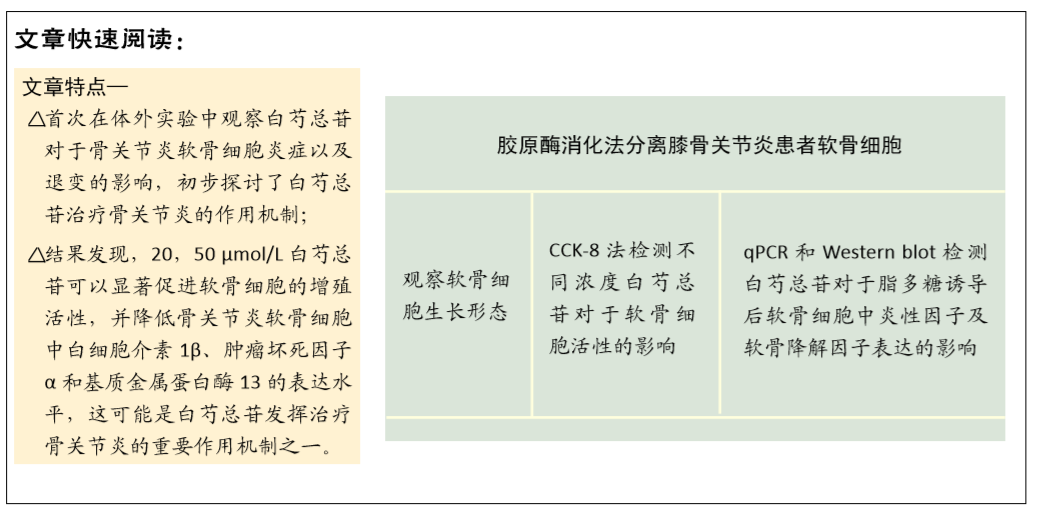
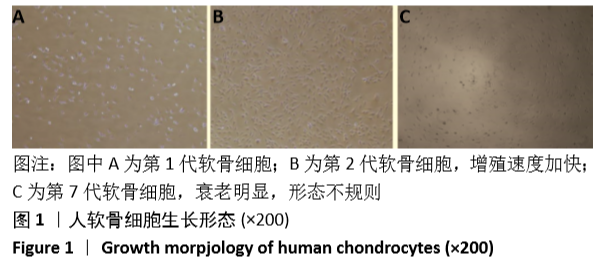
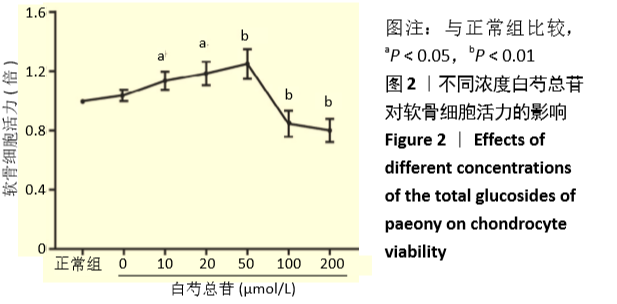
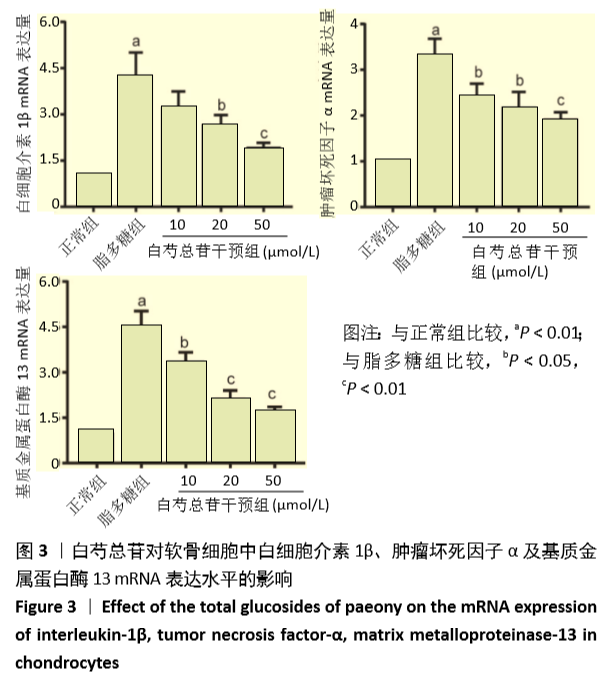
[1] MANCARELLA L, ADDIMANDA O, CAVALLARI C, et al. Synovial Inflammation Drives Structural Damage in Hand Osteoarthritis: a Narrative Literature Review. Curr Rheumatol Rev. 2017;13(1):43-50.
[2] KATO T, MIYAKI S, ISHITOBI H, et al. Exosomes from IL-1β stimulated synovial fibroblasts induce osteoarthritic changes in articular chondrocytes. Arthritis Res Ther. 2014;16(4):R163.
[3] BERENBAUM F. Osteoarthritis as an inflammatory disease (osteoarthritis is not osteoarthrosis!). Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2013;21(1):16-21.
[4] NEOGI T. The epidemiology and impact of pain in osteoarthritis. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2013;21(9):1145-1153.
[5] LANE NE, BRANDT K, HAWKER G, et al. OARSI-FDA initiative: defining the disease state of osteoarthritis. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2011;19(5): 478-482.
[6] KONTTINEN YT, SILLAT T, BARRETO G, et al. Osteoarthritis as an autoinflammatory disease caused by chondrocyte-mediated inflammatory responses. Arthritis Rheum. 2012;64(3):613-616.
[7] JIA XY, CHANG Y, SUN XJ, et al. Total glucosides of paeony inhibit the proliferation of fibroblast-like synoviocytes through the regulation of G proteins in rats with collagen-induced arthritis. Int Immunopharmacol. 2014;18(1):1-6.
[8] CHEN Z, LI XP, LI ZJ, et al. Reduced hepatotoxicity by total glucosides of paeony in combination treatment with leflunomide and methotrexate for patients with active rheumatoid arthritis. Int Immunopharmacol. 2013;15(3):474-477.
[9] ZHANG XJ, LI Z, LEUNG WM, et al. The analgesic effect of paeoniflorin on neonatal maternal separation-induced visceral hyperalgesia in rats. J Pain. 2008;9(6):497-505.
[10] 王欢,王庆甫,史榕荇,等.桂皮醛及白芍总苷对骨关节炎滑膜炎性反应的影响[J].中华中医药杂志,2018,33(8):3356-3360.
[11] 王欢,王庆甫,唐学章,等.白芍总苷对滑膜成纤维细胞增殖、凋亡及周期影响的实验研究[J].天津中医药,2017,34(12):841-844.
[12] 王欢,王庆甫,杨黎黎,等.白芍总苷对人膝骨关节炎滑膜成纤维细胞增殖的影响[J].中华中医药杂志,2016,31(11):4853-4856.
[13] GREENE MA, LOESER RF. Aging-related inflammation in osteoarthritis. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2015;23(11):1966-1971.
[14] SUANTAWEE T, TANTAVISUT S, ADISAKWATTANA S, et al. Upregulation of inducible nitric oxide synthase and nitrotyrosine expression in primary knee osteoarthritis. J Med Assoc Thai. 2015;98 Suppl 1:S91-97.
[15] LIU-BRYAN R. Synovium and the innate inflammatory network in osteoarthritis progression. Curr Rheumatol Rep. 2013;15(5):323.
[16] SANTANGELO KS, NUOVO GJ, BERTONE AL. In vivo reduction or blockade of interleukin-1β in primary osteoarthritis influences expression of mediators implicated in pathogenesis. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2012;20(12):1610-1618.
[17] LARSSON S, ENGLUND M, STRUGLICS A, et al. Interleukin-6 and tumor necrosis factor alpha in synovial fluid are associated with progression of radiographic knee osteoarthritis in subjects with previous meniscectomy. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2015;23(11):1906-1914.
[18] SHI J, SCHMITT-TALBOT E, DIMATTIA DA, et al. The differential effects of IL-1 and TNF-alpha on proinflammatory cytokine and matrix metalloproteinase expression in human chondrosarcoma cells. Inflamm Res. 2004;53(8):377-389.
[19] WANG Y, XU J, ZHANG X, et al. TNF-α-induced LRG1 promotes angiogenesis and mesenchymal stem cell migration in the subchondral bone during osteoarthritis. Cell Death Dis. 2017;8(3):e2715.
[20] ZHENG W, FENG Z, YOU S, et al. Fisetin inhibits IL-1β-induced inflammatory response in human osteoarthritis chondrocytes through activating SIRT1 and attenuates the progression of osteoarthritis in mice. Int Immunopharmacol. 2017;45:135-147.
[21] KLEIN T, BISCHOFF R. Physiology and pathophysiology of matrix metalloproteases. Amino Acids. 2011;41(2):271-290.
[22] YING X, CHEN X, CHENG S, et al. Piperine inhibits IL-β induced expression of inflammatory mediators in human osteoarthritis chondrocyte. Int Immunopharmacol. 2013;17(2):293-299.
[23] ZHAO L, YE J, WU GT, et al. Gentiopicroside prevents interleukin-1 beta induced inflammation response in rat articular chondrocyte. J Ethnopharmacol. 2015;172:100-107.
[24] 张晓哲,张栋,马玉峰,等.通络止痛凝胶制剂对膝骨关节炎大鼠的影响[J].中华中医药杂志,2019,34(5):2184-2188.
[25] 王欢,王庆甫,杨黎黎,等.桂皮醛对滑膜成纤维细胞增殖、凋亡及周期影响的实验研究[J].天津中医药,2017,34(1):54-58.
[26] 杨黎黎,王庆甫,王欢,等.通络止痛方对人膝骨关节炎关节液IL-1β,HA及NO的影响[J].中国中医骨伤科杂志,2017,25(1):1-4.
[27] 石鑫超,吴忌,王庆甫,等.桂皮醛对人膝骨关节炎滑膜成纤维细胞增殖的影响[J].中国中医骨伤科杂志,2014,22(9):1-3.
|