| [1]Kopelman PG. Obesity as a medical problem. Nature. 2000;404(6778): 635-643.[2]Zuckerman KE, Hill AP, Guion K, et al. Overweight and obesity: prevalence and correlates in a large clinical sample of children with autism spectrum disorder. J Autism Dev Disord. 2014;44(7):1708-1719. [3]Hosseini M, Navidi I, Hesamifard B, et al. Weight, height and body mass index nomograms; early adiposity rebound in a sample of children in tehran, iran. Int J Prev Med. 2013;4(12):1414-1420.[4]张洋,何玲.中国青少年体质健康状况动态分析——基于2000-2014年四次国民体质健康监测数据[J].中国青年研究, 2016(6):4-12.[5]Cai Y, Zhu X, Wu X. Overweight, obesity, and screen-time viewing among Chinese school-aged children: National prevalence estimates from the 2016 Physical Activity and Fitness in China-The Youth Study. J Sport Health Sci. 2017;6(4):404-409. [6]Skinner AC, Perrin EM, Moss LA, et al. Cardiometabolic Risks and Severity of Obesity in Children and Young Adults. N Engl J Med. 2015; 373(14):1307-1317. [7]Freedman DS, Mei Z, Srinivasan SR, et al. Cardiovascular risk factors and excess adiposity among overweight children and adolescents: the Bogalusa Heart Study. J Pediatr. 2007;150(1): 12-17.e2.[8]唐东辉,侯玉洁,白爽,等.运动结合饮食控制通过降低RAAS系统活性改善男性肥胖青少年血管内皮功能[J].体育科学, 2017,37(9):48-54,97.[9]Fan X, Cao ZB. Physical activity among Chinese school-aged children: National prevalence estimates from the 2016 Physical Activity and Fitness in China-The Youth Study. J Sport Health Sci. 2017;6(4): 388-394. [10][García-Hermoso A, Saavedra JM, Escalante Y. Effects of exercise on resting blood pressure in obese children: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Obes Rev. 2013;14(11):919-928. [11]Escalante Y, Saavedra JM, García-Hermoso A, et al. Improvement of the lipid profile with exercise in obese children: a systematic review. Prev Med. 2012;54(5):293-301. [12]Saavedra JM, Escalante Y, Garcia-Hermoso A. Improvement of aerobic fitness in obese children: a meta-analysis. Int J Pediatr Obes. 2011;6(3-4):169-177. [13]Bailey RC, Olson J, Pepper SL, et al. The level and tempo of children's physical activities: an observational study. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 1995; 27(7):1033-1041.[14]Sloth M, Sloth D, Overgaard K, et al. Effects of sprint interval training on VO2max and aerobic exercise performance: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Scand J Med Sci Sports. 2013;23(6):e341-352.[15]黎涌明.高强度间歇训练对不同训练人群的应用效果[J].体育科学,2015, 35(8): 59-75.[16]Lee S, Spector J, Reilly S. High-intensity interval training programme for obese youth (HIP4YOUTH): A pilot feasibility study. J Sports Sci. 2017;35(18):1-5. [17]Baquet G, Gamelin FX, Aucouturier J, et al. Cardiorespiratory Responses to Continuous and Intermittent Exercises in Children. Int J Sports Med. 2017;38(10):755-762.[18]Weston KL, Azevedo LB, Bock S, et al. Effect of Novel, School-Based High-Intensity Interval Training (HIT) on Cardiometabolic Health in Adolescents: Project FFAB (Fun Fast Activity Blasts) - An Exploratory Controlled Before-And-After Trial. PLoS One. 2016 ;11(8):e0159116.[19]García-Hermoso A, Cerrillo-Urbina AJ, Herrera-Valenzuela T, et al. Is high-intensity interval training more effective on improving cardiometabolic risk and aerobic capacity than other forms of exercise in overweight and obese youth? A meta-analysis. Obes Rev. 2016;17(6):531-540. [20]Costigan SA, Eather N, Plotnikoff RC, et al. High-intensity interval training for improving health-related fitness in adolescents: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Br J Sports Med. 2015;49(19): 1253-1261. [21]Liberati A, Altman DG, Tetzlaff J, et al. The PRISMA statement for reporting systematic reviews and meta-analyses of studies that evaluate healthcare interventions: explanation and elaboration. BMJ. 2009;339:b2700.[22]Cole TJ, Bellizzi MC, Flegal KM,et al. Establishing a standard definition for child overweight and obesity worldwide: international survey. BMJ. 2000;320(7244):1240-1243.[23]Norton K, Norton L, Sadgrove D. Position statement on physical activity and exercise intensity terminology. J Sci Med Sport. 2010;13(5): 496-502. [24]Gibala MJ, Little JP, Macdonald MJ, et al. Physiological adaptations to low-volume, high-intensity interval training in health and disease. J Physiol. 2012;590(5):1077-1084. [25]Koubaa A, Trabelsi H, Masmoudi L, et al. Effect Of Intermittent And Continuous Training On Body Composition Cardiorespiratory Fitness And Lipid Profile In Obese Adolescents. IOSR J Pharm. 2013;3(2): 31-37.[26]Weston KS, Wisløff U, Coombes JS. High-intensity interval training in patients with lifestyle-induced cardiometabolic disease: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Br J Sports Med. 2014;48(16):1227-1234.[27]Baker D. Recent trends in high-intensity aerobic training for field sports. Prof Strength Cond. 2011;22(4):1-6. [28]Higgins JP, Thompson SG, Deeks JJ, et al. Measuring inconsistency in meta-analyses. BMJ. 2003;327(7414):557-560.[29]Corte de Araujo AC, Roschel H, Picanço AR, et al. Similar health benefits of endurance and high-intensity interval training in obese children. PLoS One. 2012;7(8):e42747.[30]Boer PH, Meeus M, Terblanche E, et al. The influence of sprint interval training on body composition, physical and metabolic fitness in adolescents and young adults with intellectual disability: a randomized controlled trial. Clin Rehabil. 2014;28(3):221-231. [31]Farah BQ, Ritti-Dias RM, Balagopal PB, et al. Does exercise intensity affect blood pressure and heart rate in obese adolescents? A 6-month multidisciplinary randomized intervention study. Pediatr Obes. 2014; 9(2):111-120. [32]Higgins S, Fedewa MV, Hathaway ED, et al. Sprint interval and moderate-intensity cycling training differentially affect adiposity and aerobic capacity in overweight young-adult women. Appl Physiol Nutr Metab. 2016;41(11):1177-1183. [33]Murphy A, Kist C, Gier AJ, et al. The feasibility of high-intensity interval exercise in obese adolescents. Clin Pediatr (Phila). 2015;54(1):87-90.[34]Kargarfard M, Lam ET, Shariat A, et al. Effects of endurance and high intensity training on ICAM-1 and VCAM-1 levels and arterial pressure in obese and normal weight adolescents. Phys Sportsmed. 2016; 44(3):208-216. [35]Lazzer S, Tringali G, Caccavale M, et al. Effects of high-intensity interval training on physical capacities and substrate oxidation rate in obese adolescents. J Endocrinol Invest. 2017;40(2):217-226.[36]Dias KA, Ingul CB, Tjønna AE, et al. Effect of High-Intensity Interval Training on Fitness, Fat Mass and Cardiometabolic Biomarkers in Children with Obesity: A Randomised Controlled Trial. Sports Med. 2018;48(3):733-746. [37]Cvetkovi? N, Stojanovi? E, Stojiljkovi? N, et al. Exercise training in overweight and obese children: Recreational football and high-intensity interval training provide similar benefits to physical fitness. Scand J Med Sci Sports. 2018;28 Suppl 1:18-32. [38]Morrissey C, Montero D, Raverdy C, et al. Effects of Exercise Intensity on Microvascular Function in Obese Adolescents. Int J Sports Med. 2018;39(6):450-455.[39]Thivel D, Masurier J, Baquet G, et al. High-intensity interval training in overweight and obese children and adolescents: systematic review and meta-analysis. J Sports Med Phys Fitness. 2019;59(2):310-324. [40]LaForgia J, Withers RT, Gore CJ. Effects of exercise intensity and duration on the excess post-exercise oxygen consumption. J Sports Sci. 2006;24(12):1247-1264.[41]Boutcher SH. High-intensity intermittent exercise and fat loss. J Obes. 2011;2011:868305.[42]Crampes F, Beauville M, Riviere D, et al. Effect of physical training in humans on the response of isolated fat cells to epinephrine. J Appl Physiol (1985). 1986;61(1):25-29.[43]Krustrup P, Söderlund K, Mohr M, et al. The slow component of oxygen uptake during intense, sub-maximal exercise in man is associated with additional fibre recruitment. Pflugers Arch. 2004;447(6):855-866. [44]Krustrup P, Söderlund K, Mohr M, et al. Recruitment of fibre types and quadriceps muscle portions during repeated, intense knee-extensor exercise in humans. Pflugers Arch. 2004;449(1):56-65.[45]Nishida K, Harrison DG, Navas JP, et al. Molecular cloning and characterization of the constitutive bovine aortic endothelial cell nitric oxide synthase. J Clin Invest. 1992;90(5):2092-2096.[46]Pal S, Radavelli-Bagatini S, Ho S. Potential benefits of exercise on blood pressure and vascular function. J Am Soc Hypertens. 2013;7(6): 494-506. [47]Green DJ, Maiorana A, O'Driscoll G, et al. Effect of exercise training on endothelium-derived nitric oxide function in humans. J Physiol. 2004; 561(Pt 1):1-25. [48]Towler MC, Hardie DG. AMP-activated protein kinase in metabolic control and insulin signaling. Circ Res. 2007;100(3):328-341.[49]Gibala MJ, McGee SL, Garnham AP, et al. Brief intense interval exercise activates AMPK and p38 MAPK signaling and increases the expression of PGC-1alpha in human skeletal muscle. J Appl Physiol (1985). 2009;106(3):929-934. [50]Horowitz JF, Klein S. Lipid metabolism during endurance exercise. Am J Clin Nutr. 2000;72(2 Suppl):558S-563S.[51]Kim HK, Ando K, Tabata H, et al. Effects of Different Intensities of Endurance Exercise in Morning and Evening on the Lipid Metabolism Response. J Sports Sci Med. 2016;15(3):467-476. |
.jpg)
.jpg)
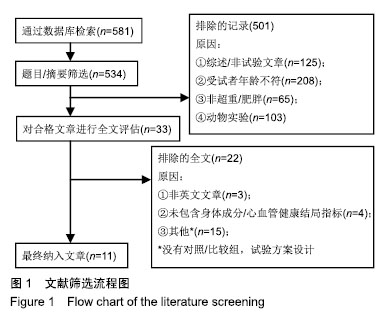
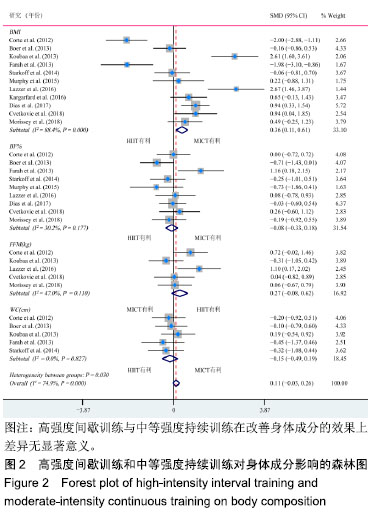
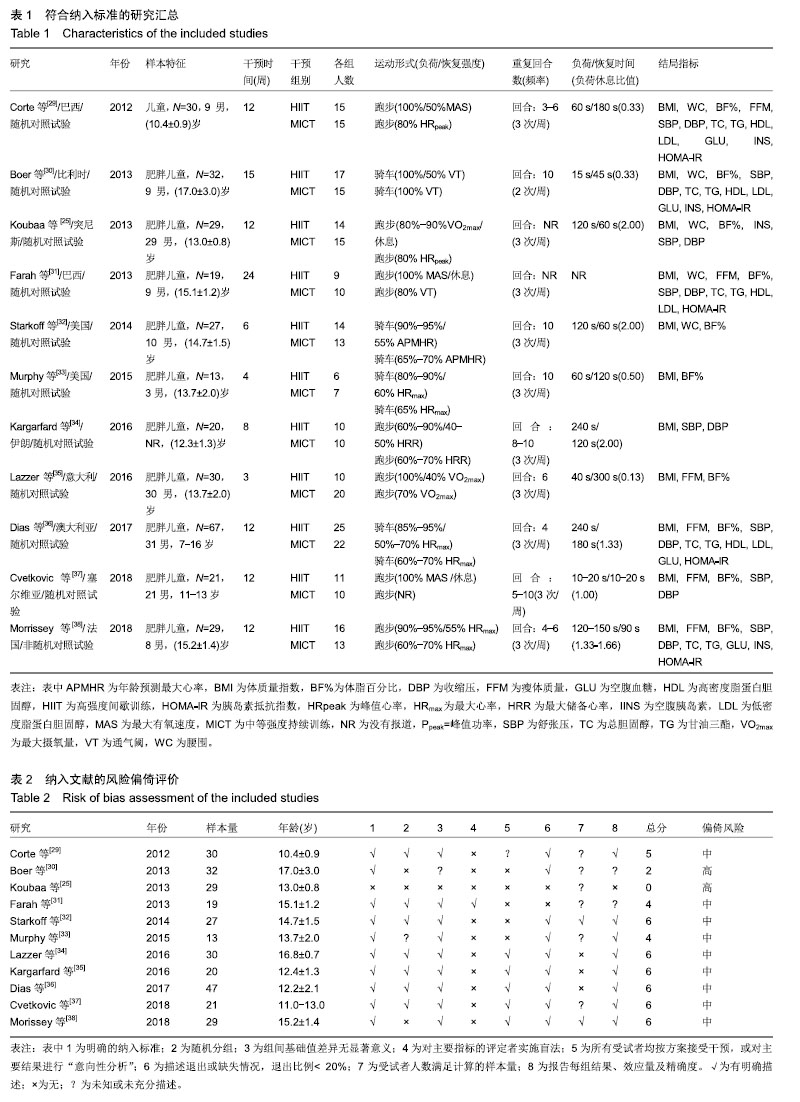
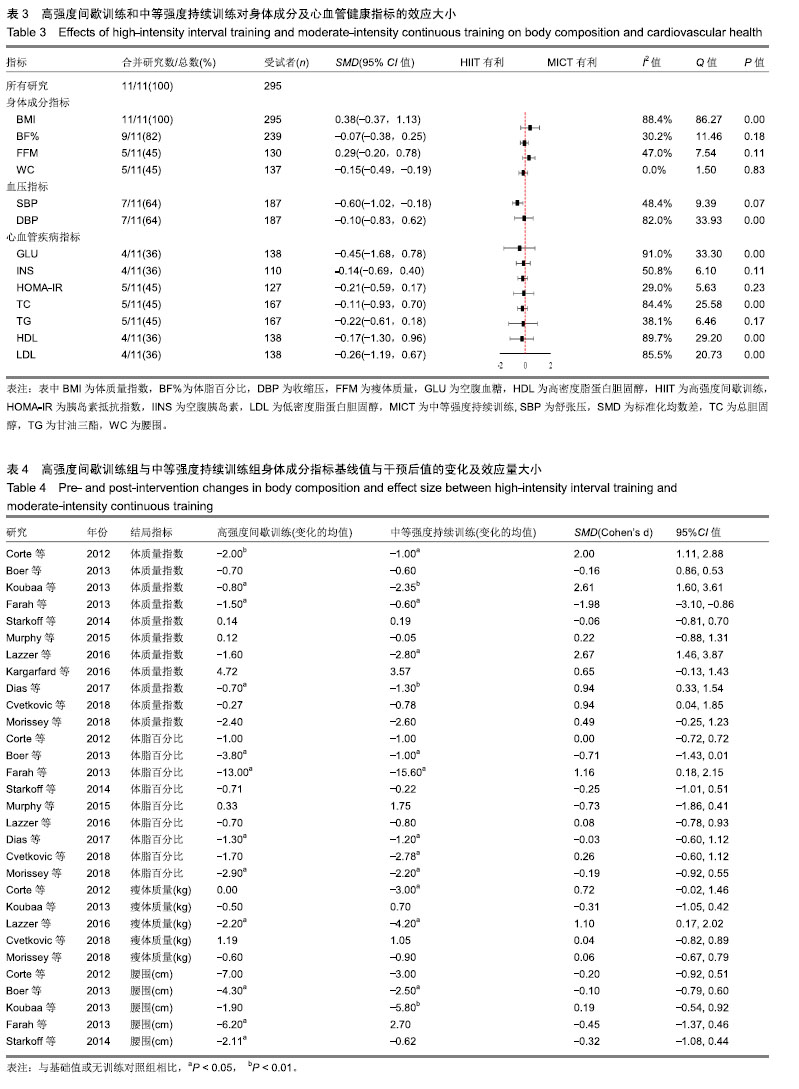
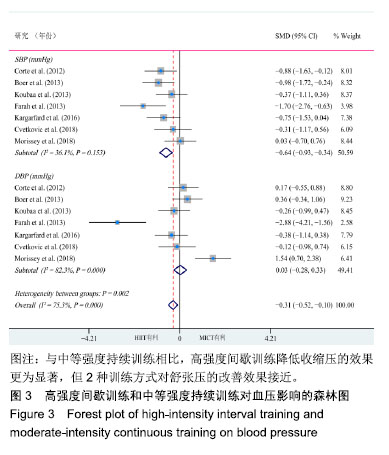
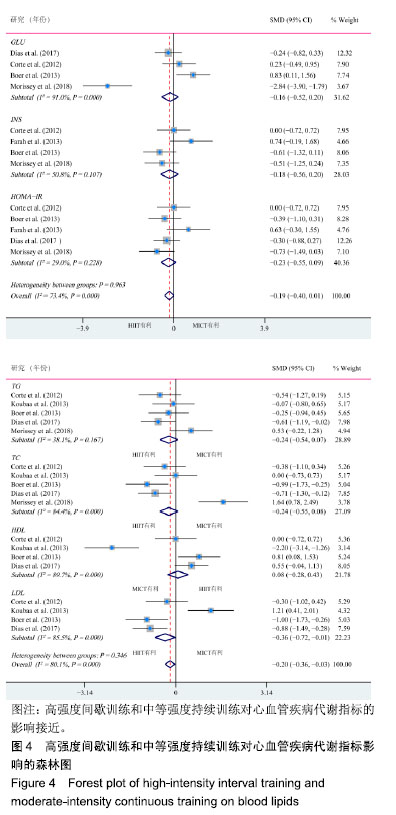
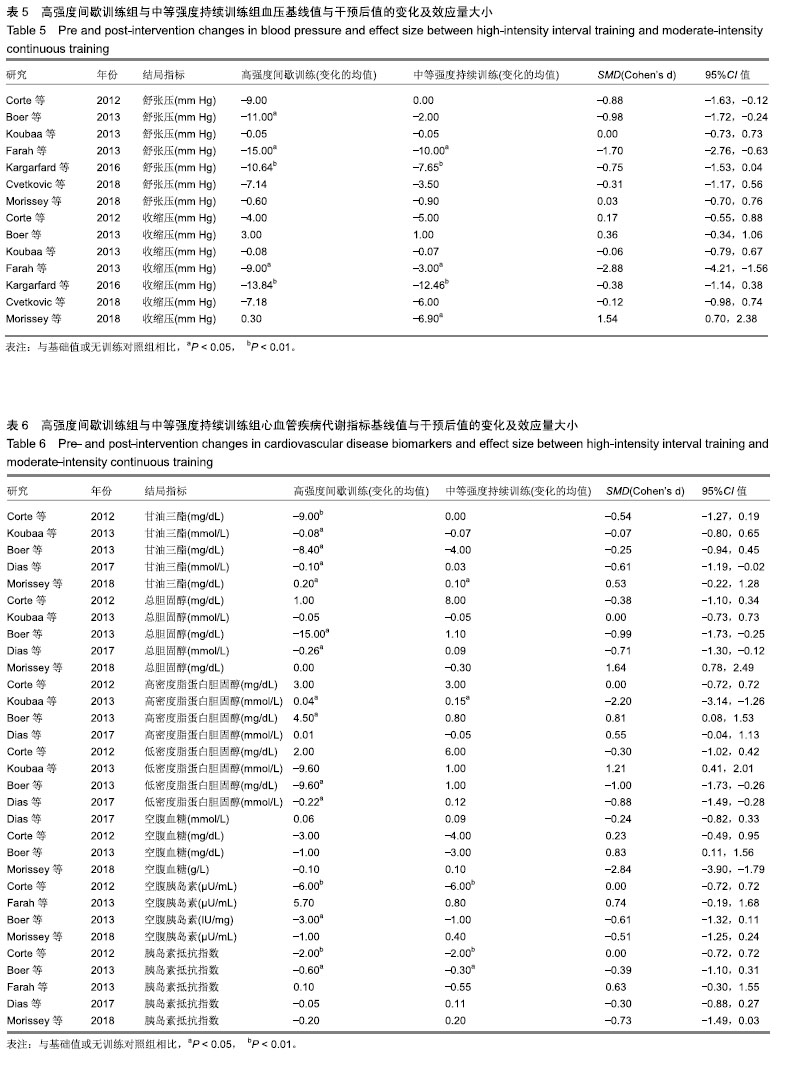
.jpg) #br#
文题释义:#br#
高强度间歇训练:更符合儿童的这一活动特征,它是由短时间高强度活动的负荷期和较低强度活动或静止休息的恢复期交替进行的一种间歇运动。近年来,成年人高强度间歇训练得到了广泛的推广和认可,但对于儿童,特别是肥胖儿童的相关研究较少,对于适合儿童的高强度间歇训练的干预形式、执行方案仍需进一步探讨。#br#
Meta分析:指的是一个科学的临床研究活动,指全面收集所有相关研究并逐个进行严格评价和分析,再用定量合成的方法对资料进行统计学处理得出综合结论的整个过程。
#br#
文题释义:#br#
高强度间歇训练:更符合儿童的这一活动特征,它是由短时间高强度活动的负荷期和较低强度活动或静止休息的恢复期交替进行的一种间歇运动。近年来,成年人高强度间歇训练得到了广泛的推广和认可,但对于儿童,特别是肥胖儿童的相关研究较少,对于适合儿童的高强度间歇训练的干预形式、执行方案仍需进一步探讨。#br#
Meta分析:指的是一个科学的临床研究活动,指全面收集所有相关研究并逐个进行严格评价和分析,再用定量合成的方法对资料进行统计学处理得出综合结论的整个过程。