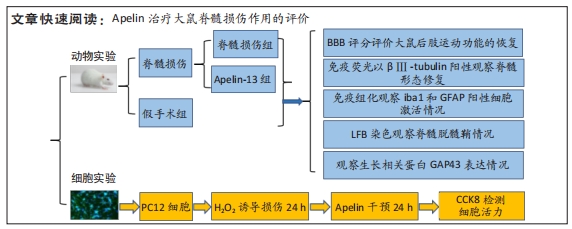
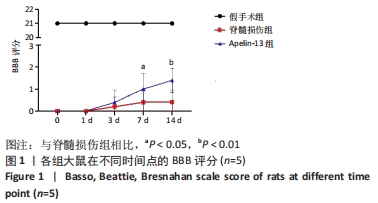
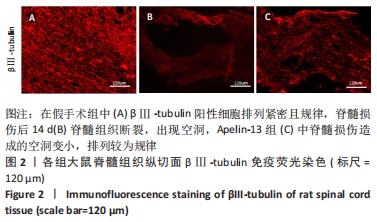
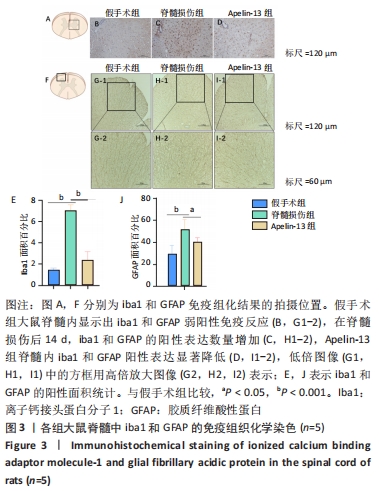
[1] YI XM, LI M, CHEN YD, et al. Neuregulin1 impacting bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell migration is conducive to functional recovery following spinal cord injury. Mol Med Rep. 2019;20(1):41-48.
[2] ZHOU X, HE X, REN Y. Function of microglia and macrophages in secondary damage after spinal cord injury. Neural Regen Res. 2014;9(20):1787-1795.
[3] LI C, JIAO G, WU W, et al. Exosomes from Bone Marrow Mesenchymal Stem Cells Inhibit Neuronal Apoptosis and Promote Motor Function Recovery via the Wnt/beta-catenin Signaling Pathway. Cell Transplant. 2019;28(11):1373-1383.
[4] CODELUPPI S, SVENSSON CI, HEFFERAN MP, et al. The Rheb-mTOR pathway is upregulated in reactive astrocytes of the injured spinal cord. J Neurosci. 2009; 29(4):1093-1104.
[5] CHOI SJ, KIM JK, KIM HK, et al. 2,4-Di-tert-butylphenol from sweet potato protects against oxidative stress in PC12 cells and in mice. J Med Food. 2013;16(11):977-983.
[6] TATEMOTO K, HOSOYA M, HABATA Y, et al. Isolation and characterization of a novel endogenous peptide ligand for the human apj receptor. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1998;251(2):471-476.
[7] LIM R, BARKER G, RILEY C, et al. Apelin is decreased with human preterm and term labor and regulates prolabor mediators in human primary amnion cells.Reprod Sci. 2013;20(8):957-967.
[8] ASHLEY EA, POWERS J, CHEN M, et al. The endogenous peptide apelin potently improves cardiac contractility and reduces cardiac loading in vivo. Cardiovasc Res. 2005;65(1):73-82.
[9] LUO H, HAN L, XU J.Apelin/APJ system: A novel promising target for neurodegenerative diseases. J Cell Physiol. 2020;235(2):638-657.
[10] DUAN J, CUI J, YANG Z, et al. Neuroprotective effect of Apelin 13 on ischemic stroke by activating AMPK/GSK-3β/Nrf2 signaling.J Neuroinflammation. 2019; 16(1):24.
[11] OLSON HE, ROONEY GE, GROSS L, et al. Neural stem cell– and schwann cell–loaded biodegradable polymer scaffolds support axonal regeneration in the transected spinal cord. Tissue Eng Part A. 2009;15(7):1797-805.
[12] CHIO CC, LIN JW, CHANG MW, et al. Therapeutic evaluation of etanercept in a model of traumatic brain injury. J Neurochem. 2010;115(4):921-929.
[13] HE S, WANG Z, LI Y, et al. MicroRNA-92a-3p enhances functional recovery and suppresses apoptosis after spinal cord injury via targeting phosphatase and tensin homolog. Biosci Rep. 2020;40(5):BSR20192743.
[14] HE Y, LI M, WUJISIGULENG, LV B, et al. Zhenbao Pill reduces Treg cell proportion in acute spinal cord injury rats by regulating TUG1/miR-214/HSP27 axis. Biosci Rep. 2018;38(6):BSR20180895.
[15] ZHAN G, SERRANO F, FENIK P, et al. NADPH oxidase mediates hypersomnolence and brain oxidative injury in a murine model of sleep apnea. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2005;172(7):921-929.
[16] ROCHA DN, BRITES P, FONSECA C, et al. Poly(trimethylene carbonate-co-epsilon-caprolactone) promotes axonal growth. PLoS One. 2014;9(2):e88593.
[17] YIN H, TIAN H, LI Q, et al. Jia-Ji Electro-Acupuncture Improves Locomotor Function With Spinal Cord Injury by Regulation of Autophagy Flux and Inhibition of Necroptosis. Front Neurosci. 2021;14:616864.
[18] XU W, LI T, GAO L, et al. Apelin-13/APJ system attenuates early brain injury via suppression of endoplasmic reticulum stress-associated TXNIP/NLRP3 inflammasome activation and oxidative stress in a AMPK-dependent manner after subarachnoid hemorrhage in rats. J Neuroinflammation. 2019;16(1):247.
[19] LIU Y, ZHANG T, WANG Y, et al. Apelin-13 attenuates early brain injury following subarachnoid hemorrhage via suppressing neuronal apoptosis through the GLP-1R/PI3K/Akt signaling.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2019;513(1):105-111.
[20] BAO HJ, ZHANG L, HAN WC, et al. Apelin-13 attenuates traumatic brain injury-induced damage by suppressing autophagy. Neurochem Res. 2015;40(1):89-97.
[21] CHEN D, LEE J, GU X, et al. Intranasal delivery of Apelin-13 is neuroprotective and promotes angiogenesis after ischemic stroke in mice. ASN Neuro. 2015;7(5): 1759091415605114.
[22] AMINYAVARI S, ZAHMATKESH M, KHODAGHOLI F,et al. Anxiolytic impact of Apelin-13 in a rat model of Alzheimer’s disease: Involvement of glucocorticoid receptor and FKBP5. Peptides. 2019;118:170102.
[23] LUO H, XIANG Y, QU X, et al. Apelin-13 Suppresses Neuroinflammation Against Cognitive Deficit in a Streptozotocin-Induced Rat Model of Alzheimer’s Disease Through Activation of BDNF-TrkB Signaling Pathway. Front Pharmacol. 2019;10:395.
[24] ZHU J, DOU S, JIANG Y, et al. Apelin-13 protects dopaminergic neurons in MPTP-induced Parkinson’s disease model mice through inhibiting endoplasmic reticulum stress and promoting autophagy. Brain Res. 2019;1715:203-212.
[25] PATIL V, O’CONNELL E, QUINLAN LR, et al. A robust platform for high-throughput screening of therapeutic strategies for acute and chronic spinal cord injury. iScience. 2021;24(3):102182.
[26] LI X, GUO Q, YE Z, et al. PPAR gamma Prevents Neuropathic Pain by Down-Regulating CX3CR1 and Attenuating M1 Activation of Microglia in the Spinal Cord of Rats Using a Sciatic Chronic Constriction Injury Model. Front Neurosci. 2021;15:620525.
[27] HUANG SQ, TANG CL, SUN SQ, et al. Demyelination initiated by oligodendrocyte apoptosis through enhancing endoplasmic reticulum-mitochondria interactions and Id2 expression after compressed spinal cord injury in rats.CNS Neurosci Ther. 2014;20(1):20-31.
[28] WALKER MR, ZHONG J, WASPE AC, et al. Acute MR-Guided High-Intensity Focused Ultrasound Lesion Assessment Using Diffusion-Weighted Imaging and Histological Analysis. Front Neurol. 2019;10:1069.
[29] ZHANG H, WU F, KONG X, et al. Nerve growth factor improves functional recovery by inhibiting endoplasmic reticulum stress-induced neuronal apoptosis in rats with spinal cord injury. J Transl Med. 2014;12:130.
[30] HUA XY, QIU YQ, WANG M, et al. Enhancement of Contralesional Motor Control Promotes Locomotor Recovery after Unilateral Brain Lesion. Sci Rep. 2016;6:18784.
[31] CHIANG JH, CHENG WS, HOOD L, et al. An epigenetic biomarker panel for glioblastoma multiforme personalized medicine through DNA methylation analysis of human embryonic stem cell-like signature. OMICS. 2014;18(5):310-323.
[32] WU Z, LU Z, OU J, et al. Inflammatory response and oxidative stress attenuated by sulfiredoxin1 in neuronlike cells depends on nuclear factor erythroid2related factor 2. Mol Med Rep. 2020;22(6):4734-4742.
[33] YUNJUN ZOU YJ, WANG B , FU W, et al. Apelin-13 Protects PC12 Cells from Corticosterone-Induced Apoptosis Through PI3K and ERKs Activation. Neurochem Res. 2016;41(7):1635-1644.
[34] FOROUGHI K, KHAKSARI M, RAHMATI M, et al. Apelin-13 Protects PC12 Cells Against Methamphetamine-Induced Oxidative Stress, Autophagy and Apoptosis. Neurochem Res. 2019;44(9):2103-2112.
[35] WALLER JD, MCNEILL EH, ZHONG F, et al. Plasma Apelin Unchanged With Acute Exercise Insulin Sensitization. J Sports Sci Med. 2019;18(3):537-543.
|