的治疗药物逐渐引起重视。文章选用成年雌性SD大鼠,用撞击损伤模型方法进行造模,方法容易重复,通过自制打击器改良Allen’s法成功建立脊髓撞击损伤模型。
文题释义:
脊髓损伤:是是指外力直接或间接作用于脊髓,引起脊髓功能性或器质性损害,以及继发一系列病理改变进一步加重脊髓损伤,从而出现不可逆性的损伤平面以下感觉、运动、括约肌功能障碍、肌张力异常及病理反射。
脊髓损伤模型:建立与人类发病相近的动物模型,探其发病机制,寻找有效的治疗药物逐渐引起重视。文章选用成年雌性SD大鼠,用撞击损伤模型方法进行造模,方法容易重复,通过自制打击器改良Allen’s法成功建立脊髓撞击损伤模型。.jpg) 文题释义:
脊髓损伤:是是指外力直接或间接作用于脊髓,引起脊髓功能性或器质性损害,以及继发一系列病理改变进一步加重脊髓损伤,从而出现不可逆性的损伤平面以下感觉、运动、括约肌功能障碍、肌张力异常及病理反射。
脊髓损伤模型:建立与人类发病相近的动物模型,探其发病机制,寻找有效的治疗药物逐渐引起重视。文章选用成年雌性SD大鼠,用撞击损伤模型方法进行造模,方法容易重复,通过自制打击器改良Allen’s法成功建立脊髓撞击损伤模型。
文题释义:
脊髓损伤:是是指外力直接或间接作用于脊髓,引起脊髓功能性或器质性损害,以及继发一系列病理改变进一步加重脊髓损伤,从而出现不可逆性的损伤平面以下感觉、运动、括约肌功能障碍、肌张力异常及病理反射。
脊髓损伤模型:建立与人类发病相近的动物模型,探其发病机制,寻找有效的治疗药物逐渐引起重视。文章选用成年雌性SD大鼠,用撞击损伤模型方法进行造模,方法容易重复,通过自制打击器改良Allen’s法成功建立脊髓撞击损伤模型。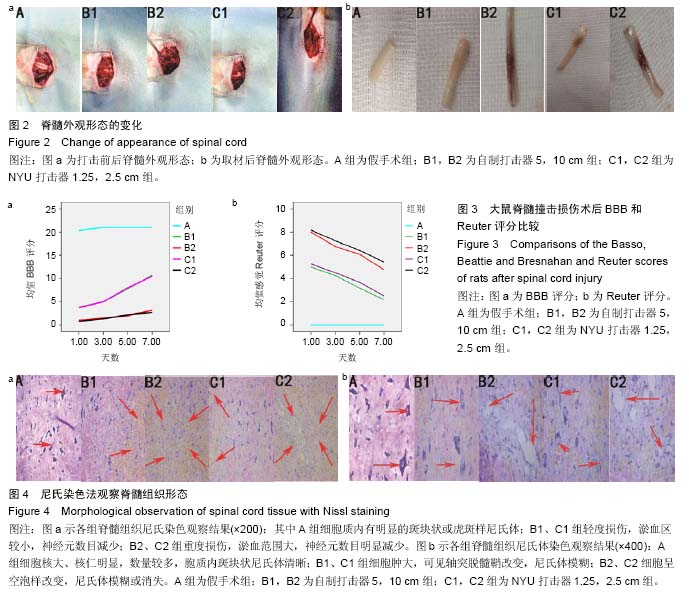
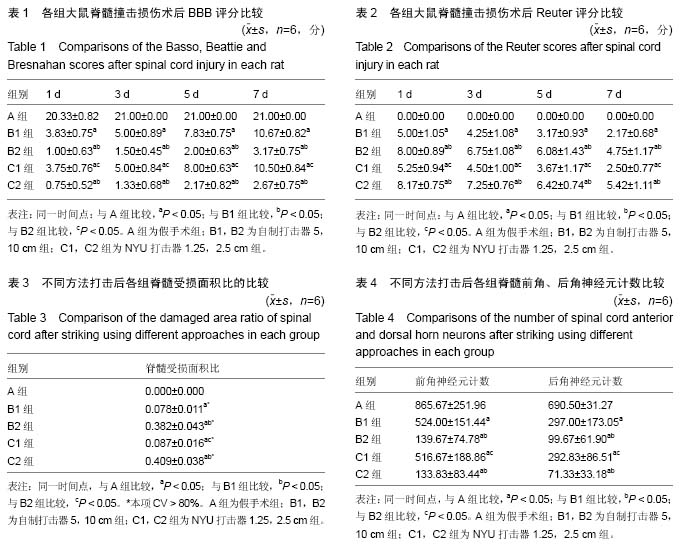
.jpg)
.jpg) 文题释义:
脊髓损伤:是是指外力直接或间接作用于脊髓,引起脊髓功能性或器质性损害,以及继发一系列病理改变进一步加重脊髓损伤,从而出现不可逆性的损伤平面以下感觉、运动、括约肌功能障碍、肌张力异常及病理反射。
脊髓损伤模型:建立与人类发病相近的动物模型,探其发病机制,寻找有效的治疗药物逐渐引起重视。文章选用成年雌性SD大鼠,用撞击损伤模型方法进行造模,方法容易重复,通过自制打击器改良Allen’s法成功建立脊髓撞击损伤模型。
文题释义:
脊髓损伤:是是指外力直接或间接作用于脊髓,引起脊髓功能性或器质性损害,以及继发一系列病理改变进一步加重脊髓损伤,从而出现不可逆性的损伤平面以下感觉、运动、括约肌功能障碍、肌张力异常及病理反射。
脊髓损伤模型:建立与人类发病相近的动物模型,探其发病机制,寻找有效的治疗药物逐渐引起重视。文章选用成年雌性SD大鼠,用撞击损伤模型方法进行造模,方法容易重复,通过自制打击器改良Allen’s法成功建立脊髓撞击损伤模型。