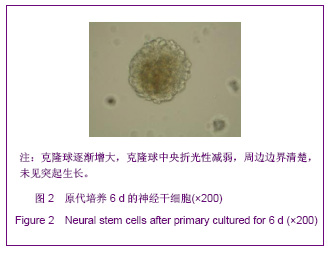
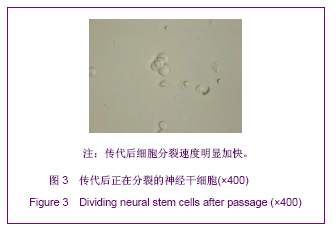
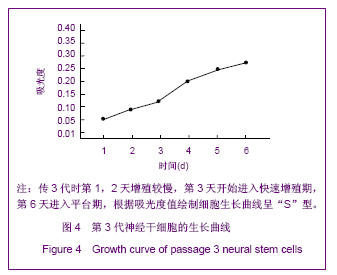
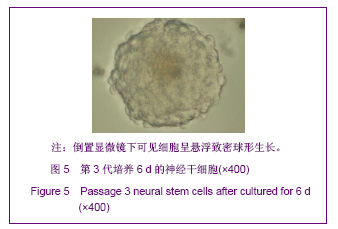
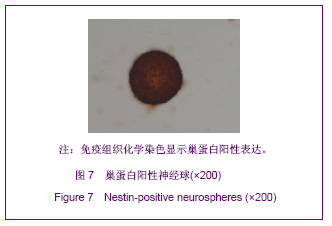
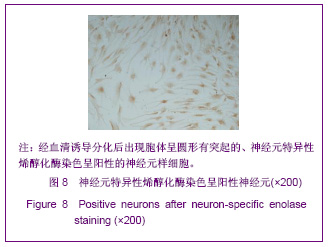
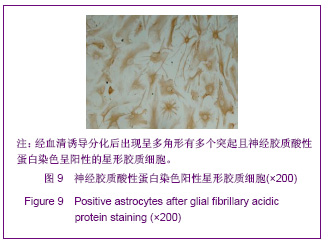
| [1] Martino G, Pluchino S.The therapeutic potential of neural stem cells. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2006;7(5):395-406.[2] Hao JR,Zhang L,Qin ZH,et al. Shenjing Yaoli Xuebao. 2011; 1(1):51-55. 郝军荣,张丽,秦正红,等.神经干细胞球和单层贴壁神经干细胞的培养及鉴定[J].神经药理学报,2011,1(1):51-55.[3] Li M,Wang XZ,Xu TJ.Zhongguo Zuzhi Gongcheng Yanjiu yu Linchuang Kangfu. 2011;15(6):985-989. 李梅,王湘臻,徐铁军. 海马神经干细胞不同传代方法的比较[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2011,15(6):985-989. [4] Hu JL,Jiang XD,Zou YX,et al. Nanfang Yike Daxue Xuebao. 2008;28(11): 1942-1946. 胡继良,姜晓丹,邹雨汐,等.成年小鼠脑室下区神经干细胞培养与鉴定体系的建立[J].南方医科大学学报,2008,28(11): 1942-1946.[5] Chu YB,Luo ZJ,Cao YL,et al. Zhonghua Shenjing Waike Jibing Yanjiu Zazhi. 2006,5(1):19-22. 褚尤彪,罗卓荆,曹延林,等.脊髓神经干细胞培养及体外诱导分化实验研究[J].中华神经外科疾病研究杂志,2006,5(1): 19-22.[6] Peng SH,Dai JB,Tian YH. Jiepou Xuebao. 2005; 36(6): 660-664. 彭绍华,戴冀斌,田毅浩.小鼠胚胎大脑皮质与中脑神经干细胞培养与分化比较的研究[J].解剖学报,2005, 36(6):660-664.[7] Yan CX,An YH,Li JH,et al. Zhonghua Shenjing Waike Zazhi. 2003;19(2):135-137. 闫长祥,安沂华,历俊华,等.大鼠脊髓源性神经干细胞的培养分化及其特异性研究[J].中华神经外科杂志, 2003,19(2):135-137.[8] Deng XL, Liu RE, Feng ZT, et al. In vitro culture and differentiation of rat embryonic midbrain-derived neural stem cells. Neural Regen Res 2008;3(11):1241-1244.[9] Zhao R, Xuan Y, Li X,et al. Age-related changes of germline stem cell activity, niche signaling activity and egg production in Drosophila. Aging Cell. 2008;7(3):344-354. [10] Liu K,Wang HY,He L,et al. Zhongguo Xiandai Shenjing Jibing Zazhi. 2006;6(1):52-56. 刘暌,王红云,何乐,等.胚胎大鼠神经干细胞培养及分化鉴定的实验研究[J].中国现代神经疾病杂志,2006,6(1):52-56. [11] Johnston MA, Lim DA. Keeping them quiet: BMPs maintain adult neural stem cell quiescence. Cell Stem Cell. 2010;7(1): 9-10.[12] Mira H, Andreu Z, Suh H,et al. Signaling through BMPR-IA regulates quiescence and long-term activity of neural stem cells in the adult hippocampus. Cell Stem Cell. 2010;7(1): 78-89.[13] Liu H,Yin HY,Yu NW,et al.Zhongguo Zuzhi Gongcheng Yanjiu yu Linchuang Kangfu. 2010;14(32):5935-5938. 刘洁,尹海燕,余能伟,等.快速老化与正常老化小鼠脑内神经干细胞增殖的差异[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2010,14(32): 5935-5938.[14] Chen ML,Shen YF,Liu KX. Guangdong Yixue. 2011;32(1): 34-37. 陈梅玲,沈岳飞,刘开祥.大鼠神经干细胞体外培养的研究[J].广东医学,2011,32(1):34-37.[15] Zhao ZY,Hu HT,Shi SH. Zhongguo Xiufu Chongjian Waike Zazhi. 2005;19(7):544-547. 赵志英,胡海涛,师社会. 新生大鼠脑源性神经干细胞培养方法的优化[J].中国修复重建外科杂志,2005,19(7):544-547. [16] Zhang ZS,Li JH,Zhang YZ. Shoudu Yike Daxue Xuebao. 2003;24(2):180-183. 张泽舜,历俊华,张亚卓.神经干细胞接种密度对其增生和分化的影响[J].首都医科大学学报,2003,24(2):180-183.[17] Milosevic J, Storch A, Schwarz J. Spontaneous apoptosis in murine free-floating neurospheres. Exp Cell Res. 2004;294(1): 9-17.[18] Geng HH,Zhao L,Zhao BM. Jiepou yu Linchuang. 2008;13(4): 291-293. 耿慧慧,赵丽,赵保明.提高胚鼠脑源性神经干细胞克隆形成的一种方法[J].解剖与临床,2008,13(4): 291-293. [19] Liu X, Djung Lilya Wati,Qi ZG,et al. Chongqing Yike Daxue Xuebao. 2010;35(9):1295-1297. 刘霞, Djung Lilya Wati,齐志国,等.体外培养神经干细胞球的离散:一种安全有效的方法[J].重庆医科大学学报,2010,35(9): 1295-1297.[20] Xing CM,Geng XL,Liu YX. Zhongguo Zuzhi Gongcheng Yanjiu yu Linchuang Kangfu. 2008; 12(16):3189-3192. 邢成名,耿秀丽,刘玉霞.胚胎大鼠原代神经干细胞培养方法的改进[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复, 2008, 12(16):3189-3192.[21] Dictus C, Tronnier V, Unterberg A,et al. Comparative analysis of in vitro conditions for rat adult neural progenitor cells. J Neurosci Methods. 2007;161(2):250-258.[22] Gao XQ,Yuan QL,Du J,et al. Zhongguo Linchuang Kangfu. 2005;9(30):58-59. 高小青,袁琼兰,杜杰,等. 新生大鼠神经干细胞培养过程中加入相关因子对其生长特性的影响[J].中国临床康复,2005,9(30): 58-59.[23] Villa A, Snyder EY, Vescovi A,et al. Establishment and properties of a growth factor-dependent, perpetual neural stem cell line from the human CNS. Exp Neurol. 2000;161(1): 67-84.[24] Yun MJ,Wang LZ,Wang YC, et al.In vitro growth, differentiation and biological characteristics of neural stem cells.Neural Regen Res 2006;1(4):364-367.[25] Gu EY,Ha F,Li LF. Zhongguo Zuzhi Gongcheng Yanjiu yu Linchuang Kangfu. 2009; 13(10):1947-1950. 顾恩妍,哈福,李林凤.神经干细胞的鉴定方法[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复, 2009, 13(10):1947-1950.[26] Lv HY,Liu Y,Li MJ. Xi’an Jiaotong Daxue Xuebao:Yixueban. 2002;23(5):428-431. 吕海侠,刘勇,李敏杰.神经干细胞的分离培养与鉴定[J].西安交通大学学报:医学版, 2002,23(5):428-431.[27] Ke CL, Chen BL, Guo SL, et al. Differentiation of embryonic versus adult rat neural stem cells into dopaminergic neurons in vitro. Neural Regen Res 2008;3(8):832-836. |