[1] LIGUORI I, RUSSO G, CURCIO F, et al. Oxidative stress, aging, and diseases. Clin Interv Aging. 2018;13:757-772.
[2] TOBORE TO. On the central role of mitochondria dysfunction and oxidative stress in Alzheimer’s disease. Neurol Sci. 2019;40(8):1527-1540.
[3] POHANKA M. Oxidative stress in Alzheimer disease as a target for therapy. Bratisl Lek Listy. 2018;119(9):535-543.
[4] MATSCHKE V, THEISS C, MATSCHKE J. Oxidative stress: the lowest common denominator of multiple diseases. Neural Regen Res. 2019;14(2):238-241.
[5] FRAUNBERGER EA, SCOLA G, LALIBERTÉ VL, et al. Redox Modulations, Antioxidants, and Neuropsychiatric Disorders. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2016; 2016:4729192.
[6] MCBEAN GJ. Cysteine, Glutathione, and Thiol Redox Balance in Astrocytes. Antioxidants (Basel). 2017;6(3):62.
[7] CABEZAS R, BAEZ-JURADO E, HIDALGO-LANUSSA O, et al. Growth Factors and Neuroglobin in Astrocyte Protection Against Neurodegeneration and Oxidative Stress. Mol Neurobiol. 2019;56(4):2339-2351.
[8] JOE EH, CHOI DJ, AN J, et al. Astrocytes, Microglia, and Parkinson’s Disease. Exp Neurobiol. 2018;27(2):77-87.
[9] GONZÁLEZ-REYES RE, NAVA-MESA MO, VARGAS-SÁNCHEZ K, et al. Involvement of Astrocytes in Alzheimer’s Disease from a Neuroinflammatory and Oxidative Stress Perspective. Front Mol Neurosci. 2017;10:427.
[10] RIZOR A, PAJARILLO E, JOHNSON J, et al. Astrocytic Oxidative/Nitrosative Stress Contributes to Parkinson’s Disease Pathogenesis: The Dual Role of Reactive Astrocytes. Antioxidants (Basel). 2019;8(8):265.
[11] MOLINARI C, MORSANUTO V, GHIRLANDA S, et al. Role of Combined Lipoic Acid and Vitamin D3 on Astrocytes as a Way to Prevent Brain Ageing by Induced Oxidative Stress and Iron Accumulation. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2019;2019:2843121.
[12] SHEFA U, JEONG NY, SONG IO, et al. Mitophagy links oxidative stress conditions and neurodegenerative diseases. Neural Regen Res. 2019;14(5):749-756.
[13] HAMDI Y, KADDOUR H, VAUDRY D, et al. The octadecaneuropeptide ODN protects astrocytes against hydrogen peroxide-induced apoptosis via a PKA/MAPK-dependent mechanism. PLoS One. 2012;7(8):e42498.
[14] SANDBERG M, PATIL J, D’ANGELO B, et al. NRF2-regulation in brain health and disease: implication of cerebral inflammation. Neuropharmacology. 2014;79:298-306.
[15] CAO S, CHAO D, ZHOU H, et al. A novel mechanism for cytoprotection against hypoxic injury: δ-opioid receptor-mediated increase in Nrf2 translocation. Br J Pharmacol. 2015;172(7):1869-1881.
[16] NITURE SK, KASPAR JW, SHEN J, et al. Nrf2 signaling and cell survival. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2010;244(1):37-42.
[17] SHU L, WANG C, WANG J, et al. The neuroprotection of hypoxic preconditioning on rat brain against traumatic brain injury by up-regulated transcription factor Nrf2 and HO-1 expression. Neurosci Lett. 2016;611:74-80.
[18] FU PC, TANG RH, YU ZY, et al. The Rho-associated kinase inhibitors Y27632 and fasudil promote microglial migration in the spinal cord via the ERK signaling pathway. Neural Regen Res. 2018;13(4):677-683.
[19] YAN Y, YU J, GAO Y, et al. Therapeutic potentials of the Rho kinase inhibitor Fasudil in experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis and the related mechanisms. Metab Brain Dis. 2019;34(2):377-384.
[20] WANG J, SUI RX, MIAO Q, et al. Retraction: Effect of Fasudil on remyelination following cuprizone-induced demyelination. CNS Neurosci Ther. 2020;26(7):778.
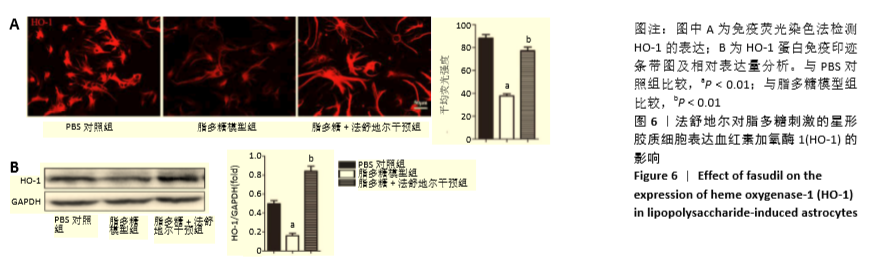
[21] 张慧宇,郭敏芳,于婧文,等.法舒地尔(Fasudil)抑制脂多糖诱导的小鼠星形胶质细胞活化和炎性反应及其机制[J].细胞与分子免疫学杂志, 2018,34(6):505-510.
[22] WANG Y, ZHAO CS. Sigma-1 receptor activation ameliorates LPS-induced NO production and ROS formation through the Nrf2/HO-1 signaling pathway in cultured astrocytes. Neurosci Lett. 2019;711:134387.
[23] POURHANIFEH MH, SHAFABAKHSH R, REITER RJ, et al. The Effect of Resveratrol on Neurodegenerative Disorders: Possible Protective Actions Against Autophagy, Apoptosis, Inflammation and Oxidative Stress. Curr Pharm Des. 2019;25(19):2178-2191.
[24] CHERBUIN N, WALSH E, BAUNE BT, et al. Oxidative stress, inflammation and risk of neurodegeneration in a population sample. Eur J Neurol. 2019; 26(11):1347-1354.
[25] SOFRONIEW MV, VINTERS HV. Astrocytes: biology and pathology. Acta Neuropathol. 2010;119(1):7-35.
[26] PACHECO SM, AZAMBUJA JH, DE CARVALHO TR, et al. Glioprotective Effects of Lingonberry Extract Against Altered Cellular Viability, Acetylcholinesterase Activity, and Oxidative Stress in Lipopolysaccharide-Treated Astrocytes. Cell Mol Neurobiol. 2018;38(5):1107-1121.
[27] SHARMA A, PATRO N, PATRO IK. Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Apoptosis of Astrocytes: Therapeutic Intervention by Minocycline. Cell Mol Neurobiol. 2016;36(4):577-592.
[28] PORTER AG, JÄNICKE RU. Emerging roles of caspase-3 in apoptosis. Cell Death Differ. 1999;6(2):99-104.
[29] SHU Q, FAN H, LI SJ, et al. Protective effects of Progranulin against focal cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury in rats by suppressing endoplasmic reticulum stress and NF-κB activation in reactive astrocytes. J Cell Biochem. 2018;119(8):6584-6597.
[30] OTTERBEIN LE, FORESTI R, MOTTERLINI R. Heme Oxygenase-1 and Carbon Monoxide in the Heart: The Balancing Act Between Danger Signaling and Pro-Survival. Circ Res. 2016;118(12):1940-1959.
[31] LOBODA A, DAMULEWICZ M, PYZA E, et al. Role of Nrf2/HO-1 system in development, oxidative stress response and diseases: an evolutionarily conserved mechanism. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2016;73(17):3221-3247.
[32] ALI T, KIM T, REHMAN SU, et al. Natural Dietary Supplementation of Anthocyanins via PI3K/Akt/Nrf2/HO-1 Pathways Mitigate Oxidative Stress, Neurodegeneration, and Memory Impairment in a Mouse Model of Alzheimer’s Disease. Mol Neurobiol. 2018;55(7):6076-6093.
[33] JO MG, IKRAM M, JO MH, et al. Gintonin Mitigates MPTP-Induced Loss of Nigrostriatal Dopaminergic Neurons and Accumulation of α-Synuclein via the Nrf2/HO-1 Pathway. Mol Neurobiol. 2019;56(1):39-55.
[34] HUNG SY, LIOU HC, FU WM. The mechanism of heme oxygenase-1 action involved in the enhancement of neurotrophic factor expression. Neuropharmacology. 2010;58(2):321-329.
|